IST 1110 Understanding Computers
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapter 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
What are binary?
a list of 0’s and 1’s that are used to represent data in computers.
Also referred to as open & closed circuits.
The computer’s natural language
What is a Bit?
The smallest unit of data that a computer can recognize.
What is a Byte?
8 Bits grouped together are referred to as a Byte.
What is a Kilobyte(KB)?
A Kilobyte is approximately 1000 bytes.
What is a Megabyte(MB)?
A Megabyte is approximately 1000 Bytes.
What is a gigabyte(GB)?
A Gigabyte is approximately 1million bytes.
What is a terabyte(TB)?
A Terabyte is approximately1billion bytes.
What is a Petabyte(PB)?
A Petabyte is approximately 1000 Terabytes.
What is an Exabyte(EB)?
An Exabyte is about 1000 Petabytes.
What is a Zettabyte(ZB)?
A Zettabyte is approximately 1000 Exabytes.
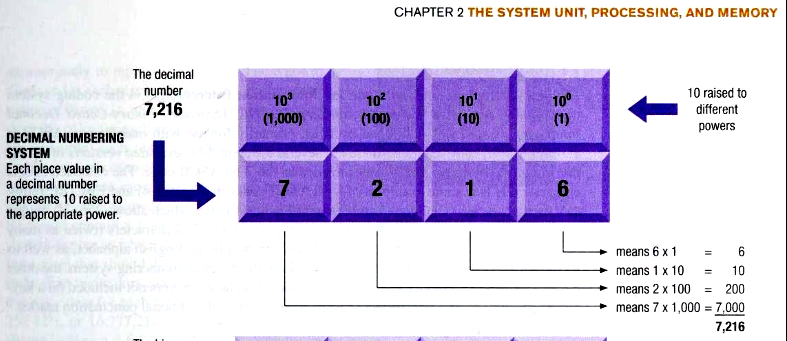
What is the Decimal Numbering System?
A numbering system that uses 10 symbols, 1-9, to represent all possible numbers.
Explain how the power of each base number increases and the order flows in a Decimal Numbering System.
The order is read from right to left.
The base number starts at zero and is increased by 10 for each one after. (The number on the top right that is multiplied by)
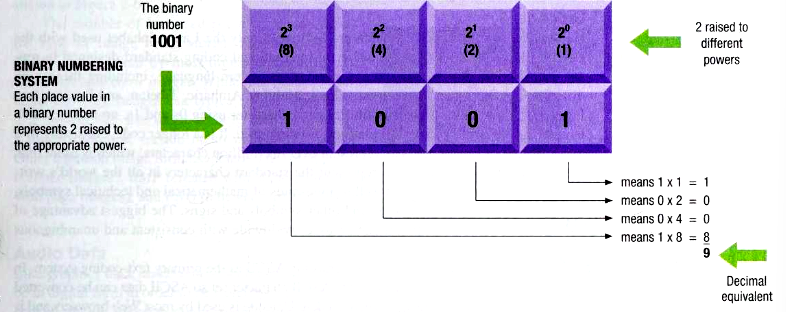
Explain how the power of each base number increases and the order flows in a Binary Numbering System.
The order goes from right to left.
The base number increases by 2.
Unlike the DNS, the overall number can translate into two different numbers. A DNS number equivalent (this example, 1001), and the Binary Number System equivalent (this example, 9 is the representation of 1001).
What is Unicode?
A universal international coding standard designed to represent text-based data written in any language.
What is Graphic Data?
Graphic data that consists of still images.
Bitmap image, is an image made up of a grid of small dots called pixels.
What is a Pixel?
A Pixel is short for picture element, which is a small colored dot on an image.
What is TIF?
A common image format used with scanned images.
What is BMF?
A common image format that is created with some painting programs.
What is BMP?
A common image format that is an older format for web page images.
What is PNG?
A common image format that is a newer format for web page images.
How is Audio Data used?
The digital representation of sound, first as a digital form to be stored in a storage medium or processed by a computer.
What is Video Data?
A collection of frames that contains a still image projected one after another, typically at a rate of 24 frames per second.
What is Machine Language?
A set of Instructions that look like a string of 0’s and 1’s that actually represent a set of specific operations.
What is a System Unit?
The main case of a computer or mobile device that houses the processing hardware.
What is a Circuit Board?
A thin board containing computer chips(IC’s/Integrated Circuits) and other electronic components.
A computer chip also contains interconnected components called Transistors that enable electrical current to perform functions.
What is the Motherboard?
The main circuit board inside the system unit.
What are processors?
The part that does the processing in a computer or mobile device.
What is a Multi-core CPU?
A CPU that contains the processing components of multiple independent processors.
Dual Core CPU = 2 cores
Quad Core CPU = 4 cores
It allows computers to work on multiple tasks at the same time.
Computers today typically have 4 cores.
What does having a higher CPU clock speed mean?
More instructions can be performed per second than at a lower Clock speed.
Today, people look for overall processing speed or performance in computers rather than Clock Speed.
What are Bench Mark test used for?
The Measurement of overall processing speed is the maximum number of instructions that the CPU can process per second.
This is the overall tester for computer processing speed at stores today.
What is Cache Memory?
A special group of very fast memory circuitry usually built into the CPU.
Cache memory is used to speed up processing by storing the data and instructions that may be needed next by the CPU.
When the Cache memory is full, it overwrites the data that is needed to make room for the next set.
Bus
An electronic path that data uses to travel.
Bus Width
The number of wires in the bus that data can use to travel.
The number of Bits that can be transmitted at one time is dependent on the Bus Width,
Bandwidth
The amount of data that can be transferred through the bus at a time. (speed)
Throughput
The amount of data that is actually transferred in real-life conditions.
Memory
Refers to chip based storage.
RAM
Random access memory / main memory / system memory, used to store essential parts of the operating system while the computer is running. (programs/data)
RAM is volatile like cache and registers, meaning its contents are erased once the power to the memory stops.
The amount of RAM you can install depends on your CPU. 32BIt CPU = 4GB RAM, more CPU = more RAM
ROM
Read On Memory and flash memory are nonvolatile.
You can’t write over the data.
NRAM (Nonvolatile)
Consumes less power, and data is retained, which can extend battery life.
MRAM (Magnetic)
Instead of an electric charge to store data, memristor-based RAM change their resistance in response to current flowing through it.
Registers
A high-speed memory built into the CPU to store data.(Fastest type of memory used by the CPU)
Flash Memory (Nonvolatile)
Used for storage by the computer, have started to replace ROM in BIOS(Basic Input Output System) or UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface / the boot up process).
Discussion Question Chapter 1
Select a technology you use every day and consider its
benefits and risks. Answer the following questions:
– What benefits does the technology provide?
– Are there any risks involved, and if so, how can they be
minimized?
– If you chose not to use this technology because of the
possible risks associated with it, how would your life
affected?
– Who should determine if the benefits of a new technology
outweigh the potential risks? Consumers? Companies? The
government?
daily lives, education, and how we communicate with each other
Own opinion.
Discussion Question Chapter 2
1.Define ROM (read-only memory). What is one important
difference between ROM and RAM (random access memory)?
• What are the general operations of a machine cycle?
2. Discuss the design of a hypothetical computer of tomorrow, the
equivalent of a desktop or notebook PC today. How big would the
computer be? Would it be portable or built into furniture or some
other object? Should it be wearable or embedded in a person’s
body? What is the ideal computer of the future?
3. Discuss products that use computer chips and microprocessors
today. What functions do the chips provide to their stated products?
Discuss other products that would benefit from the inclusion of a
processor in the future. What about products that would be
improved if they included built-in computer processing abilities?
ROM (read-only memory) consists of nonvolatile chips that permanently store data or programs, they are attached to the motherboard inside the system unit, and the data and programs are only accessed when they are needed. A unique thing about ROM is that the data inside cannot be added removed or written over, this is why it is called Read-Only, the data/content can also not be erased when the computer is powered off. Traditionally, ROM was used to permanently store instructions for a computer, an example would be firmware.
RAM (Random access memory) consists of volatile chips which is different from ROM's nonvolatile chips, this means that it only temporarily stores the data and programs that are actively being used, and this content is then erased when the computer is powered off. Unlike ROM, the data within RAM is able to be written over and changed at any time, this makes it great for multitasking and running multiple applications that only require data to be stored temporarily. The data storage of ROM is more so used to hold onto important and necessary information for a long period of time. (I didn’t write this, but it seems general )
Own opinion