Classification of stars
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lumiosity and apparent magnitude, Stefan's law, Wien's displacemenet law - A-level AQA Physics OPTIONS
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Hipparchus’ scale for apparent magnitude
m = alogb
where a is the constant of proportionality, b is the apparent brightness and m is the apparent magnitude
What is the apparent magnitude?
A measure of the star’s apparent brightness. The larger the apparent brightness, the larger the apparent magnitude.
deriving Hipparchus’ scale
m2 - m1 = -2.5log(b2/b1)
(a = -2.5)
Apparent magnitude scale (general knowledge)
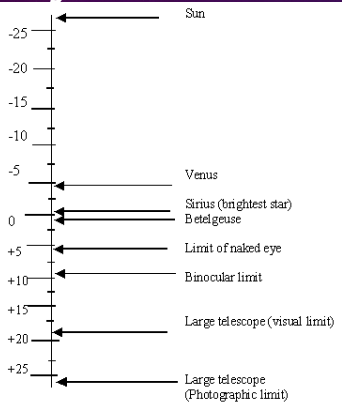
Issues with Hipparchus’ apparent magnitude scale
does not take into account the distances of the stars
it is a subjective measure
luminosities of stars could only be compared this way if they were all the same distance from the Earth
What is meant by the absolute magnitude
The apparent magnitude of a star if it were observed from a distance of 10 parsecs from the Earth
sign for absolute magnitude
M
if (m-M) is negative…
the stars are closer than 10pc
if (m-M) is positive…
the stars are further away than 10pc
What are standard candles?
Celestial objects whose luminosities are known (theoretically derived). These can be used to determine distances of objects in the universe.
what is (m-M) called?
the distance modulus
What is the astronomical unit?
The mean distance of the centre of the Earth to the centre of the sun. Mean distance as the Earth’s orbit path around the sun is an ellipse.
Also described as the distance at which 1 AU subtends an angle of 1 arcsecond.
What is a light year?
Measure of distance; the distance an EM wave travels in one year in a vacuum.
What is meant by parallax?
The apparent change of position of a nearer star in comparison to distant stars in the background. This happens as a result of the Earth’s orbit around the sun.
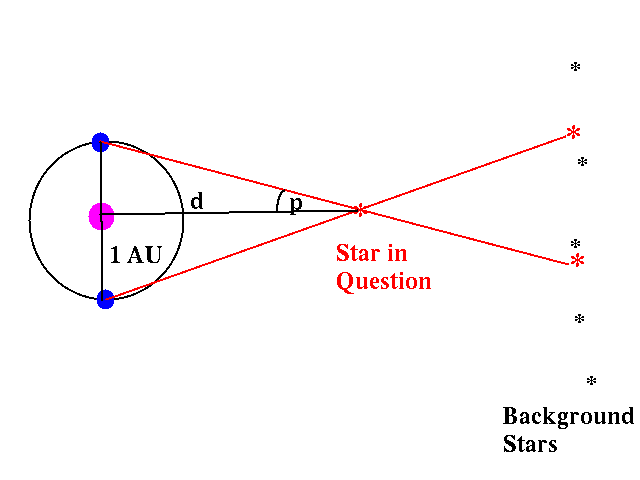
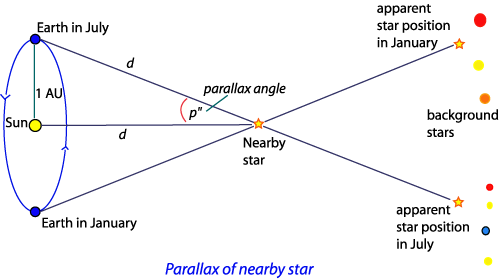
What is the parallax angle/angle of parallax? Identify it.
The angle between the earth at one time of the year and the Earth six months later, as measured from a nearby star. The greater the angle of parallax, the closer the star is to Earth.
What is an arcsecond?
A unit used to measure small angles, 1 arcsec = 1/3600 degrees.
What is an arcmin?
An angle is divided like an hour. 1 degree has 60 minutes of arc called arcmin. 1 arcmin = 1/60 degrees.
What is a parsec?
The distance at which the angle of parallax is 1 arcsecond.
Inverse square law for apparent brightness
b = L / (4πR²)
The apparent brightness of a star is inversely proportional to the radius squared, L is luminosity
Units and symbol for apparent brightness
b, Wm-2

what do the terms in the apparent magnitude equation mean?
m: apparent magnitude of star
M: absolute magnitude of a star
d: distance of star IN PARSECS (from Earth?)
equation relating absolute magnitude and luminosities of two stars.
M2 - M1 = -2.5log(L2/L1)
equation relating apparent magnitude and brightness of two stars.
m2 - m1 = -2.5log(b2/b1)
Equation relating the energy produced by a star to its temperature
E = σT4
where σ is the Stefan-boltzmann constant and T is temperature in Kelvin.
How does Luminosity relate to the power produced by the star.
Luminosity = power produced by the star
(can be measured in Watts or J/s)
What is the intensity/radiation flux?
(Generalise apparent brightness formula for any radiating object)
I = P/(4πd²)
where I is the intensity (radiation flux - W/m²), P is the power radiated (W), and d is the distance from the object (m)
What is the solar constant
The amount of energy radiated by the sun each second that falls on the Earth.
What is a black-body?
A body that absorbs and emits all wavelengths of light.
Perfect black body radiators are theoretical
Stars are the best approximations of black bodies there is (they are not perfect black-body radiators)
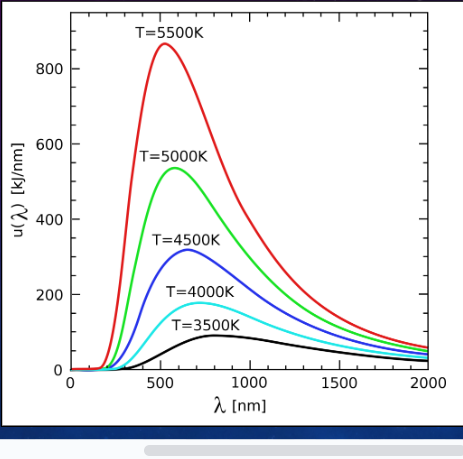
What is a black body curve? What does it show?
A curve of intensity against wavelength
as the temperature increases, the peak of the curve moves towards a lower wavelength and higher intensity
Shows how the power of a star is distributed over several wavelengths of EM radiation and that it is dependent on the temperature of the star.
Spectral class O characteristics
blue
25 000 - 50 000 K
He+, He, H absorption lines
Spectral class B characteristics
blue
11 000 - 25 000 K
He, H absorption lines
Spectral class A characteristics
blue/white
7 500 - 11 000
H (strongest) and ionised metals absorption lines
Spectral class F characteristics
white
6 000 - 7 500
ionised metals absorption lines
Spectral class G characteristics
yellow/white
5 000 - 6 000
ionised and neutral metals absorption lines
Spectral class K characteristics
orange
3 500 - 5 000
neutral metals absorption lines
Spectral class M characteristics
red
< 3500
neutral atoms, TiO absorption lines