Organic Reactions
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
What do all organic molecules contain
Carbon
What is a homologous series
family of organic compounds with same functional group
Why are alkenes not used as fuels
They release less energy per mole in combustion. causing incomplete combustion
What does reacting alkenes with hydrogen do
Turn it into an alkane. At 60`C. Needs Nickel Catalyst
What is the reaction of alkene with steam (water)
Make alcohol
Requires heat and high pressure. Reversible reaction
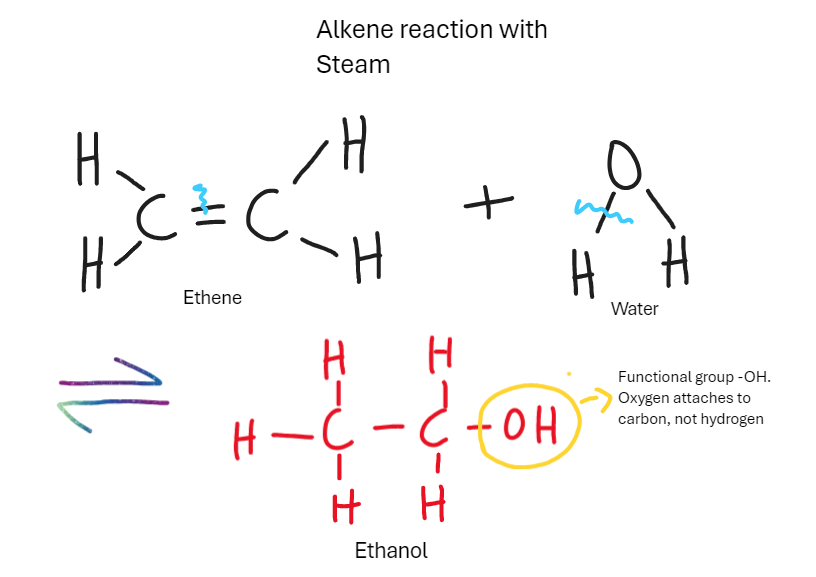
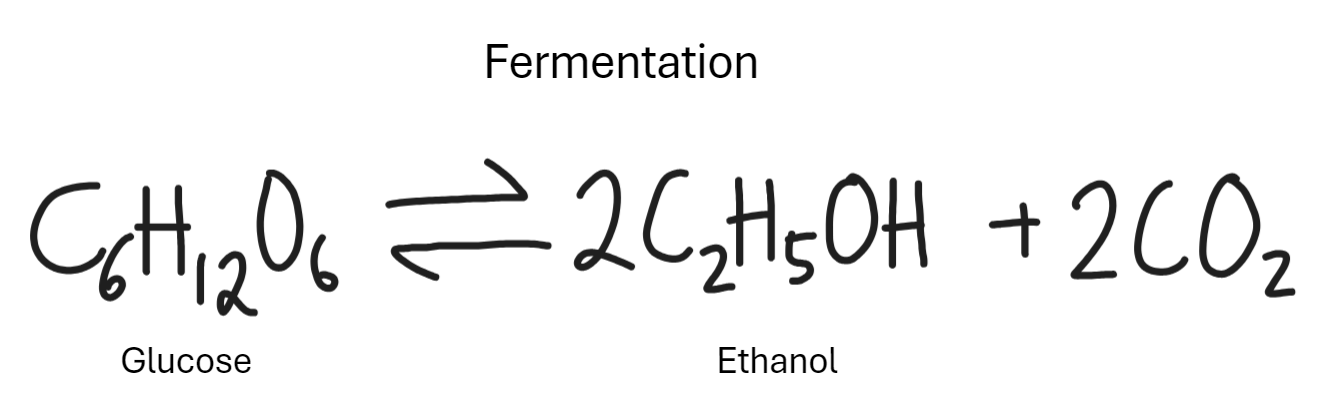
What is the reaction of alcohol with alkenes in fermentation
Breaking down of glucose into alcohol. Uses yeast.
Mixing alcohols with water gives neutral solution. Dissolve organic compounds like ink.
Yeast acts as catalyst
What is the reaction of alcohol with alkenes in combustion (reaction with oxygen)
Flammable.
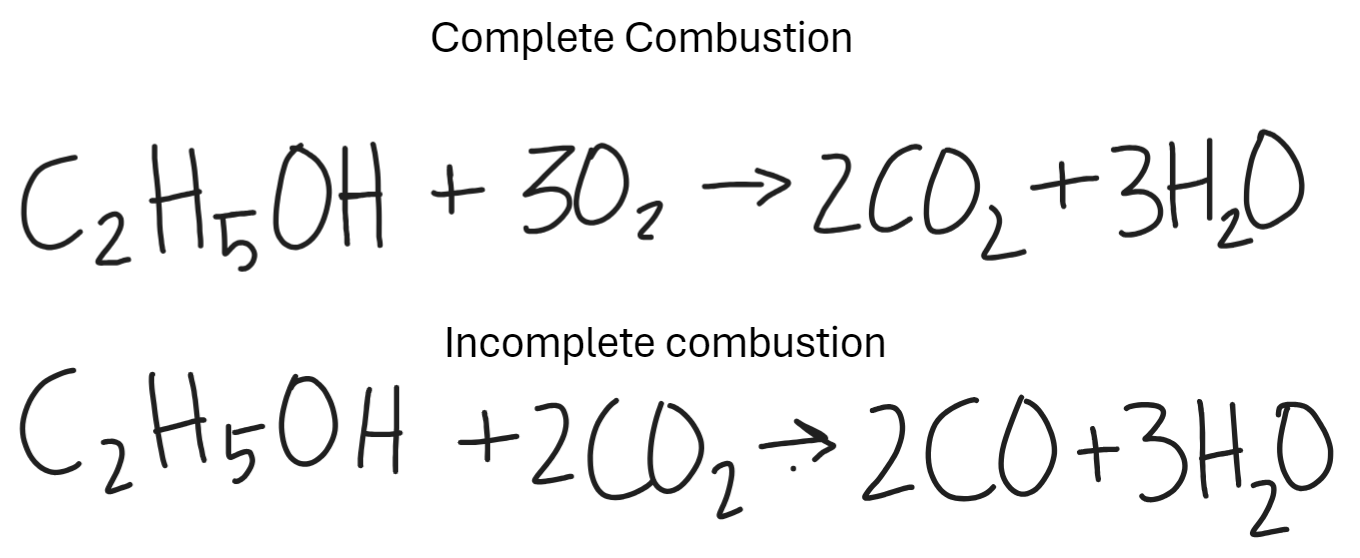
What is the reaction of alcohol with alkenes in Oxidation (Carboxylic Acid)
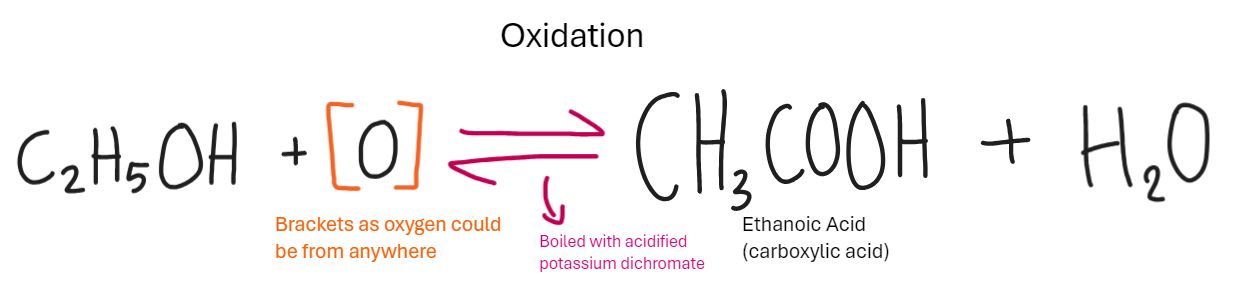
What is a carboxylic Acid
All contain -COOH functional group
Form acidic solution when dissolved in water
E.g. ethanoic acid main acid in vinegar
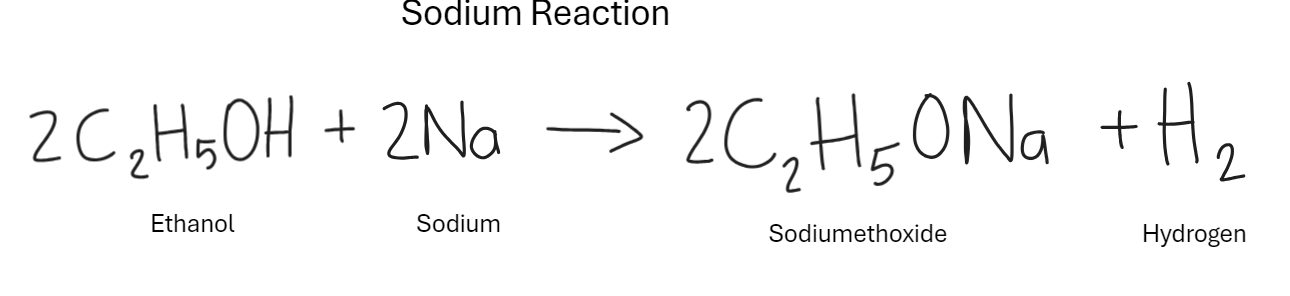
What is the reaction of alcohol with sodium
Effervesces (gives off gas bubbles)
Ethanol can also be oxidised by action of microbes in air
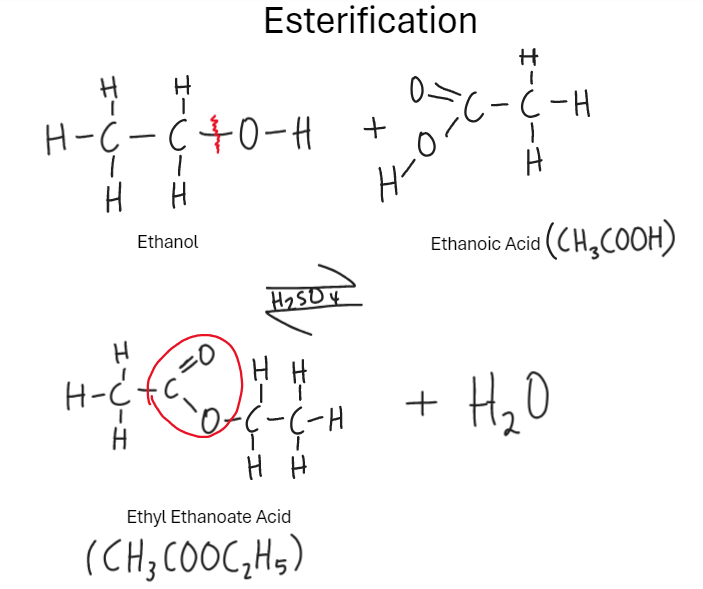
What are Esters
Reaction of alcohols with carboxylic acids (esterification). Replace H atom in -COOH by hydrocarbon (alkyl) group. Is Volatile (evaporates easily) and nice smell.
Why are carboxylic acids called ‘weak acids’
Only a small proportion of the atoms will ionise as it has a higher pH, so lower H+(aq) concentration. Incomplete ionisation because reaction is reversible.
CO2 given off more slowly when metal carbonate reacts with carboxylic acid
E.g. Methanoic acid has lower pH than ethanoic so is a stronger acid as it has higher concentration of hydrogen ions so more collisions per unit time.
What is the homologous series of carboxylic acids
Methanoic acid: HCOOH
Ethanoic acid: CH3COOH
Propanoic acid: C2H6COOH
Butanoic Acid: C3H7COOH