AP Psychology: Topic 5.5 - Treatment of Psychological Disorders
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
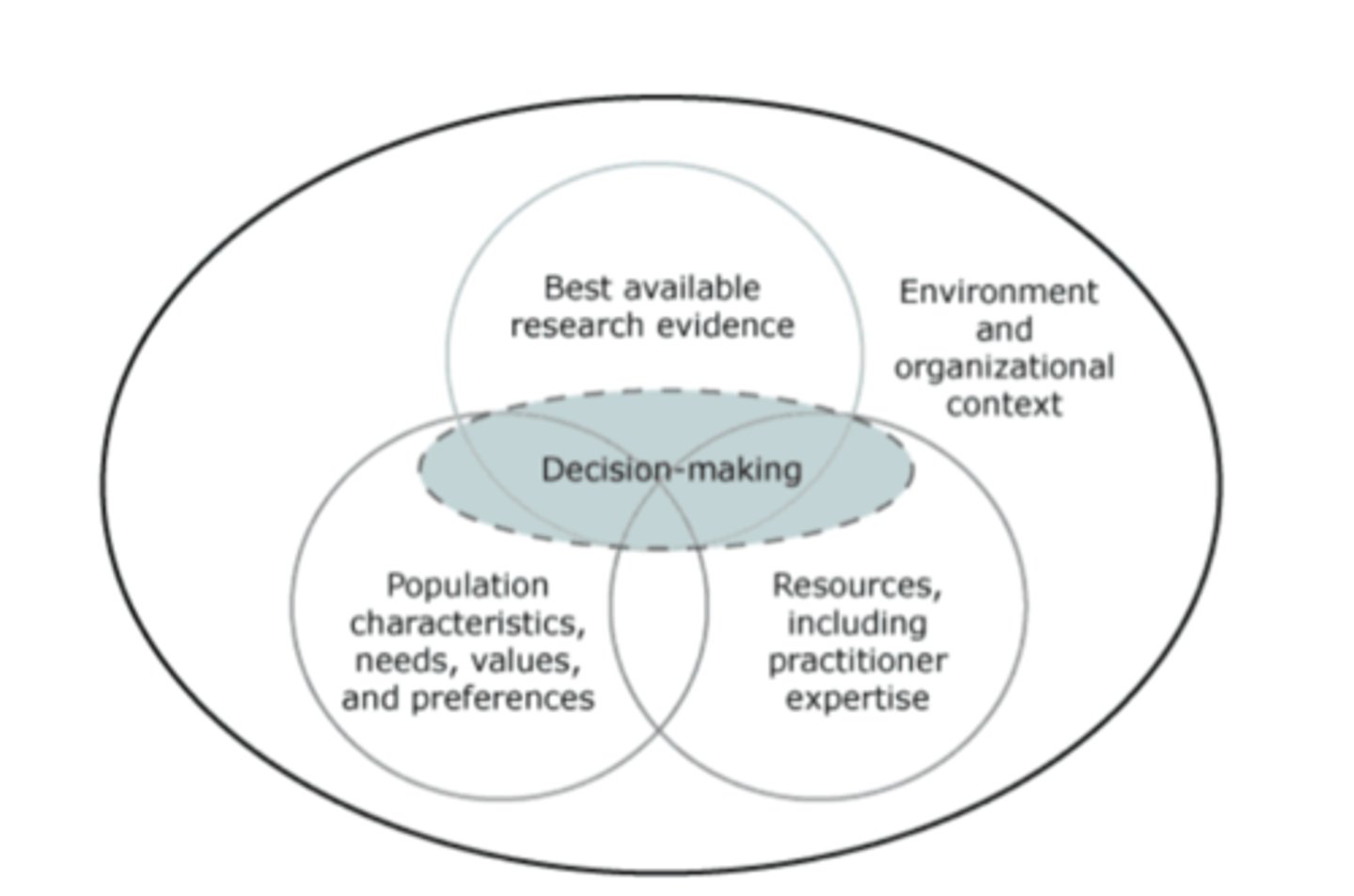
Evidence-based interventions
therapeutic treatments designed with the best available research that also consider patients' unique needs and preferences (also knowns as Evidence-Based Practice)
Cultural humility
a practice of therapists who honor a patient's beliefs, customs, and values while being aware of their own limitations and biases

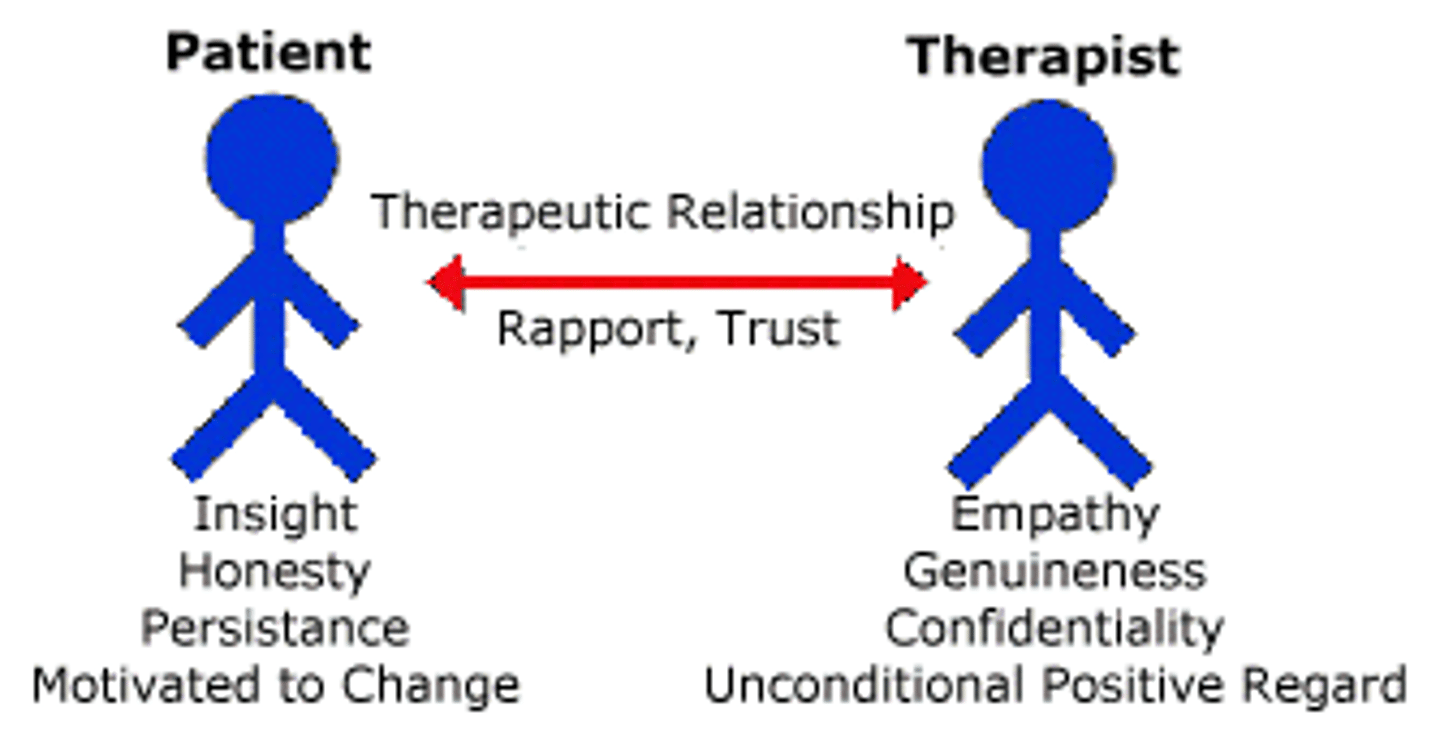
Therapeutic alliance
the bond of trust between a patient and therapist and their agreement to work together for the patient's well-being
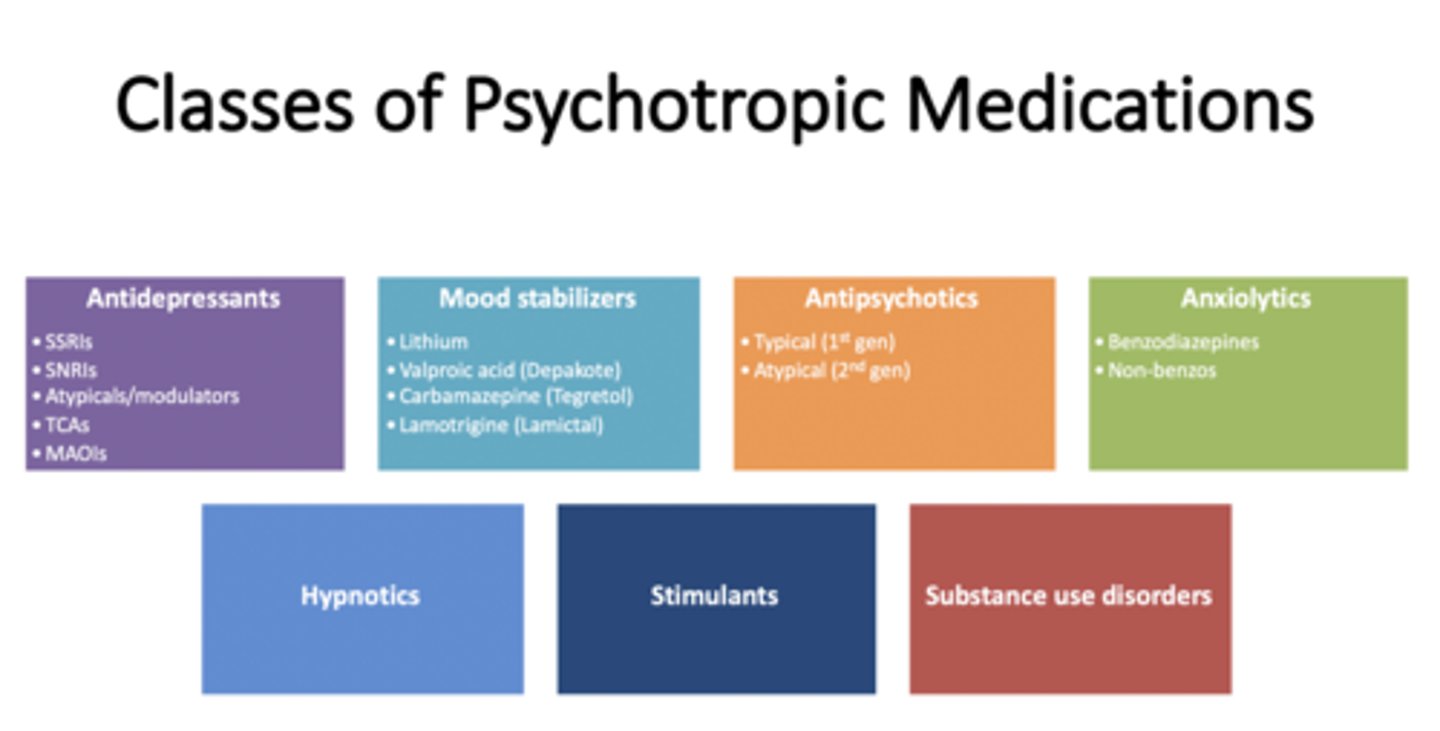
Psychotropic medication
a drug that treats mental illness by altering the brain and nervous system's chemical balance
Decentralized treatment (deinstitutionalization)
the practice of moving people with mental health conditions from long-term psychiatric hospitals to community-based care (sometimes with poor results)

Nonmaleficence
the ethical principle of not causing intentional harm to a patient

Fidelity
a measure of how closely a psychotherapeutic treatment follows the intended method

Integrity
a characteristic of a therapist who is truthful, trustworthy, and upholds high standards of professionalism

Respect
protecting a patient's rights, dignity, and privacy and making them a partner in decision-making

Psychodynamic therapies
treatments that focus on unconscious mental processes (usually about past experiences) and how these influence current behavior

Free association
a method of exploring the unconscious in which a person relaxes and says whatever comes to mind, no matter how trivial or embarrassing

Dream interpretation
the process of analyzing dreams to understand their meaning and uncover unconscious desires and conflicts

Cognitive therapies
treatments based on the theory that when a person changes their thoughts (as opposed to their behaviors), they can change how they feel and how they respond

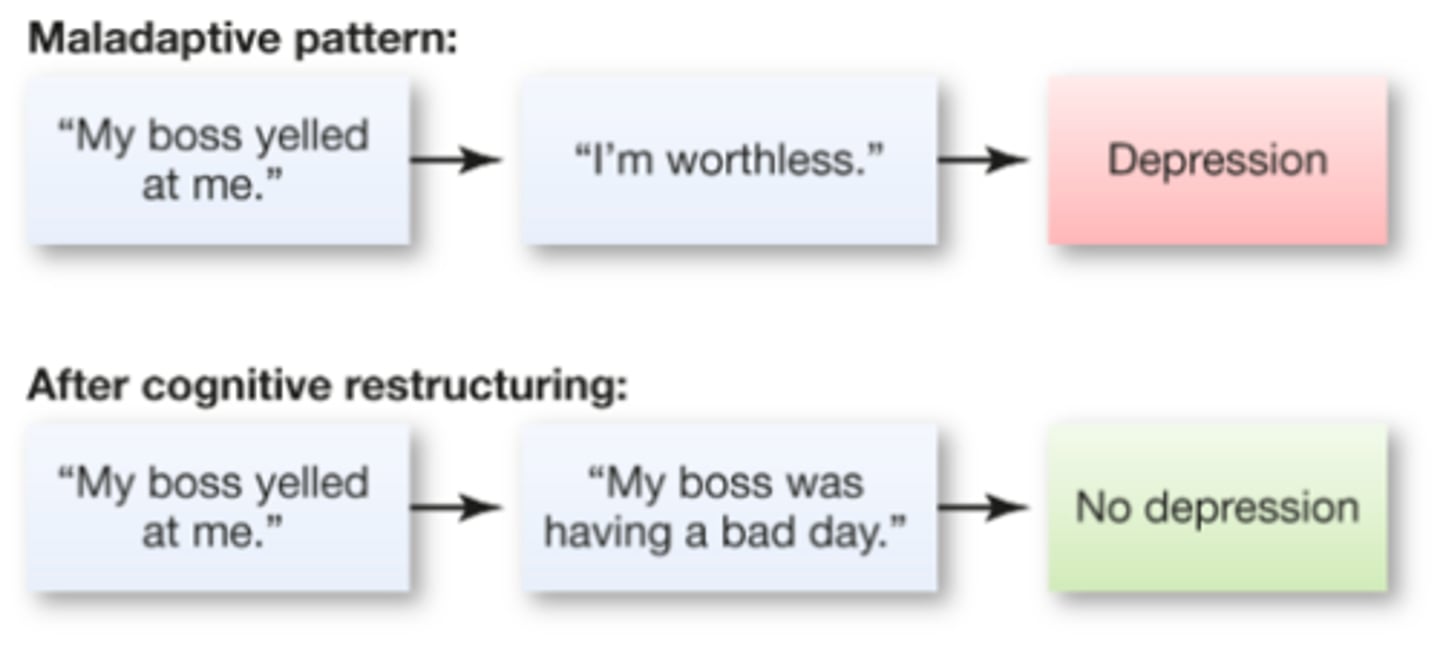
Cognitive restructuring
a therapy that helps a patient: identify their negative or irrational beliefs, refute them, and modify them so they are adaptive and reasonable
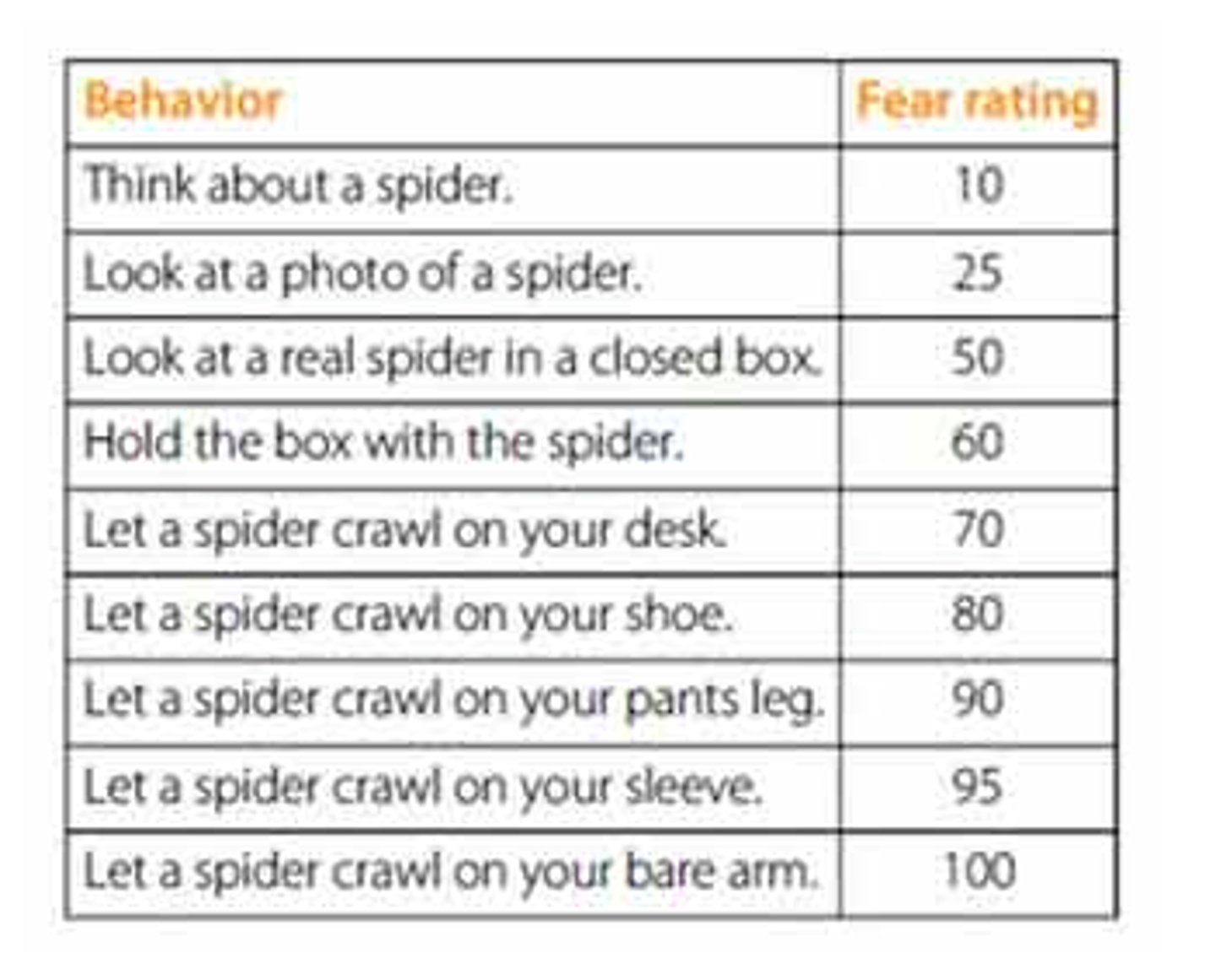
Fear hierarchies
a form of exposure therapy to treat phobias in which a patient makes a list of feared situations ranked from least to most anxiety-provoking

Combating maladaptive thinking
the process of changing harmful thought patterns into more realistic ones

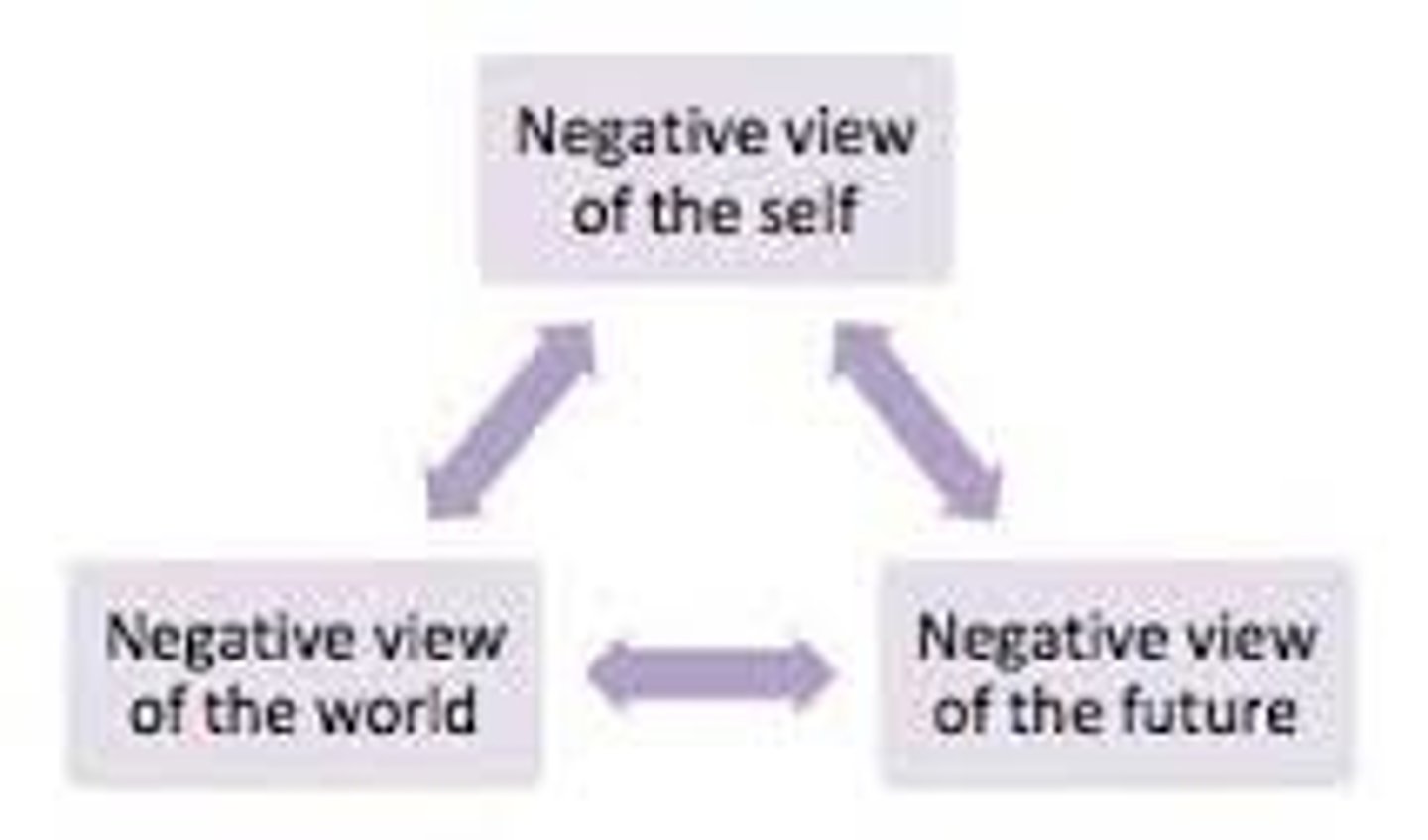
Cognitive triad
a person's negative thoughts about themselves, their world, and their future (which lead to feelings of depression according to cognitive therapists)
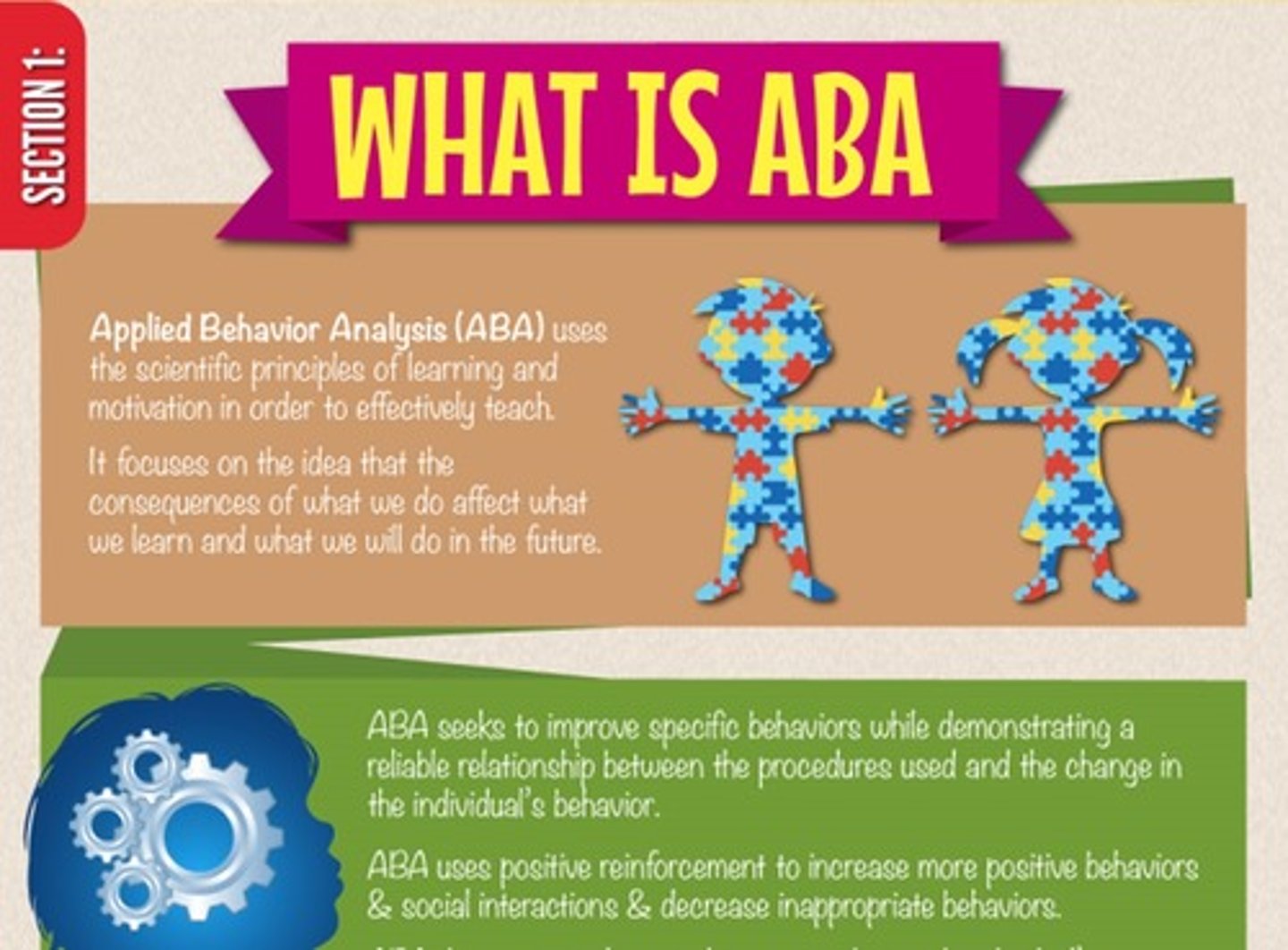
Applied behavior analysis
therapy that uses principles of conditioning to address mental
disorders and developmental disabilities
Exposure therapies
treatments for anxieties that safely expose people (in imagination or actuality) to the things they fear and avoid

Systematic desensitization
a treatment for phobias that gradually exposes a person to a feared stimulus while they are relaxed
Aversion therapies
treatments that pair a negative behavior with a negative stimulus to reduce or eliminate the behavior (also known as aversive conditioning or counter conditioning)
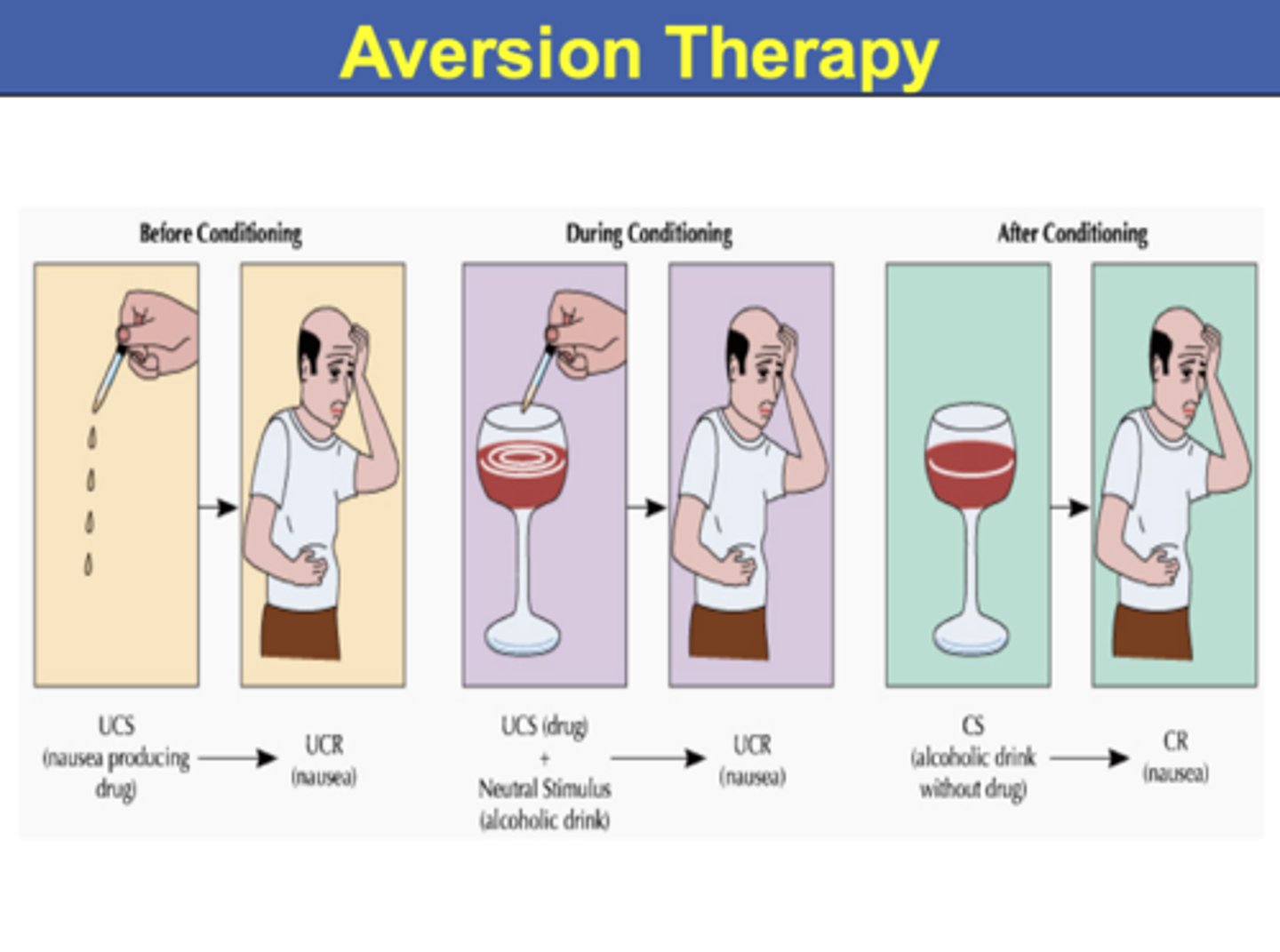
Token economies
a behavioral management technique that uses tokens to reward desired behaviors

Biofeedback
a technique that uses external devices to monitor a person's physiological state with the goal of controlling bodily functions to improve health

Cognitive-behavioral therapies (CBT)
a therapy based on the idea that thoughts and behaviors reinforce each other and that changing these can make a person feel better
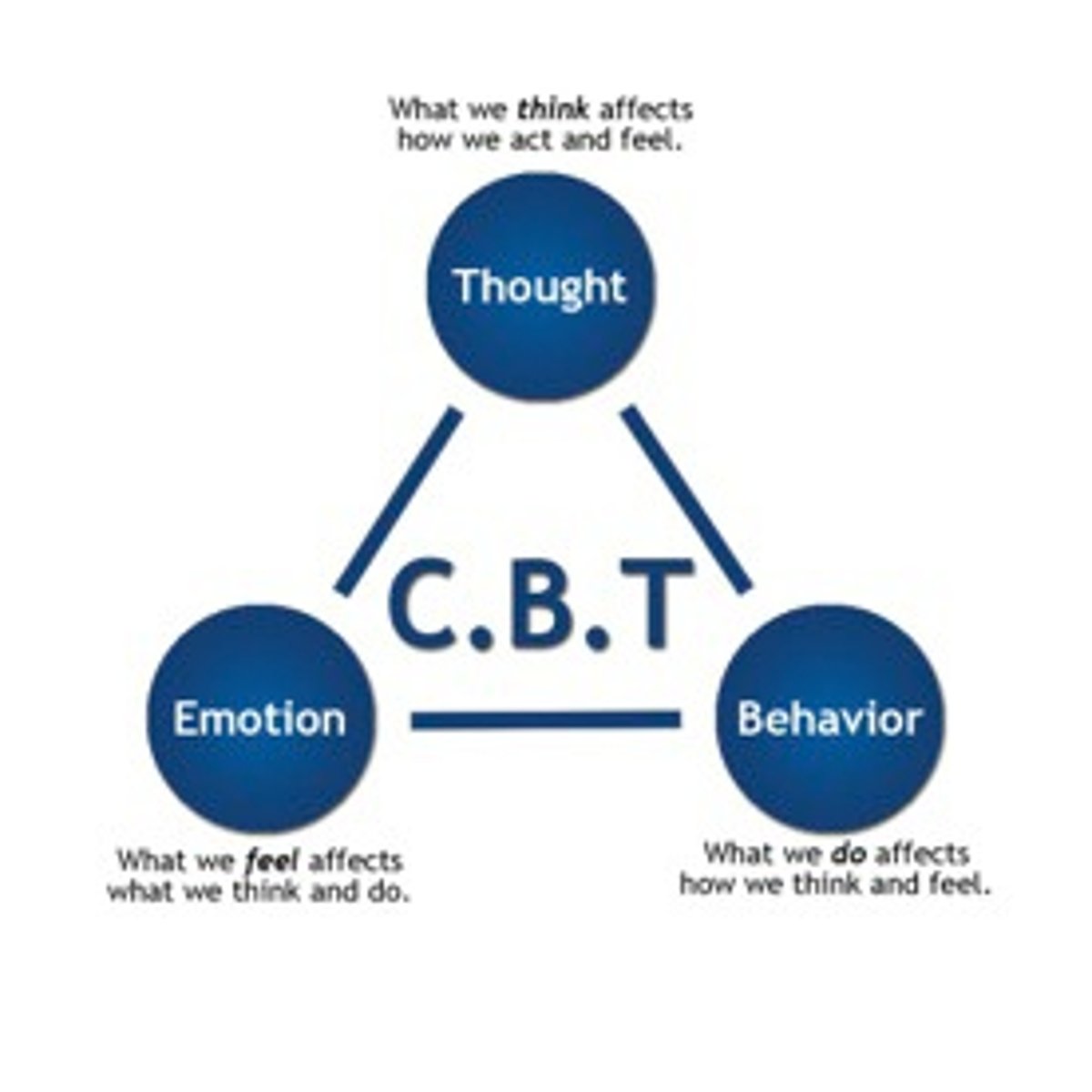
Dialectical behavior therapy (DBT)
a CBT treatment that helps people learn to accept reality and manage their emotions and relationship skills

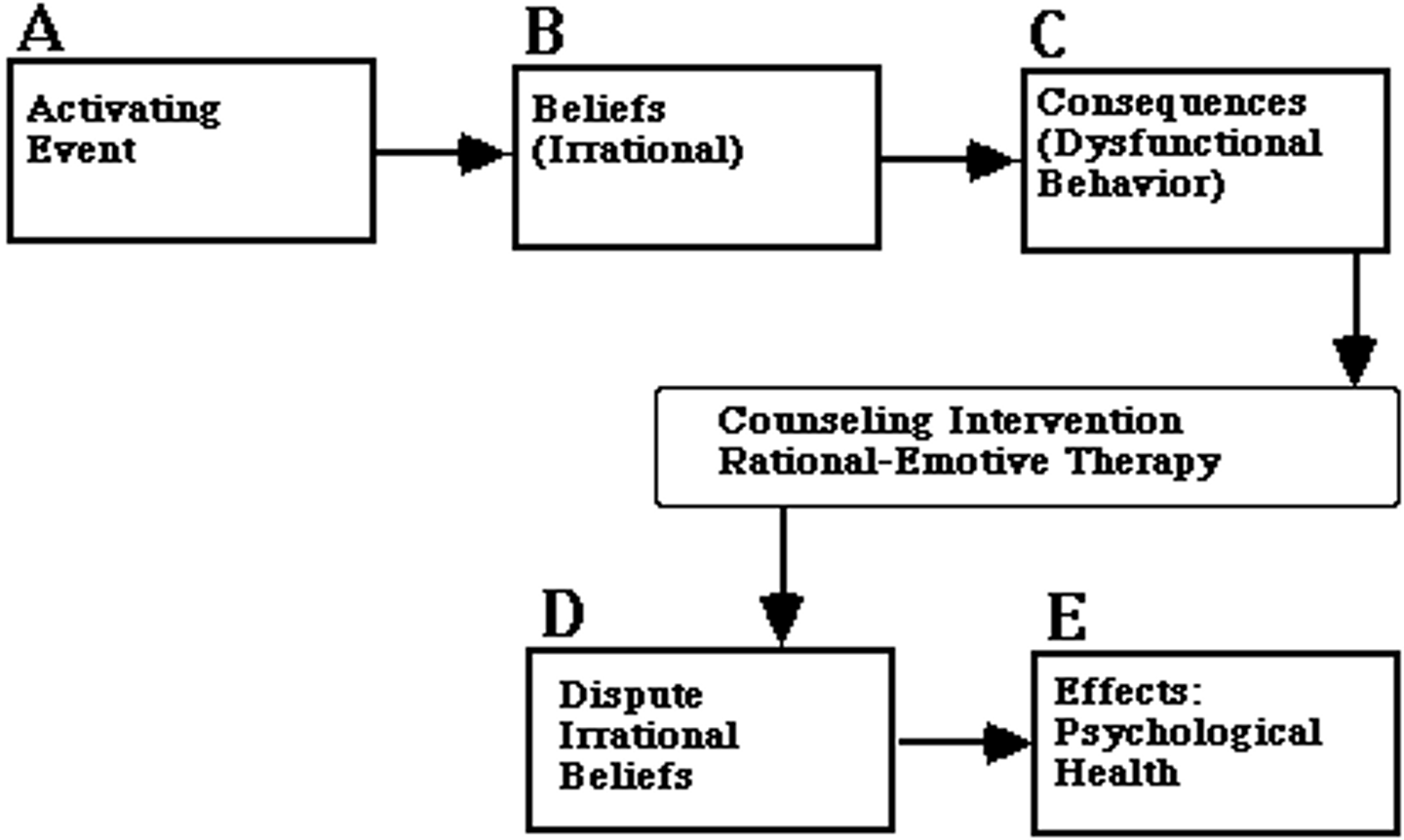
Rational emotive behavior therapy (REBT)
a CBT treatment that that helps people identify self-defeating thoughts and feelings, challenge the nature of irrational and unproductive feelings, and replace them with healthier beliefs
Person-centered therapy
a treatment from the humanistic perspective that focuses on creating a supportive and non-judgmental environment for clients to help them develop self-acceptance and personal growth

Active listening
a crucial part of person-centered therapy in which the therapist closely listens then demonstrates that they understand through clarifying questions and feedback

Group therapy
treating several people with similar problems in regular meetings with a trained counselor or therapist

Hypnosis
a state of consciousness characterized by focused attention, increased suggestibility, and heightened mental relaxation used by therapists to treat pain and anxiety

Psychoactive medication
drugs that interact with specific neurotransmitters in the central nervous system to address possible biochemical causes of mental disorders
Antidepressants
psychoactive medications that alter the brain's use of neurotransmitters (e.g., serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine) to improve mood and behavior
Antianxiety drugs
psychoactive medications that slow down brain activity and increase serotonin levels to alleviate fear, dread, uneasiness, and muscle tightness

Lithium
a psychoactive medication used as a mood stabilizer (most commonly for bipolar disorder, mania, and depression)
Antipsychotic medications
psychoactive medications that are used to treat symptoms of psychosis, such as hallucinations and delusions
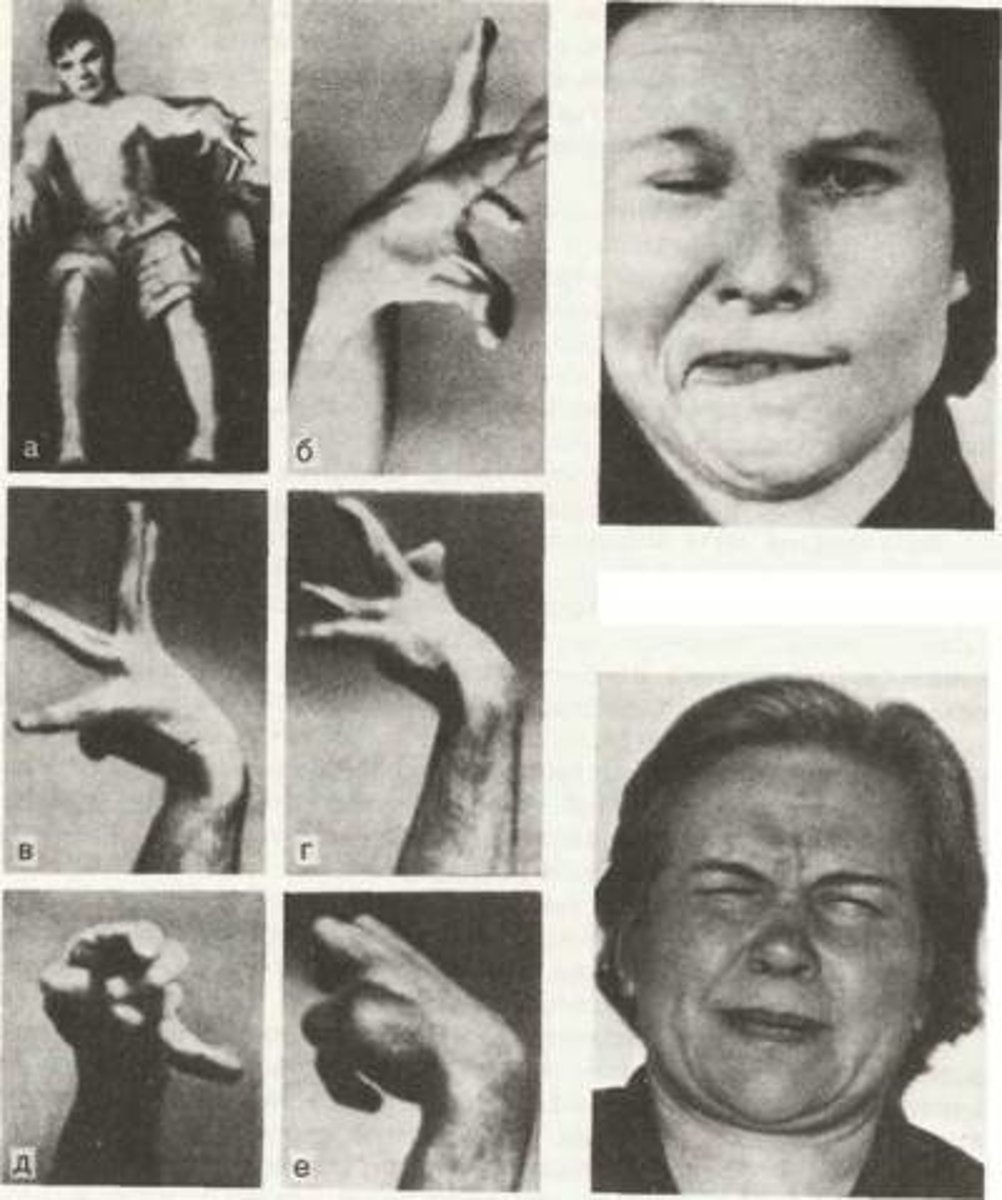
Tardive dyskinesia
a side effect of long-term use of traditional psychoactive medications in which people have uncontrollable movements, tremors, or spasms (related to the regulation of dopamine
in the nervous system)
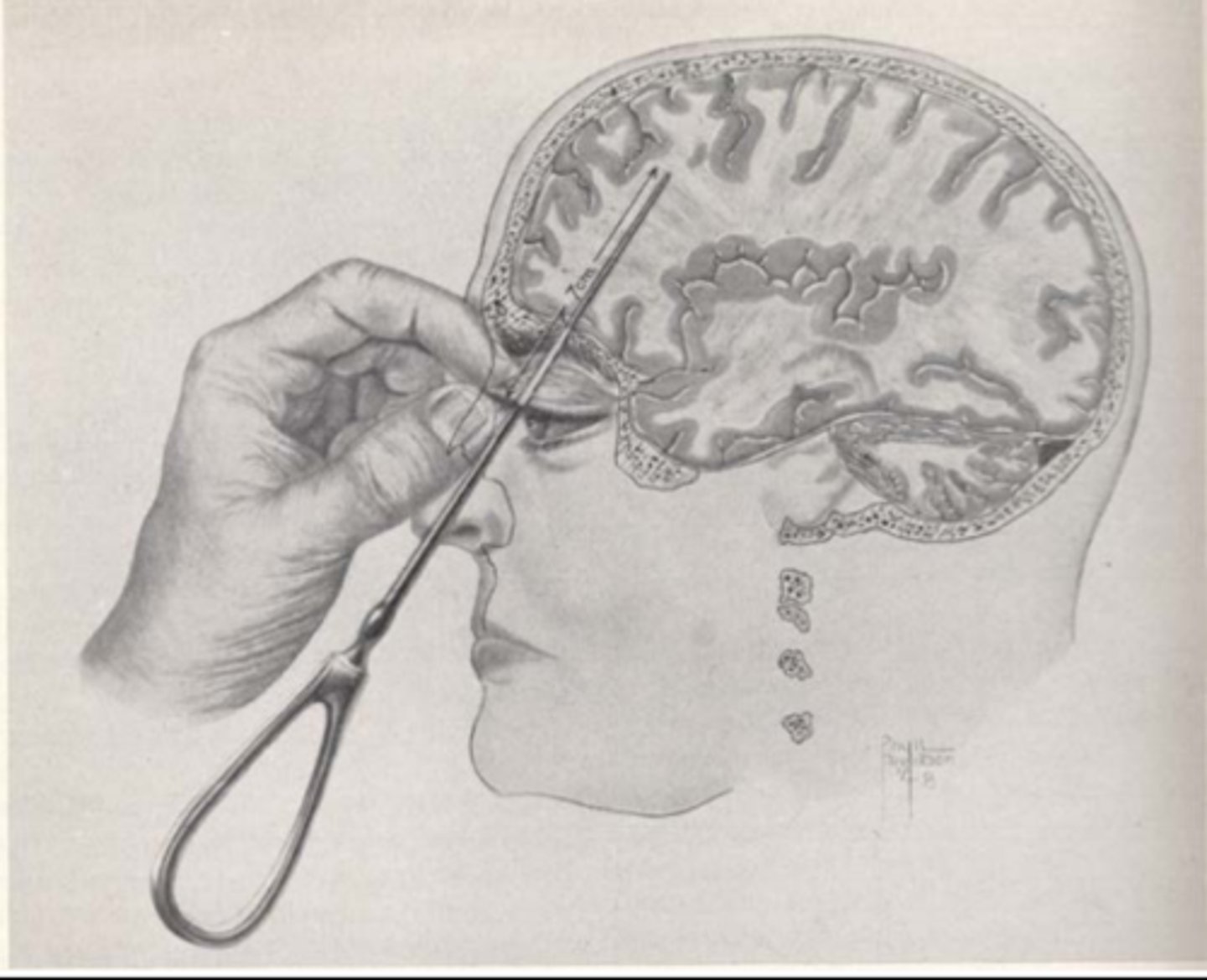
Psychosurgery
surgical procedures on brain tissue that remove or disconnect nerve pathways to treat mental disorders
Lesioning
a form of psychosurgery involving the removal or destruction of part of the brain
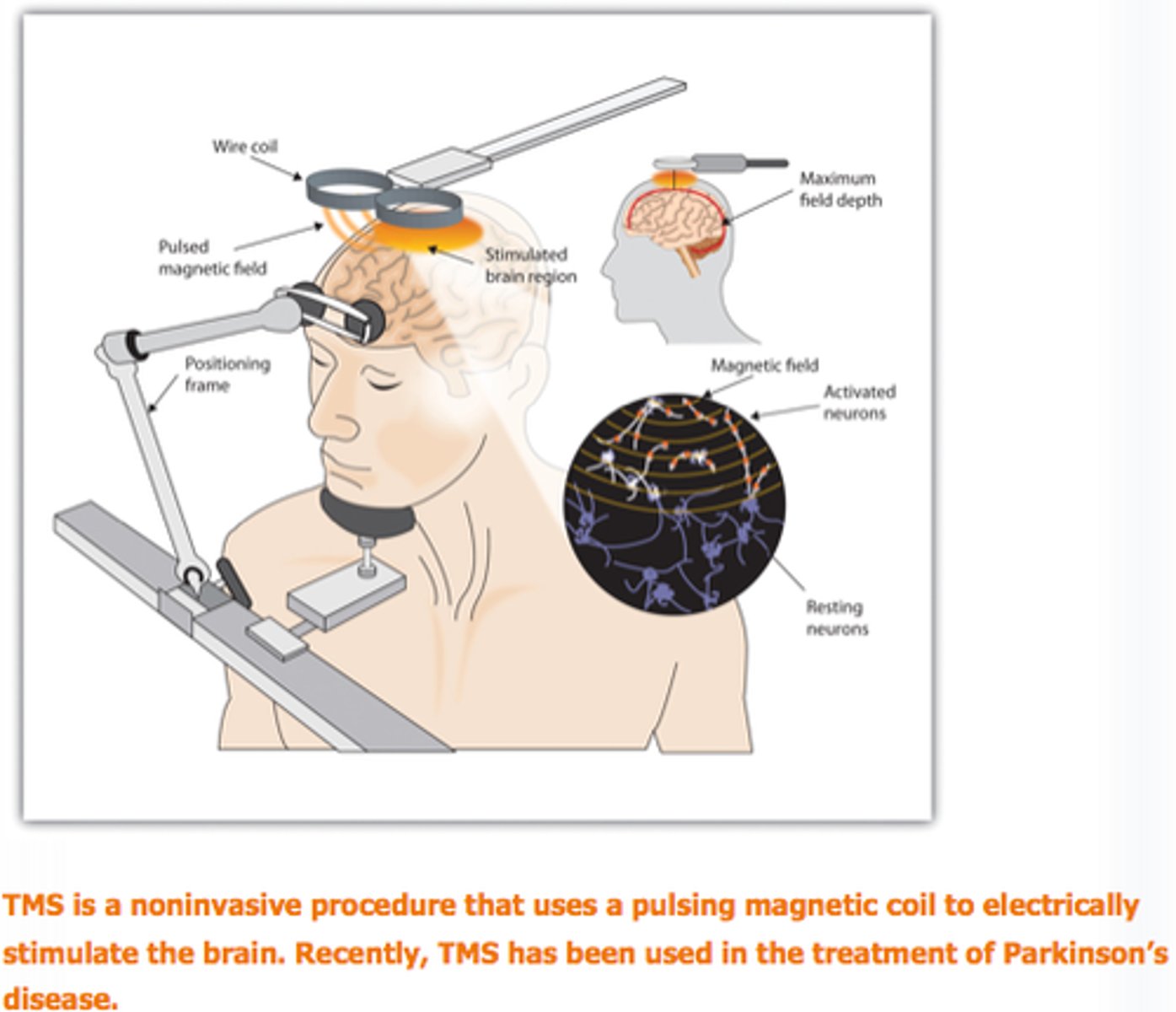
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS)
a non-invasive intervention that uses magnetic fields to stimulate the brain (used for depression, obsessive-compulsive disorder, and other conditions)
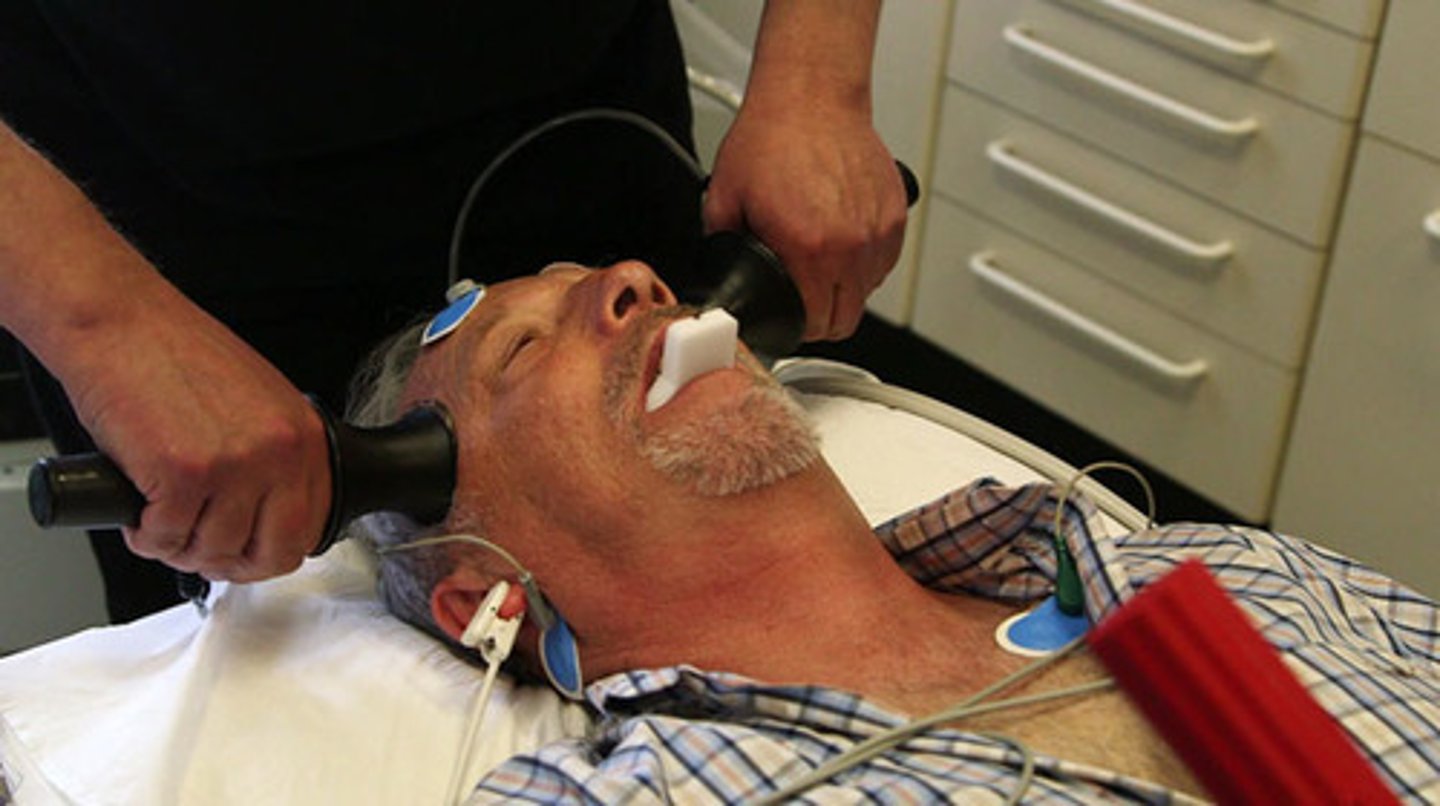
Electroconvulsive therapy
a treatment that uses electric shock to induce a seizure in the brain most commonly for drug-resistant or severe disorders
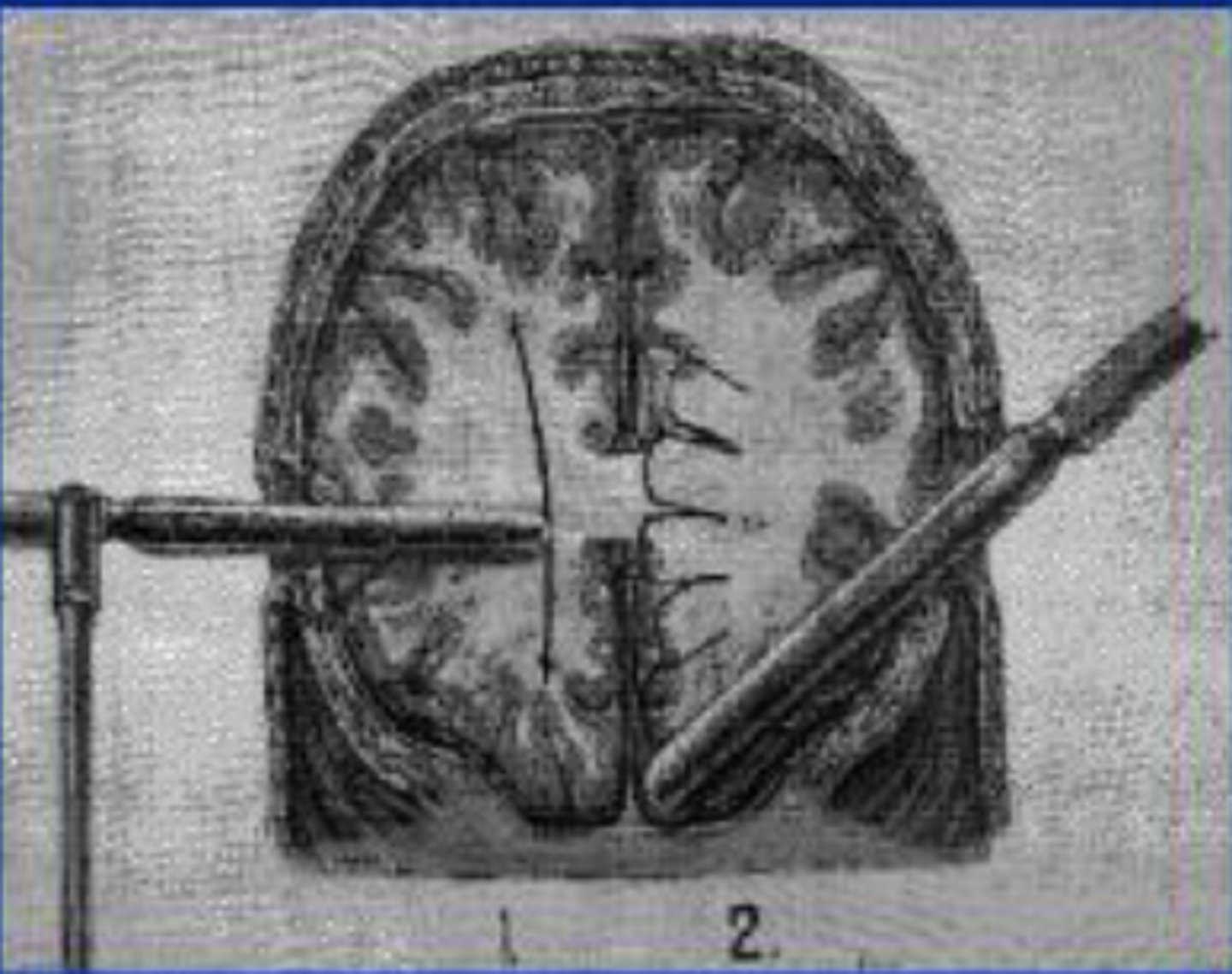
Lobotomy
a now-rare psychosurgical procedure used to calm uncontrollably emotional or violent patients by cutting the nerves that connect the frontal lobes to the emotion-controlling centers of the inner brain