MCAT Psych/Soc: Major Sociological Theories
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
macro sociology
top-down; focuses on large-scale social structures and drills down to how these structures affect groups/individuals
micro sociology
bottom-up; focuses on the smallest building blocks of society (one-on-one interactions) to build up to larger structures
functionalism
In macro sociology, individual parts work together to maintain solidarity, order, balance, and social stability. comparative to living organisms
dynamic equilibrium
many independent parts working together to maintain stability. healthy societies can achieve and maintain this equilibrium, unhealthy ones would not.
Functionalism Theorist
Durkheim
common consciousness
the beliefs, morals, and ideas that are the social facts in a given society
anomie
a mismatch between the wider social standards and the standards of individuals
manifest function
intended and recognized consequence of some element of society
latent function
the unrecognized and unintended consequences of any social pattern
conflict theory
macro, society is a competition for limited resources (wealth, power, and prestige) and individuals and groups compete for social, political, and material power
class struggle
conflict between social or economic classes (especially between the capitalist and proletariat classes)
Conflict Theorists
Karl Marx and Max Weber
socialism
an economic system in which most means of production are collectively owned in order to benefit all members of society equally
class consciusness
members of a subordinate social class are actively aware of themselves as a group that is exploited by the wealthy
false consciusness
lack of class consciousness, see themselves as individuals
Max Weber Conflict theory
said he did not believe the collapse of capitalism was inevitable but argued that several factors moderate people's reaction to inequality
rationalization
societies trend toward increasing efficiency and away from traditional religious standards, promotes impersonal bureaucracies
symbolic interactionism
a micro-level theory in which shared meanings, orientations, and assumptions form the fundamental motivations behind people's actions
symbols
culturally derived social objects that have shared meaning, which is created and maintained through social interaction
Social Interactionism Theorist
Mead
generalized other
the organized and generalized attitude of a large social group
Mead's "I" and "Me"
"me": develops through interactions with others and consists of our interpretation of how the generalized other views us
"I": response to the "me", one's personal identity and individuality
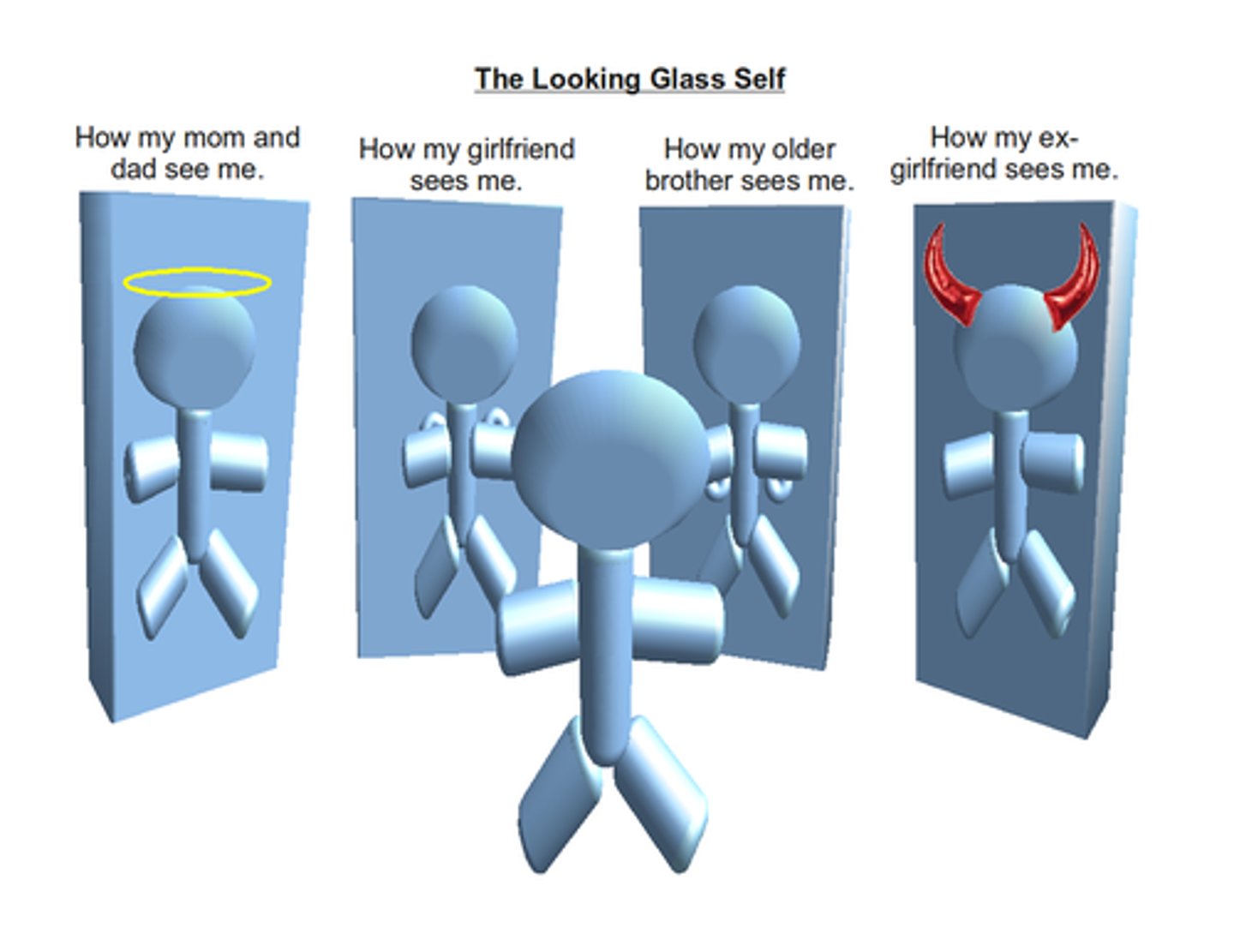
looking glass self
The self is shaped by others' thoughts and opinions, interactions with others, and perceptions. Individuals shape themselves based on others' perceptions to confirm their expectations.
social constructionism
reality is not inherent but socially constructed
social construct
anything that appears natural or obvious to the people who accept it a bit is largely the invention of a given society; it changes with time and culture. (ex: childhood). can be a macro or micro-level theory
socialization
the process by which individuals internalize the values, beliefs, and norms of a given society and learn to function as members of that society and learn to function as a member of that society
rational choice theory
Individuals make decisions by comparing the costs and benefits: max benefits and minimize costs
exchange theory
individuals respond to rewards and punishments; max rewards, minimize punishments
feminist theory
a variety of perspectives on the treatment of women vs men in society. can be either macro or micro
first wave feminism
focused on women's suffrage (vote, own property, equal rights)
second wave feminism
focused on women's social liberties (equality, equal pay, reproductive rights)
third wave feminism
focused on intersectionality: how different social identities interact
glass escalator
the way men are often fast-tracked to advanced positions when entering "pink-collar" professions
glass ceiling
a metaphor representing an invisible barrier that prevents a given demographic from rising beyond a certain level