A103 Lab Practical
1/42
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Be able to put a halter on an animal. Define the parts of a halter (headstall and chin rope). Which side of a a haltered animal should you stand while handling?
headstall = around the animal’s ears and horns
chin rope = under the animal’s chin
stand on the animal’s left side to lead it
if placed properly, tension on the rope will close the animal’s mouth and lift the head up
What is the length of the pregnancy for sheep?
5 months
144-152 days
Describe normal lambing management and post-lambing care.
wear appropriate PPE
look for any signs of lambing
ewe isolating herself, a ewe with a water bag or fetal body part presenting, a ewe that is straining or having abdominal contractions
three stages of parturition
preparation
expulsion of fetus
expulsion of fetal membranes (placenta)
front feet and head should present at vulva first during delivery (lookout for abnormal presentations or positions)
after a lamb is born, immediately…
break the amniotic membrane and clean the nose so it can breathe
lift and rub it hard on its side to make sure it’s sternal
dip the umbilicus cord (or navel) to decrease risk of infection
within the first hour of life, ensure the lamb is standing and nursing
acquires fluid and energy
maintains body temperature
receives antibodies in colostrum
Define zoonotic disease and list 4 routes of transmission of zoonotic diseases.
zoonotic disease = pathogens that could be transmitted from an animal to a human
direct contact (biting, scratching, feces/urine, saliva)
vector-borne (ticks, mosquitoes, fleas)
food-borne (consumption of contaminated food)
water-borne (drinking or washing in contaminated water)
Define PPE and list 5 types of PPE worn on farms.
PPE = Personal Protective Equipment
goggles
masks
coveralls
gloves
boots
Identify the equipment used for lamb processing, and explain the rationale for each step.
ear tagger
weight scale
elastrator bander and bands
burdizzo or emasculotome
hot docker
paint brander
Selenium or Vitamin E injections
ear tagger and ear tag
to identify the individual lamb
weight scale
assess health right from the get-go
can compare to later weight and calculate rate of gain → indirectly evaluate mom’s milk production
elastrator bander and bands
placed about three movable joints down tail (obstructs blood flow leading to testicular atrophy and fall-off)
burdizzo or emasculotome
clamp positioned three moveable joints down tail and held in place for two minutes (crushes blood vessels and nerves)
scalpel blade brought in to cut
hot docker
slowly cuts through tail (cauterizes blood vessel)
paint brander
to associate a lamb to its mother
Selenium or Vitamin E injections
work together for immune system muscle and nerve functions (without, muscles undergo degeneration)
selenium/vit E deficient lambs could display signs of white muscle disease
Define a dental formula. What is the dental formula for sheep dentition. To calculate the total number of permanent teeth, multiply by what number? What is another term for a sheep’s lower canine?
dental formula = a way of summarizing the number and kind of teeth in an animal’s mouth
sheep dental formula
I = upper out of 3/lower out of 3
C = upper out 1/ lower out of 1
P = upper out of 3/lower out of 3
M upper out of 3/lower out of 3
to calculate the total number of permanent teeth, multiply by 2
lower canine = incisor 4
What can be used to estimate a sheep’s age? Be able to provide eruption times for a permanent tooth.
although not entirely reliable, eruption times can be used to estimate a sheep’s age.
eruption times
incisor 1 = 1-1.5 yrs
incisor 2 = 1.5-2 yrs
incisor 3 = 2.5-3 yrs
incisor 4/canine 1 = 3.5-4 yrs
premolars = 1.5-2 yrs
molar 1 = 3 months
molar 2 = 9-12 months
molar 3 = 1.5-2 yrs
List and identify the characteristics of healthy and unhealthy animals.
healthy animals
bright/alert responses
eating and drinking
normal urinating and defecation
natural sleep cycle
chewing cud
normal hair coat
good posture
in-context vocalizing and normal behavior/socializing
normal vital signs (TPR - temperature post-respiration)
unhealthy animals
visible lesions
lethargy
depressed/anxious
immobile/down
unusual vocalizing
coughing/sneezing
nasal/eye discharge
poor hair coat
not eating or drinking
abnormal defecation or urinating (blood/mucus)
List factors in an animal’s environment that impact health
bedding quality
water quality (+ outside water temperatures)
feeders (cleanliness and contents)
ambient temperature and air quality
manure pile-up
safe pens (structure and set-up)
lighting (exposure)
biosecurity protocols
List the average and ranges of normal vital signs (TPRR Chart + CRT) for sheep, goats,cattle, horses, and pigs.
temperature
heart rate, bpm
respiratory rate, brpm
rumination
crt
sheep
temperature = 101-103.5
rectum (anus)
heart rate, bpm = 70-80 [60-120]
inside of hind leg
stethoscope to left side of chest just behind elbow or at “girth line”
respiratory rate, brpm = 12-24
rumination = 1-2 per min
left flank between last rib and pelvis
capillary refill time = < 10 sec
goats
temperature = 101-103.5
heart rate, bpm = 70-80 [60-120]
respiratory rate, brpm = 12-24
rumination = 1-2 per min
capillary refill time = < 10 sec
cattle
temperature = 100-102.8
heart rate, bpm = 60 [40-80]
respiratory rate, brpm = 10-36
rumination = 3 every 2 min
capillary refill time = < 10 sec
horses
temperature =99-101
heart rate, bpm = 24-44
respiratory rate, brpm = 10-24
capillary refill time = < 10 sec
pigs
temperature =101-103.5
heart rate, bpm = 60-80
respiratory rate, brpm = 10-20
capillary refill time = < 10 sec
Define withdrawal period, ELDU, AMDUCA, PO, ID, SC/SQ, IP, IM, IV, and IC.
withdrawal period = time from last drug treatment to when animal or products enters food production chain
extra-label drug use (ELDU) = drug product has animal specifications, but is still safe to use on other species
use of FDA-approved drug in manner not labeled, yet met by conditions of AMDUCA
drugs that pose a risk to humans and drugs only meant for humans are not considered ELDU
Animal Medicinal Drug-Use Clarification Act of 1994 (AMDUCA) = species are not always labeled because companies would need to spend $
per-os (PO) = oral (mouth)
slow/intermediate absorption
intradermal (ID) = layer of skin (caudal tail folds or neck)
slow absorption
TB tests
subcutaneous (SC/SQ) = under skin (neck, over the back)
intermediate absorption
intraperitoneal (IP) = into abdomen
rapid absorption
rodents
intramuscular (IM) = muscle (neck muscles)
rapid absorption
intravenus (IV) = vein (jugular vein, tail vein, milk vein, etc)
immediate absorption
intracardiac (IC) = heart
immediate absorption
Food and Drug Administration
Which government agency assures the safety and efficacy of drugs and regulates labels?
Be able to explain the the advantages of producing and processing milk on the same farm. What is A1/A1 milk and A2/A2 milk?
producing and processing
know the process in and out (complete control)
cost and time efficient
more customers & wholesales (services)
A1/A1 and A2/A2 milk
A1/A1 = contains A1 beta-casein protein that people can find difficult to digest
A2/A2 = contains A2 beta-casein protein that causes less digestive harm on people
neither is better over the other in terms of nutrition, but rather compete in preference of individual consumer digestive issues
At what age are Alta Cow Watch Collars placed on heifers? What is their purpose?
age = 10-11 months
purpose
cow identification
weight tracker
rumination tracker
activity tracker (movement)
temperature tracker
stress tracker
illness?
When are heifers bred for the first time? What percent of cows are bred by AI with semen from Jersey bulls at Mapleline farm? Angus bulls?
first time breeding = 11-12 months or 700-800 lbs
Jersey bulls = 30%
Angus bulls = 70%
Be able to identify different types of dairy barns and milking parlors.
dairy barns
free-stall = individual stalls with free-roaming cows
tie-stall = individual stalls with tethered cows
milking parlors
parallel = side by side
tandem = nose to tail
herringbone = 45˚ angle smaller parallels
rotary = carousel
robotic = self-service walk-in unit
Be able to identify factors on a dairy farm that impact cow comfort.
feed (tillage)
space
bedding (cleanliness)
air ventilation
How is manure managed and stored at Mapleline? What is the manure used for?
stored = large blue tanks outside the barn
use = on field as fertilizer
Define restraint, and explain why restraint is necessary for animals.
restraint = physical/chemical/physiological methods for limiting/controlling animal movement
work w/ animals (handling) - maximizes handler safety
complete tasks/medical procedures (necessary welfare)
maximize animal safety (during procedures)
minimize stress (on animals and handlers)
Identify, demonstrate, &/or describe the restraint techniques that we discussed for dogs, cats, horses, cattle, sheep, goats, and pigs.
dogs
sandbags (x-rays)
harness
Elizabethan collar
muzzles
vocal (voice command/training)
chemical sedation
grooming/genital slings
fences, crates. kennels
cats
sandbags (x-rays)
cat bags, burritos, wraps
Elizabethan collar
scruffing (clipnosis) [trying to step away]
cat gloves
vocal (voice command/training)
chemical sedation
cat carriers
horses
halter / tack (for riding)
cross ties
chain kicks
lip or nose, neck, ear twitch
fences, stalls
chain shank over nose/gums
hobbles (females)
blinders
cattle
headlocks
squeeze chutes
tail jacking
casting (pressure points with ropes)
bull rings, nose tongs
hobbles
dogs
tilt table
pigs
v trough
vertical hold (piglet)
pig snare
pig board
shaker paddles
farrowing or gestation crates
vocal (voice command/training)
chemical sedation
small ruminants
halter
chin hold
tip/tilt on rump
horns (adult)
hoof trimming chutes
hammock (tipped-back cradles)
dogs (sheep > goats)
slings (insemination)
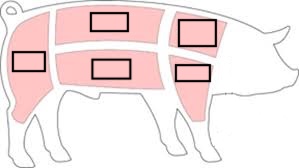
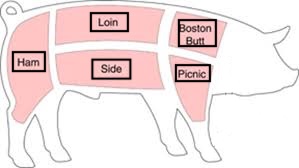
Be able to label the major wholesale cuts (or primal cuts) of pork.
What is the length of pregnancy for pigs?
3 months, 3 weeks, and 3 days
or
114 days
Describe normal farrowing and post-farrowing care for a sow and her piglets.
farrowing crate
temperature 50-70˚F for sows
temperature 85-90˚F for piglets
weighing of piglets (2-4.5 lbs)
normal farrowing duration 2-3 hrs
litter size around 10-12 piglets
What is the difference between a farrowing crate and a gestation crate?
gestation crate = sow’s house before farrowing for monitoring and individual safety
farrowing crate = sow’s house during and after farrowing to minimize piglet mortality during early lactation
What is the “wean-to-estrus” interval for sows? At what age are piglets weaned in a modern production setting?
wean-to-estrus = 4-7 days
piglets weaned = 5-6 weeks (≤ 3 weeks)
Describe each step in piglet processing. Be able to identify the equipment used, list the age range of piglets for each step, and explain the reason for each step.
weigh
clip 8 needle teeth
dock tail
ear notch
inject iron
castrate
weigh
first week (1-3 days)
make breeding decisions
clip 8 needle (or wolf) teeth
1-3 days old
prevent sharp bites of teats, management
dock tail
1-3 days old
prevent boredom/aggressive behavior
ear notch
1-3 days old
identify individual piglets
inject iron
1-3 days old
provide mineral not in mom’s milk for oxygen transport in blood
inject in neck (IM)
castrate
3-14 days old
prevent pregnancies, limit aggressive behavior, avoid boar taint in meat
scapal
Be able to distinguish between a gilt piglet and a boar piglet.
gilt piglets
shorter and slimmer snouts
ears are more “perky” closer to forehead
vulva (external opening of reprod tract)
just below anus
boar piglets
more rectangular head shape
deeper and wider snouts
ears further out and away from forehead
larger and more robust build
scrotum
b/w rear legs below anus
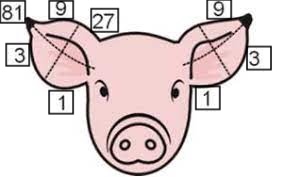
Be able to interpret and apply ear notches.
right ear = litter #
left = individual #
List the vital signs (TPR) for an adult horse at rest.
respiratory rate
heart rate/pulse
mucous membrane color
crt
temperature
respiratory rate (RR) = 10-24 brpm
stomach
heart rate (HR) or pulse (P) = 24-44 bpm
transverse facial artery or facial artery blood vessels
digital pulse = 2 arteries under fetlock
mucous membrane color = pink
gums
capillary refill time (CRT) = ≤ 2 sec
blanche gums
temperature = 99-101˚F
rectul (anus)
List factors that could alter a horse’s vital signs.
weather conditions
physical activity - exercise
stimuli - environment
illness
pending parturition
age

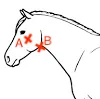
Demonstrate where you would feel the transverse facial artery and the facial (orsubmandibular) artery on a horse.
a. transverse facial artery
b. facial (orsubmandibular) artery
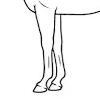
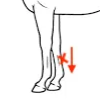
Where would you feel for digital arteries, and what is the significance of a bounding digital pulse?
very faint pulse = good, healthy
heavy pulse = bad, injury or laminitis
distilled limb → inflammation
infection of foot
Demonstrate where you would listen to a horse’s heart, lungs, and cecum.
a. heart
b. cecum
c. lungs
What is a farrier? What is the rate of hoof growth for horses? On average, how often should a farrier evaluate a horse’s hooves?
farrier = a specialist in horse hoof care (trimming, balancing, shoe fitting)
rate of hoof growth = 0.24-0.4 inches per month
farrier visits = every 6-8 weeks
List 3 reasons for shoeing a horse.
basic hoof protection
traction/support
treatment
Identify the 6 areas that should be evaluated to assign a BCS to a horse.
loin
withers
ribs
neck
tailhead
shoulder
What is the scoring range of a horse’s body condition? What are 7 factors that affect a horse’s BCS and what are 5 aspects that are affected by a horse’s BCS? What does the BCS system not tell you?
1 = poor
2 = very thin
3 = thin
4 = moderately thin
5 = moderate (optimal)
6 = moderately fleshy
7 = fleshy
8 = fat
9 = obese
BCS is affected by…
food availability
reproductive activities
weather
performance or work activities
parasites
dental problems
feeding practices
BCS affects…
reproductive capability
performance ability
work function
health status
endocrine status
BCS does not tell you…
how fit a horse is for performance (fat level ≠ muscle tone, cardiovascular fitness, or any other measures of athletic conditioning)
type of fat deposited
Define and explain the purpose of the passive stay apparatus and reciprocal mechanism.
passive stay apparatus = ligaments, tendons, and muscles lock allowing horse to support body weight while standing/resting with 3 legs straight and 1 hind-leg relaxed without using significant enrgy or muscle activity
sleep laying down (rem sleep) = approx 1 hour
sleep standing up (PSA) = majority of time
prey animals need the ability to run from predators at any moment
Define clinical mastitis and subclinical mastitis.
clinical mastitis = visible infection/inflammation of mammary gland/milk
off-color, viscosity milk
hard mammary gland
subclinical mastitis = non-visible infection/inflamation of mammary gland
less milk but don’t know why
cell damage, scar tissue
How is the California Mastitis Test performed? What does the CMT measure?
California Mastitis Test
involves collecting milk samples from each quarter (teat) and adding a reagent to see if a gel or slime-like reaction occurs
discard first few squirts
use a four-well plastic paddle
collect around ½ teaspoon milk from each teat
gently swirl paddle in circular motion to mix reagent and milk
reaction is scored (0 = no gel and 3 = almost solid gel)
negative reaction = no gel formation, milk is normal (no infection)
positive reactions = formation of gel or slime-like consistency
determine # of somatic cells
Compare and contrast Popular, Trade, and Scholarly publications.
include
purpose
audience
reviewed
citations
frequency
ads
popular publications
current events; general interest
inform, entertain, or elicit an emotional response
written by staff writers, journalists, freelancers
general public
reviewed by staff editor
possible informal citations
weekly/monthly publications
numerous ads
simple, generic terminology or explanations
ex. Time, Vogue, Rolling Stone
scholarly publications
research results/reports; reviews of research; book reviews
share research or scholarship with academic community
written by scholars/researchers
scholar, researcher, and student audiences
reviewed by editorial board and some are peer-reviewed
many citations including bibliographies, references, endnotes, footnotes
quarterly/semi-annually publications
minimal ads (usually only in scholarly products like books)
specialized terminology, lack of basic definitions or explanations, extensive citations, often peer-reviewed
ex. American Literature, New England Journal of Medicine, Developmental Psychology
trade publications
certain businesses or industries
inform about business or industry news, trends, or products
written by staff writers, business/industry professionals
business/industry professional audiences
reviewed by staff editor
few citations (may or many not have any)
weekly/monthly publications
ads for products geared towards specific industry
ex. Pharmacy Times, Oil and Gas Investor Magazine
Define database, literature search, literature review, peer review, primary research, and review article.
database = storing and organizing information
manages customer data, stores bibliographic information, manages inventory
literature search = identifying relevant sources for research
uses databased, search engines, and other resources to find scholarly articles, books, and other relevant publications
literature review = source summarizer
critically examines and synthesizes findings of existing research, identifying gaps, and providing an overview of the current state of knowledge on the topic
peer review = critical component of academic publishing
ensures the quality and validity of research by having experts in the field evaluate the manuscript before publishing
primary research = collection of original data through surveys, experiments, or observations
review article = comprehensive summary of existing research on a specific topic
analyzes and synthesizes findings from primary research, highlighting key trends, debates, and areas for future research