HK 253 Final Exam
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/385
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 8:59 PM on 4/30/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
386 Terms
1
New cards
Define Biomechanics
the study of biological systems from a mechanical perspective
2
New cards
List five careers that utilize biomechanics
\-orthopedic surgeons
\-athletic coaches
\-rehab engineers
\-therapists
\-kinesiologists
\-prosthesists
\-orthotists
\-sports equipment designers
\
\-athletic coaches
\-rehab engineers
\-therapists
\-kinesiologists
\-prosthesists
\-orthotists
\-sports equipment designers
\
3
New cards
Statics
the study of bodies at rest
\-moving at constant velocity or not moving
\-moving at constant velocity or not moving
4
New cards
Dynamics
the study of bodies in motion
5
New cards
Kinematics
describing motion, not the cause of motion
\-distance, displacement, velocity, speed, acceleration
\-distance, displacement, velocity, speed, acceleration
6
New cards
Kinetics
study of the causes and forces behind motion
\-force, moment, work, power
\-force, moment, work, power
7
New cards
Quantitative measures
he jumped 5 meters
8
New cards
qualitative measures
\-he jumped very high
\-the man walked very slowly, leaning to the left, and his gait was asymmetrical
\-the man walked very slowly, leaning to the left, and his gait was asymmetrical
9
New cards
superior
closer to the head
10
New cards
inferior
farther away from the head
11
New cards
proximal
closer to the trunk
12
New cards
distal
away from the trunk
13
New cards
sagittal plane
divides body into right and left halves
14
New cards
frontal plane
splits body into front and back halves
15
New cards
transverse plane
divides body into top and bottom halves
16
New cards
longitudinal axis
\-vertical
\-transverse plane rotation
\-pirouette
\-transverse plane rotation
\-pirouette
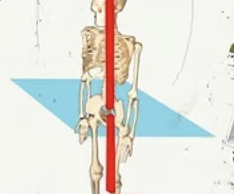
17
New cards
antero-posterior axis
\-frontal plane rotation
\-cartwheel
\-cartwheel
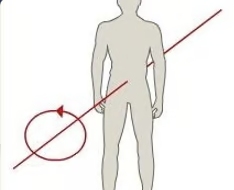
18
New cards
medio-lateral axis
\-sagittal plane rotation
\-somersault
\-somersault
19
New cards
most human movement is a combination of
linear and angular
20
New cards
6 muscle groups
\-hip extensors
\-hip flexors
\-knee flexors
\-knee extensors
\-planterflexors
\-dorsiflexors
\-hip flexors
\-knee flexors
\-knee extensors
\-planterflexors
\-dorsiflexors
21
New cards
shoulder hyperextension
moving from a resting position of the arm to behind the body
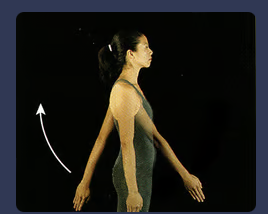
22
New cards
Which of the following are transverse plane movements at the shoulder?
both horizontal abduction and medial rotation
23
New cards
Most human movement falls into which category?
general
24
New cards
Nodding the head "yes" occurs in which plane?
sagittal
25
New cards
elbow extension takes place in what plane?
sagittal
26
New cards
which of the following professions regularly use qualitative observations?
teachers, coaches, clinicians
27
New cards
movements in the transverse plane occur around which axis?
longitudinal
28
New cards
what does the word qualitative mean?
pertaining to quality
29
New cards
which of the following is true regarding qualitative analysis?
it does not involved the use of numbers and it can be general or specific
30
New cards
which of the following limb movements occur during "jumping jacks"?
adduction and abduction
31
New cards
Which of the following is not an example of a sagittal plane movement?
lateral flexion
32
New cards
Primarily in which plane does the swinging of a baseball bat occur?
transverse
33
New cards
which of the following motions occur primarily in the frontal plane?
cartwheel
34
New cards
linear motion
\-rectilinear
\-curvilinear
\-curvilinear
35
New cards
angular motion/rotation
rotating around one point
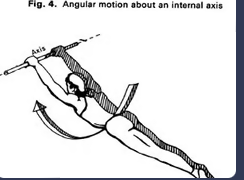
36
New cards
rectilinear motion
motion along a straight line
37
New cards
curvilinear
motion along a curved line
38
New cards
Sagittal plane movements
\-extension and flexion
\-dorsiflexion and plantar flexion
\-dorsiflexion and plantar flexion
39
New cards
shoulder flexion
moving the arm from the resting position to in front of the body
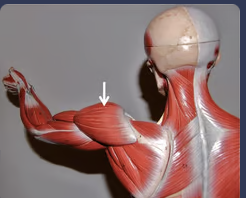
40
New cards
shoulder extension
moving the arm from a flexed position to the resting position
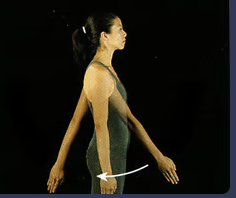
41
New cards
shoulder hyperextension
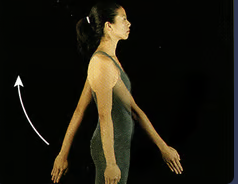
42
New cards
Frontal plane movements
\-abduction and adduction
\-ulnar and radial deviation
\-left and right lateral trunk flexion
\-inversion and eversion
\-ulnar and radial deviation
\-left and right lateral trunk flexion
\-inversion and eversion
43
New cards
transverse plane movements
\-left/right rotation(head, neck, trunk)
\-forearm pronation/supination
\-medial rotation /lateral rotation of hip
\-horizontal shoulder adduction and abduction
\-forearm pronation/supination
\-medial rotation /lateral rotation of hip
\-horizontal shoulder adduction and abduction
44
New cards
three forms of motion
rectilinear, curvilinear, angular motion
45
New cards
Qualitative analysis
description, adjective, nonnumerical, general or specific
46
New cards
biomechanical research relies heavily on
quantitative
47
New cards
If you are a clinician, and you want to improve a person's gait, and you aren't familiar with the task apart from your own experience, what would you do to obtain the relevant knowledge?
consider both qualitative and quantitative assessments
\-use terminology
\-use terminology
48
New cards
Degrees of freedom
1 DOF-movement in one plane
2 DOF-movement in 2 planes
2 DOF-movement in 2 planes
49
New cards
linear/skiing
1 dof in the x axis
50
New cards
angular/knee
1 dof in the y axis
51
New cards
ankle has 2 DOF
1 DOF in the x axis (plantar flexion/dorsiflexion)
1 DOF in the z axis (inversion/eversion)
1 DOF in the z axis (inversion/eversion)
52
New cards
etch a sketch dof
1 in the x axis and 1 in the y axis
53
New cards
hip has 3 dof
flex/ext
abd/add
ext/int
abd/add
ext/int
54
New cards
joints with 3 DOF
hip and shoulder
55
New cards
how many dof at knee
1: flex/ext
56
New cards
how many dof at ankle
2: flex/ext
inv/ev
inv/ev
57
New cards
ipsalteral
refers to the same side
58
New cards
Contralateral
refers to the opposite side
59
New cards
discrete variable
a measure that has a single value
\-step length, gait speed, blood pressure
\-step length, gait speed, blood pressure
60
New cards
continuous variable
a measure that is tracked over time, provides a time series
61
New cards
the loco mat therapy robot allows knee flexion and extension. how many DOF is that?
1
62
New cards
hip extension
bring down leg
63
New cards
flexion
brings two body segments closer together
64
New cards
bead on bar
1 dof
65
New cards
BOS
center of mass must stay within base of support to avoid person falling
66
New cards
6 concepts of kinematics
\-linear displacement
\-linear velocity
\-linear acceleration
\-angular displacement
\-angular velocity
\-angular acceleration
\-linear velocity
\-linear acceleration
\-angular displacement
\-angular velocity
\-angular acceleration
67
New cards
distance is
scalar
68
New cards
displacement is
vector
69
New cards
vector
has magnitude and direction
70
New cards
scalar
has magnitude only
\-distance and speed
\-distance and speed
71
New cards
length is
scalar
72
New cards
speed
The distance an object travels per unit of time
\-will never be negative
\-will never be negative
73
New cards
velocity
displacement/time
74
New cards
to convert from m/s to mph
multiple by 2
75
New cards
negative value tells you
you're going in a negative direction
76
New cards
speed is the product of
stride frequency and stride length
77
New cards
elite sprinters
greater stride frequencies with average stride length
78
New cards
elite skaters
greater stride frequencies with average stride length
79
New cards
positive acceleration
\-subject is increasing velocity and moving in positive direction
\-subject is decreasing velocity and moving in negative direction
\-subject is decreasing velocity and moving in negative direction
80
New cards
negative acceleration
\-subject is increasing velocity and moving in negative direction
\-subject is decreasing velocity and moving in positive direction
\-subject is decreasing velocity and moving in positive direction
81
New cards
If a dropped ball has a negative acceleration, what does that mean?
it means the ball is accelerating in a negative direction
82
New cards
What are the possible explanations for a negative acceleration?
subject could be decreasing velocity or they could be accelerating in a negative direction
\-ve, +direct
\+ve, -direct
\-ve, +direct
\+ve, -direct
83
New cards
What are the possible explanations for a positive acceleration?
subject could be increasing velocity or they could be accelerating in a positive direction
\+ve, +direct
\-ve, -direct
\+ve, +direct
\-ve, -direct
84
New cards
When displacement reaches a peak, what is velocity?
0 m/s
85
New cards
What has occurring in the displacement when velocity reaches a peak?
when velocity reaches a peak, we have reached the maximum vertical displacement
86
New cards
Toe clearance
minimum toe height during swing
\-indicated likelihood of stubbing foot and tripping
\-indicated likelihood of stubbing foot and tripping
87
New cards
You have collected some gait data. During the swing phase, the foot is moving in a negative direction in the antero-posterior plane. during the mid-swing , the foot velocity is -4 m/s and at heel contact, the foot velocity is at -0.1 m/s
=the foot is decelerating, and the foot acceleration will be positive \*
\-think of subject in book, velocity is negative bc moving in negative direction
\-, -=+
\-think of subject in book, velocity is negative bc moving in negative direction
\-, -=+
88
New cards
Which of the following is not a kinematic quantity?
force
89
New cards
You have collected some gait data. during the swing phase, the foot is moving in a POSITIVE direction in the ant-posterior plane. during mid-swing the foot velocity is 4 m/s and at heel contact the foot velocity is 0.1 m/s
the foot is decelerating and the foot acceleration will be negative
90
New cards
Linear distance traveled per unit of time describes what?
speed
91
New cards
cart lewis changes his velocity from 8 m/s to 11 m/s. Michael Johnson changes his from 7 m/s to 10 m/s. Who has the greater acceleration?
need more info to answer (no time segment)
92
New cards
A runner's acceleration is -6 m/s, Which of the following describes the motion of the runner?
the runner may be EITHER: decreasing velocity(decelerating) in a positive direction or increasing velocity(accelerating) in a negative direction
93
New cards
Which of the following in a scalar quantity
distance and speed
94
New cards
a car is moving at a velocity of 120 m/s at time\=5 seconds. at time\=15 seconds, the car velocity is 20 m/s. What is the acceleration?
=-10 m/s/s
(120-20/5-14=100/-10)
(120-20/5-14=100/-10)
95
New cards
it takes a swimmer 1 hour to cross one lake that is 0.5 km long. What is the swimmer's acceleration?
it cannot be determined from the info given (need velocity, it isn’t always constant)
\-0.5km/1hr is speed
\-0.5km/1hr is speed
96
New cards
If velocity is constant, then acceleration is what?
zero
97
New cards
What is the average speed of a cyclist who covers 10 km in 30 mins
20 km/hr
10km/0.5 hr=20
10km/0.5 hr=20
98
New cards
A stick figure is a kinematic description of
\-linear displacement(position of body in space)
\-segment and joint angles
\-with more than one frame, determine velocity
\-segment and joint angles
\-with more than one frame, determine velocity
99
New cards
What is greater velocity: 118 m/s or -150 m/s?
-150 m/s
100
New cards
Projectile
bodies projected into the air that are in free fall