Psychology unit 2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/115
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
116 Terms
1
New cards
Neurotransmitters
Chemicals that transmit information from one neuron to another
2
New cards
neurotransmitters influence
Our mood and emotions (fear, pleasure, manading mood).
3
New cards
Acetylcholine
A neurotransmitter that enables learning and memory and also triggers muscle contraction
4
New cards
dopamine
influences movement, learning, attention, and emotion
5
New cards
serotonin
Affects mood, hunger, sleep, and arousal
6
New cards
norepinephrine
helps control alertness and arousal
7
New cards
GABA
A major inhibitory neurotransmitter. Undersupply linked to seizures, tremors, and insomnia.
8
New cards
glutamate
A major excitatory neurotransmitter; involved in memory
9
New cards
endorphins
natural, opiate-like neurotransmitters linked to pain control and stress
10
New cards
agonists
drugs that increase the action of a neurotransmitter
11
New cards
Antagonists
drugs that block the function of a neurotransmitter
12
New cards
SSRIs
selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors
13
New cards
how a reflex works
Receptor receives stimuli -> sensory neuron transmits messages -> to interneurons (in spine) -> to motor neuron -> effector receives response from motor neuron to act
14
New cards
Interneurons
Central nervous system neurons that internally communicate and intervene between the sensory inputs and motor outputs
15
New cards
endocrine system
the body's "slow" chemical communication system; a set of glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream
16
New cards
hormones
chemical messengers that are manufactured by the endocrine glands, travel through the bloodstream, and affect other tissues
17
New cards
Hormones vs. Neurotransmitters
Hormones move slower because they move through the bloodstream while neurotransmitters travel through synapses
18
New cards
adrenal glands
a pair of endocrine glands that sit just above the kidneys and secrete hormones (epinephrine and norepinephrine) that help arouse the body in times of stress.
19
New cards
Epinephrine (adrenaline)
Neurotransmitter secreted by the adrenal medulla in response to stress.
20
New cards
Norepinephrine (noradrenaline)
helps control alertness and arousal
21
New cards
pituitary glands
The endocrine system's most influential gland. Under the influence of the hypothalamus, the pituitary regulates growth and controls other endocrine glands.
22
New cards
phrenology
the detailed study of the shape and size of the cranium as a supposed indication of character and mental abilities.
23
New cards
lesion
a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue
24
New cards
EEG (electroencephalogram)
An amplified recording of the waves of electrical activity that sweep across the brain's surface. These waves are measured by electrodes placed on the scalp.
25
New cards
MRI
a technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce computer-generated images that distinguish among different types of soft tissue; allows us to see structures within the brain
26
New cards
fMRI
A technique for revealing blood flow and, therefore, brain activity by comparing successive MRI scans.
27
New cards
CT Scan
a series of x-ray photographs taken from different angles and combined by computer into a composite representation of a slice through the body
28
New cards
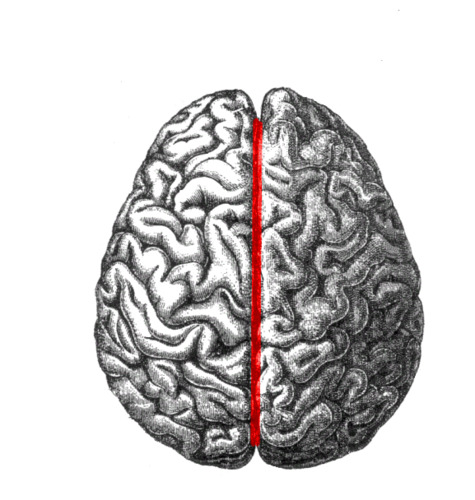
logitudinal fissure
indentation that separates the cerebrum into right and left hemispheres.
29
New cards
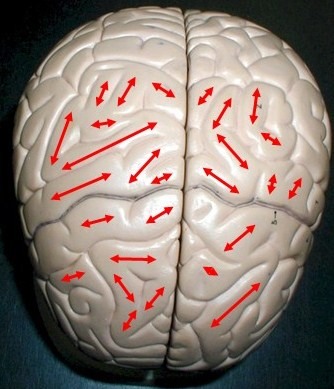
gyri
ridges of the brain
30
New cards
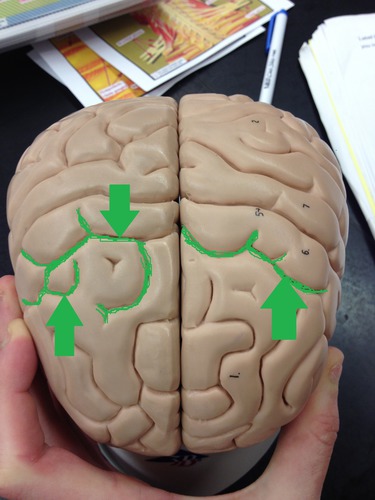
sulci
shallow grooves that separate gyri
31
New cards
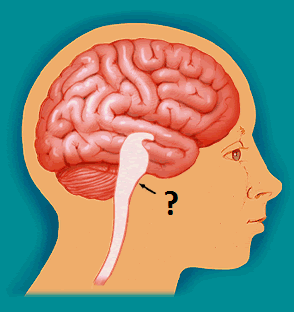
brainstem
beginning where the spinal cord swells as it enters the skull; is responsible for automatic survival functions
32
New cards
medulla
the base of the brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing
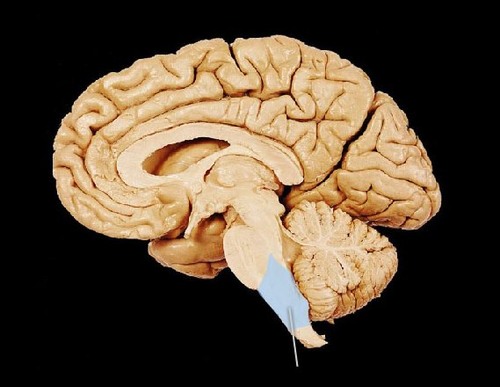
33
New cards
pons
Part of the brainstem that relays information from the cerebellum to the rest of the brain
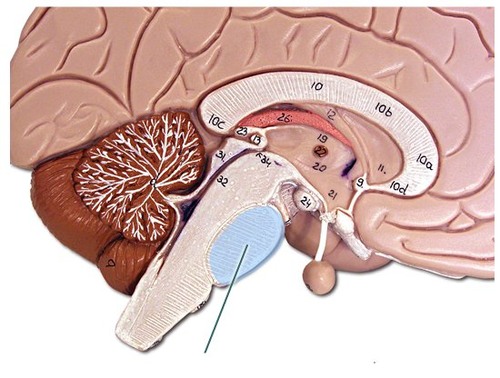
34
New cards
reticular formation
a nerve network in the brainstem that plays an important role in controlling arousal
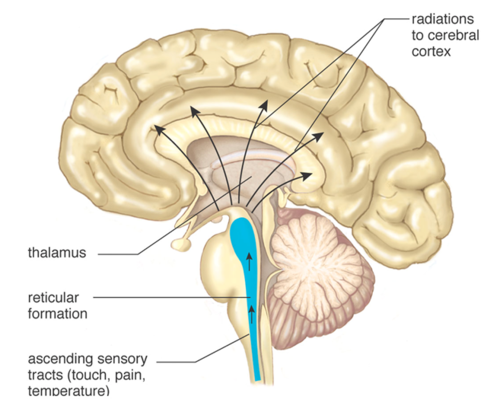
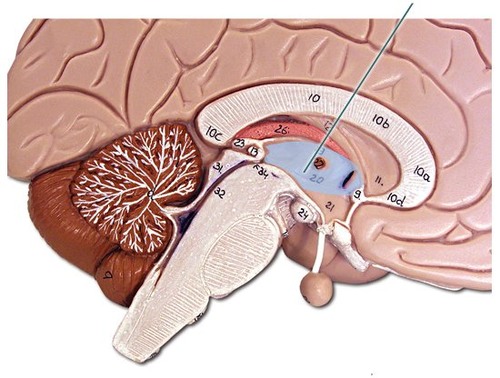
35
New cards
thalamus
the brain's sensory switchboard, located on top of the brainstem; it directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex and transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla
36
New cards
cerebellum
A large structure of the hindbrain that controls fine motor skills.
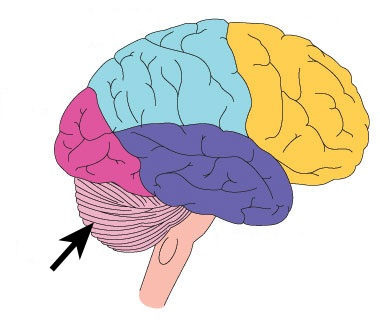
37
New cards
limbic system
neural system located below the cerebral hemispheres; associated with emotions and drives
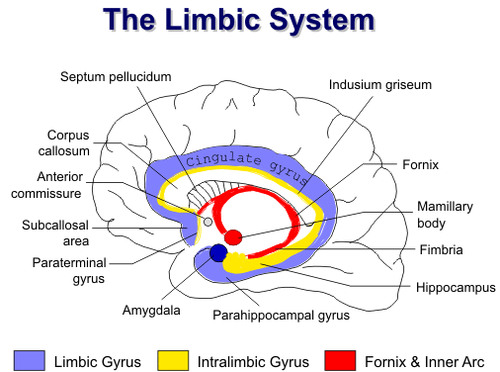
38
New cards
amygdala
A limbic system structure involved in memory and emotion, particularly fear and aggression.
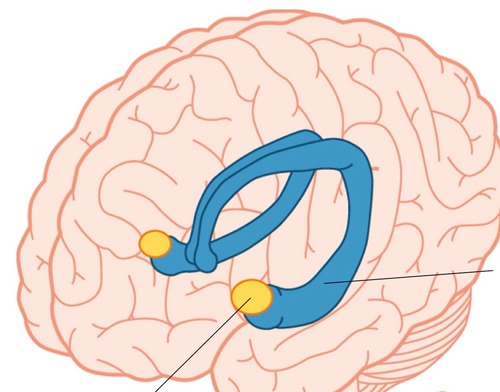
39
New cards
hippocampus
A neural center located in the limbic system that helps process explicit memories for storage.
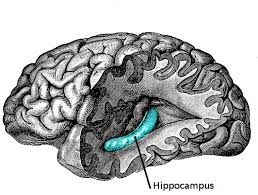
40
New cards
hypothalamus
a neural structure lying below the thalamus; directs eating, drinking, body temperature; helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland, and is linked to emotion
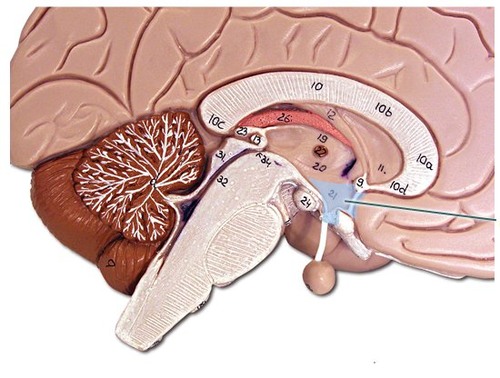
41
New cards
cerebral cortex
The intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells covering the cerebral hemispheres; the body's ultimate control and information-processing center.
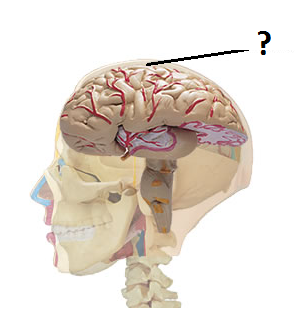
42
New cards
gilal cells
cells in the nervous system that support, nourish, and protect neurons
43
New cards
frontal lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex that has specialized areas for movement, abstract thinking, planning, memory, and judgement
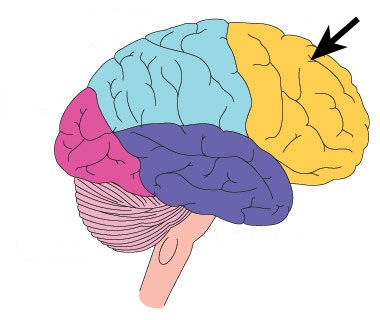
44
New cards
parietal lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex whose functions include processing information about touch.
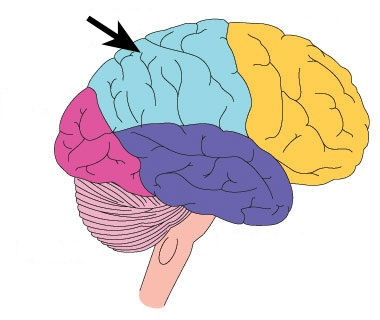
45
New cards
temporal lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex responsible for hearing and language.
46
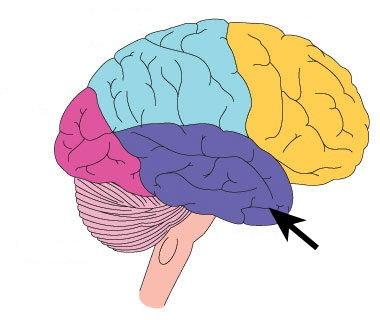
New cards
occipital lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information
47
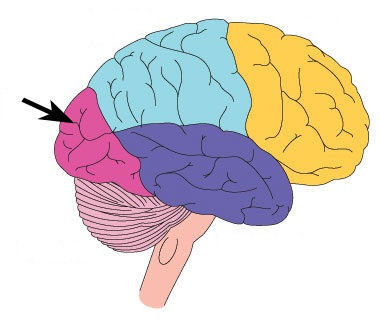
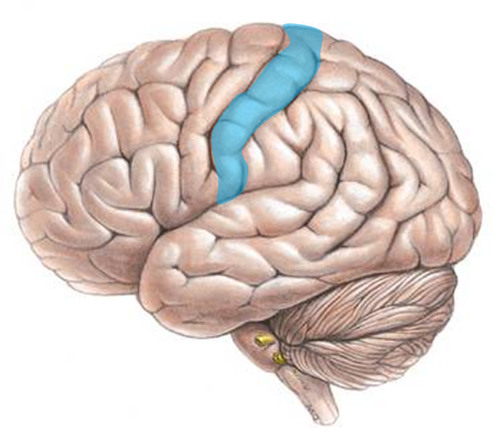
New cards
motor cortex
an area at the rear of the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movements
48
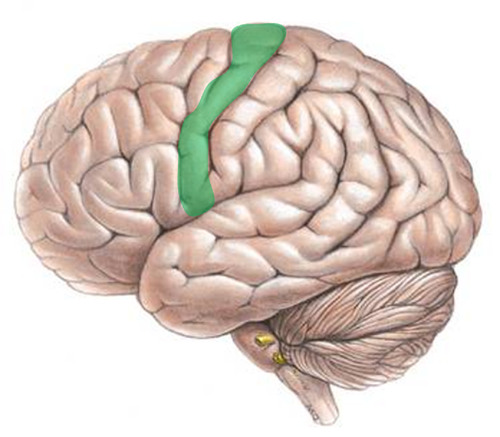
New cards
sensory cortex
area at the front of the parietal lobes that registers and processes body touch and movement sensations
49
New cards
association areas
areas of the cerebral cortex that are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions; rather, they are involved in higher mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking, and speaking
50
New cards
aphasia
impairment of language, usually caused by left hemisphere damage either to Broca's area (impairing speaking) or to Wernicke's area (impairing understanding).
51
New cards
visual cortex
The visual processing areas of cortex in the occipital and temporal lobes.
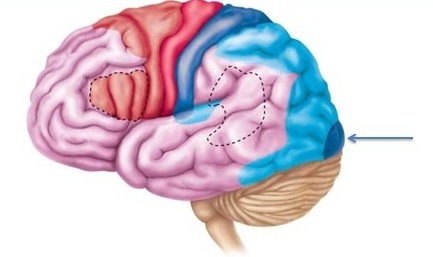
52
New cards
angular gyrus
transforms visual representations into an auditory code
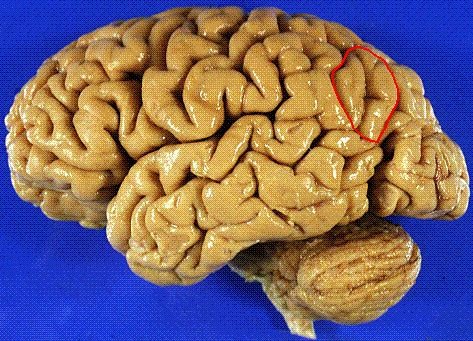
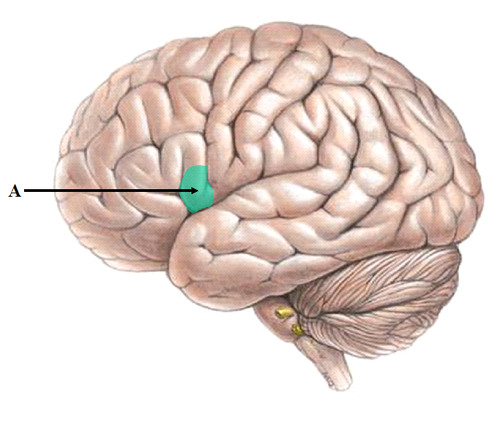
53
New cards
Wernicke's area
controls language reception - a brain area involved in language comprehension and expression; usually in the left temporal lobe
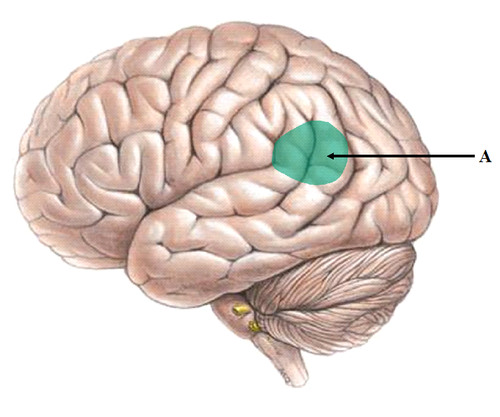
54
New cards
broca's area
Controls language expression - an area of the frontal lobe, usually in the left hemisphere, that directs the muscle movements involved in speech.
55
New cards
neurogenesis
the formation of new neurons
56
New cards
corpus callosum
the large band of neural fibers connecting the two brain hemispheres and carrying messages between them
57
New cards
split brain
a condition resulting from surgery that isolates the brain's two hemispheres by cutting the fibers (mainly those of the corpus callosum) connecting them
58
New cards
Why split-brain surgery is done
to treat epilepsy and laterlization
59
New cards
cells
The basic unit of structure and function in all living things
60
New cards
genes
DNA segments that serve as the key functional units in hereditary transmission.
61
New cards
Chromosomes
threadlike structures made of DNA molecules that contain the genes
62
New cards
Heritability
The proportion of variation among individuals that we can attribute to genes. The heritability of a trait may vary, depending on the range of populations and environments studied.
63
New cards
heredity
the passing on of different physical and mental traits from one generation to another.
64
New cards
nature
Our genetics, biology, and heredity, is what shapes us today.
65
New cards
nurture
Our environment, how our parents raised us, what peers we had, the amount of education and wealth we had at our disposal, that shapes us as individuals.
66
New cards
Charles Darwin
argued that our behaviors and bodies were shaped through natural selection.
67
New cards
reciprocal determinism
environment, behaviour, and the individual can influence and impact each other.
68
New cards
epigenetics
the study of how the environment and a person’s behaviour affect their genes and how they work together.
69
New cards
brain plasticity
The adaptability of the brain to change in response to a person’s experience. This can be done by reorganizing or building new neural pathways.
70
New cards
the nervous system
the fast acting, electrochemical communication network that uses neurons and nerve cells to coordinate activities of the organism.
71
New cards
the endocrine’s system’s hormones
growth hormones, insulin, melatonin, estrogen, and testorene
72
New cards
the pineal gland
Controls the production of melatonin and regulates your sleep cycles.
73
New cards
thyroid gland
produces a thyroid hormone (when signaled by the pituitary gland) which helps regulate metabolism. The thyroid also produces a hormone known as calcitonin- which controls levels of calcium and phosphate in the blood.
74
New cards
parathyroid gland
small gland contained in the small area of the thyroid gland, and secretes parathyroid hormone-which is involved in control of calcium and phosphate metabolism.
75
New cards
pancreas
secretes hormones insulin and glucagon which together regulate blood sugar and carbs.
76
New cards
gonads
reproduce sex hormones
77
New cards
homeostasis
the regulation of the body’s internal environment.
78
New cards
the central nervous system
The brain and spinal cord. This area is reading incoming messages from the peripheral nervous system and sending orders to the rest of the body.
79
New cards
peripheral nervous system
the nerves that are outside the brain and spinal cord. They are taking information from the brain and sending it to the rest of your body, as well as picking up information from those other parts and sending it back to your brain.
80
New cards
affrent (sensory) neurons
neurons conduct impulses from outside the body to the central nervous system.
81
New cards
effrent (motor) neurons
neurons that transmit messages from the central nervous system to the body.
82
New cards
sensory receptors
receptor cells in sense organs that are sensitive to stimuli
83
New cards
somatic nervous system
sensory and motor neurons of the sense organs and the skeletal muscles. These muscles are mostly controlled voluntarily- comparted to the autonomic nervous system.
84
New cards
autonomic nervous system
autonomic responses are involuntary such as heart rate, digestions, perspiration (further divided into the sympathetic and parasympathetic).
85
New cards
sympathetic nervous system
neurons that facilitate the fight or flight response.
86
New cards
parasympathetic nervous system
controls rest or repair, enjoyment, and more. It stimulated digestion decreases heart rate, and more.
87
New cards
neurons
the basic functional unit of the nervous stem. send and receive nerve impulses and chemical signals.
88
New cards
action potential
the message being sent by the neuron through an electrical impulse travelling down the axon.
89
New cards
synapse
the junction between the sending neuron and the receiving neuron
90
New cards
synaptic gap (syanptic cleft)
the space between the axon terminal and the dendrite/ cell body of the receiving neuron where the neurotransmitters are released.
91
New cards
mirror neurons
type of neurons in the brain that makes us mirror the actions of another or yourself.
92
New cards
permeability
the ability for certain ions to cross the cell membrane.
93
New cards
resting potential
When the neuron has mostly negative ions inside and positive ions outside.
94
New cards
threshold
the minimum intensity of a stimulus that is needed to trigger and action potential.
95
New cards
repolarization
the movement of positive ions outside of the membrane after depolarization in order for the cell to return to its resting state.
96
New cards
refractory period
a short time when no other action potentials can occur until the axon is back in its resting state.
97
New cards
axon terminal
the knob-like branches at the ends of the axon that form junctions with other cells.
98
New cards
electrical synapses
for messages that need to be sent quickly and immediately, they have no space between the neurons.
99
New cards
chemical synapses
junctions between 2 neurons that use neurotransmitters to send neural signals.
100
New cards
excitary neurotransmitters
depolarizes the postsynaptic neurons- resulting in a greater likelihood of an action potential.