Lecture 1: ENT
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Treatment of auricular hematoma
Incision & Drainage with compressive bolsters
Antibiotics: Staph coverage
Mastoiditis
Can be otitis media complication
Displaced pinna
Subperiosteal abscess
Petrous apicitis: Abducen’s palsy (CN 6) and Retro-orbital/mastoid pain
Facial paralysis (CN 7)
Labyrinthitis (CN8): Vertigo/Hearing loss/Nystagmus
Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Rapidly progressing (less than 3 days)
No trauma
Etiology: Viral or Vascular
Ear examination is normal
Hearing loss, aural fullness, tinnitus, vertigo
Asymmetric audiogram/tuning forks
2/3 recover hearing
Initial severity and responsiveness to corticosteroids help predict outcome
Malocclusion and open bite
Midface Fracture
Septal Hematoma
Nasal fracture
Chin hypesthesia & floor of mouth hematoma
Mandible Fracture
Raccoon eyes
Temporal Bone Fracture
Malar depression
Zygoma Fracture
Inability to perform an upward gaze
Orbital Floor Fracture
Bell’s Palsy
Acute facial paralysis
Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV)
Neural edema within the sheath of the temporal bone
Acute/rapid onset
No hearing loss or vertigo
Facial or ear pain is possible but less common
Corticosteroids and antivirals (acyclovir)
Eye Care is most important:
Patient education
Lubrication/tear replacement/eye closure
Ophthalmology consultation
Prognosis:
85% recover in 3 weeks
15% recover in 3-6 months
Synkinesis and residual weakness in 10-15%
Ramsay Hunt Syndrome
Aka Herpes Zoster Oticus
Shingles of the geniculate ganglion
Differentiation from Bell’s Palsy:
Severe pain accompanies facial paralysis
Vesicular eruption: Face, Ear or external auditory canal/TM, Palate
Hearing loss and vertigo in 10-40%
Worse prognosis vs Bell’s
60% normal recovery
Worse if complete paralysis
Otitis Externa Treatment
Ototopical agents
Epistaxis
Anterior Epistasis:
Keisselbach’s Plexus aka Little’s Area
Spray with decongestant (ie oxymetazoline)
Pressure (10 minutes or more)
Silver nitrate
Anterior packing
Posterior:
Posterior packing
Endoscopy, arterial ligation, embolization
Sphenopalatine artery or ethmoid arteries
Invasive Fungal Rhinosinusitis
Immunocompromised patient:
Uncontrolled diabetic
Oncologic patient (neutropenia)
Few symptoms - discharge, pain
Intranasal exam - blackened mucosa
CT/ MRI to evaluate invasion
Amphotericin B and debridement
Prognosis - very poor:
Correct underlying immunodeficiency:
Control blood sugar
Granulocyte stimulating factor
Microbes in deep neck space infection
Most common is Strep and Staph
Gram negative
Ludwig’s Angina
Submandibular/sublingual infection
Secure airway early
Rapid progression common
Respiratory distress
Angioedema
Acute painless mucosal edema: Face, lips, tongue, larynx
Airway obstruction
Etiology: ACE Inhibitor - most common
Foreign Body Aspiration
History very important
Young child - <3 years old
Paroxysm of coughing
Nuts, plastic toy, popcorn
Examination - negative (40%-50%)
Radiology- 80% radiolucent
Chest x-ray normal (10%-34%)
Inspiratory/ expiatory x-ray
Fluoroscopy
Rigid bronchoscopy
Diagnostic and therapeutic
Children:
Symptoms often subtle
Drooling, sore throat
Coin (#1), Food
Adult:
Diagnosis straightforward
Associated esophageal pathology
Fishbone, meat, denture
Foreign Body Aspiration Radiology
Air-trapping on the affected side seen as hyperinflation on expiratory view (or unilateral atelectasis if complete obstruction)
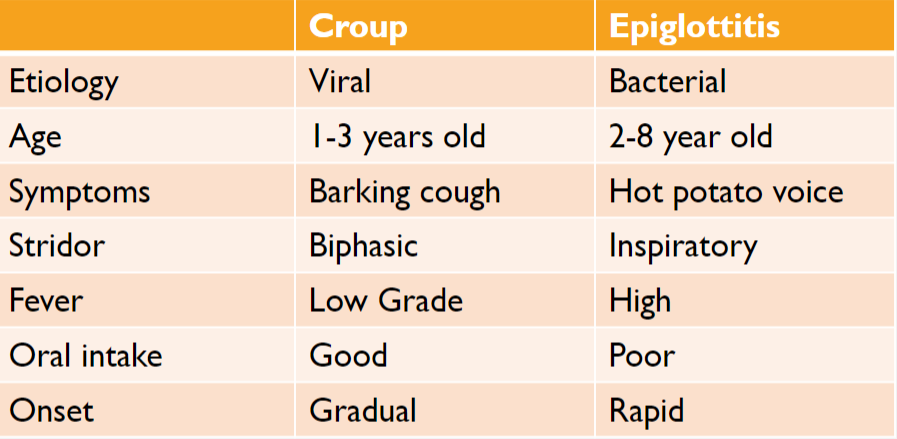
Croup vs Epiglottis
Croup: Subglottic narrowing
Epiglottis: Epiglottic swelling