physics p1 - matter (copy)
1/51
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
What was j.j Thomsons thoery of the atom
plum pudding model
discovered electrons which are dotted around inside spheres of positive charge
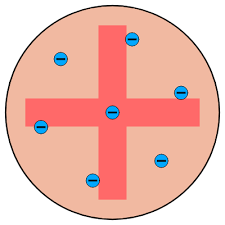
what was rutherfords theory if the atom
atoms have a central, positively charged nucleus with most of the mass
nucleus surrounded by cloud of negative electrons so most of atom is empty space
what experiment did rutherford and marsden conduct
aimed beams of positively charged alpha particles at very thin gold foil.
According to the plum pudding model, these particles should have passed straight through. However, many of them changed direction instead.
this meant it had to have a small positively charged nucleus as the nucleus was positive, repelling other positive charges
whats was bohrs model of the atom
a problem with Rutherford's model - the electrons would eventually fall into the nucleus because they are negatively charged and so attracted to the positive nucleus.
Niels Bohr improved Rutherford's model. Using mathematical ideas, he showed that electrons occupy shells around the nucleus.
how big is the diameter of an atom
1 x 10 to the power of -10 m
what is an atom
a positively charged nucleus surrounded by negatively charged electrons, with the nucleus size being much smaller than that of the atom and with the most mass in the nucleus
what does the nucleus of an atom contain
protons and nutreons ( so positively charged)
what is density
a measure of ‘ compactness’
Mass per unit volume
what is the equation for density
denisty (kg/m³) = mass (kg)/ volume (m³)
p = m/v
describe the particle arrangement for a solid
tightly packed in a regular arrangement
particles can only vibrate on the spot
describe tha particle arrangement of a liquid
close together but irregular arrangement
can flow past each other
describe the particle arrangement of a gas
separated with no regular arrangement
particles can move freely
whats the order (most to least) of density for the states of matter
most dense : solid
liquid
least dense : gas
why is a solid denser than gas
because the particles are tightly packed in a regular structure whereas in a gas the particles are spread out
what are the 5 main ways a substance can change state
melt
freeze
evaporate
condense
sublimate
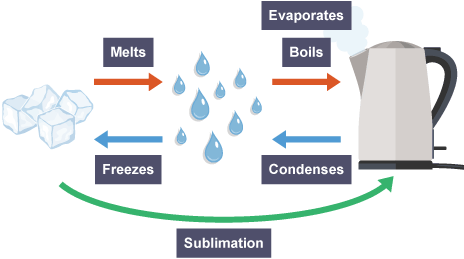
whats sublimation
when a substance transitions from a solid straight into a gas without transitioning into a liquid in between
using the particle model, how does condensation occur
in gases the particles have enough energy to overcome the forces between them so spread out randomly
when the temperature is lowered , they will no longer have the energy to overcome these attractive forces so the particles will move closer together and condense into a liquid
using the particle model, how does melting occur
in solids, strong attractive forces hold the particles in place so they can only vibrate
as the substance is heated the particles gain energy and vibrate more quickly
eventually the particles have so much energy they overcome the forces holding them together and it melts into a solid to a liquid
using the particle model how does boiling occur
as heat is applied to a liquid the particles gain kinetic energy and move faster
with enough energy, the forces of attraction between the particles will break
at this point the liquid boils into a gas
how is a change of state different to a chemical change
in a change of state the material can return to having its previous properties if the change is reversed
in a chemical change, its irreversible
when a substance changes state, does the mass change and why
no as the mass of a substance is the mass of its particles and the particles arent changing they’re just being rearranged
when a substance changes state, does the density change and why
yes as when a substance changes state its volume changes as the partciles are closer together in a solid and further away in a liquid + gas. (spacing between the particles changes)
denisty = mass/ volume so density must change too
solids are most dense and gasses are least
how do you measure the denisty of a solid cuboid
find out mass by weighing it
for volume do length x width x height
mass / volume
how do you find the density of an irregular object
find out mass by weighing it
for volume use a eurika beaker
mass / volume
how do you use a eurika beaker to find the volume of an object
fill eurika beaker so water level is just under the spout
place measuring cylinder under spout and put object in water
the volume of water collected in the measuring cyclinder is the volume of the object
what are the units of density
kg/m³ or g/cm³
how do you convert from g/cm³ into kg/cm³
multiply the g/cm³ value by 1000
e.g. 0.525 g/cm³ = 525 kg/cm³
whats internal energy
the total energy stored by the particles making up a substance or system (kinetic energy + potential energy)
whats temperature
the measure of the average internal energy of a substance
how do you increase the kinetic energy of particles in a substance
heating the particles transfers energy to kinetic energy store which increases their internal energy
is measured by an increase in temperature
the more _______ _________ a substance has, the higher its ____________ will be
the more internal energy a substance has, the higher its temperature will be
what 2 things can heating a substance do
raise its temperature
change the state of the substance
What's specific heat capacity?
the energy required to raise the temperature of 1kg of a substance by 1 degree
what does a low heat capacity mean
it heats up quickly
what does a high heat capacity mean
it takes longer to get hot
whats the equation for specific heat capacity
∆E = m x c x ∆T
change in Energy = mass x specific heat capacity x temp joules (J) = (Kg) x (J/Kg) x (°C)
whats specific latent heat
the amount of energy needed to change the state of 1 kg of material without changing its temperature
whats the equation for specific latent heat
E = m x L
energy (J) = mass (kg) x specific latent heat (J/kg)
when a substance is melting or boiling, why dosnt the temperature change until the substance has turned into a liquid or a gas
the energy is used for breaking bonds between the particles rather than raising the temperature
shown by the flat spots on the heating graph
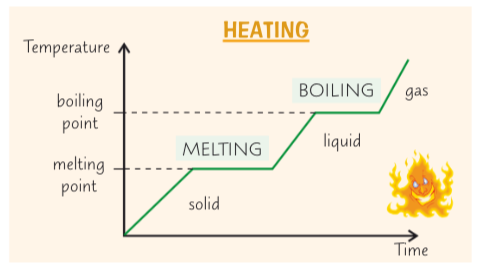
what are the 2 types of specific latent heat
Specific latent heat of vaporisation
Specific latent heat of fusion
whats specific latent heat of vaporisation
energy change when a substance changes between a liquid + gas
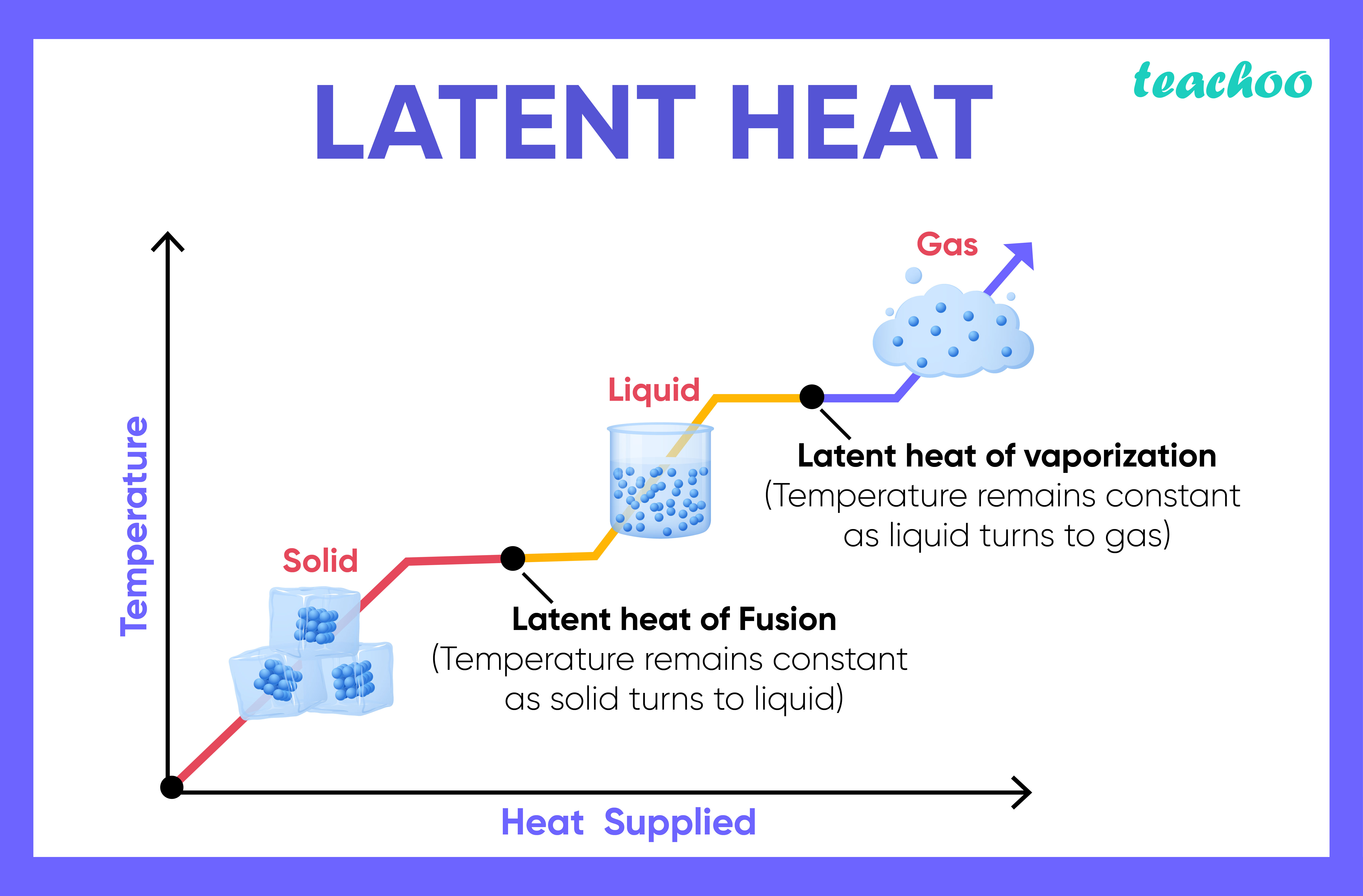
whats specific latent heat of fusion
energy change when a substance changed between a solid + liquid
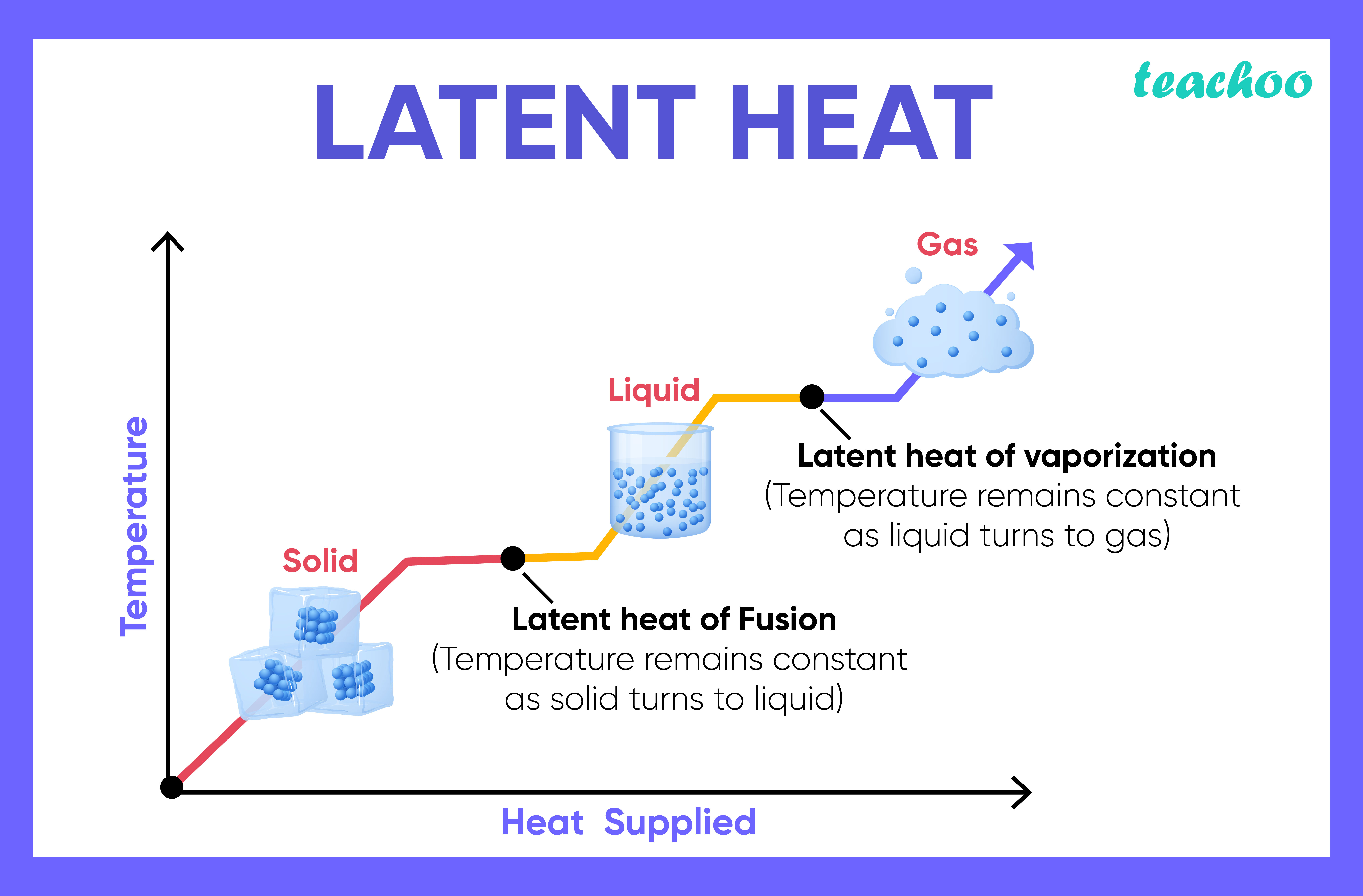
when cooling a substance, what would the specific latent heat of vaporisation/fusion be
the amount of energy released, rather than required at each stage
whats pressure
a measure of the force per unit area
whats the equation for pressure
p = F/A
pressure = force/ area
what are the units for pressure
pascals (Pa)
how do gas particles trapped in a container behave
they move about randomly travelling in straight lines until they collide with another particle or a wall at which point they will bounce off
how does a gas inside a container exert pressure on the container
the particles of the gas are moving randomly and collide with the walls of the container
this exerts a pressure on the container wall
how does decreasing the volume of a container affect the pressure of a gas
will increase the pressure
decreasing volume of the container whilst keeping number of gas particles the same will increase the concentration
there will be a smaller distance between the walls
these both increase the collisions between the particles and the container meaning more force will be exerted on a smaller area of the container resulting in higher pressure
how does increasing the temperature of a gas in a fixed container will affect the pressure
higher temperatures mean the particles have more kinetic energy
means they will collide with the walls more frequently and with more force so the pressure will increase
how does increasing the concentration of gas in a flexible container (like a balloon) will affect the volume
a higher concentration of particles means more particles in the same volume
extra particles will collide with walls of the container pushing it outwards increasing the volume
whats the relationship between the pressure and volume of a gas (assuming temperature is kept contant)
when at a constant temperature, the pressure and a volume of a gas are inversely proportional
e.g. if you decrease the volume of a container, then the pressure will increase