AP Micro Econ Unit 9
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
1
New cards
Profit Formula
Total Revenue - Total Cost
2
New cards
Total Opportunity Cost Formula
Total explicit cost+ total implicit cost
3
New cards
What does it mean if your total revenue is higher than the sum of your implicit and explicit costs?
Operating your business is better than another activity.
4
New cards
What does it mean if your total revenue is lower than the sum of your implicit and explicit costs?
Another activity aside from your business is better for your time and resources.
5
New cards
What is the optimal output rule?
Profit is maximized by producing the quantity of output at which the marginal revenue of the last unit produced is equal to its marginal cost.
6
New cards
What is the principle of marginal analysis?
Every activity should continue until marginal benefit equals marginal cost.
7
New cards
Marginal Revenue Formula
Change in total revenue/change in qty of output
8
New cards
What is the optimal output rule?
Profit is maximized by producing the qty of output at which the marginal revenue of the last unit produced is equal to its marginal cost.
9
New cards
Grpah showing marginal revenue curve, marginal cost curve, and optimal output.
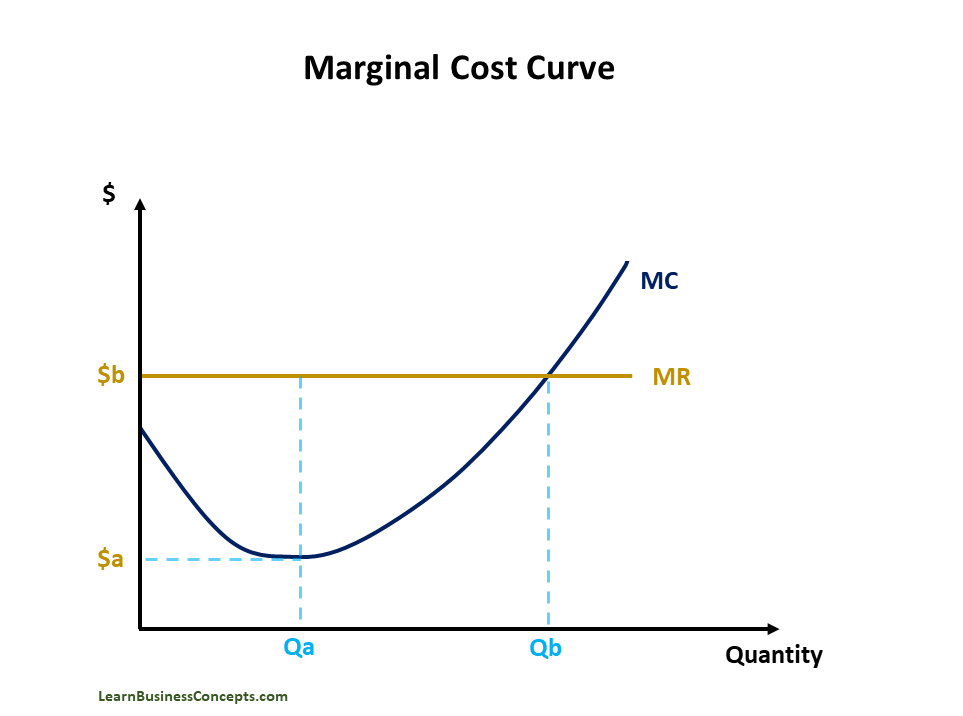
10
New cards
What is the production function?
The relationship between the qty of outputs a firm uses and the qty of output it produces
11
New cards
What is the relationship between quantity and the long run?
All inputs can be varied
12
New cards
What is the relationship between quantity and the short run?
At least one input is fixed
13
New cards
Total Product Curve
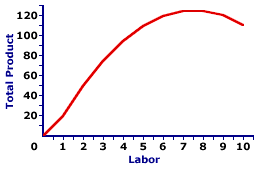
14
New cards
Marginal Product of Labor Formula
Change in qty/change in labor
15
New cards
Marginal product of labor graph
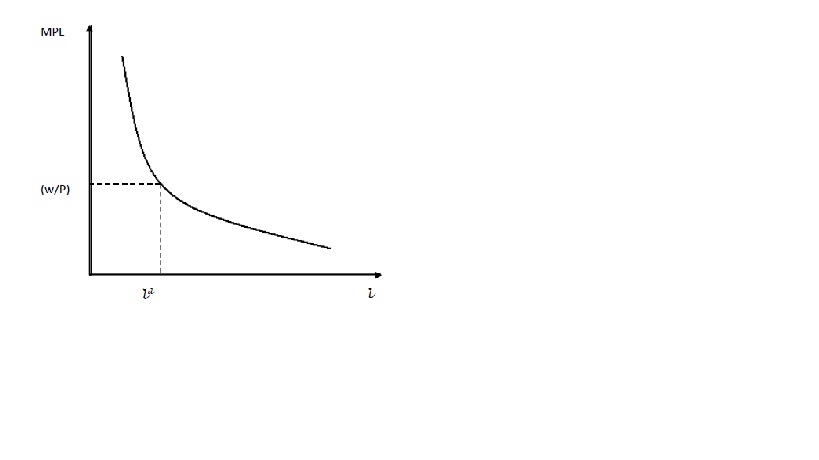
16
New cards
Total Cost Curve
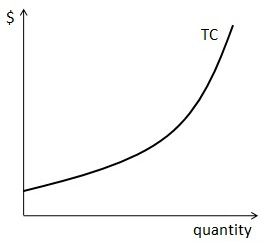
17
New cards
Marginal Cost Formula
Change in total cost/ Change in qty of output
18
New cards
Marginal Cost Curve
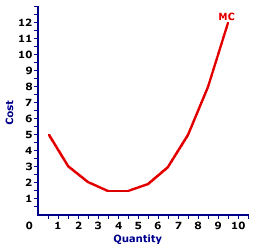
19
New cards
Average Cost formula
total cost/qty of output
20
New cards
Average Total Cost Curve
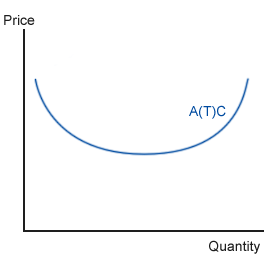
21
New cards
Average Fixed Cost Formula
Fixed cost/ qty of output
22
New cards
Average variable cost formula
Variable cost/ qty of output
23
New cards
What is the spreading effect
The larger the output, the greater the qty of output over which fixed cost is spread, leading to a lower average fixed cost.
24
New cards
What is the diminishing returns effect?
The larger the output, the greater the amount of variable input required to produce additional units, leading to a higher average variable cost.
25
New cards
Graph with mcc, atc, avc, afc
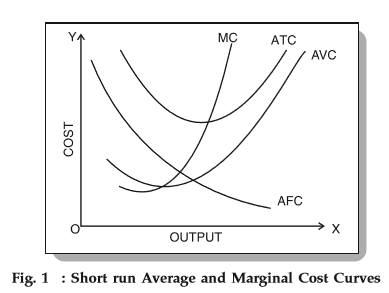
26
New cards
What is the minimum cost output
The qty of output at which avg total cost is lowest, it corresponds to the bottom of the U shaped average total cost curve.
27
New cards
What are the three general principles that are always true about a firm’s marginal cost and average total cost curves?
1. At the minimum cost, average total cost is equal to marginal cost
2. At output less than the minimum cost of output, marginal cost is less than average total cost and average total cost is falling
3. At output greater than the minimum cost of output, marginal cost is greater than atc, and atc is rising
28
New cards
What is the actual curvature of the mcc?
It curves downward as a firm increases its production from zero up to some low level, sloping upward only at higher levels of production.
29
New cards
What is the actual curvature of the atc?
It is U shaped, mcc goes through the min point of atc
30
New cards
What is the actual curvature of the avc?
It’s U shaped
31
New cards
What is the actual curvature of the average fixed cost curve?
Backwards exponential
32
New cards
Average fixed cost curve
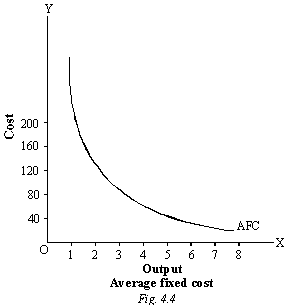
33
New cards
When do low fixed costs yield lower average total cost?
At low output levels
34
New cards
When do high fixed costs yield higher average total cost?
At high output levels
35
New cards
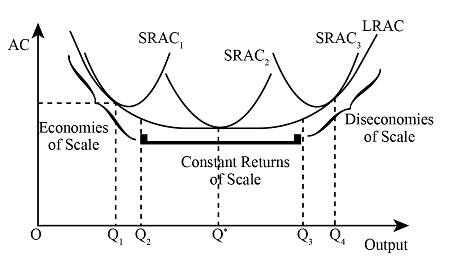
Graph that shows lratc, economies and diseconomies of scale
36
New cards
What determines the shape of the lratc?
Returns to scale