Carboxylic Acids
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapter 20 guide to carboxylic acids
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
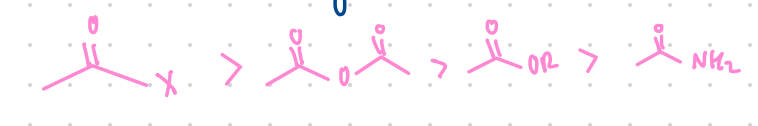
Acid halides > anhydride > esters > amides
What is the order of reactivity of molecules in a nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction?
Begin with acid halides > …
E.W.G.
Which is more acidic?
E.W.G. or E.D.G
(withdrawing) or (donating)
acidity of carboxylic acid
What does the R group determine?
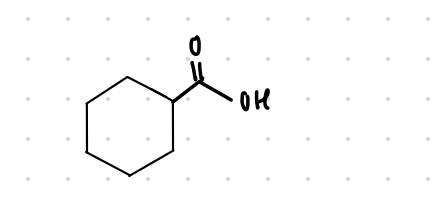
cyclohexanecarboxylic acid
What is the common name of this structure?
1
When number in nomenclature, what number is the carbon carbonyl given?
-oic acid
In nomenclature, the parent name ends how for carboxylic acids?
weak (weak acid)
Br, Cl, F, I are examples of what types of electron-withdrawing groups?
strong (very acidic)
moderate (acidic)
weak (weak acid)
strong (very acidic)
NO2, CN, N+R3, SO3H are examples of what types of electron-withdrawing groups?
strong (very acidic)
moderate (acidic)
weak (weak acid)
moderate (acidic)
-C=O groups are usually considered to be what type of electron withdrawing group?
strong (very acidic)
moderate (acidic)
weak (weak acid)
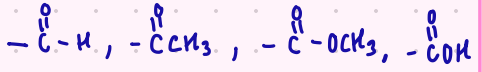
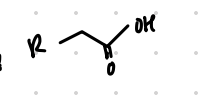
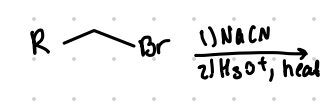
replace Br with COOH
Reagent:
NaCN
———>
H3O+, heat
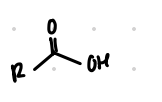
replace Br with COOH
Reagent:
1.) Mg
———>
2.) CO2
3.) H3O+
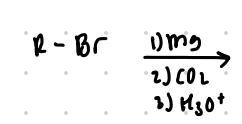
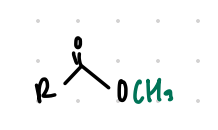
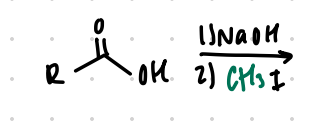
replace H with CH3
Reagent:
NaOH
———>
CH3I