2024 DHS AP Psychology - Genetics, Neurons, Nervous System and Endocrine System Diagram | Quizlet
1/54
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
Biological psychology
The scientific study of the links between biological and psychological processes
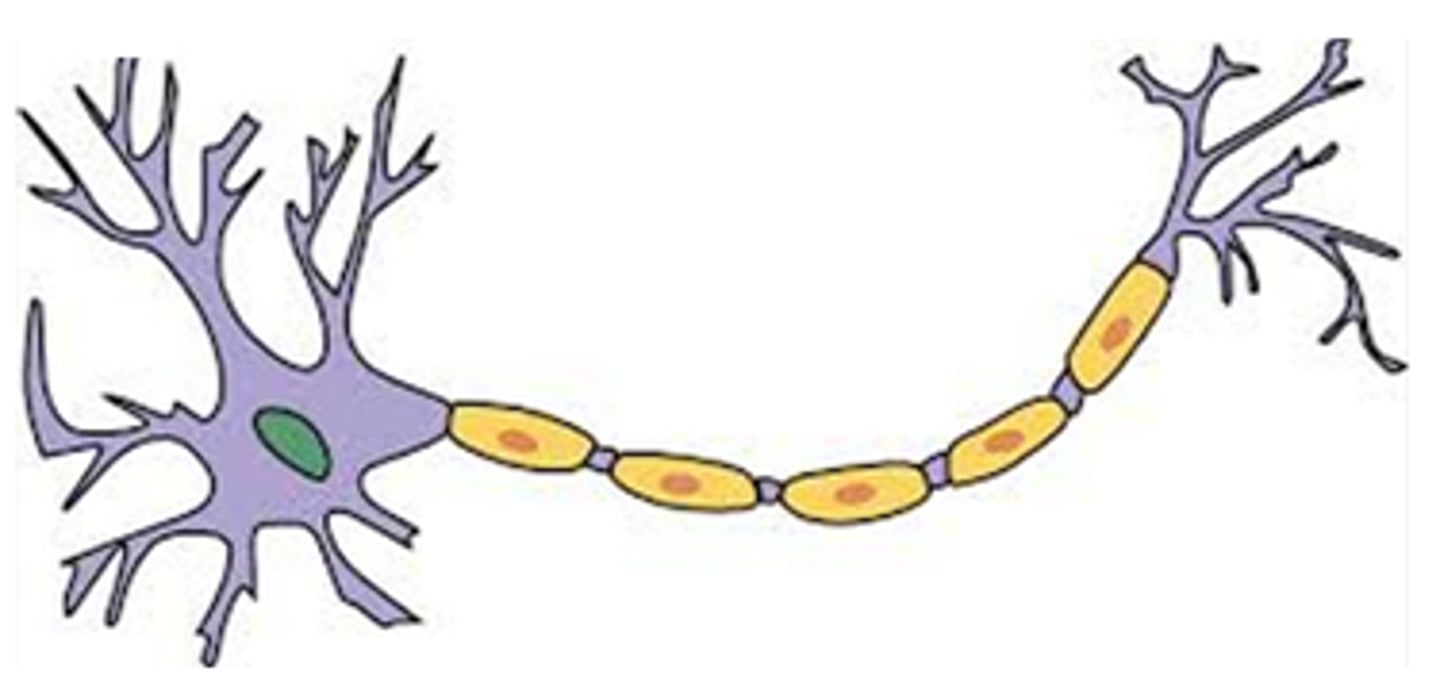
Neuron
A nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system
Dendrites
A neurons bushy branching extensions that receive messages and conduct impulses toward the cell body
Axon
The narrow an extension that passes messages through its branches to other neurons or two muscles or glands
Myelin sheath
A layer of fatty tissue that insulates them and speeds their impulses
Action potential
A neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down and axon
Refractory period
A period of inactivity after a neuron has fired
Threshold
The level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse
All or none response
A Neurons reaction of either firing or not firing
Synapse
Junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron
Neurotransmitters
Chemical messengers that cross between the synaptic gaps between neurons
Reuptake
Neurotransmitters reabsorption by the sending neuron
Endorphins
"Morphine within" natural opiate like neurotransmitters linked to pain control and to pleasure
Agonist
A molecule that by binding to a receptor site stimulates a response - mimics a neurotransmitter - Morphene
Antagonist
A molecule that by binding to receptors site inhibits or blocks a response - example - Curare poisoning
Nervous system
Refers to the body's speedy electrochemical communication network consisting of all the nerve cells and the Peripheral and Central Nervous System
Endocrine system
Communication system glands secrete another form of chemical messengers hormones which travel through the bloodstream-slow moving communication.
Hormones
Chemical messengers that are manufactured by the endocrine glands travel through the bloodstream and affect other tissues
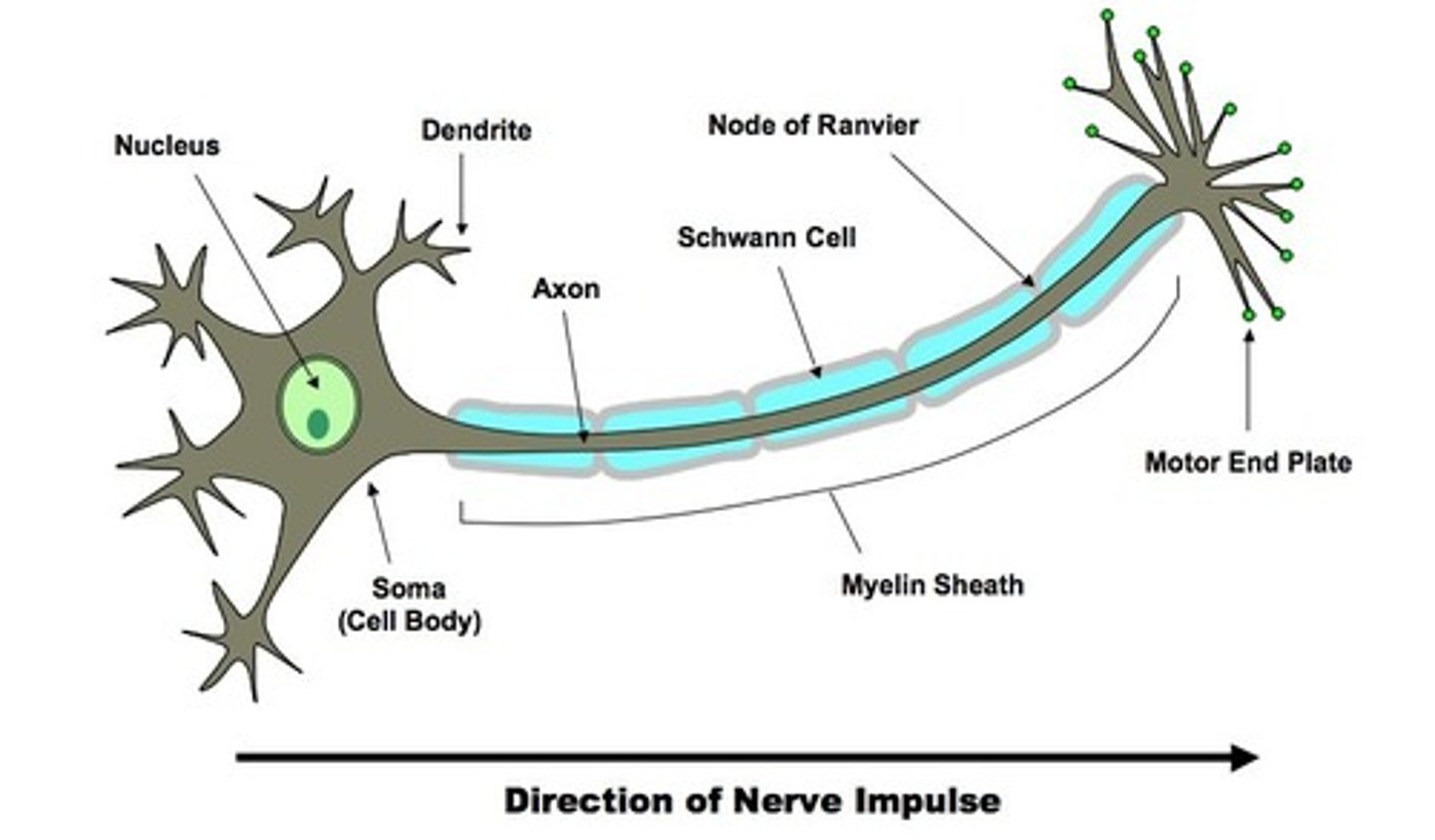
Soma
Body of the Cell
Node of Ranvier
Spaces between the Myelin Sheath
Myelin Sheath
Insulates and protects the axon-ensures a constant electrical impulse
Axon
Fiber through which the electrical impulse travels
Schwann Cells
Cells that make up the myelin sheath
Axon Terminals/Terminal Branches
Send information to the next neuron
Nucleus
Provides nutrients and genetic material
Neuron
a nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system
Glial cells
In the nervous system that support, nourish, and protect neurons
central nervous system (CNS)
Part of the nervous system that consists of the brain and the spinal cord

peripheral nervous system
Neurons that connect the CNS to the rest of the body, including muscles and glands. All nerves outside of bone.
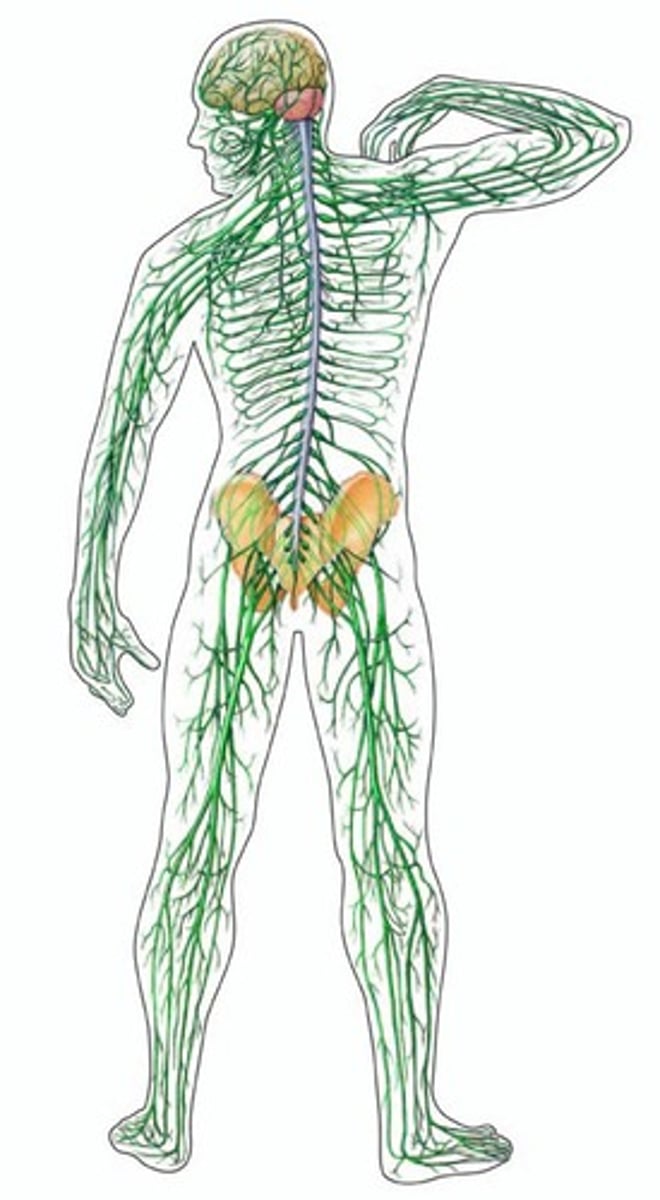
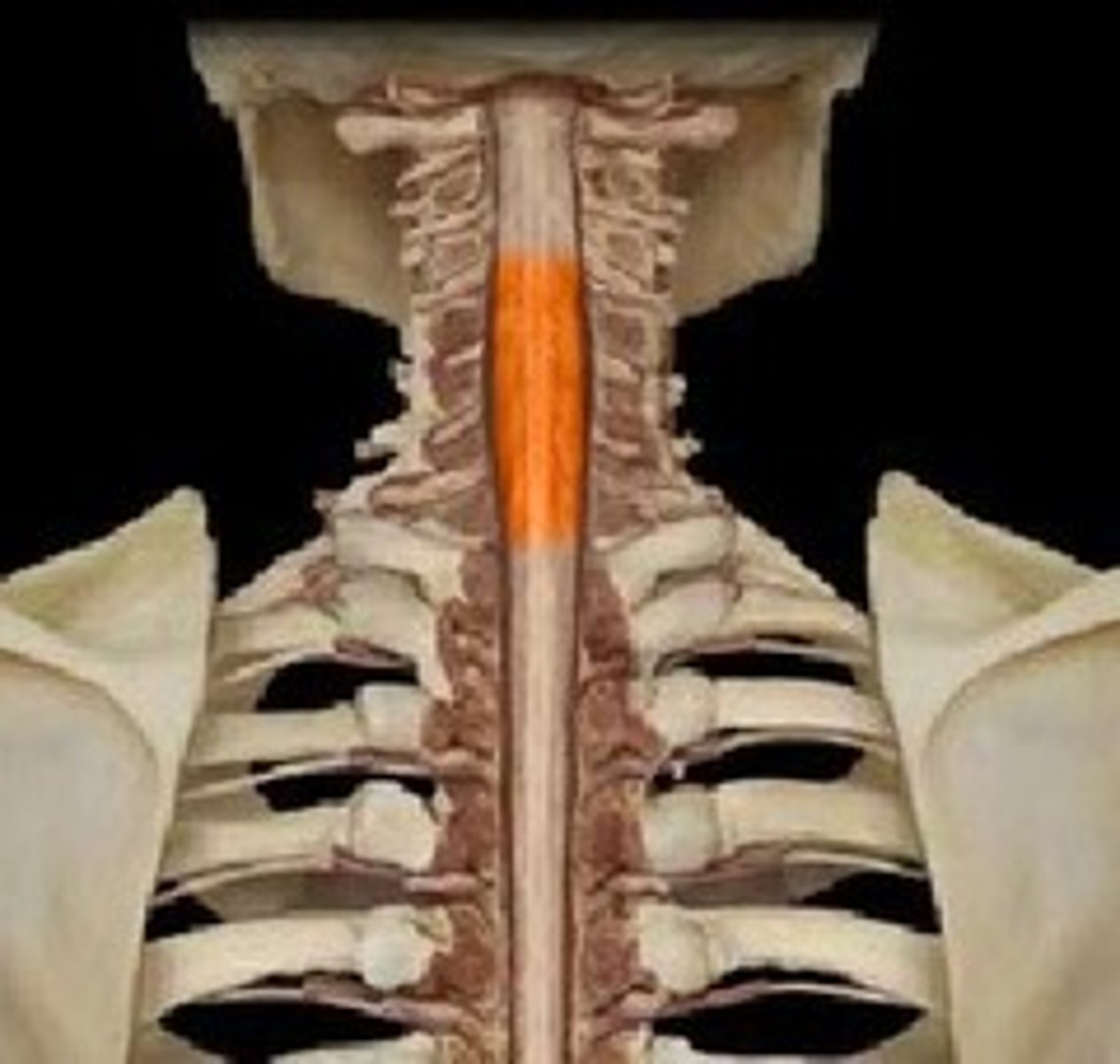
spinal cord
a column of nerves within the spine that transmit messages to and from the body to the brain
somatic nervous system
the part of the nervous system that directs all voluntary movement.
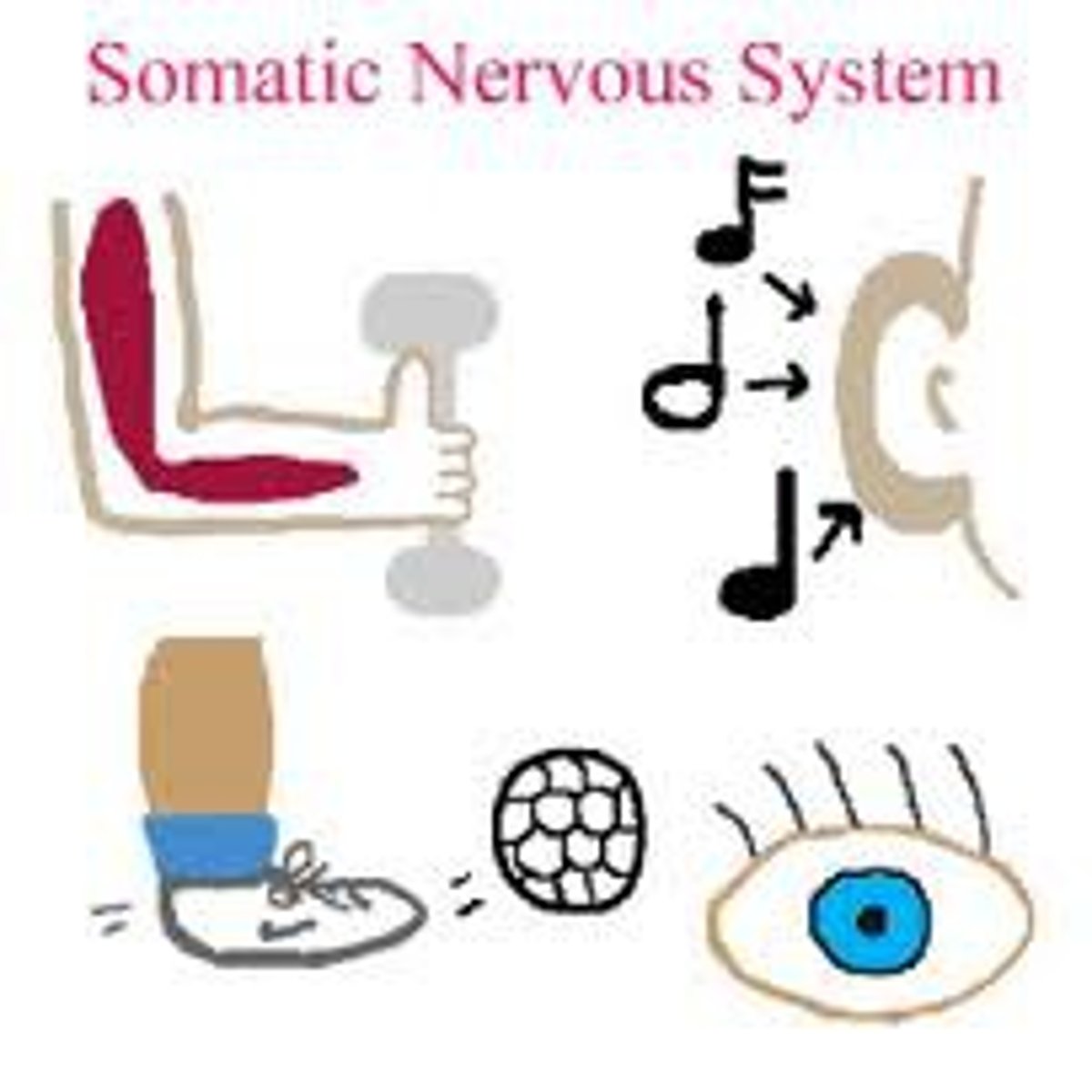
autonomic nervous system
the part of the nervous system that regulates all automatic body functions, such as respiration and digestion.
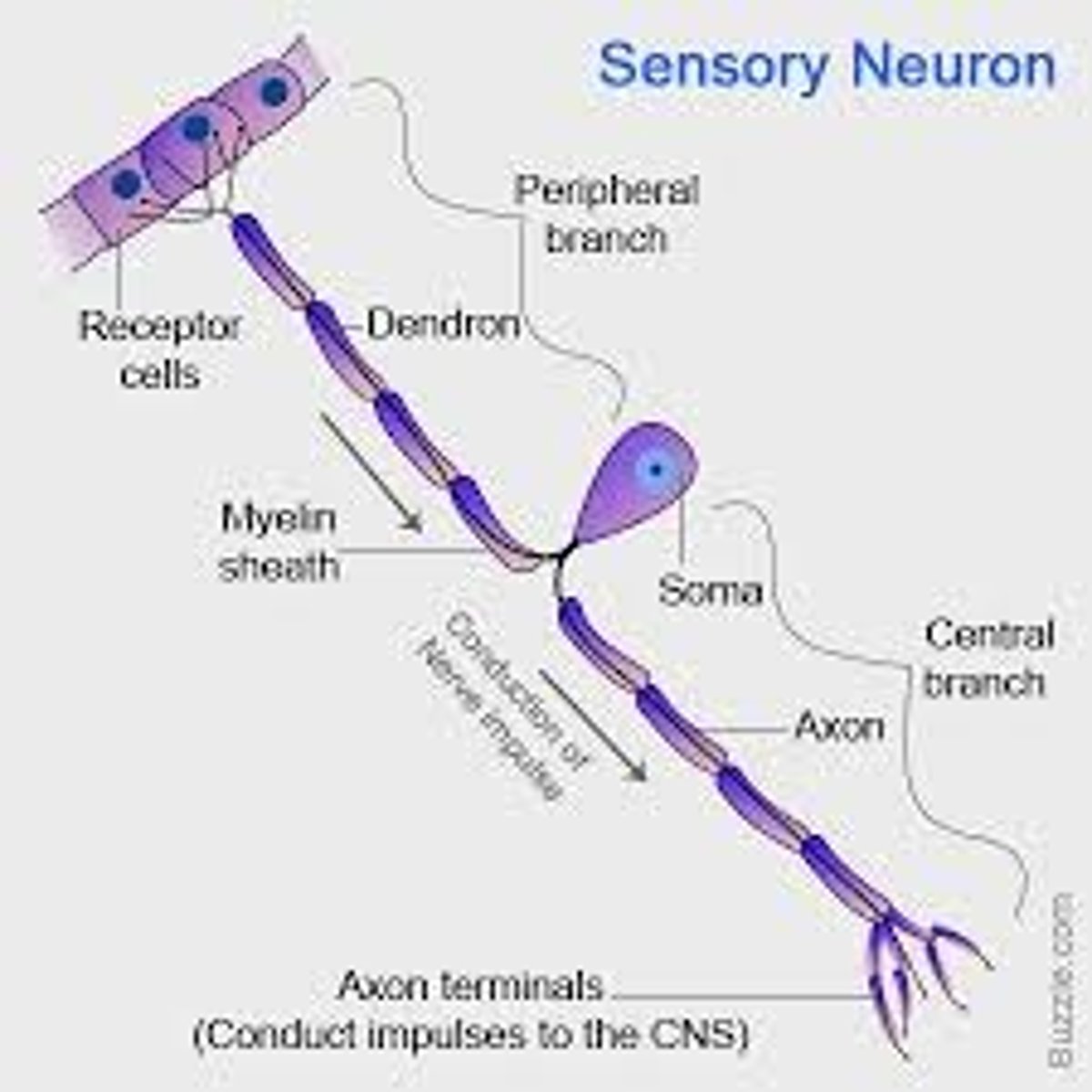
sensory neurons
AKA afferent neuron - it takes sensory information to the brain
motor neuron
AKA efferent neuron it takes messages away from the brain
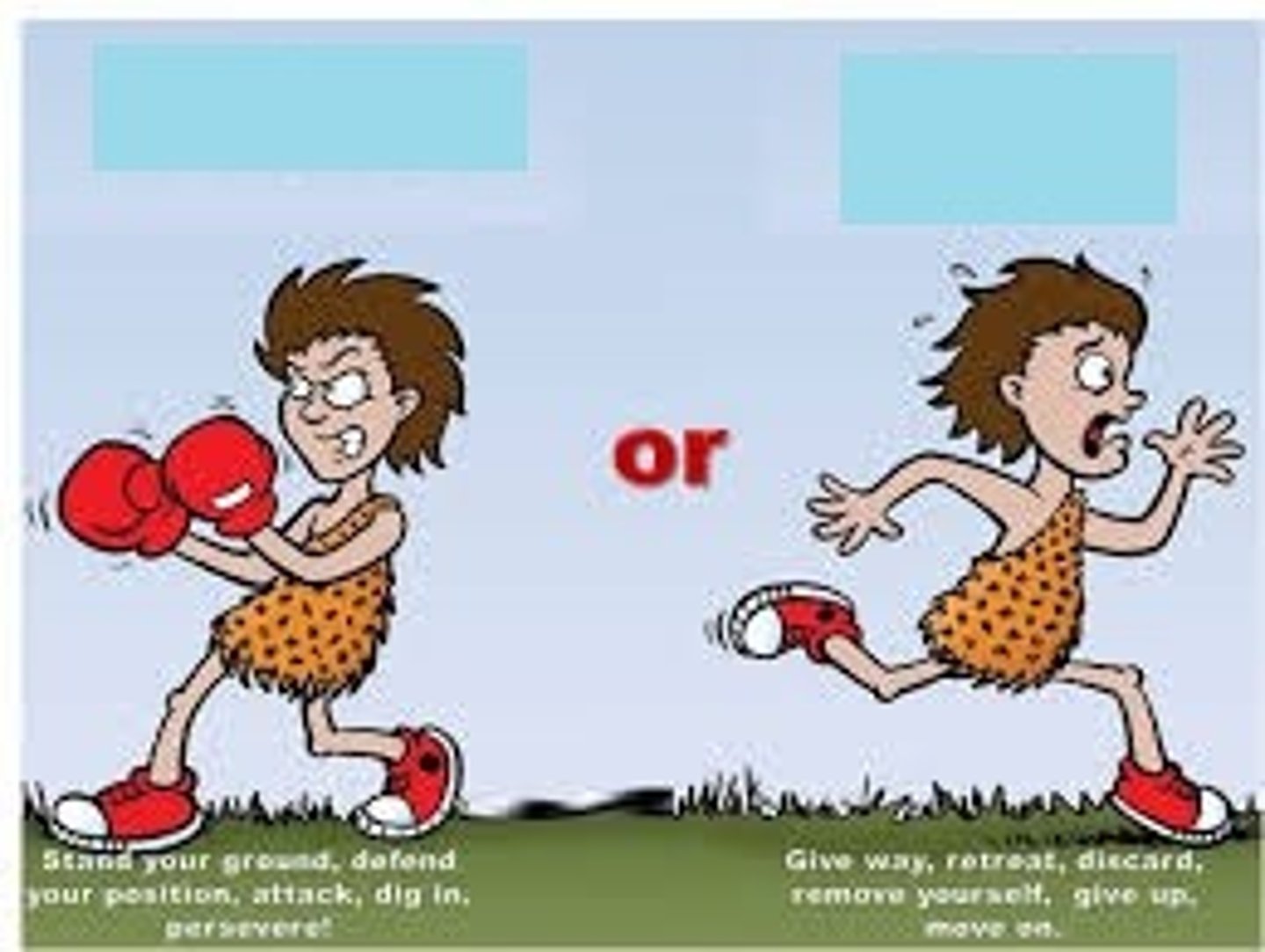
sympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic that prepares the body for action in challenging or threatening situations. - fight or flight

parasympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that calms the body, conserving its energy . Helps you recover from a stressful situation.

Interneurons
neurons within the brain and spinal cord that communicate internally and intervene between the senses and and muscles.
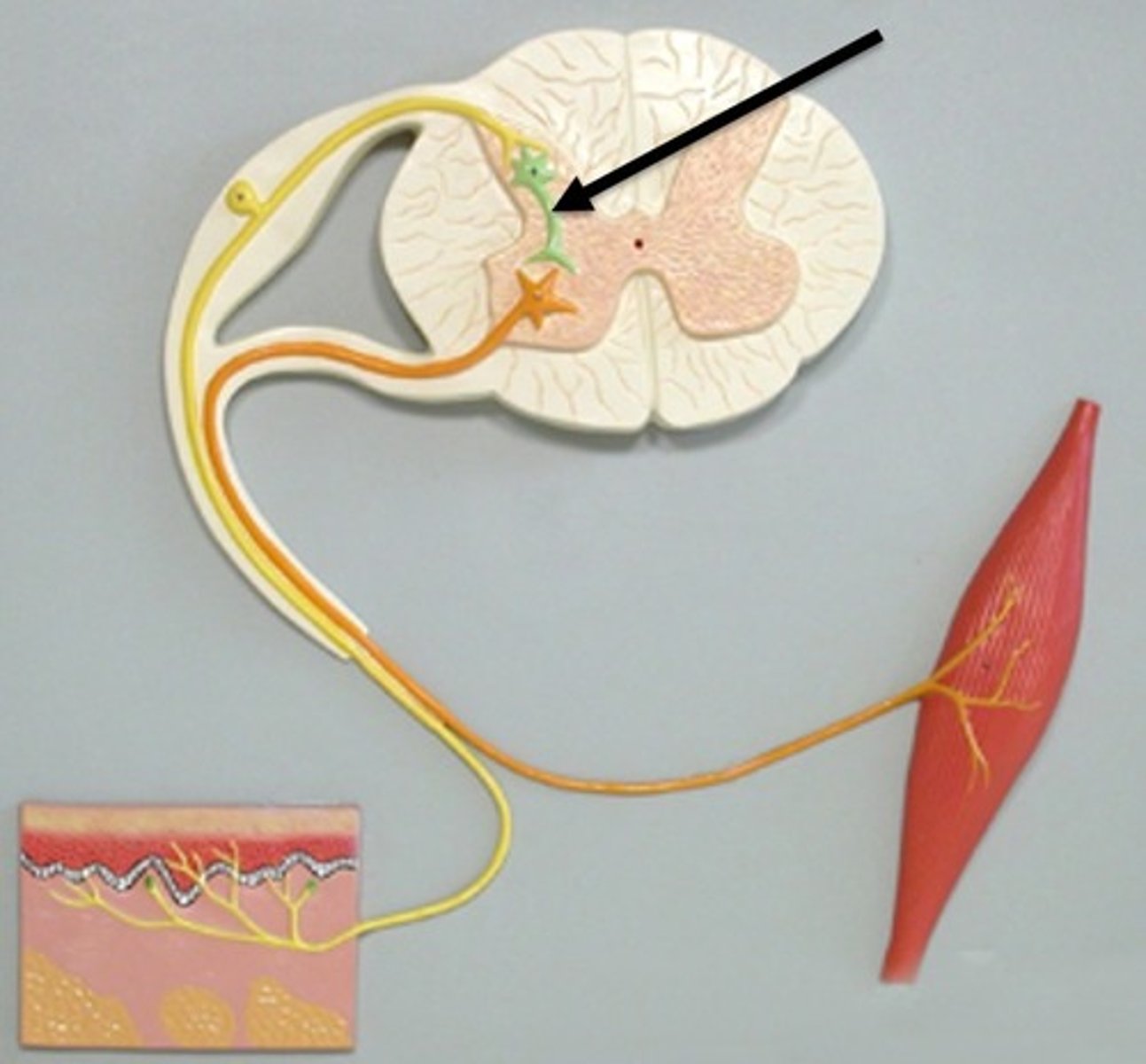
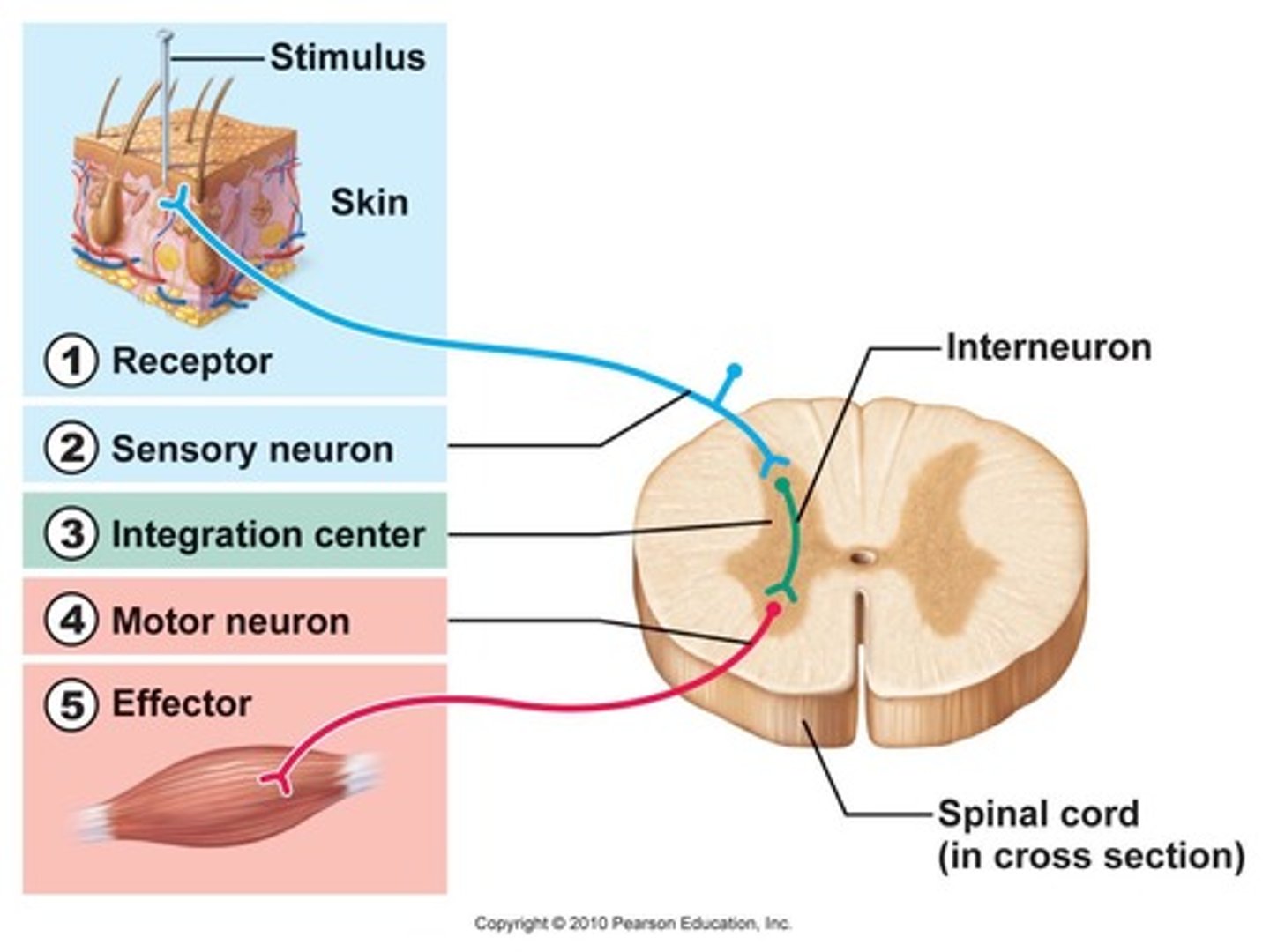
reflex arc
the nerve pathway involved in a reflex action including at its simplest a sensory nerve and a motor nerve with a synapse between.
A simple, automatic response to a sensory stimulus, such as the knee-jerk response
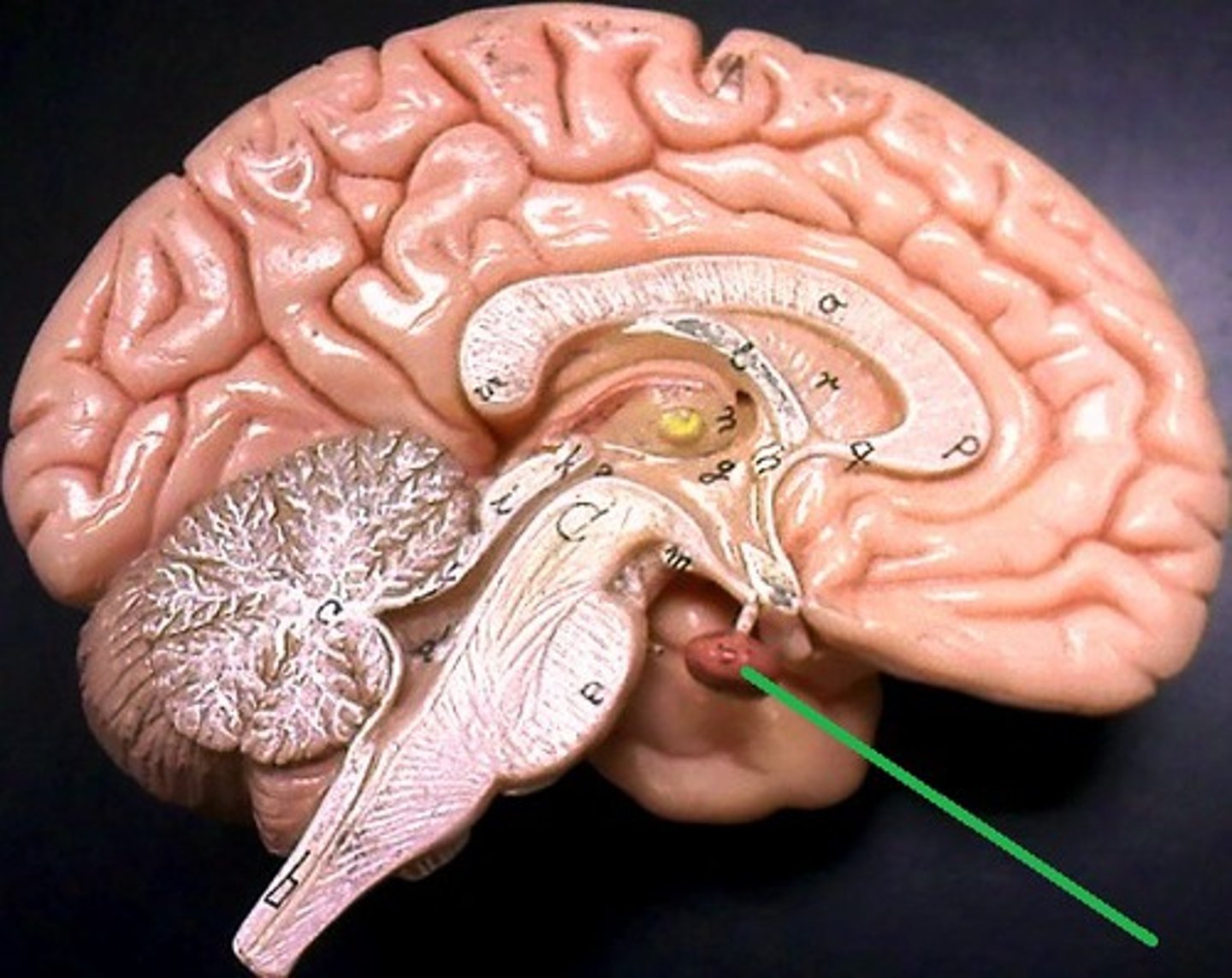
pituitary gland
Known as the "Master Gland" most influential! Regulates a person's growth and controls other endocrine glands.
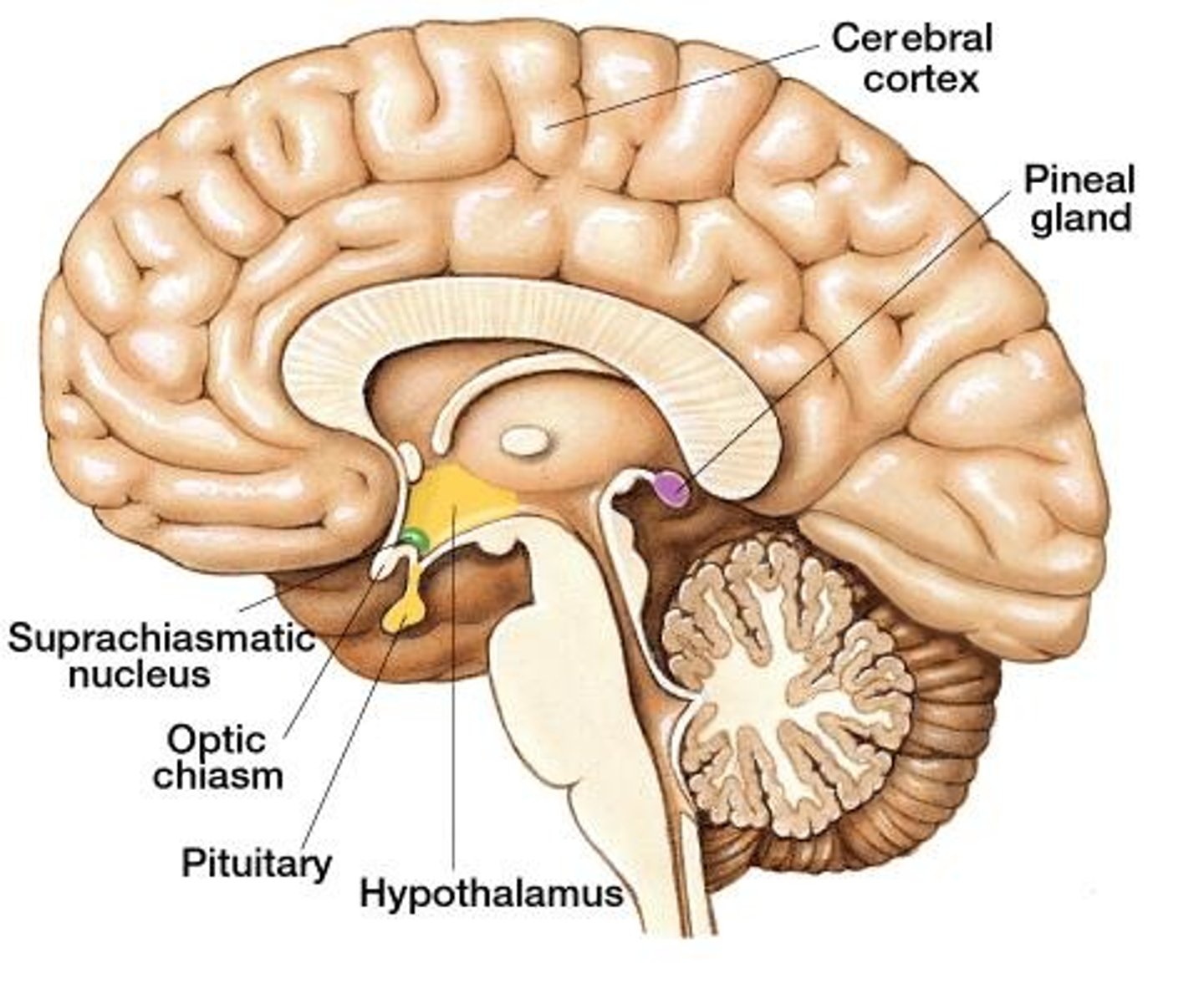
melatonin
Produces by pineal, regulates sleep-wake cycle
adrenal glands
Secretes adrenaline (epinephrine and norepinephrine) that help arouse the body in times of stress. Activate body for emergencies.
Ghrelin
Hormone secreted by empty stomach; sends "I'm hungry" signals to the brain

Leptin
Hormone produced by fat cells to signal satiety (feeling of fullness) to reduce appetite and increase the amount of energy.
Oxytocin
The bonding hormone - it helps us create social and maternal bonds
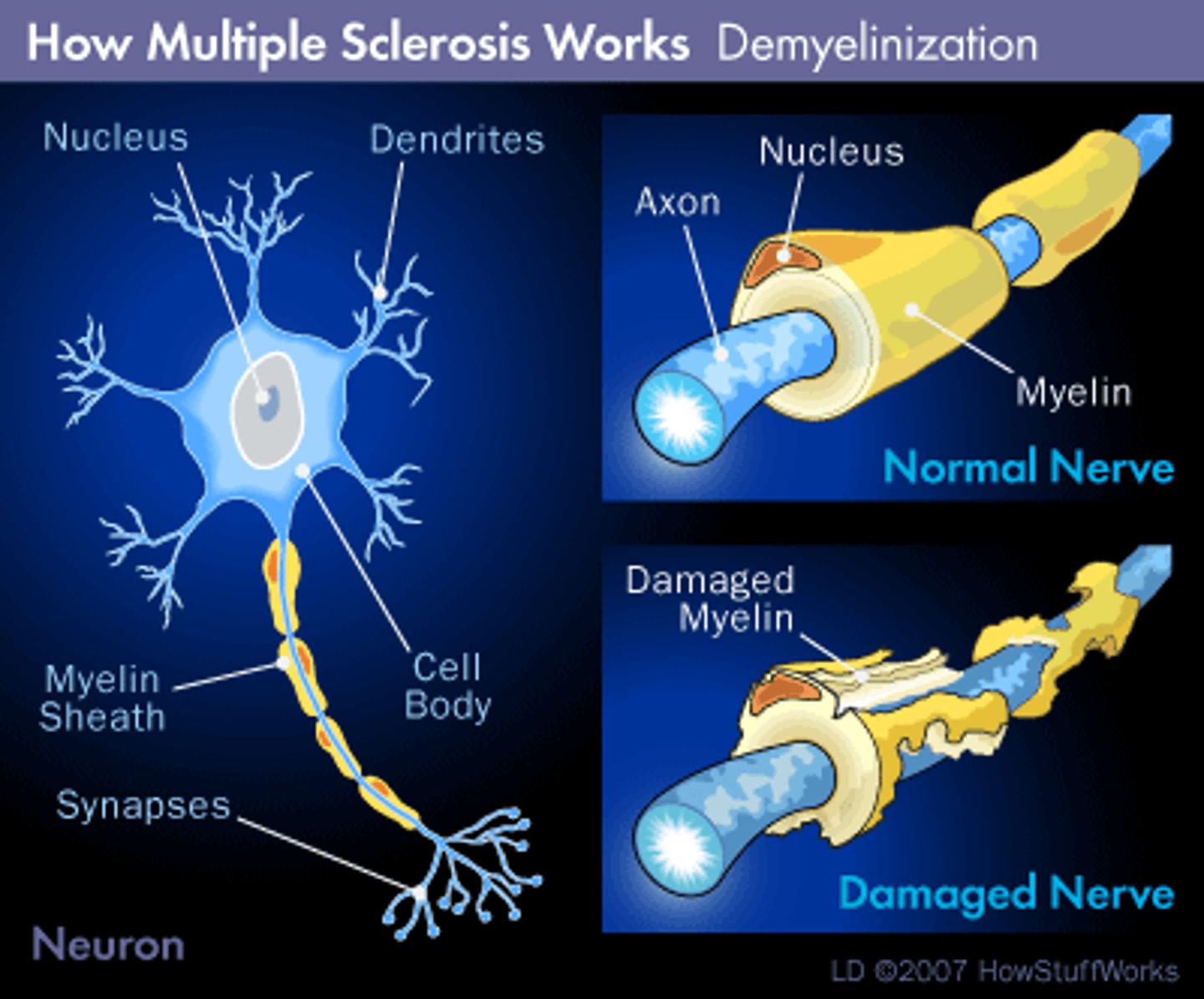
multiple sclerosis (MS)
Disease of the central nervous system characterized by break down of the myelin sheath leading to impaired motor function.
myasthenia gravis
Autoimmune neuromuscular disorder characterized by weakness of voluntary muscles and fatigue.
natural selection
A process in which individuals that have certain inherited traits tend to survive and reproduce at higher rates than other individuals because of those traits.
Eugenics
practice of selective breeding to create ideal specimens

survival of the fittest
A natural process resulting in the evolution of organisms best adapted to the environment.

behavior genetics
The study of the interaction of genes and environment on behavior.

monozygotic twins
identical twins formed when one zygote splits into two separate masses of cells, each of which develops into a separate embryo
dizygotic twins
fraternal twins, occurring when two eggs each get fertilized by two different sperm, resulting in two zygotes in the uterus at the same time

heritability
an estimate that indicates how how much of a trait can be attributed to genes.
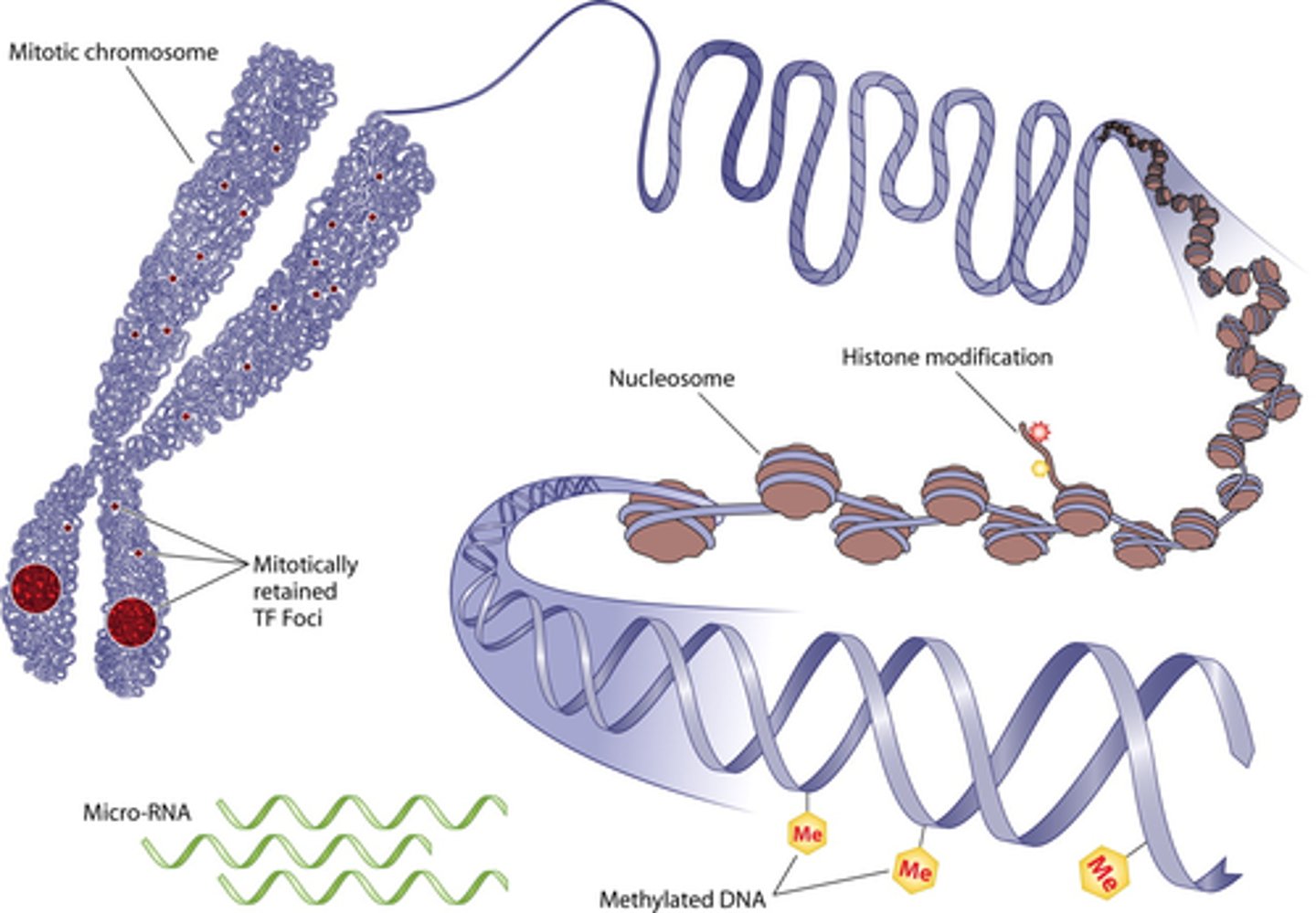
Epigenetics
the study of influences on gene expression that occur without a DNA change
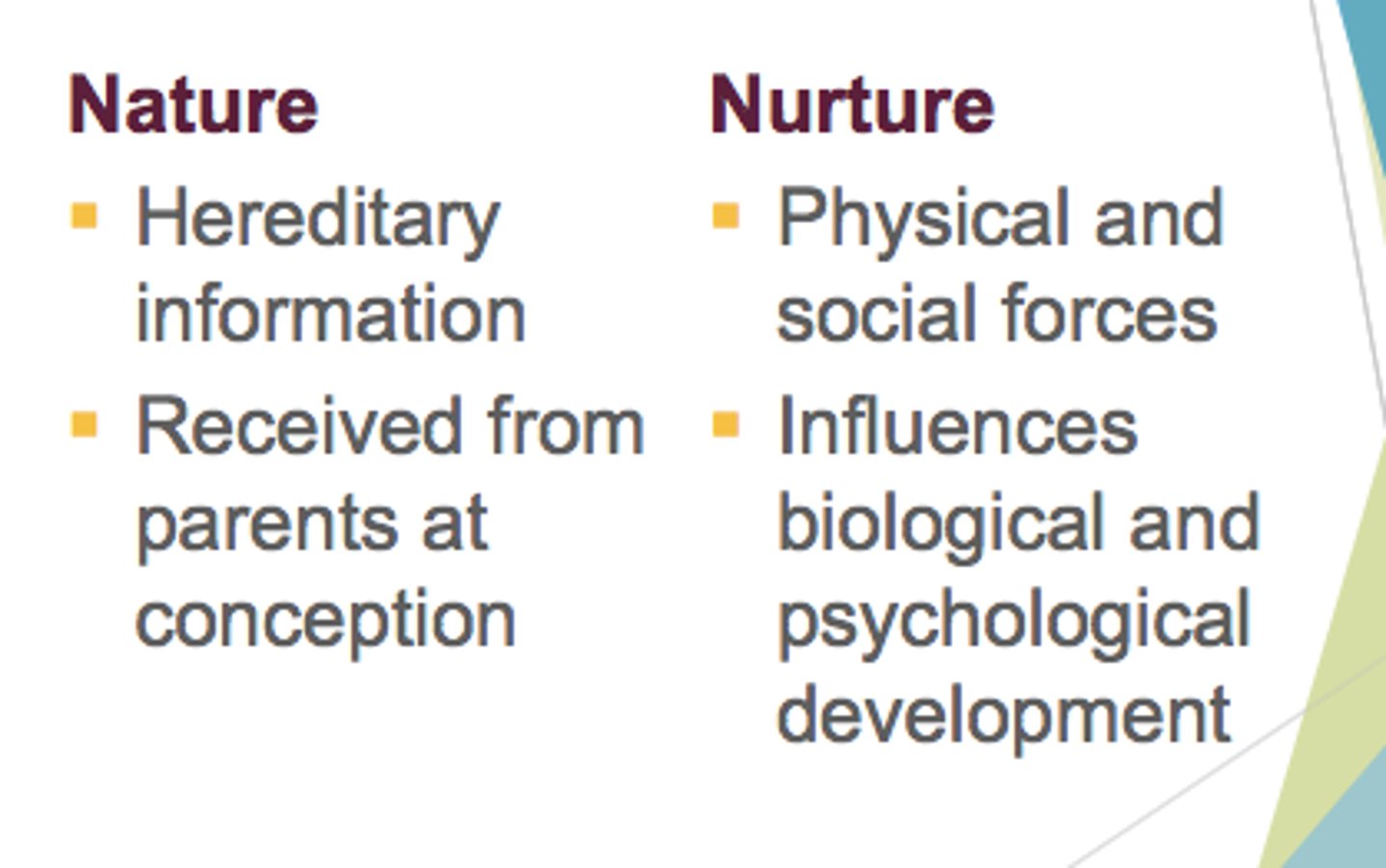
Nature vs. Nurture
name for a controversy in which it is debated whether genetics or environment is responsible for driving behavior