AP Psych Biological Bases (focus on Brain) review 3
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
It section of Unit 2 that is so long that it needed it's deck
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
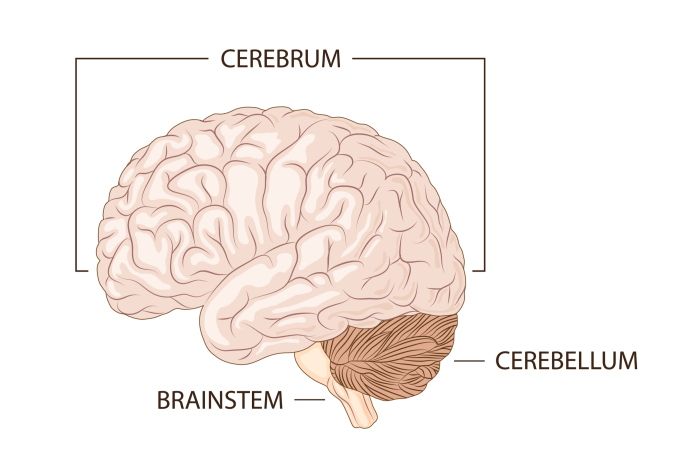
Brainstem
Controls flow of messages between brain and the rest of the body
Regulates central nervous system
Begins on top of spinal cord after entering skull
Breathing, swallowing, heart rate, blood pressure
Crossover Point: Nerves for each side of the brain connect with the opposite side of the body
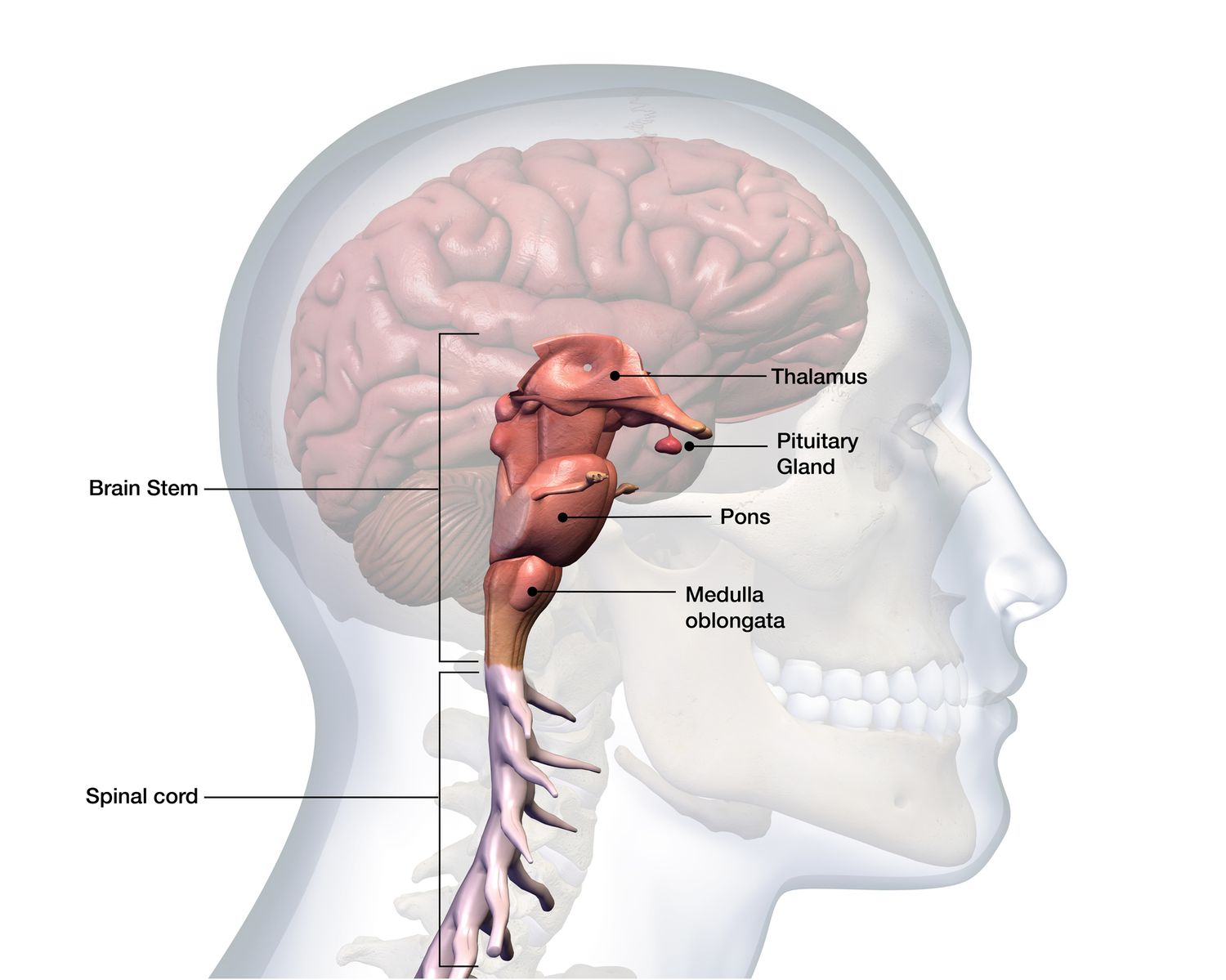
Medulla (Oblongata)
The Base of the brain stem
Controls heartbeat and breathing
Pons
Part of brainstem linking medulla oblangata and thamalus
Connects upper/lower parts of brain
Acts as a relay station for the cortex and cerebellum
Relays signals related to sleep and arousal
Midbrain
Located above the pons and smallest part of brainstem
Responsible for transmitting hearing and visual information
Also coordination and motor coordination
An assitant, not central processing area
M is for MID AF
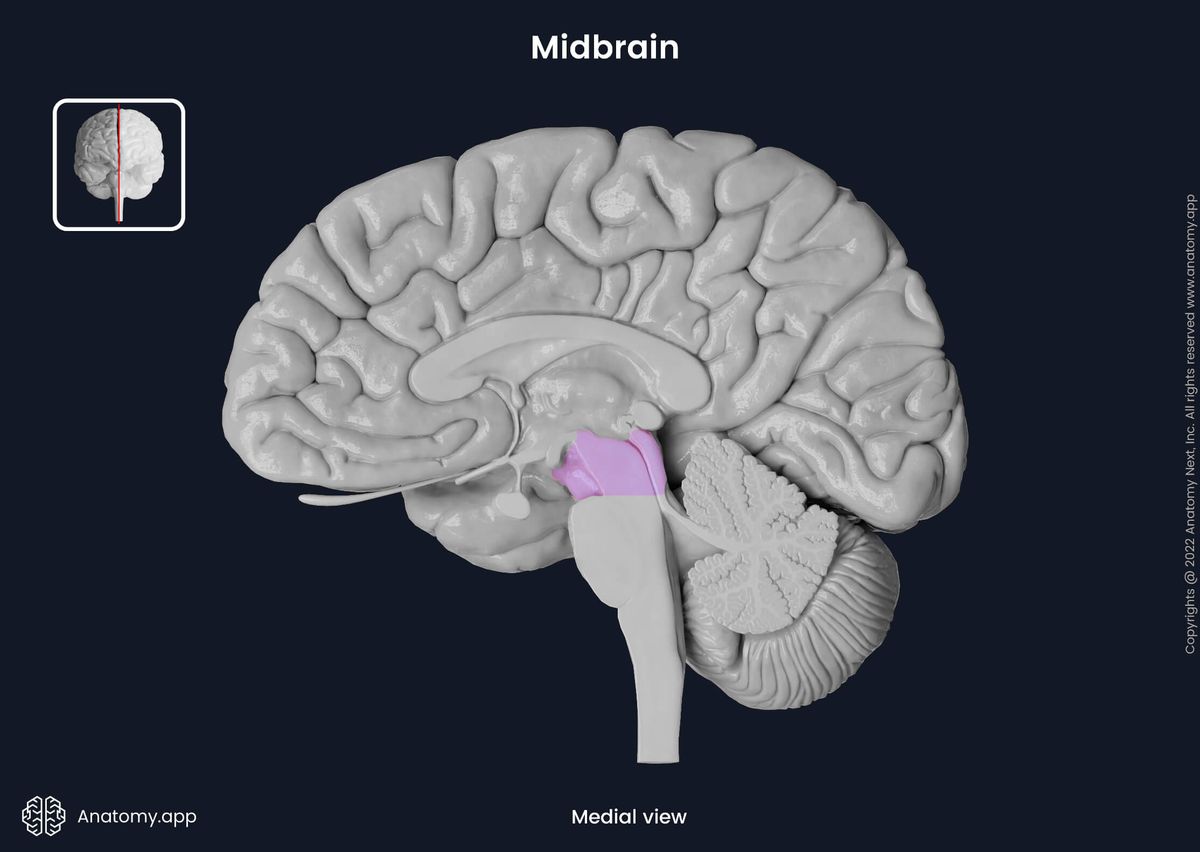
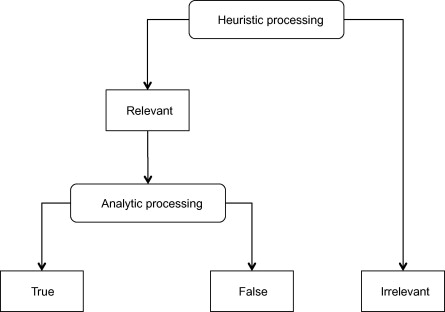
Reticular Formation
Nerve network that travels through the brainstem and thalamus
F in formation is for FILTERS incoming stimuli and relays info into other brain areas
Enables/controls arousal and states of consciousness (alertness/sleep)
Cats were experimented on specifically with their RF
Zapping the RF instantly woke them up
Severing the RF put them in a permanent coma
Reticular Activating System (RAS): Part of RF, regulates sleep-wake cycle
Turns on/off processing stimuli so you can get some sleep brodie
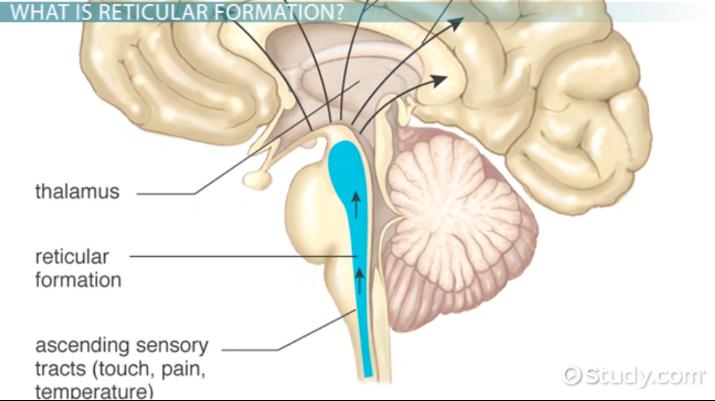
Cerebellum
Extends from bottom rear of brainstem
“Little brain”
Processes sensory input retaining to coordinates movement and balance
Enables non-verbal learning/memory
Helps us judge time, modulate emotions, discriminate sound/textures
Injuries = trouble walking, keeping balance, jerking
DOES A LOT MORE THAN MOTOR ACTIVITY FROM STUDIES
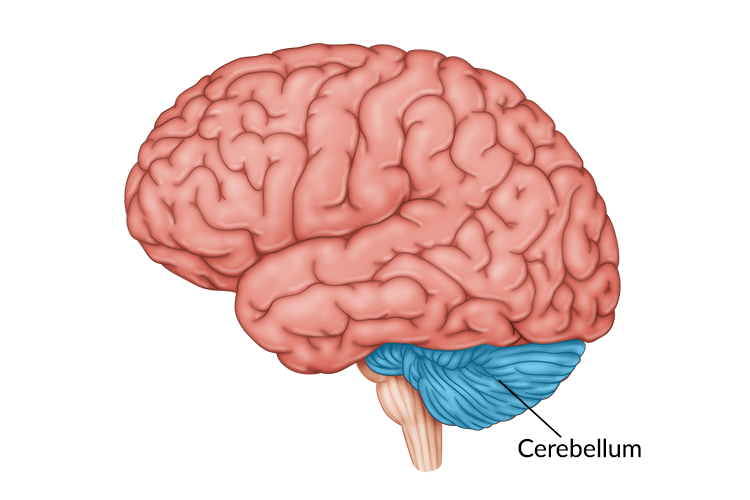
The Limbic System
The mammalian brain
Connects “old” brain parts with “neo/new mammalian” brain
Associated with emotion, behavior, motivation
Consists of
Thamalus
Amygdala
Hippocampus
Hypothalamus
Technically the pituitary gland as well
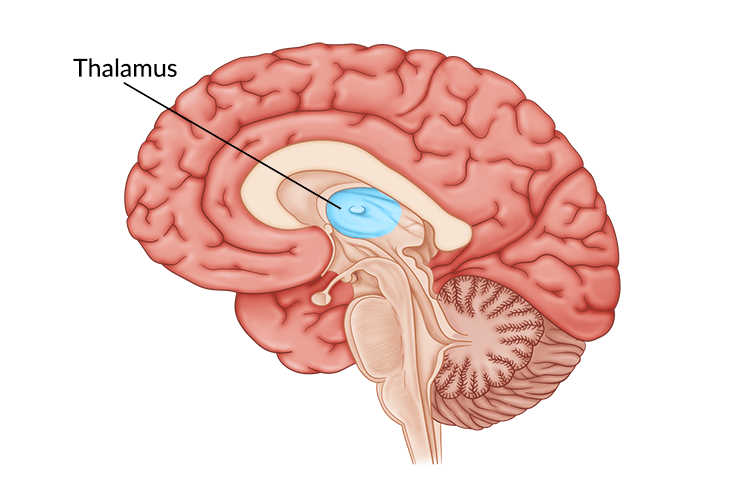
Thalamus
Top of brainstem
Brain’s sensory control center
Directs incoming sensory info to sensory-receiving areas in the cortex, transmits replies to cerebellum and medulla
Like a travel-hub
Th is for travel hub, or traffic hub
Controls 4 of 5 total senses
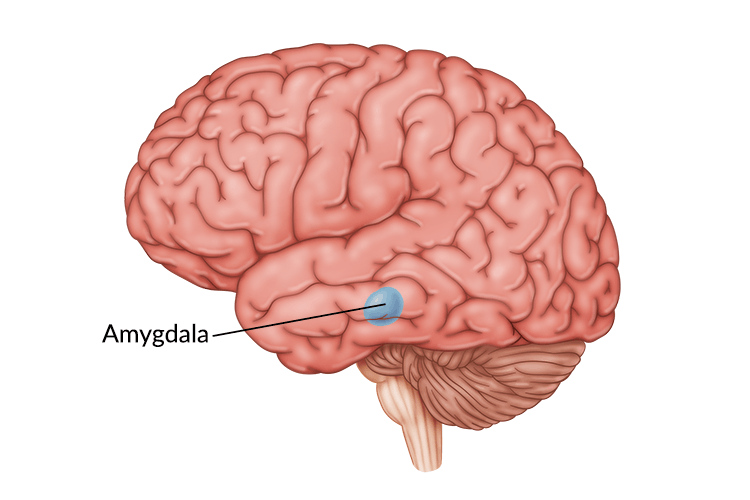
Amygdala
Neural clusters linked to aggression and fear
Animal research
Removing amygdala, animal becomes docile/mellow, completely unafraid
Electrical stimulation
Can produce massive aggression or fear (cats being afraid of mice for example)
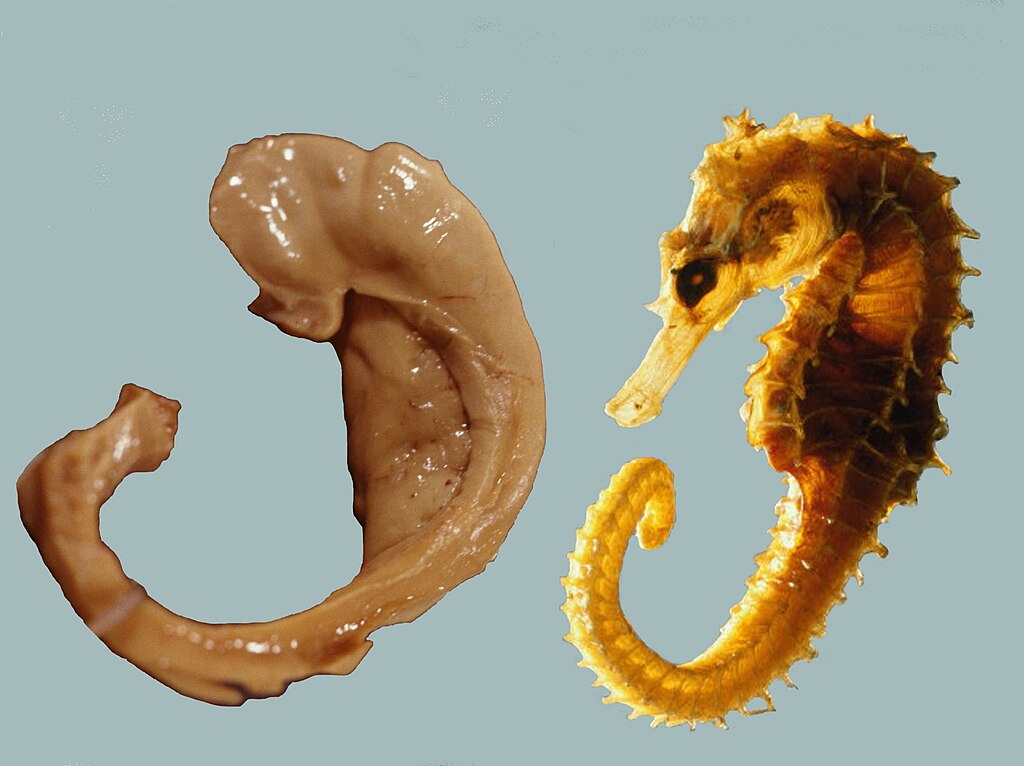
Hippocampus
Processes conscious memories
Seahorse shape
if it breaks, humans lose the ability to form new memories of facts/events
involved in spaital awareness (perception of bodily self in relation to objects)
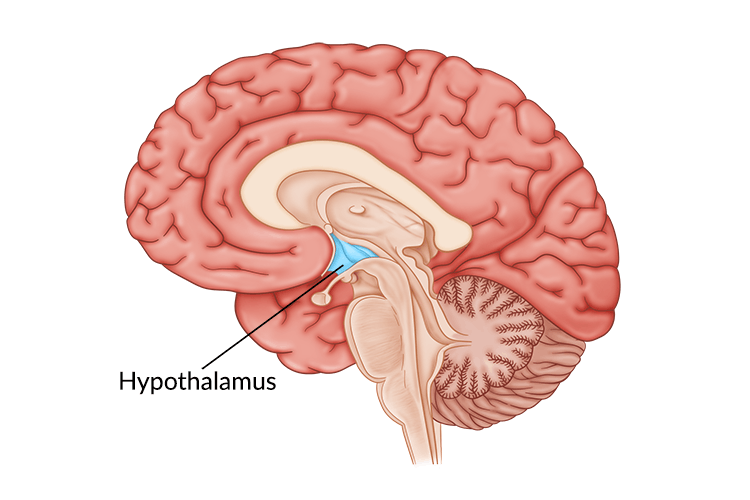
Hypothalamus
Located below thalamus, governs many bodily “maintenance” activites
Governs endocrine systems via pituitary gland
2 Sides: Lateral/Ventromedial Hypothalamus
Lateral Hypothalamus (LH) = Regulates hunger
If damaged, no appetite
“limit hunger”
Ventromedial Hypothalamus (VMH) = Regulates satiety/fullness
If damaged, never feel full
“very much hunger”

Small Break!
Evolutionary perspective = animals/humans are built with a reward center associated with sex, drinking, and eating
Since we feel pleasure from doing these things, it helps us keep doing it
Some maladaptive behaviors like drugs, alcohol, binge eating, etc can become associated in the reward center too
The 4 F’s: FIGHTING, FLEEING, FEEDING, MATING (AYO)

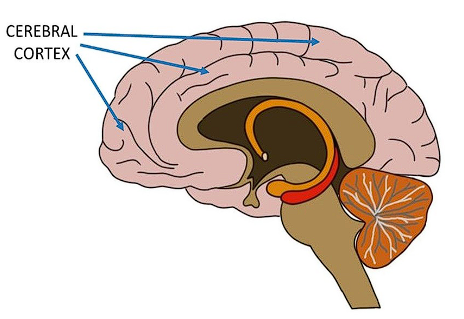
The Cerebral Cortex
The neo-mammalian brain
thin surface layer of interconnected neural cells that acts as our body’s control and information-processing center
covers the 2 hemispheres of the brain
enable perceptions, speaking, thinking- more sophisticated, complex activities
20+ billion neurons and over 300 trillion synaptic connections
Cerebrum
The two hemispheres of the brain and largest part
85%
Neural networks in the brain contribute ? % of its weight

Left/Right Hemispheres
interior is filled mainly with axons connecting the cortex to other regions of the brain
Gyri and Sulci
Elevations/bumps and depressions/grooves that gives the brain its wrinkly shape
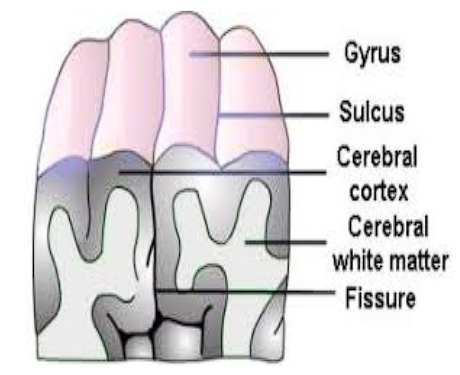
Grey Matter
Outost layer of cerebral cortex (visible)
Comprised of neuron cell bodies (somata) and unmyelinated axons

White Matter
Inner layers of the cerebrum
Comprised of myelinated axons of neurons

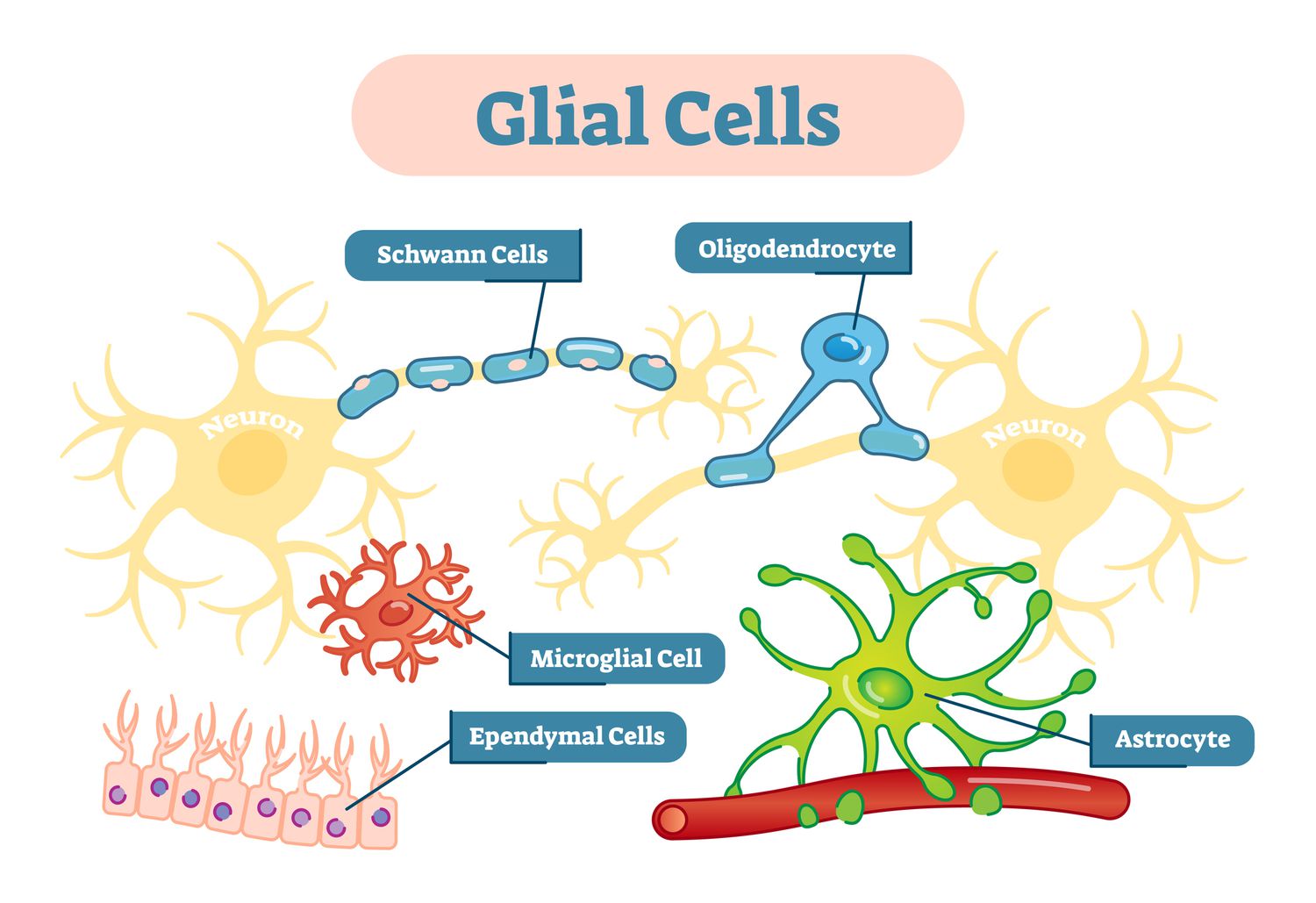
Glial Cells
Cells in nervous system that support/nourish/protect neurons
Neurons are like queen bees, they can’t feed/protect themselves
There’s 3 types
Oligodendroglia
Schwann Cells
Astrocytes
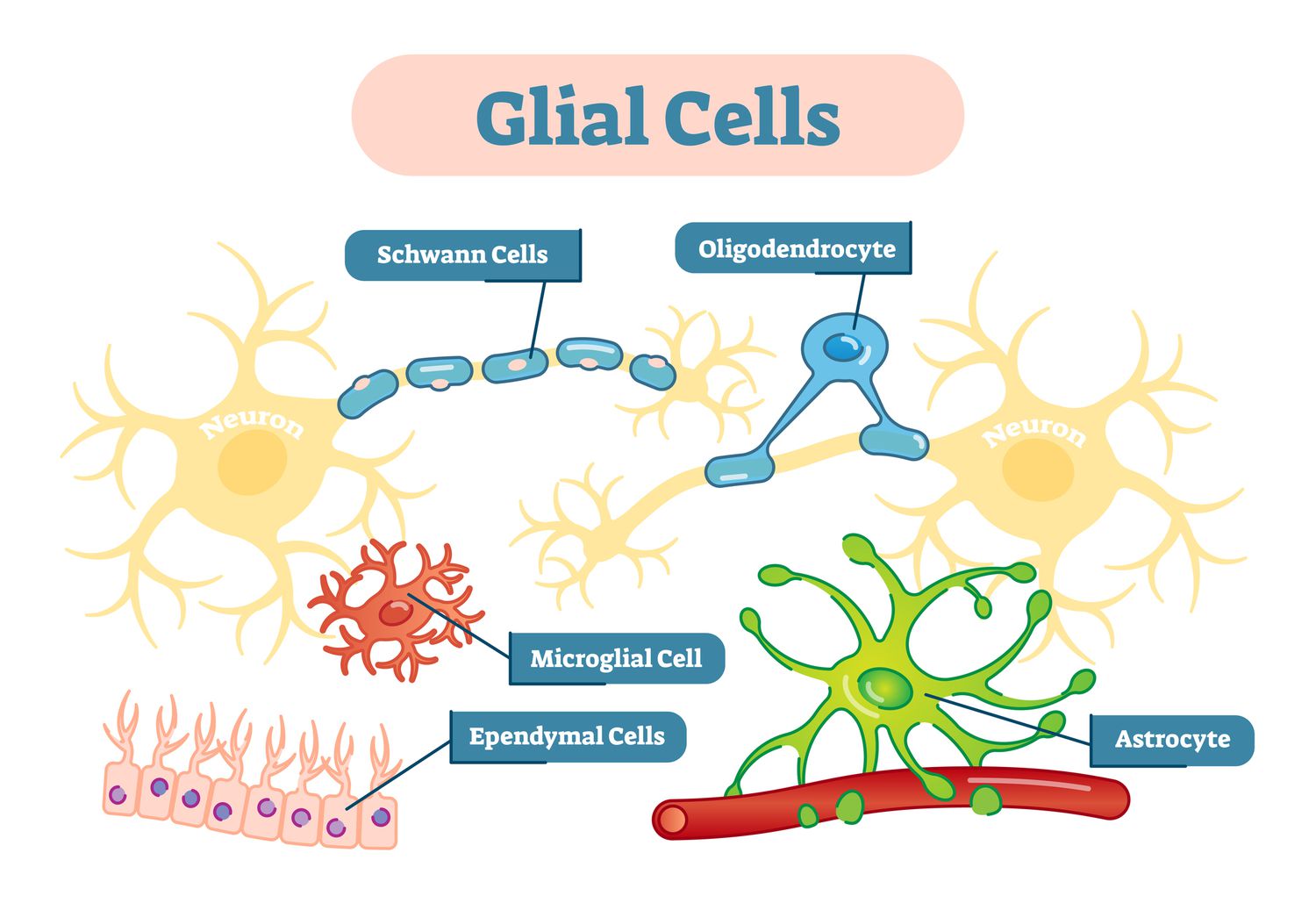
Schwann Cells
Produce myelin/regenerate axons
In PNS
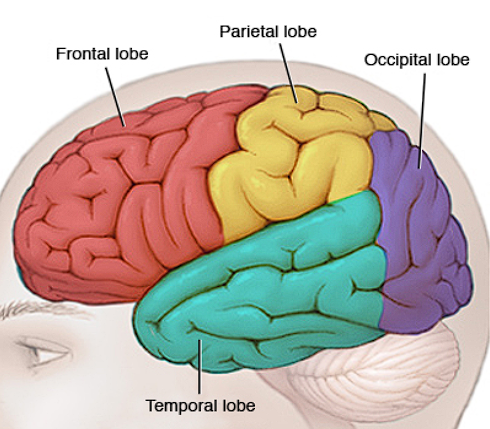
Lobes
Each hemispheres’ cortices are subdivided into 4 ?
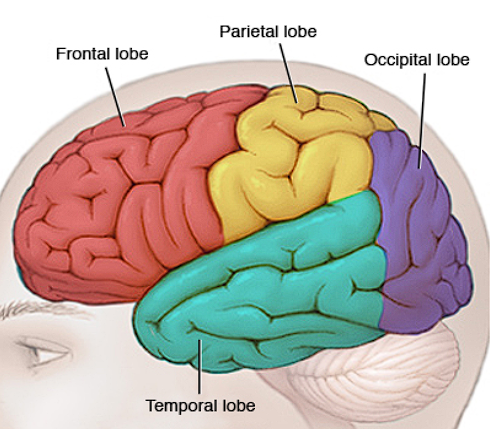
Frontal Lobe
Located in front, behind forehead
Thinking/judgement, speech, muscle movements, problem-solving skills
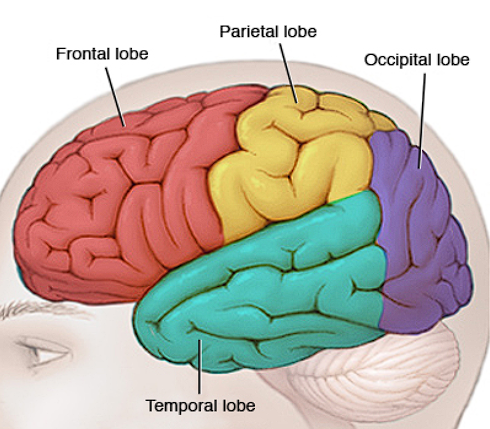
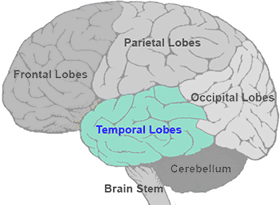
Temporal Lobe
Located beside ears
Hearing
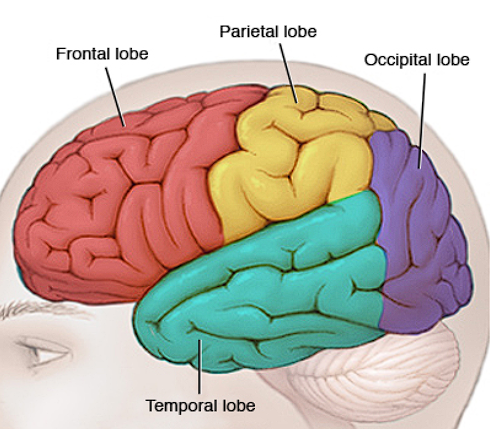
Occipital Lobe
Located in back of head
Vision
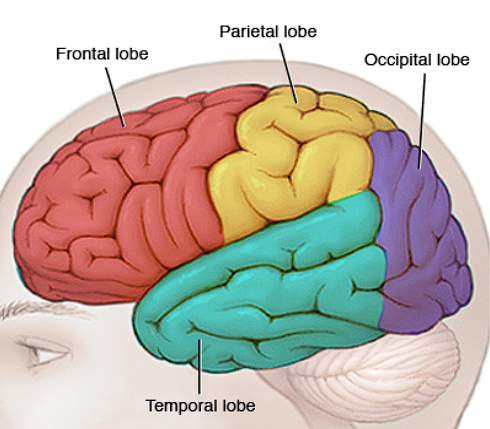
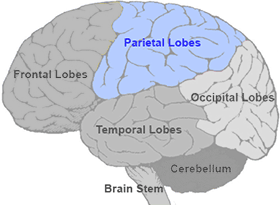
Parietal Lobe
Top/Back of head
Touch/sensory processing
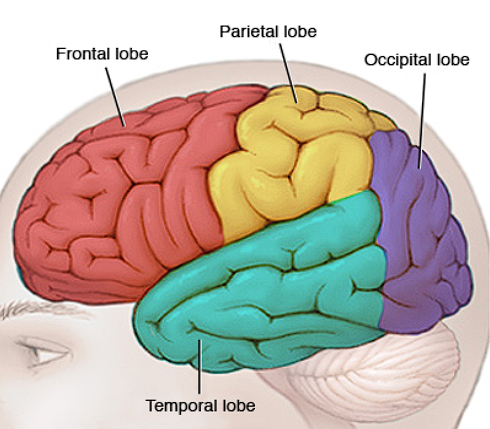
2
Technically there’s ? lobes for each left and right side of the brain
Somatosensory Cortex
In parietal lobes; registers/processes body touch, sensation of movement
Receives incoming sensory info (like an inbox)
More sensitive regions has the samatosensory cortex be more deovted to them (lips, rats’ whiskers, owls’ hearing)
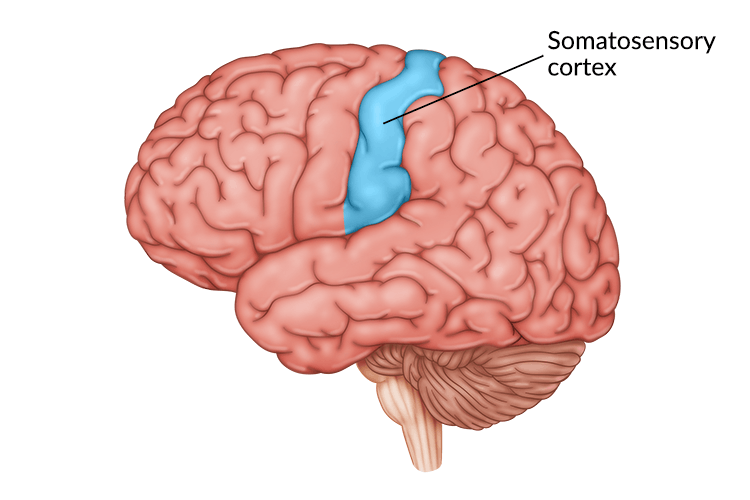
Motor Cortex
Area at rear of frontal lobes; controls movement
Sends messages out to body (Outbox, movement, motor activity)
Body parts that require precise control and higher sensitivity occupy more motor cortex space (fingers, mouth) than others (back, calves, etc)
Fritsch/Hitzig (1870): Stimulated with a shock animals’ motor cortex which forced them to move parts of their body
Stimulating one hemisphere of the brain had a reaction with the opposite side of the body (Crossover Point)
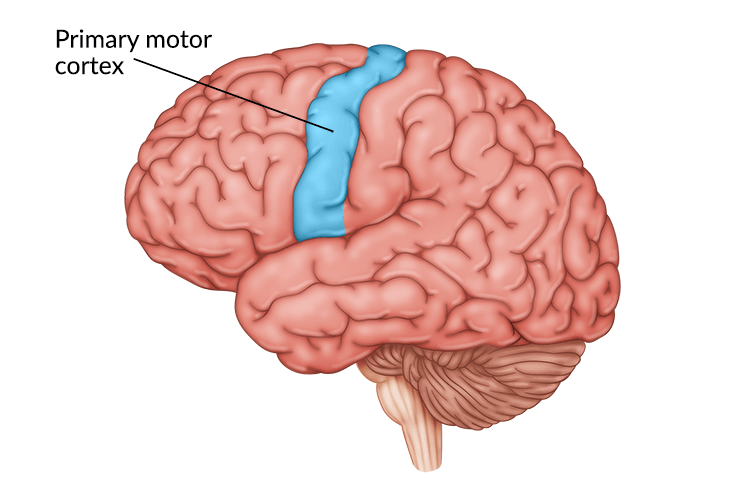
Somatosensory Cortex
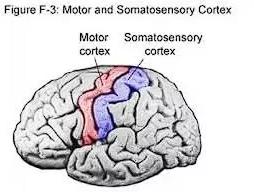
Motor Cortex
? = Sensory/Afferent neurons
? = Motor/Efferent neurons
sensory
The brain has no ? receptors so it doesn’t feel pain
Doctors keep patients awake during brain surgery to observe responses
In other words, if they stop doing a certain activity, they done goofed

Association Areas
75% of the cerebral cortex that is dedicated to higher level cognitive functions
thinking, speaking, learning, memory
primarily involved in processing/integrating info from the senses
to provide you with your perceptual experience
how you interpret sensory input
Harder to map and “place” some of these functions
doesn’t have specific locations as clearly: complex mental functions don’t reside in one place, but have interconnections with other parts of brain
IN ALL 4 LOBES
synchronized/coordinated
Memory, language, attention skills result from ? (2 words) activity among different brain areas

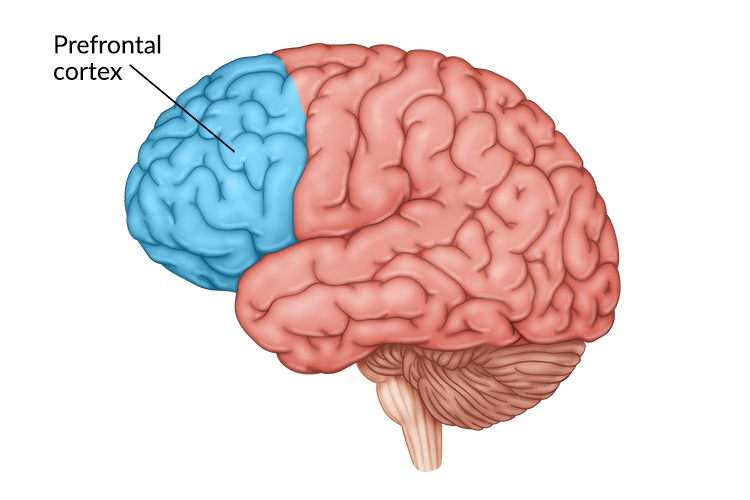
Prefrontal Cortex
In front of frontal lobe
enable judgment, planning, processing of new memories, emotional control
damage can alter personality and lower inhibitions (Phineas Gage)
Inhibitions = Voluntary restriction of yourself
Parietal Lobe (Association Area Definition)
Enables math/spatial reasoning, spatial awareness (of your body)
Temporal Lobe (Association Area Definition)
Enables facial recognition
If damaged = loss of facial memory
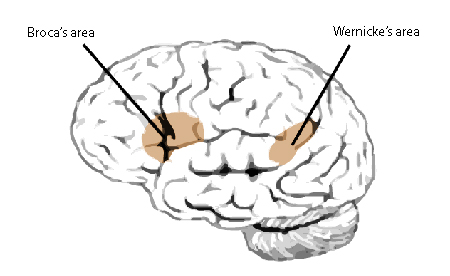
(Paul) Broca’s Area
Located in left frontal lobe
Disrupts speaking ability, but comprehension is fine (Broca’s Aphasia)
Broca is for babbling, improperly formed words and slow speech
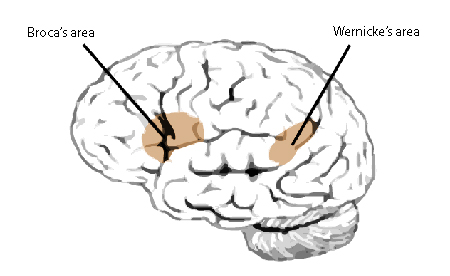
(Carl) Wernikes’s Area
Left temporal lobe
Disrupts comprehension AND expression
You can’t comprehend anything and you speak gibberish (Wernicke’s Aphasia)
Wernike is for WORSE, you’d rather have Broca’s
Hemisphere
Each ? usually performs/assists with its own functions
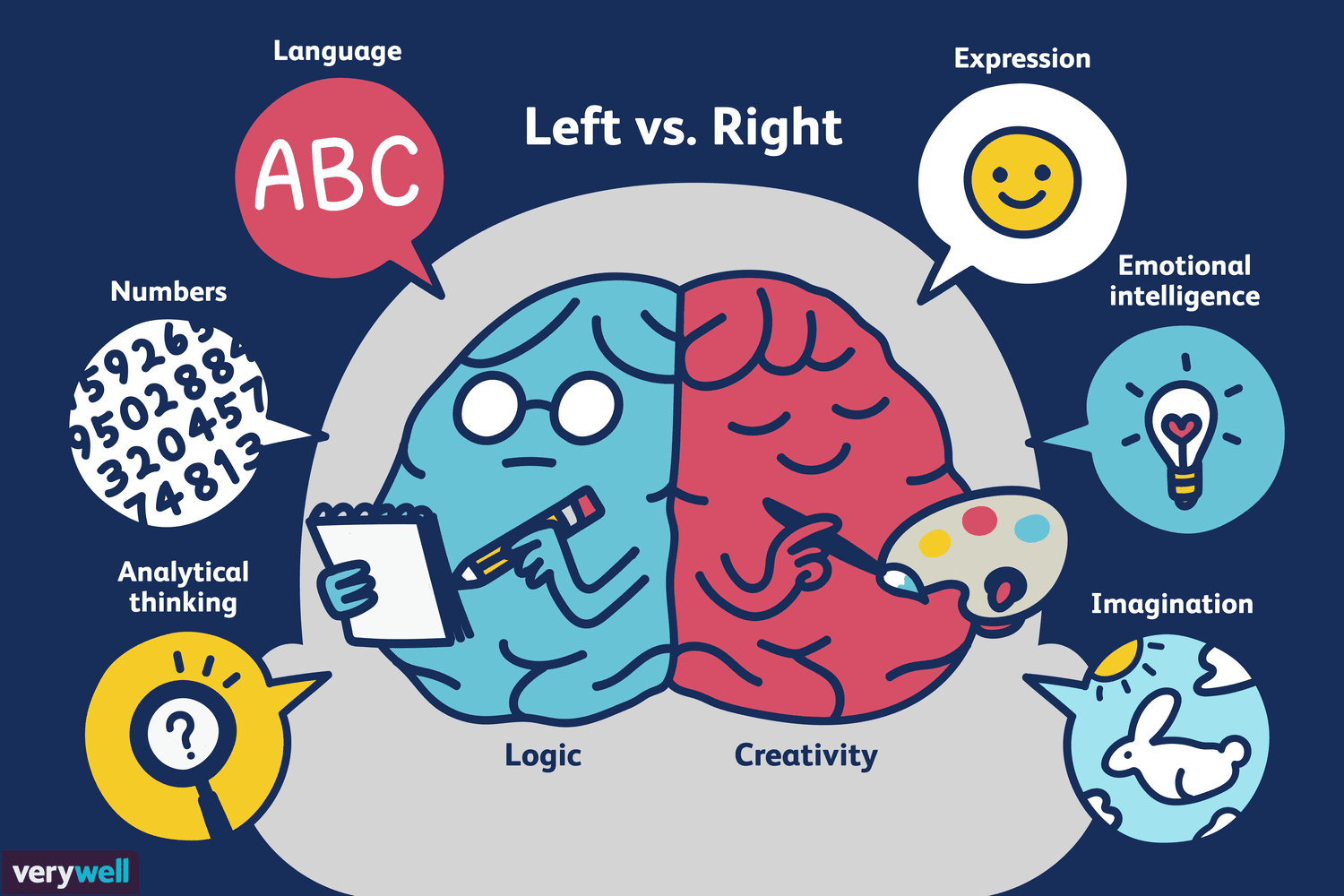
Right Hemisphere
Intuition, spatial, creative

Left Hemisphere
Logical, verbal, linear tasks

Dual Processing
Most daily thoughts/feelings/actions operate unconsciously
Intensely focusing on a task only increases brain activity 5% above baseline (normal functioning) rate
There’s still activity in a diminshed conscious (sleeping)
The brain interprets numerous stimuli/events simultaneously
Brain taking incoming info and connects it to established, older info
Brain lets in relevant info, filters out what we don’t need to consciously notice
Automatic functions are largely ignored
We have a manual override function (conscious) over what is automatic (unconscious) like manually breathing