A&P Chapter 1
1/72
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Introduction to Anatomy & Physiology I Chapter 1 Terms
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
Cell
smallest independently functioning unit of a living organism
Organelles
small functional units within cells enclosed by membrane
Tissue
group of many similar cells (sometimes of a few related types) that work together to perform a specific function
Organ
anatomically distinct structure of the body composed of two or more tissue types
Organ system
group of organs that work together to perform major functions
The order of increasing structural units of the human body
Organelles → Cell → Tissue → Organ → Organ system
Metabolism: Catabolic reactions
Break materials down, releases energy and also requires energy
Metabolism: Anabolic reactions
Building reactions, require energy
Growth and three definitions
Increasing in body size
1. Increasing the no of existing cells
2. Increasing the amount of non-cellular material around cells
3. Within very narrow limits, increasing the size of existing cells
Requirements for human life
Oxygen
Nutrients
Temperature (37C)
Atmospheric pressure (1atm)
Homeostasis
The state of steady internal conditions maintained by living things within the physiological state in a range compatible with life.
Homeostasis: Negative feedback
Reverses a deviation (too much or too little) from the set point
Homeostasis: Positive feedback
Intensifies a change until the set point (endpoint) is reached
Homeostasis: Negative Feedback Loop
Stimulus arrives (the deviation) → Monitors condition + Registers change → processes information + communicates with effector if needed → negates the change to return to set point
Blood Pressure
Pressure exerted by blood onto blood vessels
Risks for High Blood Pressure
Too much strain on vessel (thickening) might led to damage
Risks for Low Blood Pressure
Not enough blood/supplies reaching body tissues
Childbirth Positive feedback loop
It is a endless loop until the baby leaves the mother.
→ Head of baby pushes against cervix →
Nerve impulses from cervix transmitted to the brain →
Brain stimulates pituitary gland to secrete oxytocin →
Oxytocin carried in the bloodstream to uterus →
Oxy stimulated uterine contractions and pushes the baby towards the cervix →
Blood Clot Positive Feedback loop
A later enzyme in the clotting cascade either enables o greatly accelerates an earlier step →
Injured blood vessels attract platelets to bind and to release chemicals that attract more platelets blood vessel is sealed
Standard Anatomical Position
Front facing
Palms rotated anteriorly
Legs slightly apart
Supine
Lying while face up
Prone
Lying while face down
Superior
Cranial, closer to the head
Inferior
Caudal, closer to the toes
Anterior
Ventral, towards the face
Posterior
Dorsal, towards the bum
Superficial
Outer
Deep
Inner
Proximal
Close to the trunk of the body
Distal
Away from the trunk of the body
Lateral
Away from the midline
Medial
Toward the midline
Ipsilteral
On the same side of the body
Contralateral
On the opposite side of the body
Sagittal/Medial Plane
Seperates the left and right, down the middle
Frontal/Coronal Plane
Seperates the front and back
Transverse (Horizontal) Plane
Seperates the top and bottom
Oblique Transverse Plane
Seperates top and bottom at an angle
Dorsal Body Cavity
Cranial Cavity + Vertebral Cavity
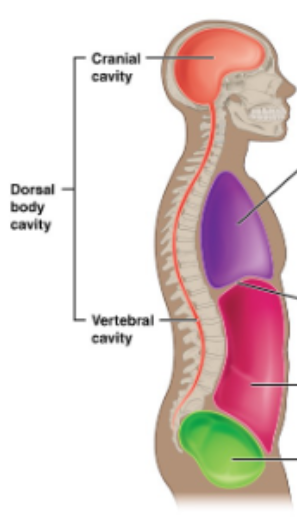
Ventral body cavity
Thoraic cavity + Abdominopelvic cavity

What are Serous Membranes and Cavities?
Thin membranes that cover the walls and organs in the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavity. This allows seperate movement of different organs preventing friction and the spread of infections.
Part of a Serous Membranes and Cavities
Parietal Layer
Visceral Layer
Fluid-filled cavity
Serous Membranes and Cavities: Parietal Layer
Member on the outer side, further from the organ
Serous Membranes and Cavities: Visceral Layer
Member on the inner side, on the organ
Type of Serous Membranes and Cavities
Pleura
Pericardium
Peritoneum
Cavities: Pleura
Around lungs, Pleural Cavity
Cavities: Pericardium
Around the heart/ Pericardial Cavity
Cavities: Peritoneum
Around many organs/ abdominopelvic cavity

What is the name of this Cavity? What group of cavities do they belong to?
Carnial Cavity; Dorsal Body Cavity
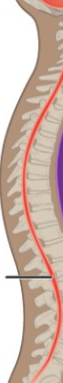
What is the name of this Cavity? What group of cavities do they belong to?
Vertebral Cavity/ Dorsal Body Cavity
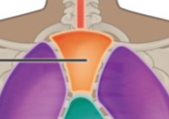
What is the name of this Cavity? What group of cavities do they belong to?
Superior mediastinum Cavity/Thoracic Cavity; Ventral body Cavity
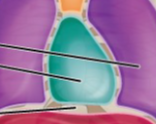
What is the name of this Cavity? What group of cavities do they belong to?
Pericardial Cavity/ Thoracic Cavity; Ventral body Cavity
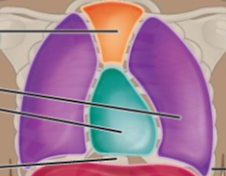
What is the name of this Cavity? What group of cavities do they belong to? (Purple)
Pleural Cavity/ Thoracic Cavity; Ventral body Cavity
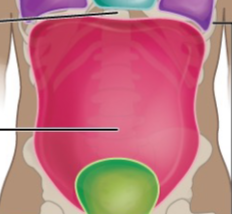
What is the name of this Cavity? What group of cavities do they belong to?
Abdominal Cavity/ Abdominopelvic Cavity; Ventral body Cavity
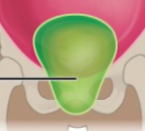
What is the name of this Cavity? What group of cavities do they belong to?
Pelvic cavity/ Abdominopelvic Cavity; Ventral body cavity
What seperates the Thoracic and Abdominopelvic cavities?
Diaphragm
What is the middle region of the peritoneal cavity?
Umbilical region
What is the top middle region of the peritoneal cavity?
Epigastric region
What is the lower middle region of the peritoneal cavity?
Hypogastric region
What is the upper left region of the peritoneal cavity?
Right Hypochondriac region
What is the upper right region of the peritoneal cavity?
Left Hypochondriac region
What is the middle left region of the peritoneal cavity?
Right lumbar region
What is the middle right region of the peritoneal cavity?
Left lumbar region
What is the lower right region of the peritoneal cavity?
Left iliac region
What is the lower left region of the peritoneal cavity?
Right iliac region
Electromagnetic radiation
Stream of mass-less particles, called photons, traveling in a wave like pattern at the speed of light.
Magnetism
Force exerted by magnets when they attract or repel each other. Magnestism is caused by the motion of electric charges
Sound Waves
Longitudinal pressure waves in any material medium regardless of whether they constitute audible sound
X-rays
High energy electromagnetic radiation, penetrates solid and ionizing gases stopped by a backboard.
Single Snapshot
CT
Cross section scanner taking 360 x-ray images
Details allow to measure the size of a mass down to a millimeter
MRI
Magnetism and radio waves (no radiation)
Cancer tissue emit differently than normal tissue
MRI with contrast uses a liquid injected visibility of internal organs (Color images)
PET Scan
Most invasive
Uses short-lived ingested radio pharmaceuticals
Physiologic activity detected from emitted radiation
ie. blood flow, heart disease, infections, spread of cancer
Ultrasonography
Least invasive
High frequency sound waves
Image quality operator-dependent
Cannot penetrate bone and gas
Commonly used for pregnancy and gall bladder disease