UNL: AHIS 101 Exam 3
1/132
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
133 Terms
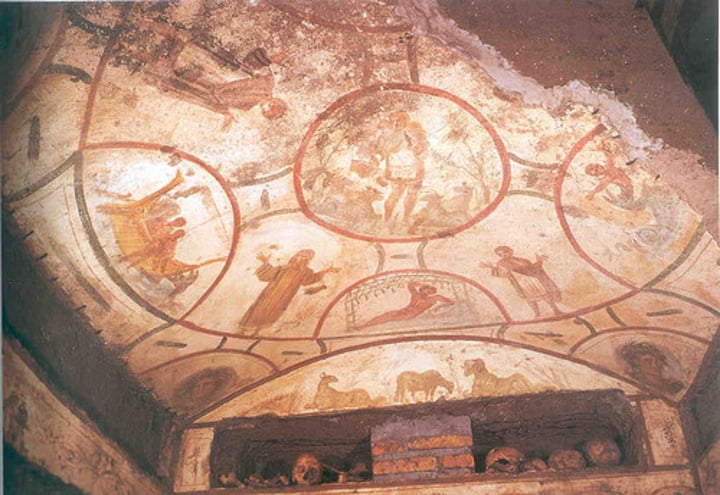
Catacomb of St. Callixtus, Rome, 4th Cent.
-place where people were buried and cremated
-Late Antique and Early Christian Art (Catacomb Art)
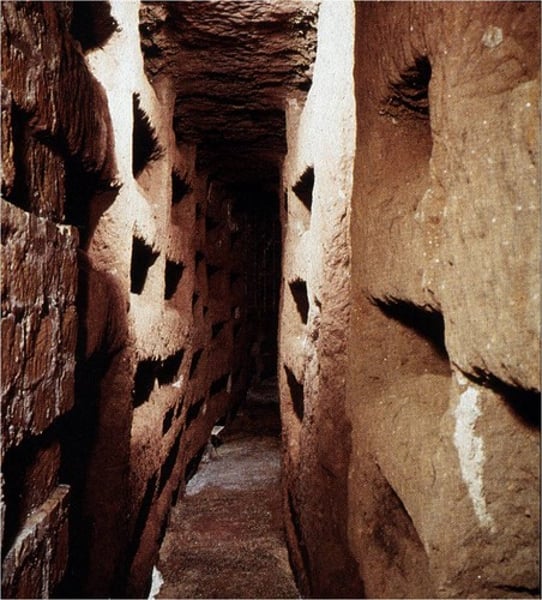

Catacomb of SS. Peter and Marcellinus, Rome, early 4th cent.
-Late Antique and Early Christian Art (Catacomb Art)

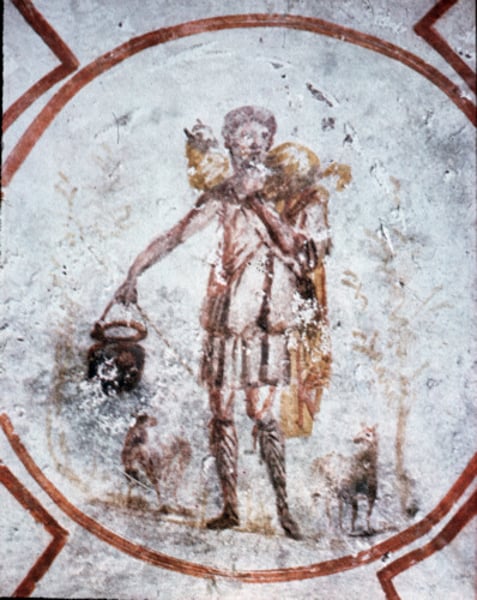
Good Shepherd
-metaphor for Christ, not a representation
-Late Antique and Early Christian Art (Catacomb Art)

Jonah and the Whale
-depicted from the Old Testament
-metaphor for the death and resurrection of Christ
-Late Antique and Early Christian Art (Catacomb Art)
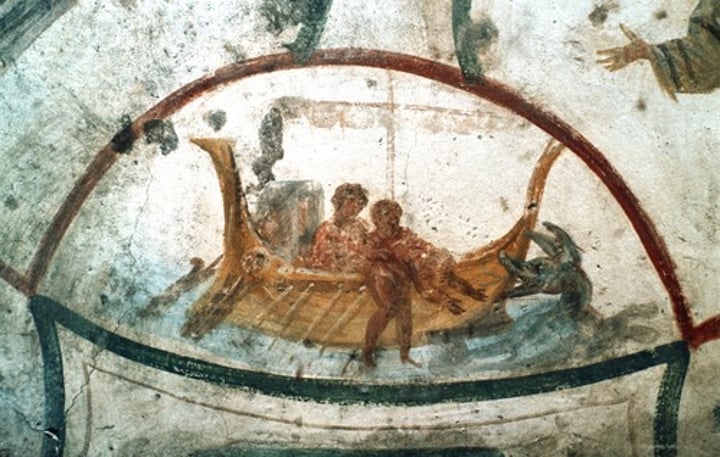

Christ as Orpheus, Catacombs of Domatilla
-image of Dionysus to represent Christ
-Late Antique and Early Christian Art (Catacomb Art)

Good Shepherd Sarcophagus, from Cata. of Praetextus, Rome, late 4th cent.
-Late Antique and Early Christian Art (Catacomb Art)

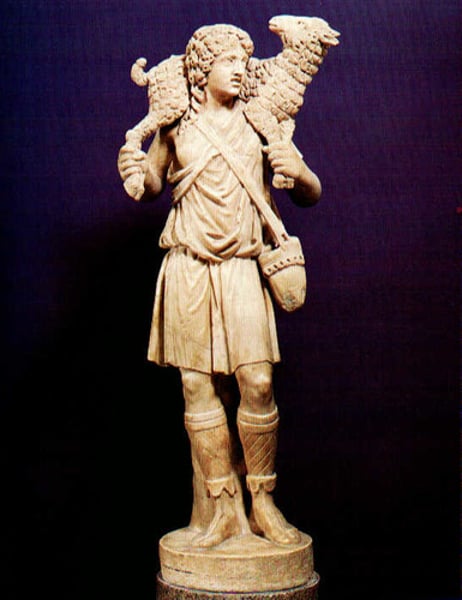
Good Shepherd Statuette, from Rome, 300
-Late Antique and Early Christian Art (Catacomb Art)

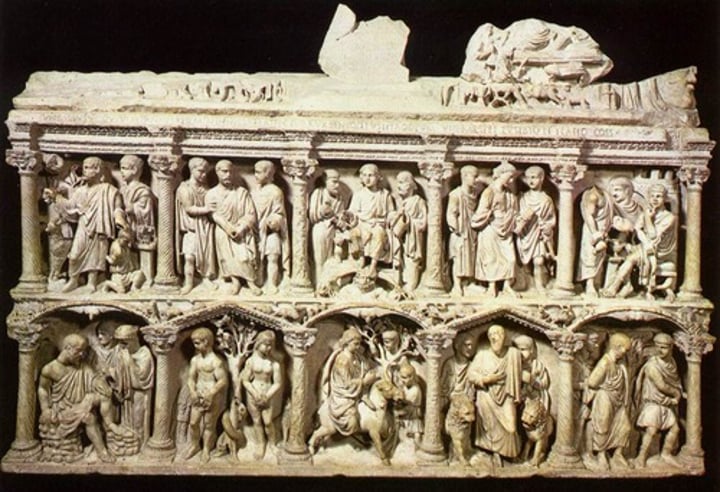
Sarcophagus of Lucuis Junius Bassus, from Rome, AD 359
-earliest depiction of Christ in heaven
-lots of recognizable bible scenes from Old Testament
-Dionysus referrenced again
-Late Antique and Early Christian Art (Catacomb Art)

Old St. Peter's Rome (Vatican), AD 320
-built by Constantine
-basilica plan: based on Roman basilica with atrium, narthex, transept
-Late Antique and Early Christian Art (Architecture)
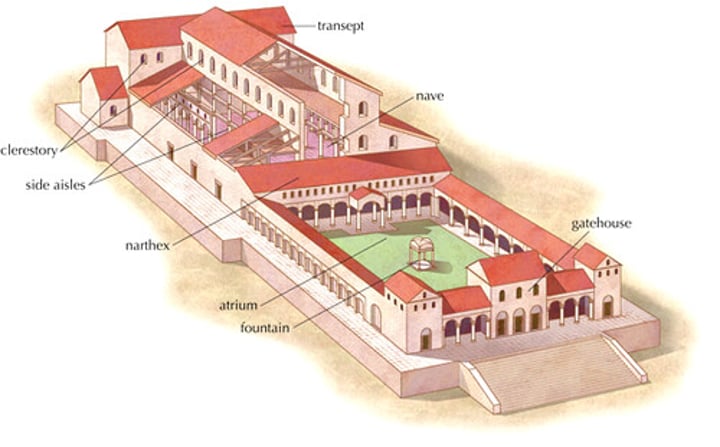
Atrium
open colonnaded courtyard
Narthex
vestibule, entry hall/porch
Transept
an area perpendicular to the nave between the nave and the apse, forms a 'T' shape in the church
Santa Constanza, Rome, 350
-Centralized plan: building's elements are of equal dimensions around the center (looks like a circle)
-Late Antique and Early Christian Art (Architecture)

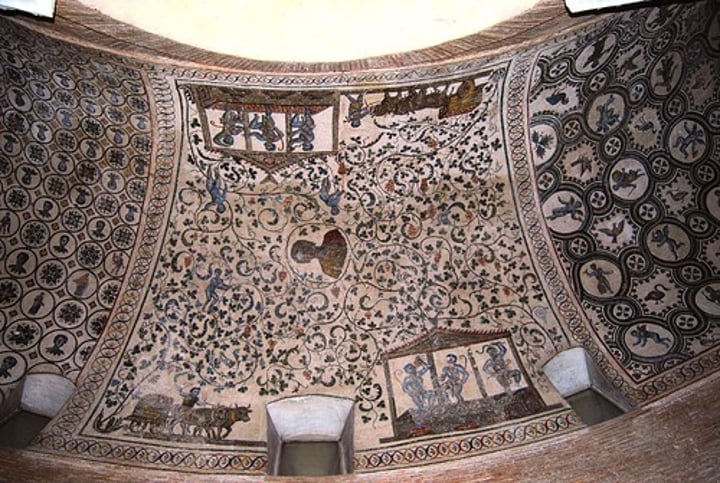
Santa Constanza, Ambulatory Vault Mosaic
-Ambulatory: place for walking, usually around an apse or altar
-Vault mosaic: the mosaic (vine pattern) that is above the ambulatory
-Late Antique and Early Christian Art (Architecture)

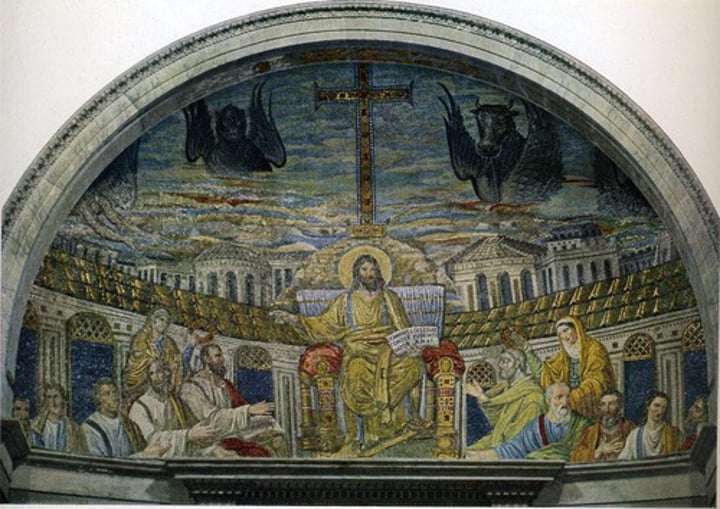
Christ Enthroned, Santa Pudenziana, Rome, 410-417
-apse mosaic
-Roman themes and crowns
-4 Evangelists symbols: Matthew=winged-man, Mark=lion, Luke=ox, John=eagle
-Late Antique and Early Christian Art (Architecture)

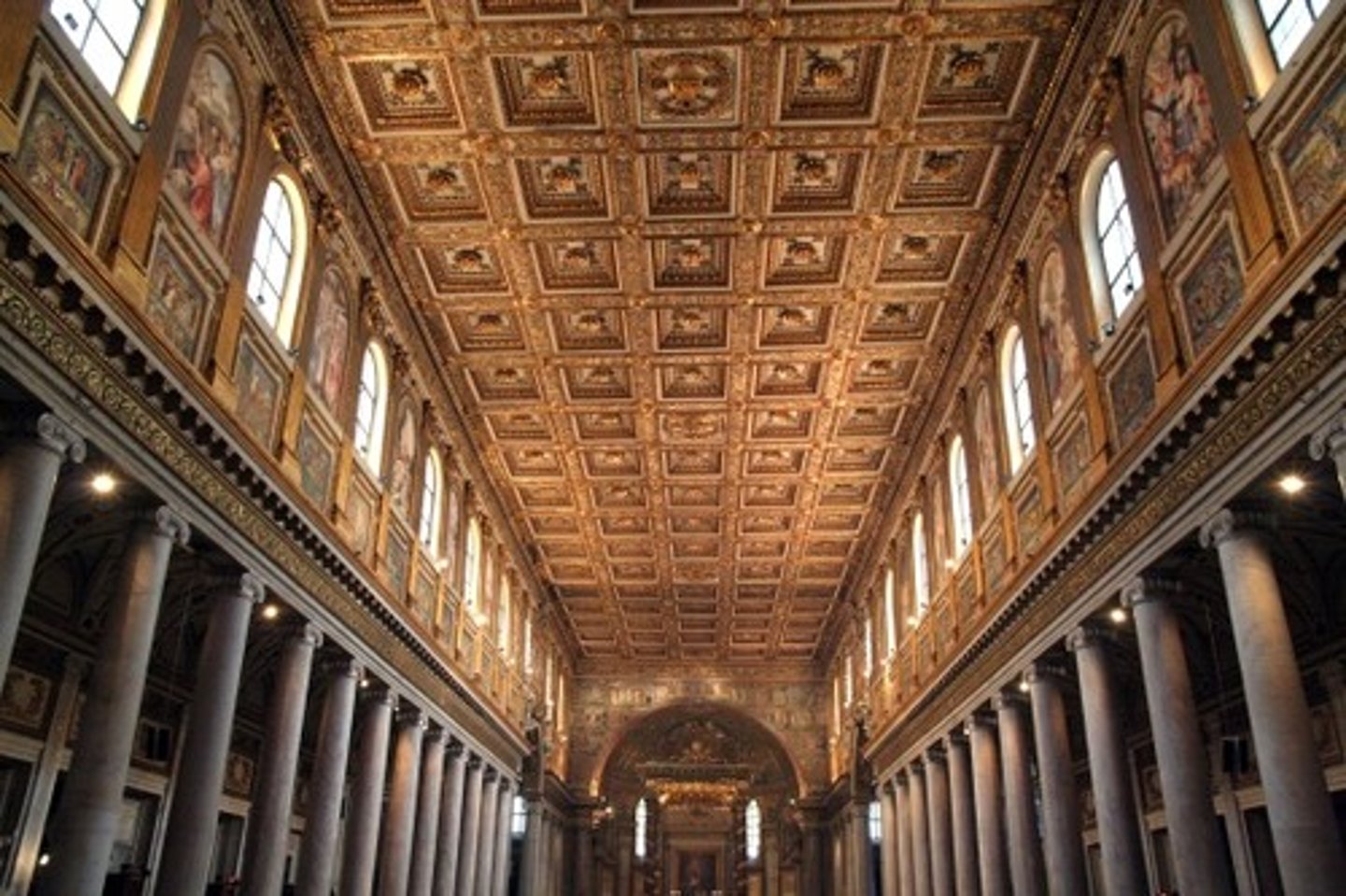
Nave, Santa Maria Maggiore, Rome, 430-440
-modern copper ceiling
-coffering
-Late Antique and Early Christian Art (Architecture)

Coffering
series of sunken panels in a ceiling or vault
The Parting of Lot and Abraham
-mosaic in Santa Maria Maggiore
-no longer representative, used to be directly narrative and tell stories
-Late Antique and Early Christian Art (Architecture)
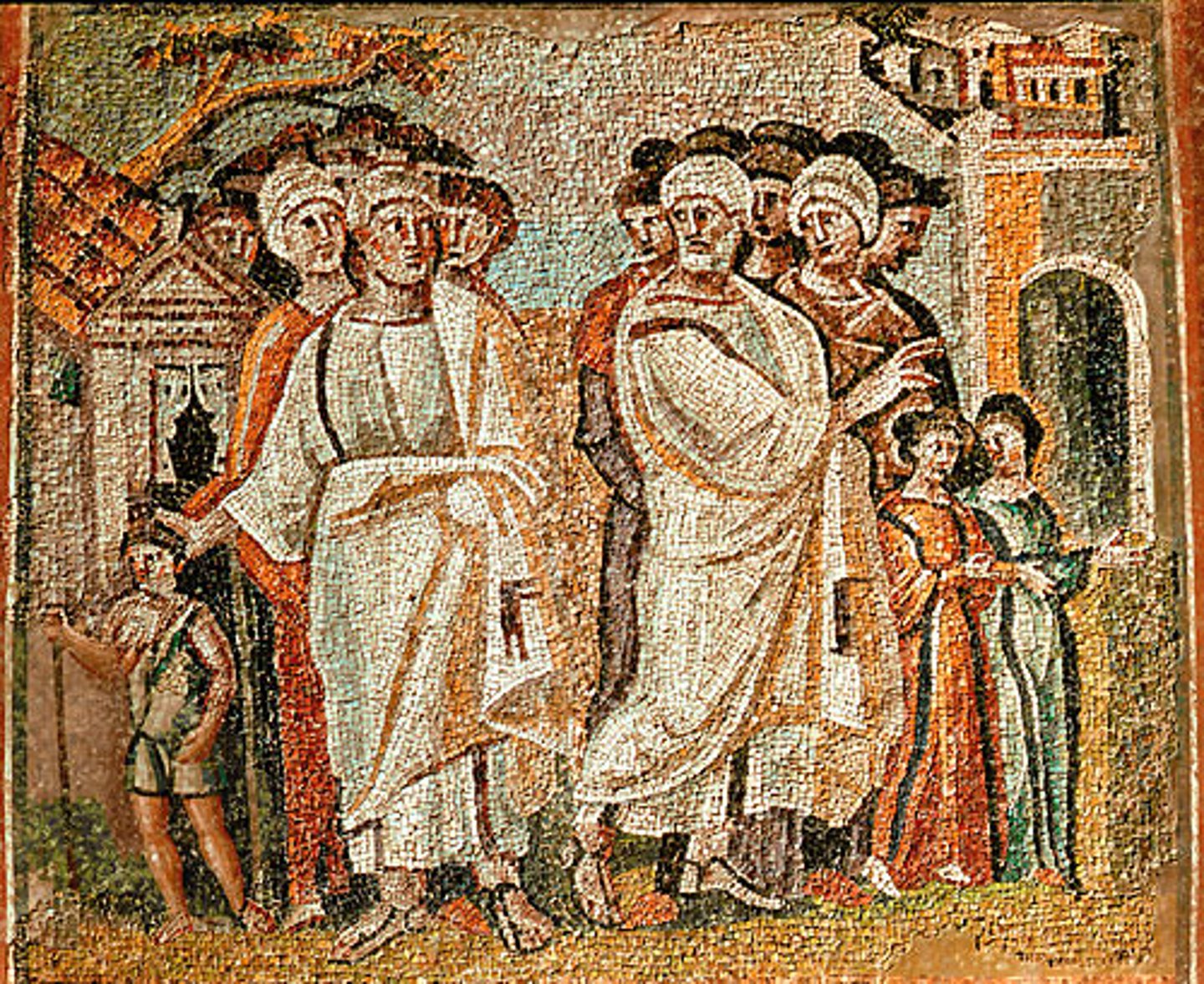

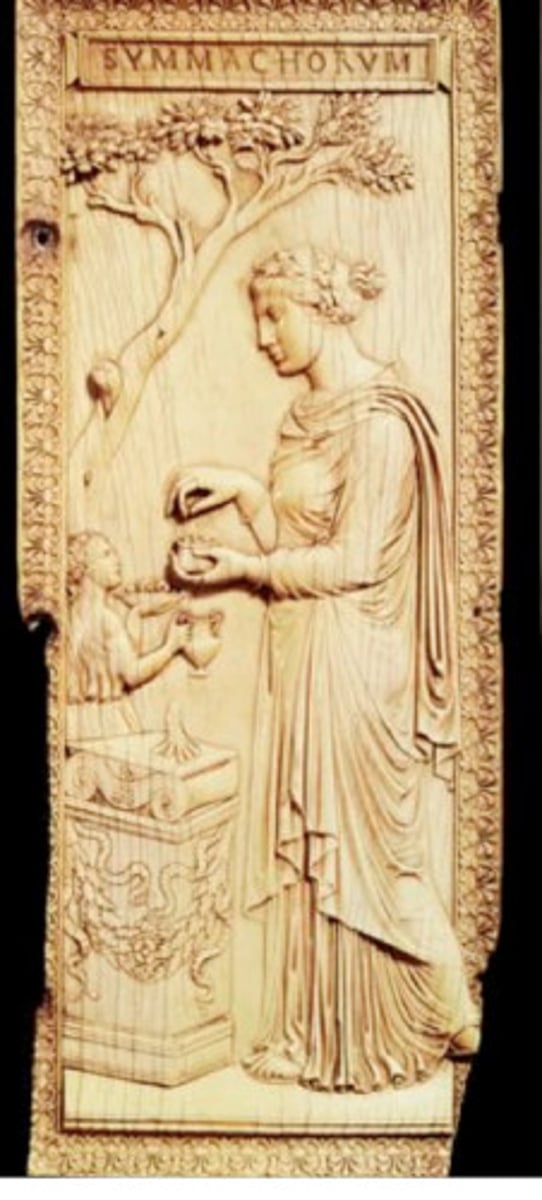
Ivory Diptych of the Symmachi, 400
-bookcover
-priestess performing a sacrifice
-Late Antique and Early Christian Art (Minor Art)

Catacomb
vast underground networks of chambers designed as cemeteries for bury Christian dead
Lunette
semicircular frame
Loculian
architectural compartment or niche that houses a body
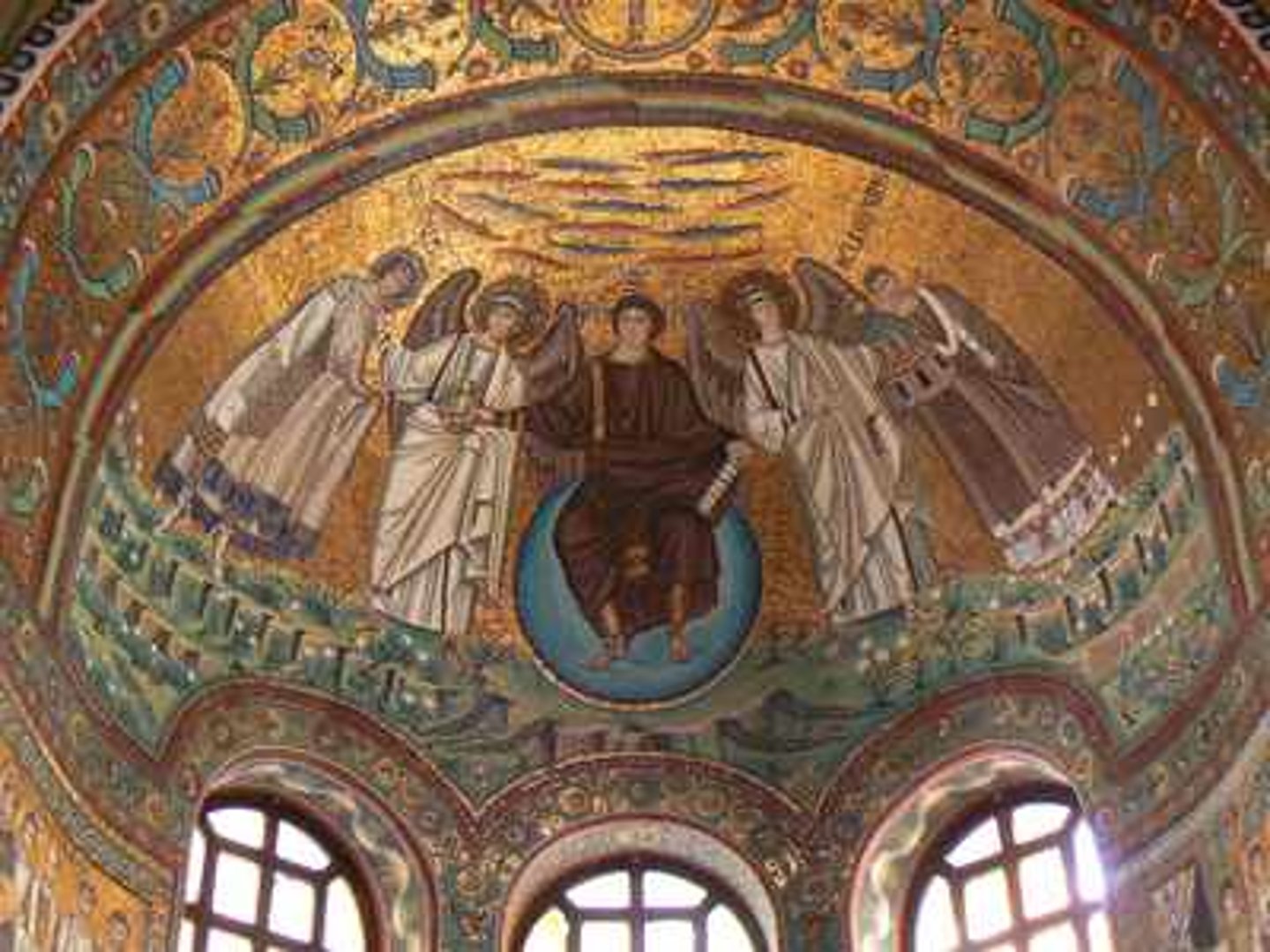
Mausoleum of Galla Placidia, Ravenna, 425
-placeholder for the soul that resides within (plain exterior, beautiful interior)
-Byzantine Art (Architecture)
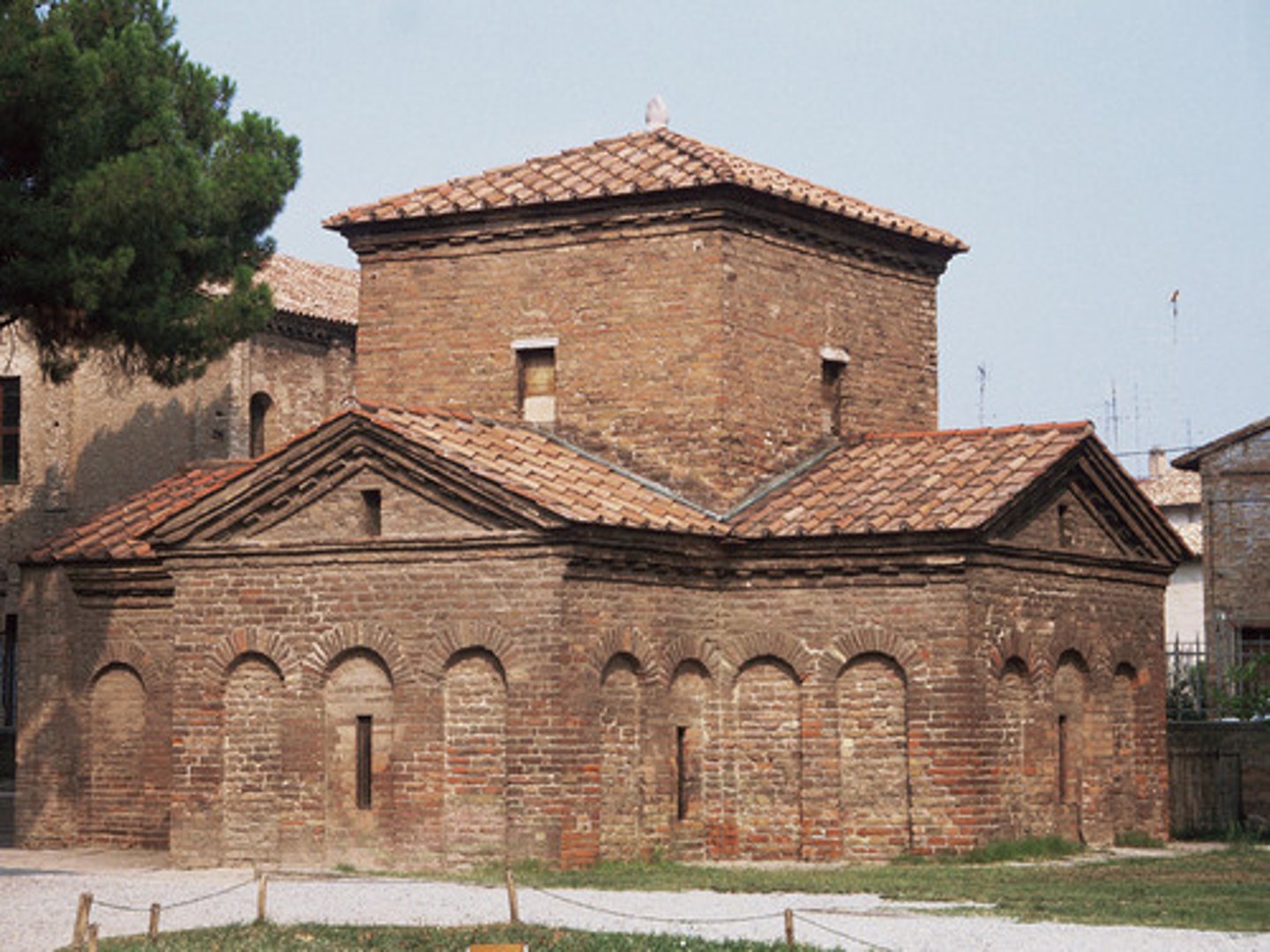

Mausoleum
monumental tomb
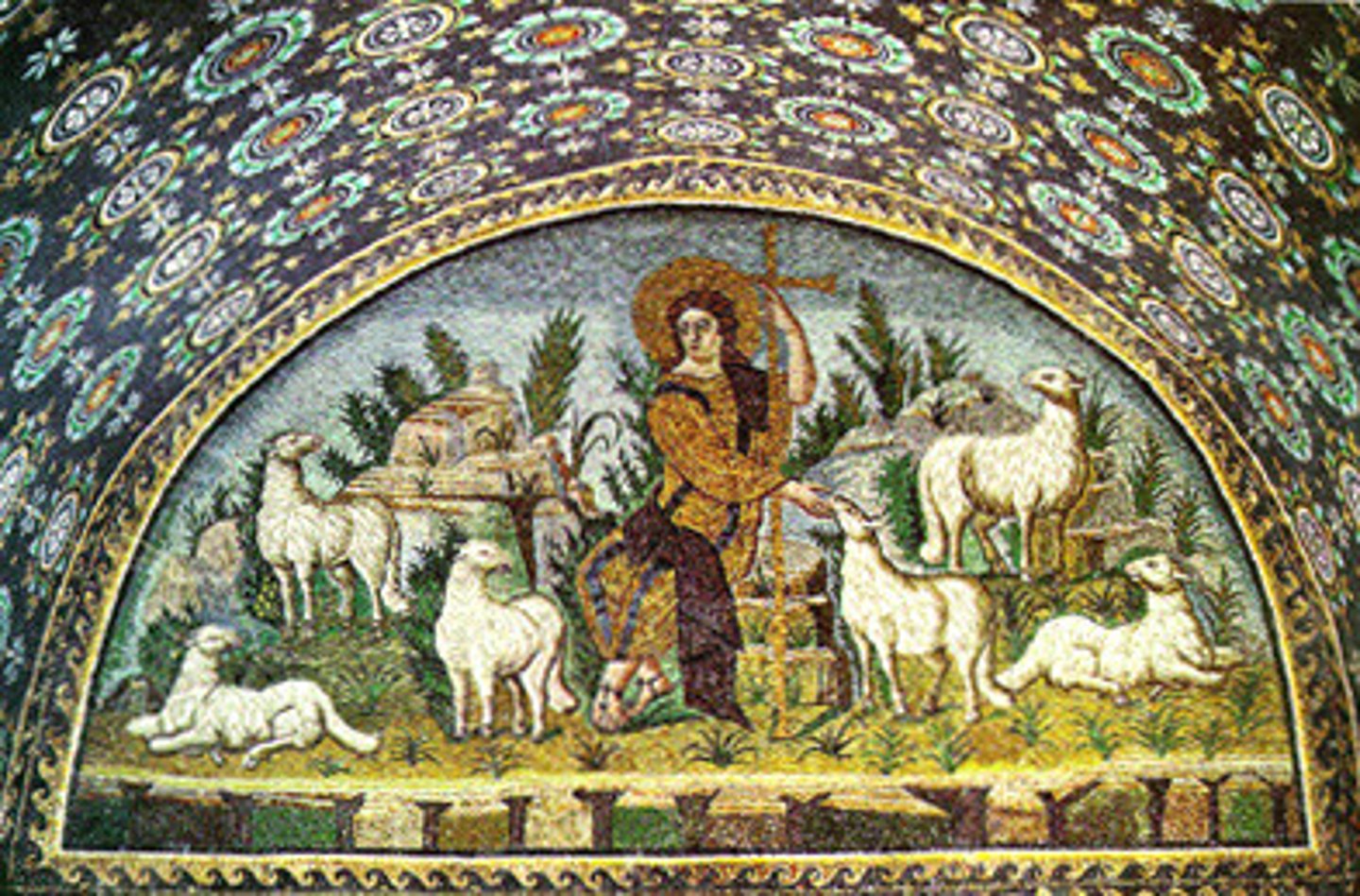
Mausoleum of Galla Placidia, Good Shepherd
-lunette mosaic on a barrel vault
-naturalism
-tessarae
-Byzantine Art (Architecture)

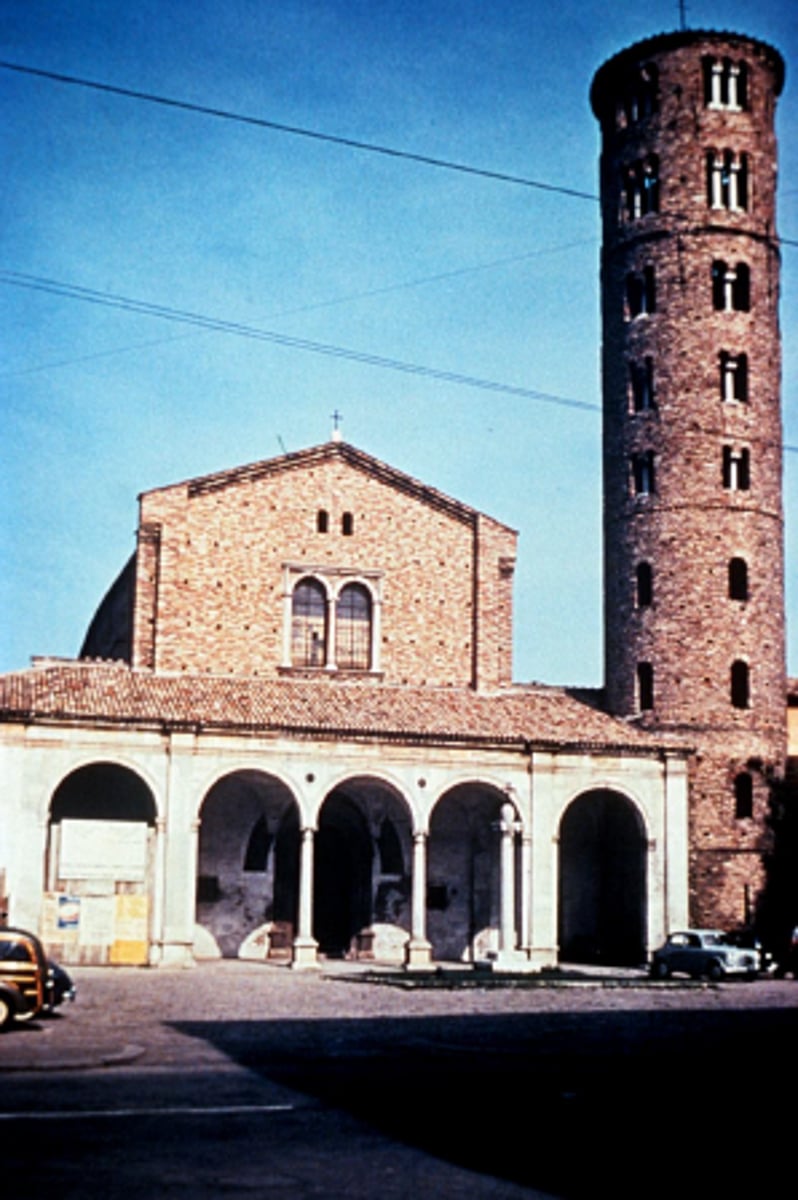
S. Apollinaire Nuovo, Ravenna, 504
-bell tower not part of a Roman basilica, German inspired (closer to god with the high bell tower)
-Byzantine Art (Architecture)

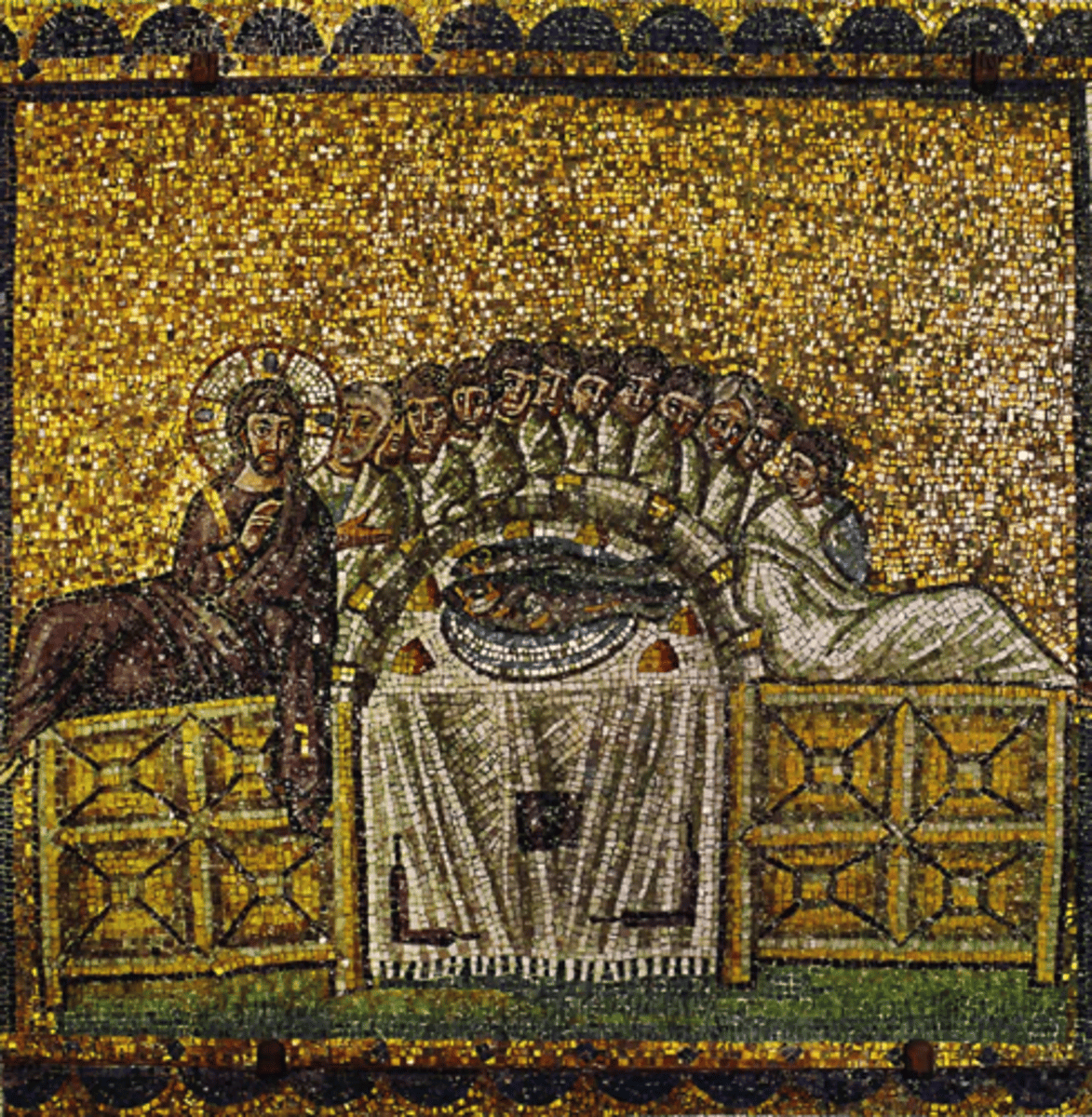
Miracle of the Loaves and Fishes
-nave mosaic of S. Apollinaire Nuovo
-Nimbus: luminous cloud or halo that surrounds a holy figure, signifies divinity
-Byzantine Art (Architecture)
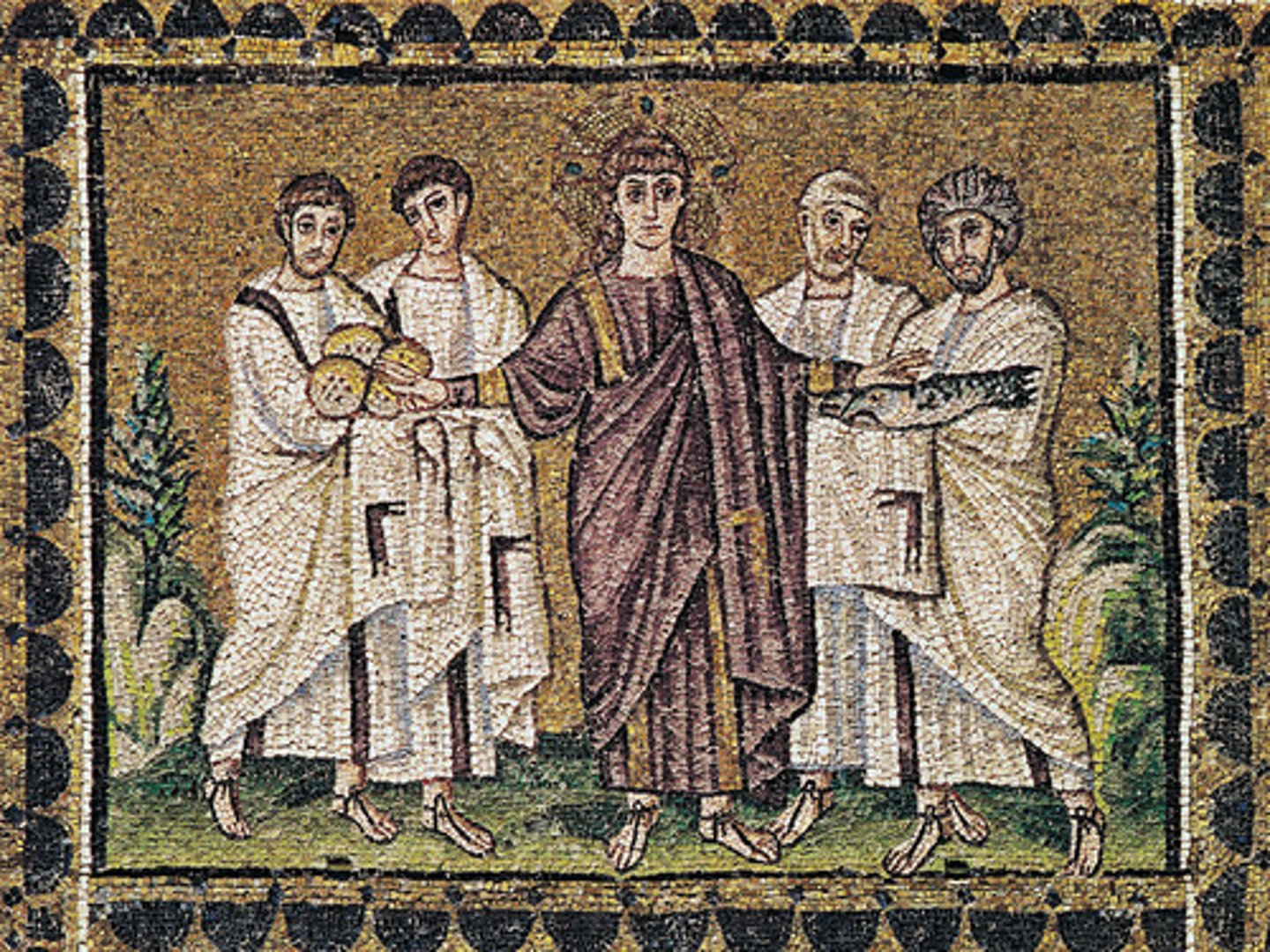

Last Supper
-mosaic of S. Apollinaire Nuovo
-Byzantine Art (Architecture)

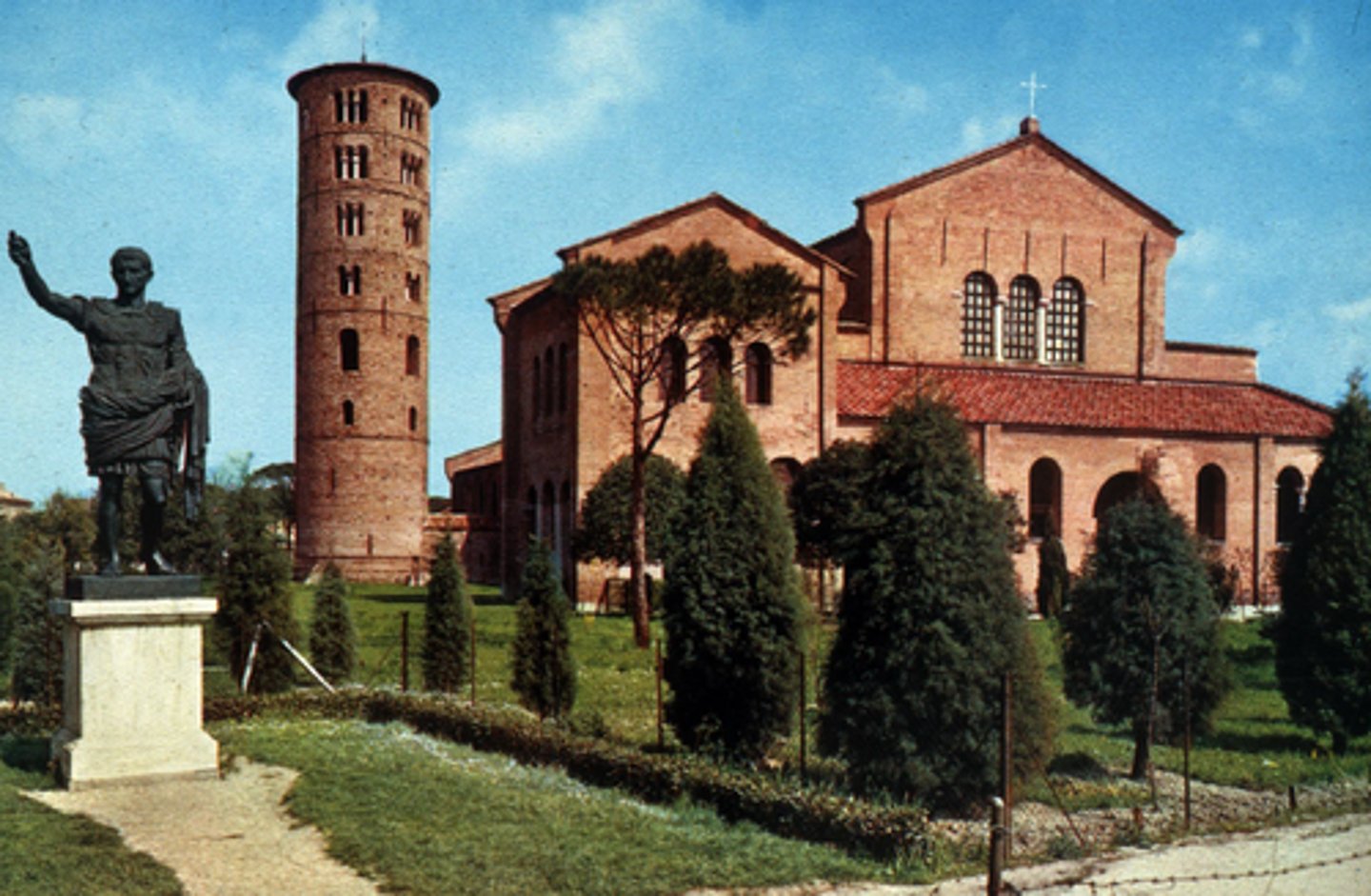
S Apollinaire in Classe, Ravenna, 533-49
-Augustus of Primaporta statue, to commemorate the founder
-exonarthex
-Byzantine Art (Architecture)

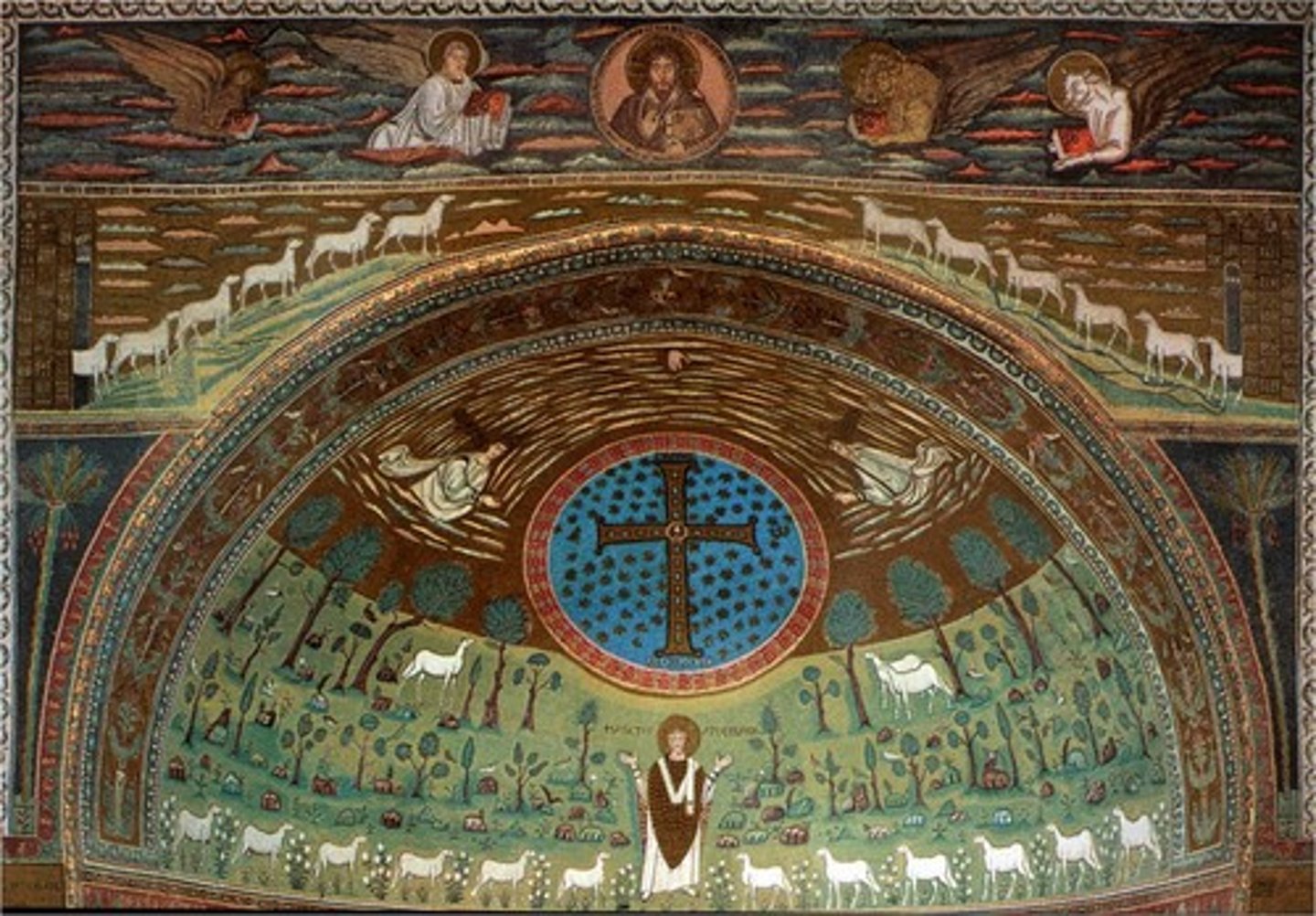
S. Apollinaire in Classe, Saint Apollinaire
-apse mosaic
-12 sheep represent apostles surrounding Christ
-Byzantine Art (Architecture)

S. Vitale, Ravenna, 526-47
-centralized church plan (included apse, narhtex, and 4 towers)
-Matrimoneum: the second level of the apse that was reserved for married women (gallery level)
-gallery was for "V.I.P's"
-Byzantine Art (Architecture)
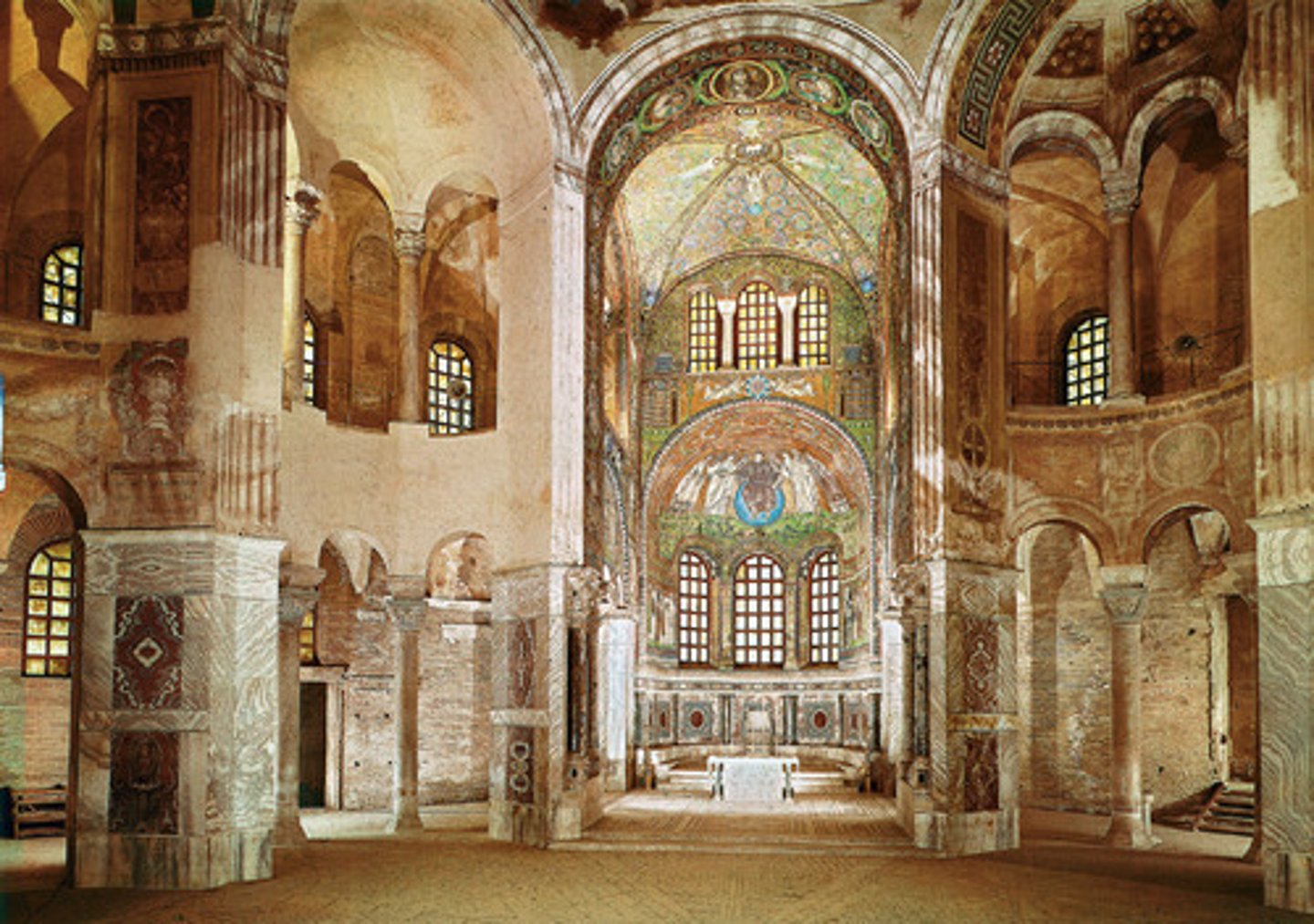

Justinian and Theodora
-choir mosaic of S. Vitale
-Byzantine Art (Architecture)
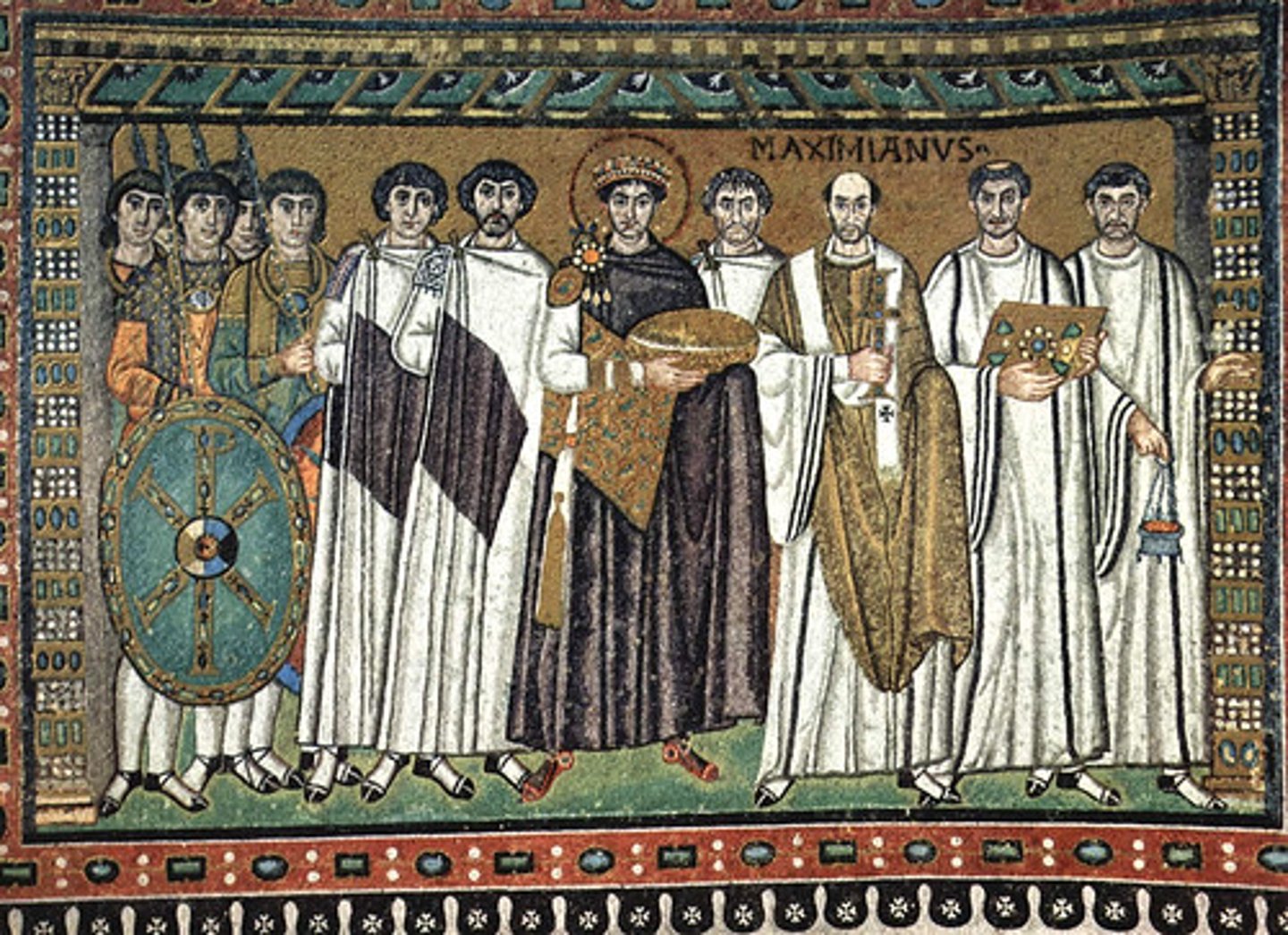

Second Coming of Christ
-apse mosaic of S. Vitale
-Byzantine Art (Architecture)

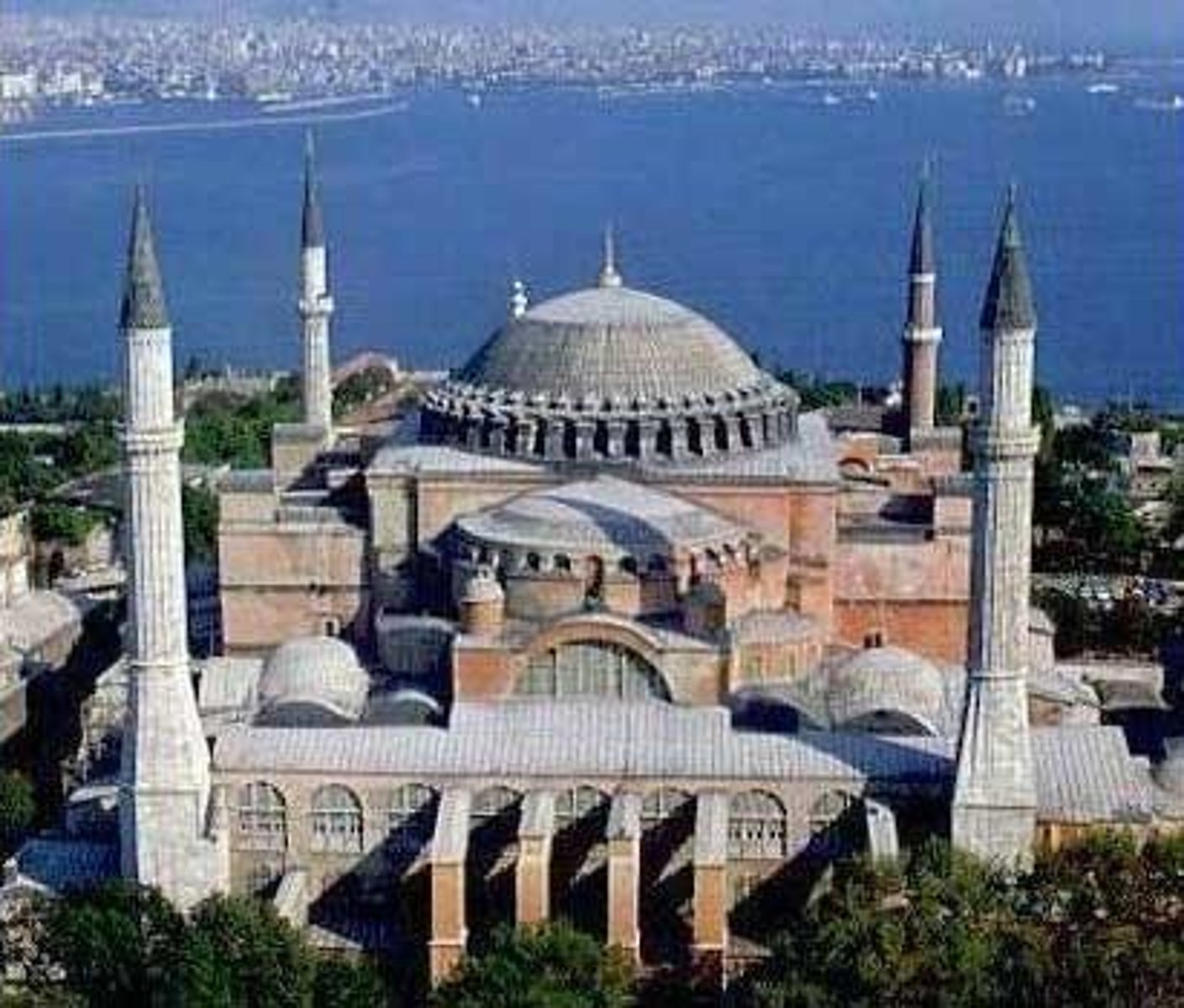
Hagia Sophia, Constatinople (Istanbul), 532-37
-Architects: Anthemius of Tralles and Isidorus of Miletus
-Period of Justinian
-Pendentives: a curved triangle of vaulting formed by the intersection of a dome with its supporting arches (fitting a basketball into a square box)
-Gallery level: covered passageway open on one side, second floor for elites to sit in and look down

Iconoclasm
the destruction of religious icons and other images or monuments for religious or political motives (8th-9th century), results in the 2nd flowering of Byzantine Art years later
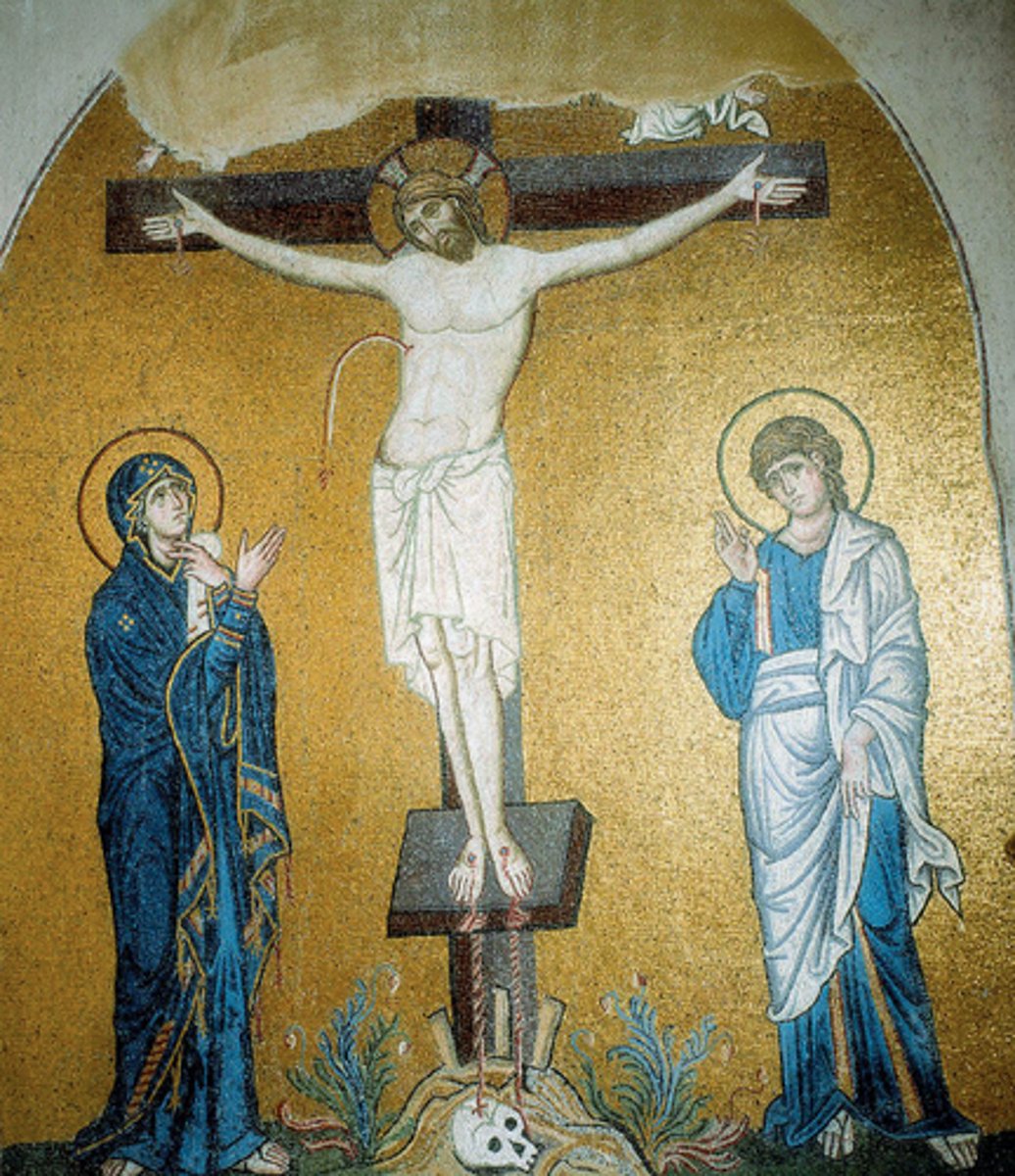
Crucifixion, Daphni Monastery (Greece), 1100
-somber atmosphere
-detachment between the individuals
-Christ contraposso stance
-Idealized qualities of the face
-Byzantine Art (Second Flowering)

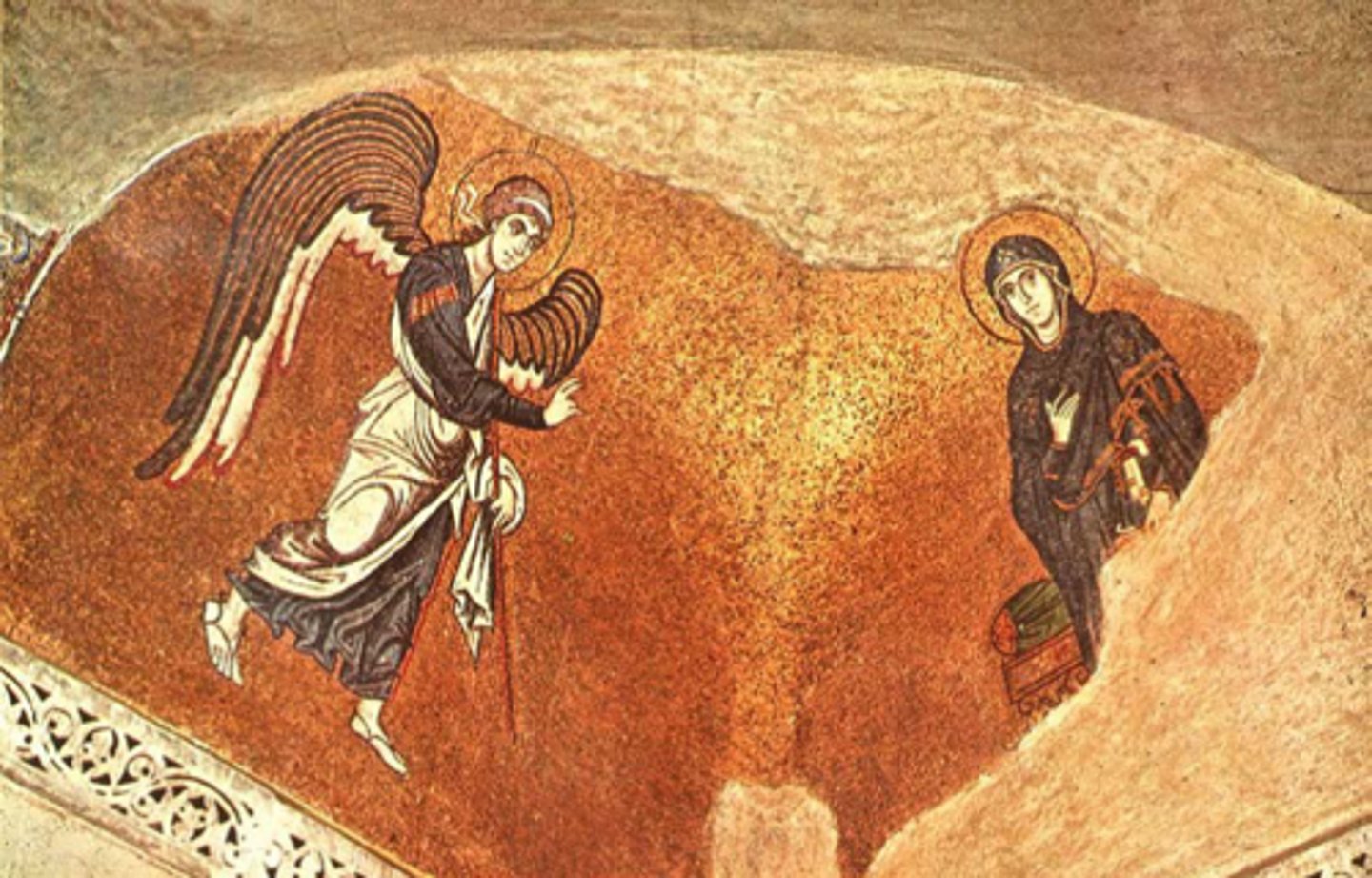
Annunciation
-squinch mosaic in Daphni Monastery
-Byzantine Art (Second Flowering)

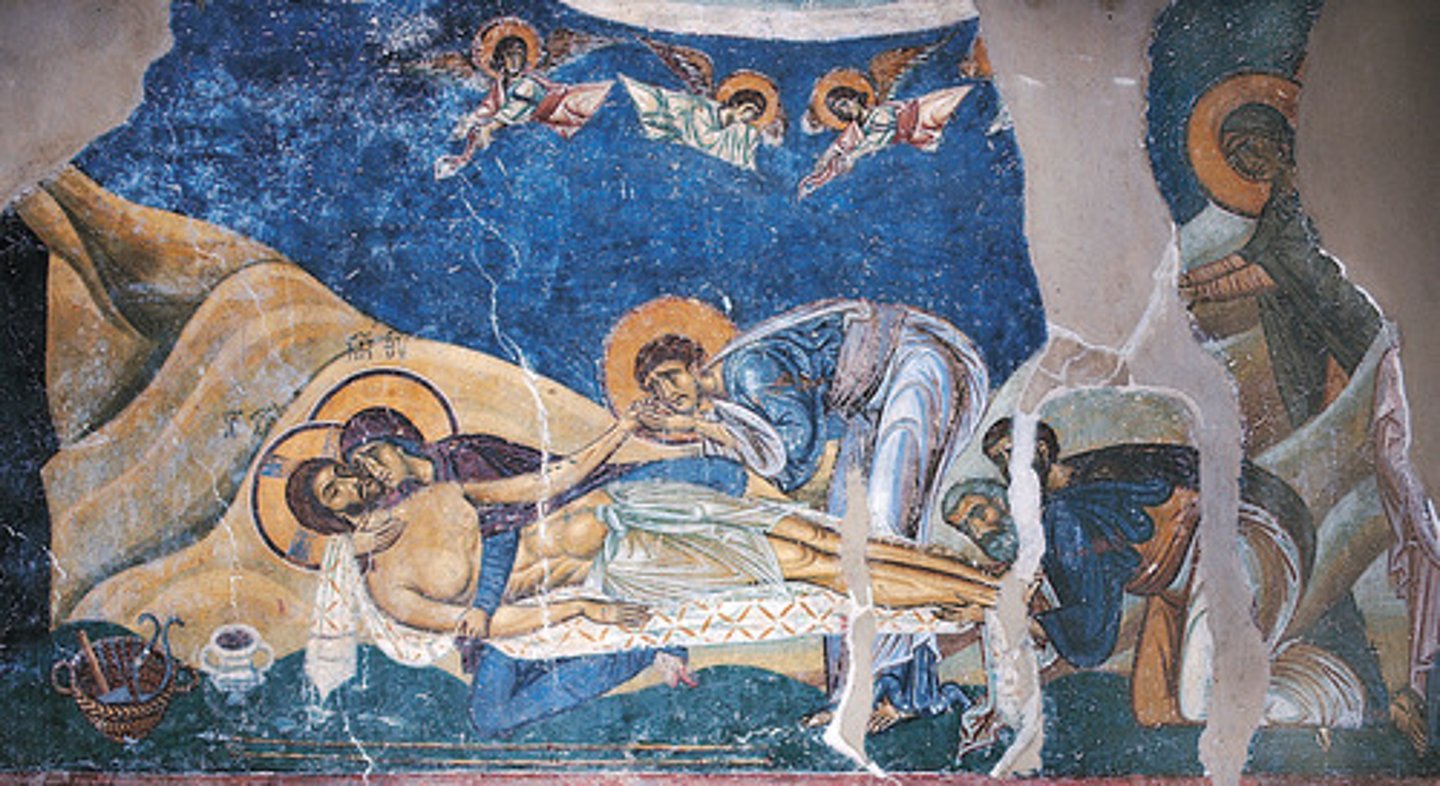
Lamentation Over the Dead Christ, Nerezi (Macedonia), 1164
-emotionally charged scene
-Byzantine Art (Second Flowering)

Vladimir Madonna, early 12th cent.
-Devotional panel (icon)
-Made out of wood (oak)
-Small and can be transported
-Meant to be simple so they can be easily understood and read
-Madonna looks at the audience to draw attention into the picture (pathos)
-Use of countor lines
-Byzantine Art (Second Flowering)

Icon
a portrait or image, especially in Byzantine Art, a panel with a painting of sacred personages that are objects of veneration
Countor lines
an individual line that delineates the edge or outline of the one of the main shapes or forms in the image
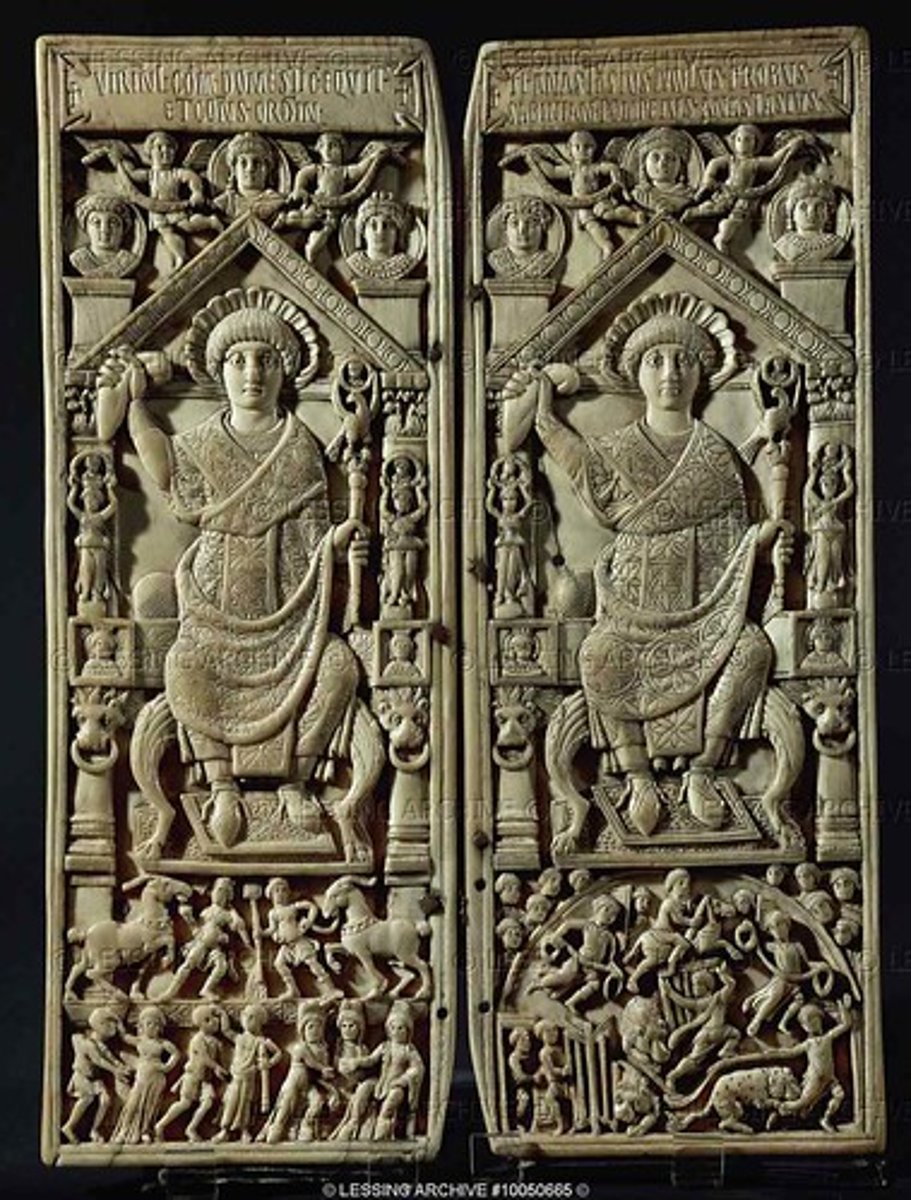
St. Michael Ivory Diptych, early 6th cent.
-St. Michael the archangel
-bookcover
-Byzantine Art (Minor Art)
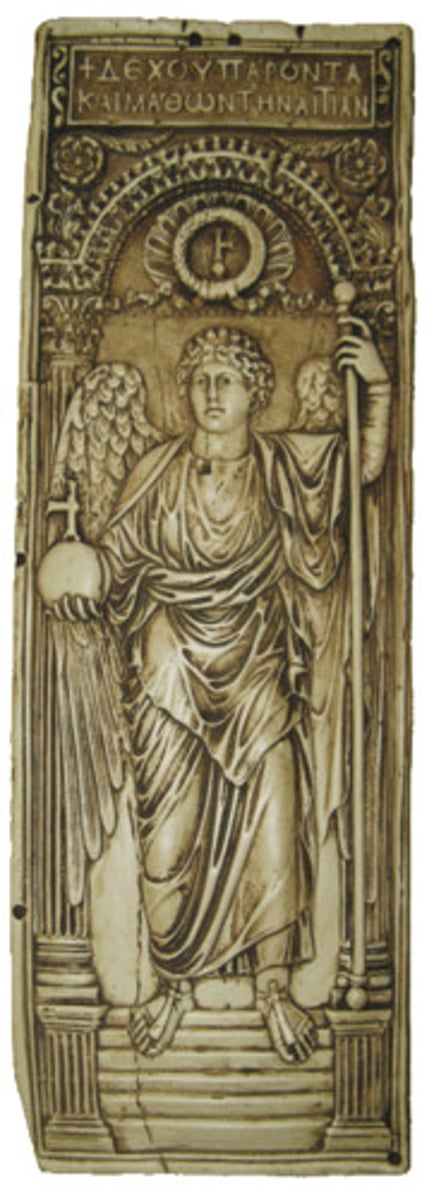

Anastasius Ivory Diptych, early 6th cent.
-Putti: a representation of a naked child, especially a cherub or a cupid (babies)
-Mappa: signal the start of a chariot race
-Hippodrome: a course for chariot or horse races
-Abstraction, moving away from the realism presented in lunettes
-bookcover
-Byzantine Art (Minor Art)

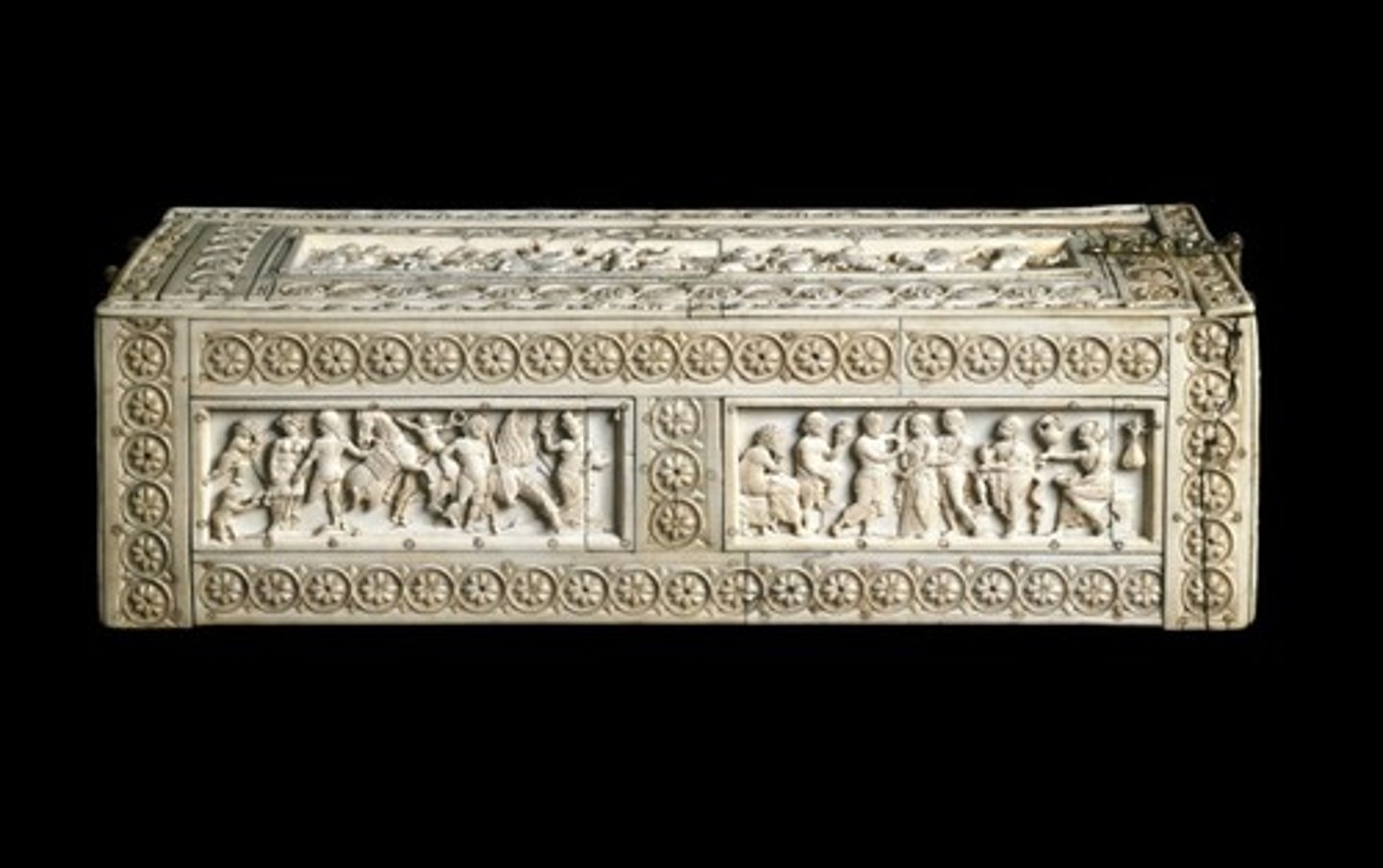
Veroli Casket, from Constantinople, early 11th cent.
-Byzantine Art (Minor Art)

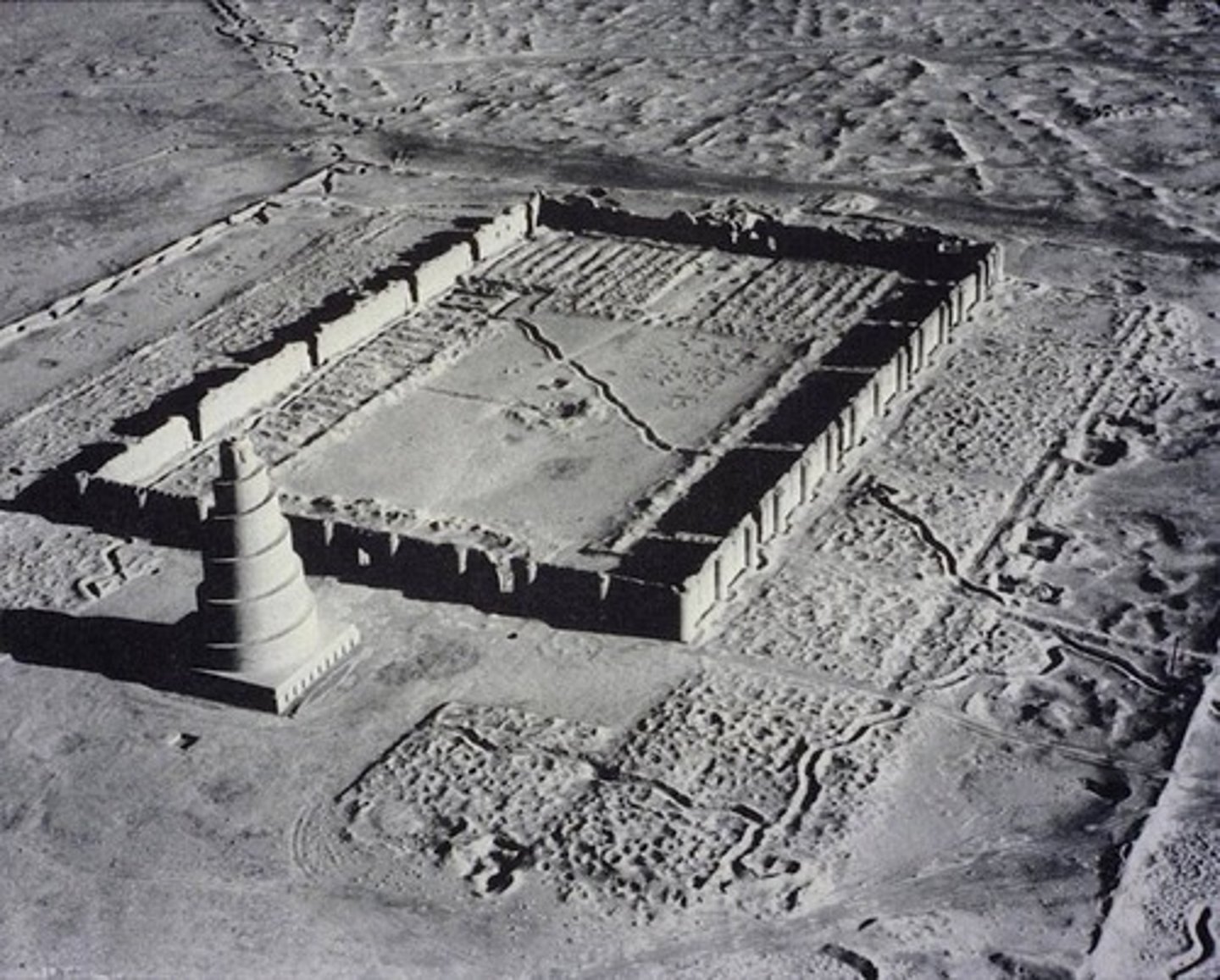
Great Mosque, Samarra (Iraq), 848-52
-no longer standing
-Minaret: a tall slender tower, with a balcony from which a muezzin calls Muslims to prayer
-Central court: where the prayers were carried out
-Mihrab: niche in the wall for the mosque that is facing in the direction of Mecca
-Islamic Art

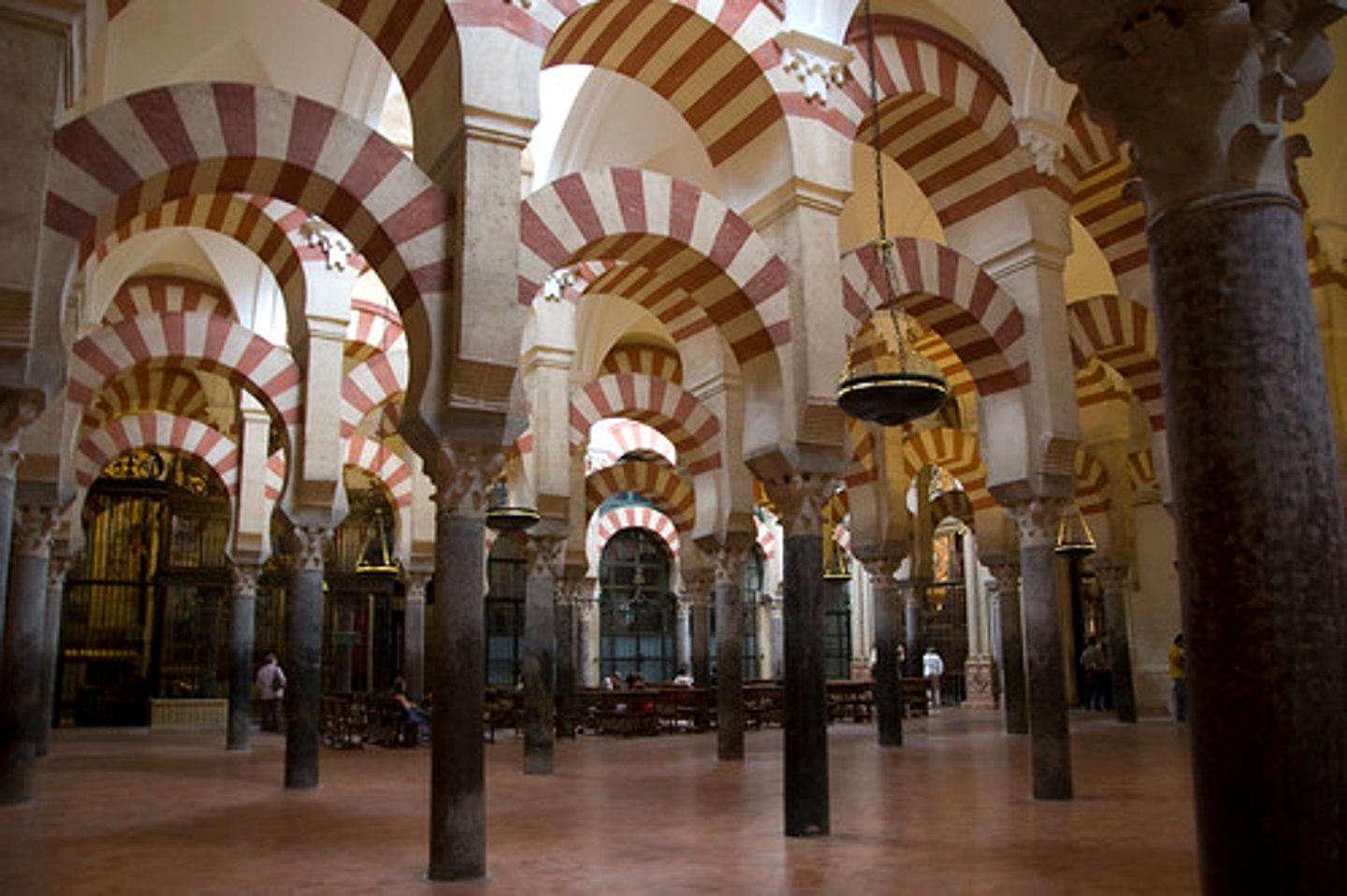
Mosque of Cordoba, Spain, 8-10th cent.
-double tier of arcades
-corinthian columns
-brick floor covered with tapestries
-dome is abstract and decorative (not architecturally sound)
-colorful arches add billowing effect
-geometric patterns surround niche
-Islamic Art

Alambra, Granada (Spain), 1354-91
-secular palace
-Islamic Art

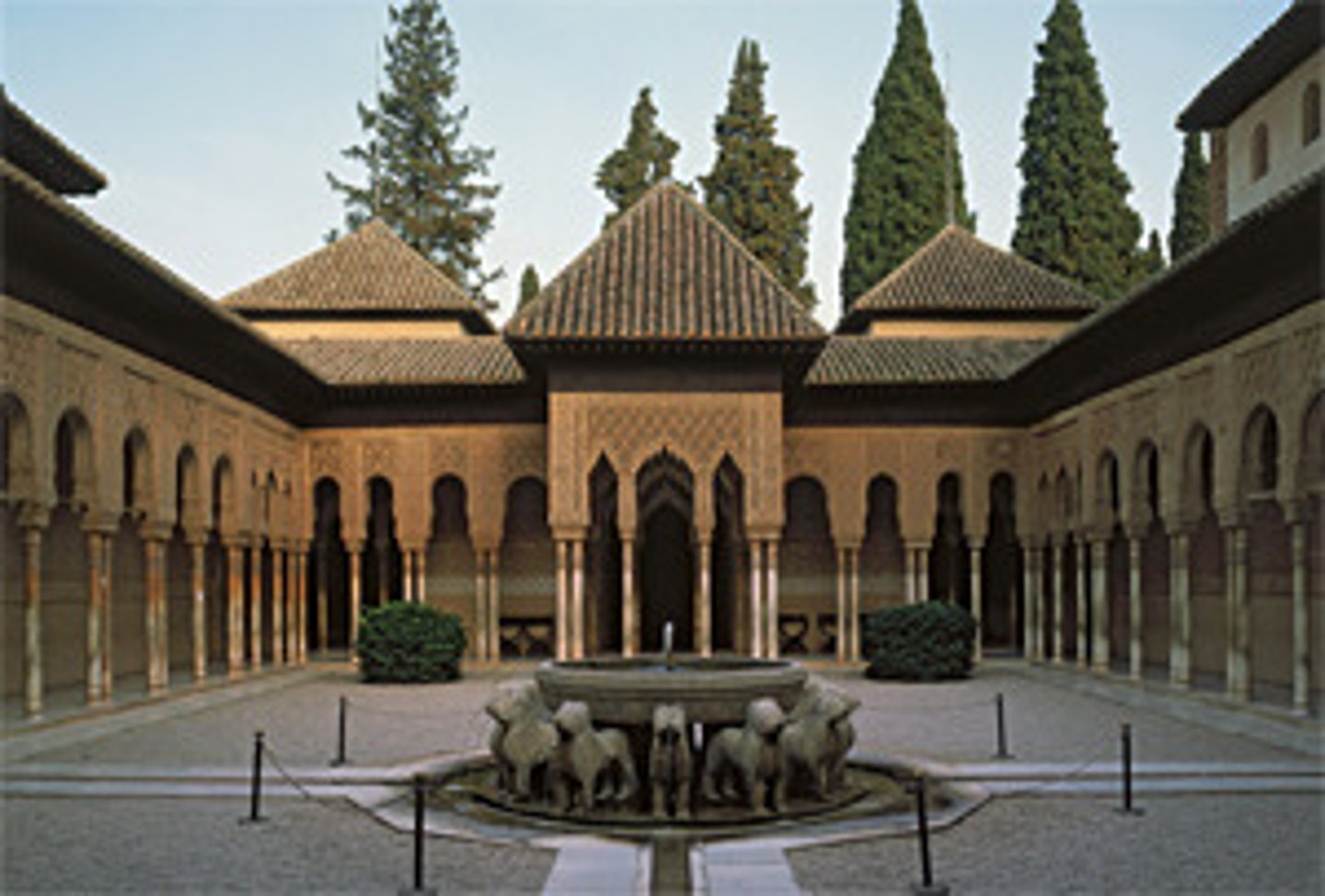
Court of the Lions
-similar to basilica
-geometric design done in stucco (plaster) to resemble tapestries
-Islamic Art

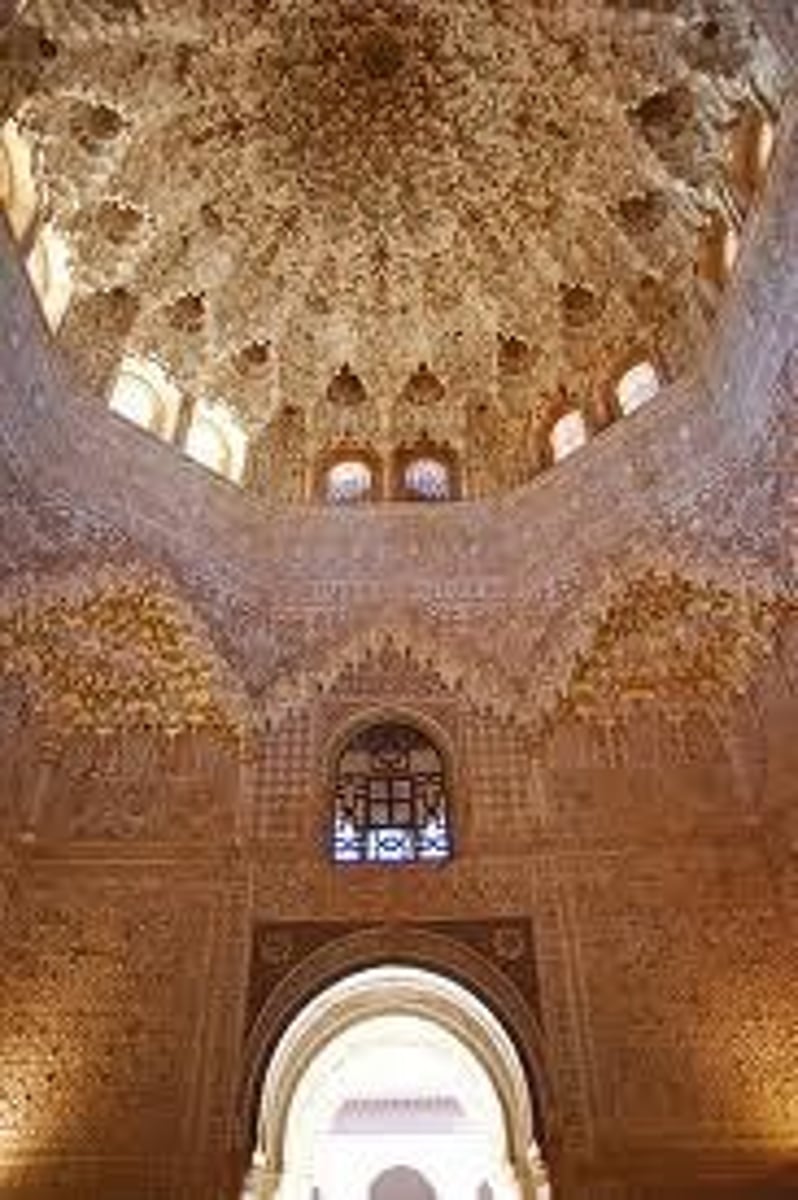
Hall of the Two Sister (Abencerrajes)
-Abencerrajes knights were beheaded here
-Islamic Art

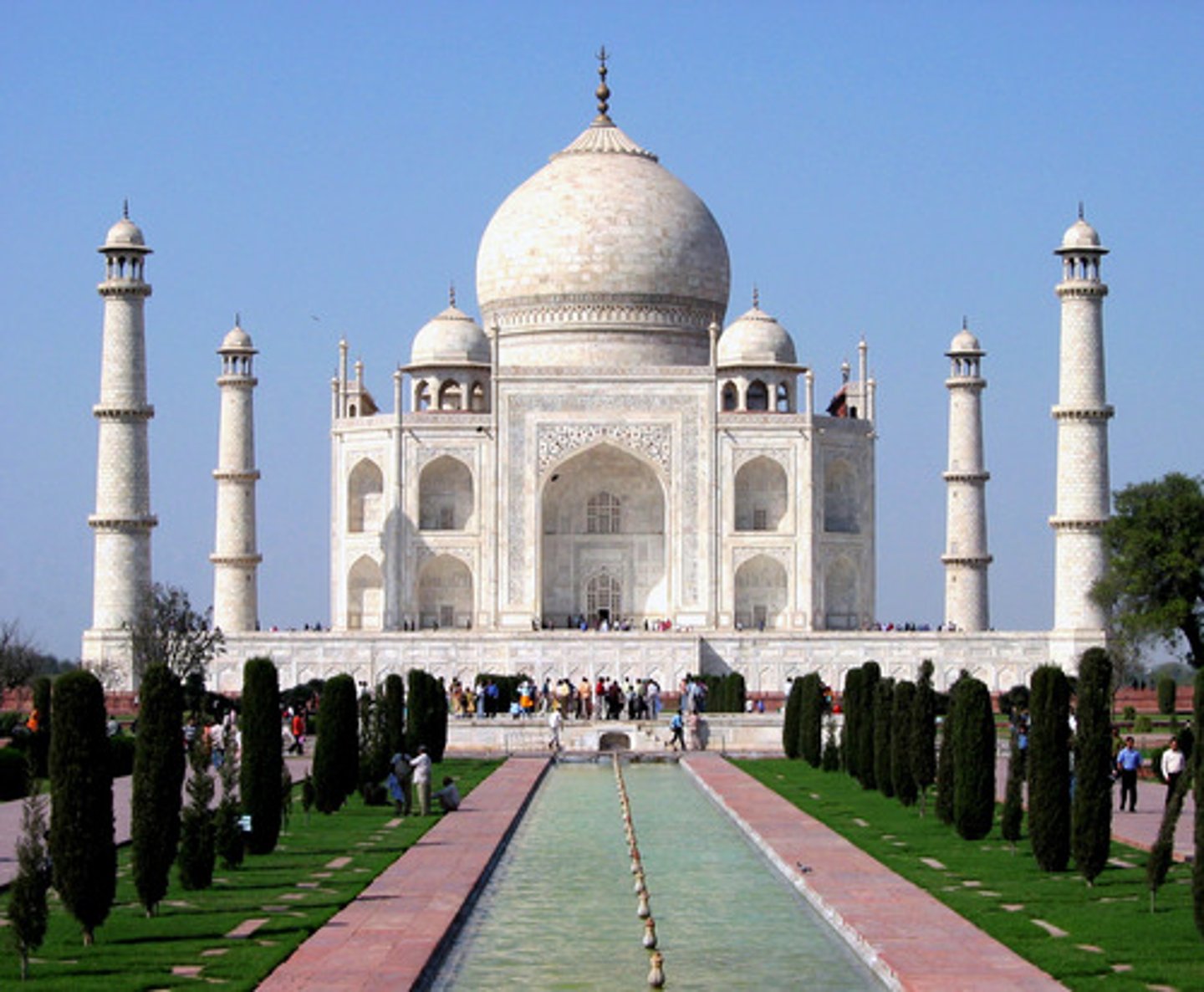
Taj Mahal, Agra (India), 1632-54
-Mausoleum for the wife of Shah Jahan
-Facade made of limestone
-Pointed arch: begins with a bulb but then comes inward has a curved and a counter curve, more curvilinear, less structural and filled with light and air
-Domes: curves followed by a counter-curve (look like bulbs)
-Minarets
-Islamic Art

Carpet from Mosque of Shaykh Safi al-Din, from Iran, 1540
-woven carpet made of silk
-Islamic Art tradition
-aray of colors and designs (lamp of the world)

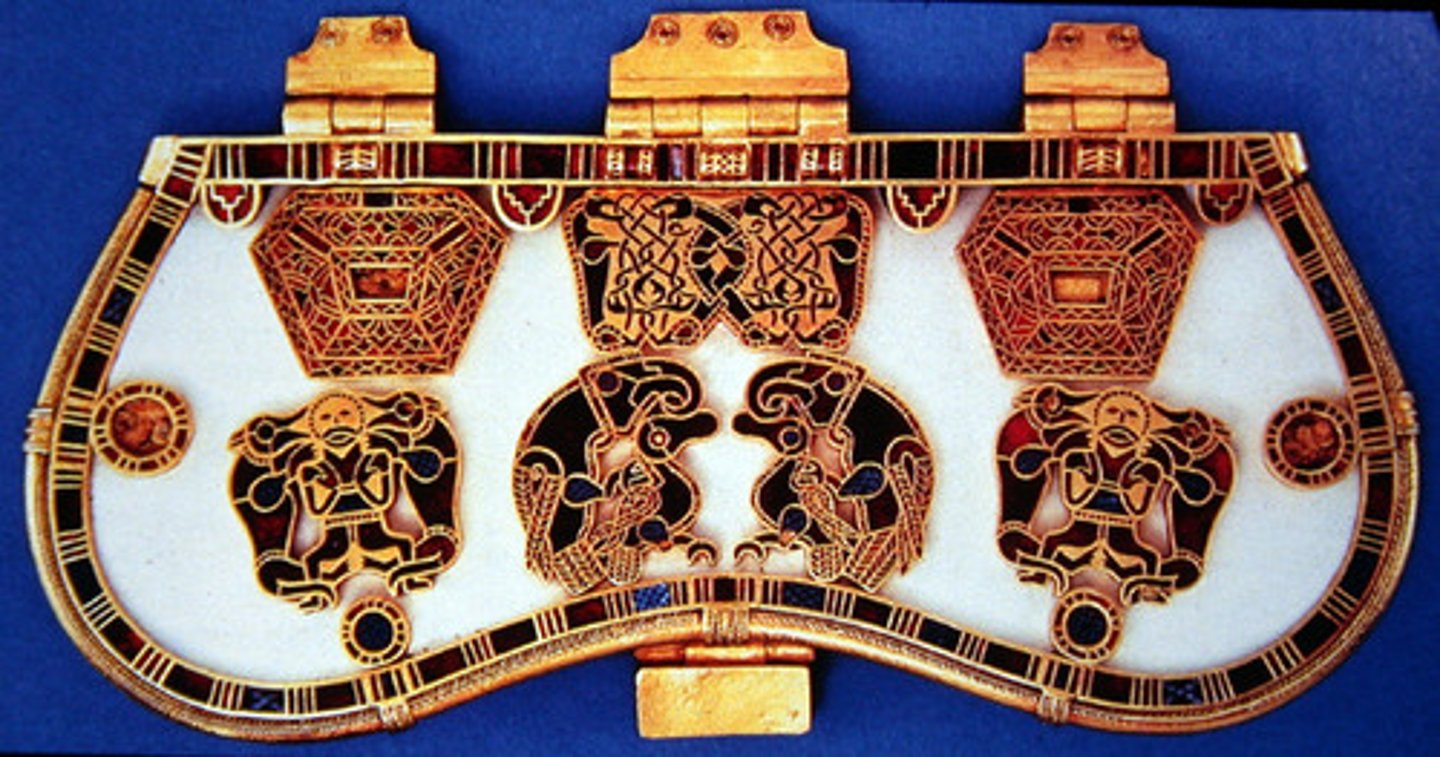
Sutton Hoo Ship Burial, Suffolk (England), 625
-made of cloisonne
-abstract design
-Migration Art (Anglo-Saxon)

Cloison
a cell made of metal wire or a narrow metal strip soldered to a metal base to hold enamel or other decorative materials
Cloisonne
a process of enameling employing cloisons
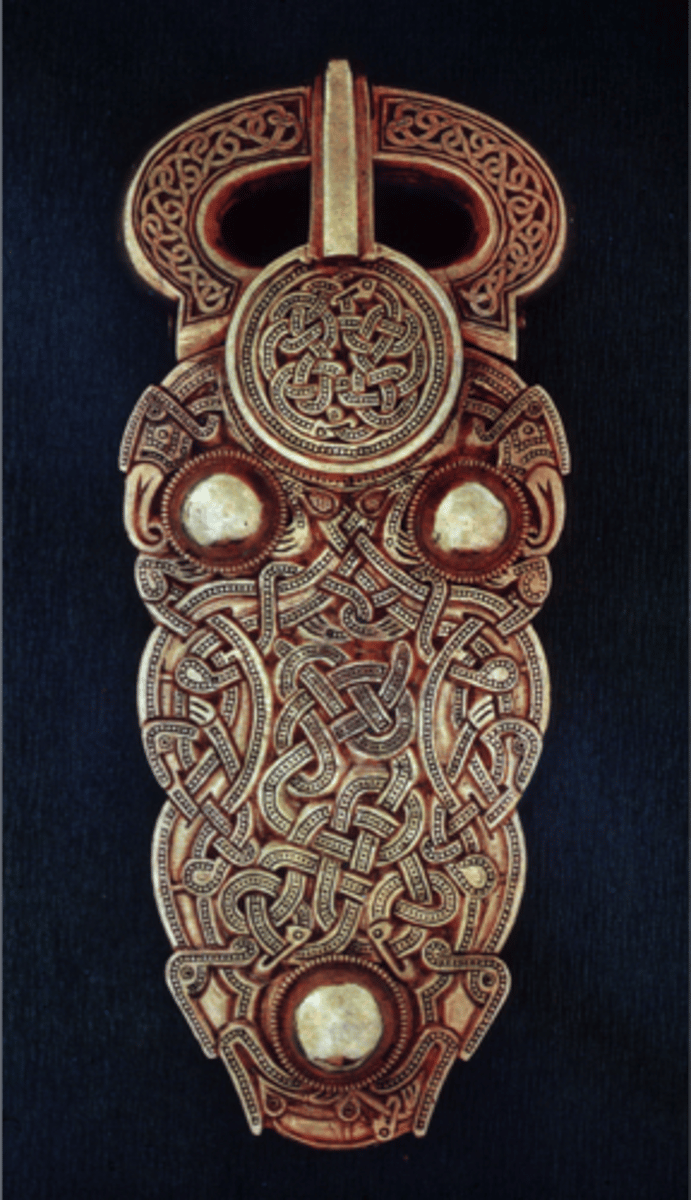
Visigothic Brooch, 6th cent.
-intricate woven pattern
-pattern is signature of German and Keltic Art
-Migration Art (Anglo-Saxon)

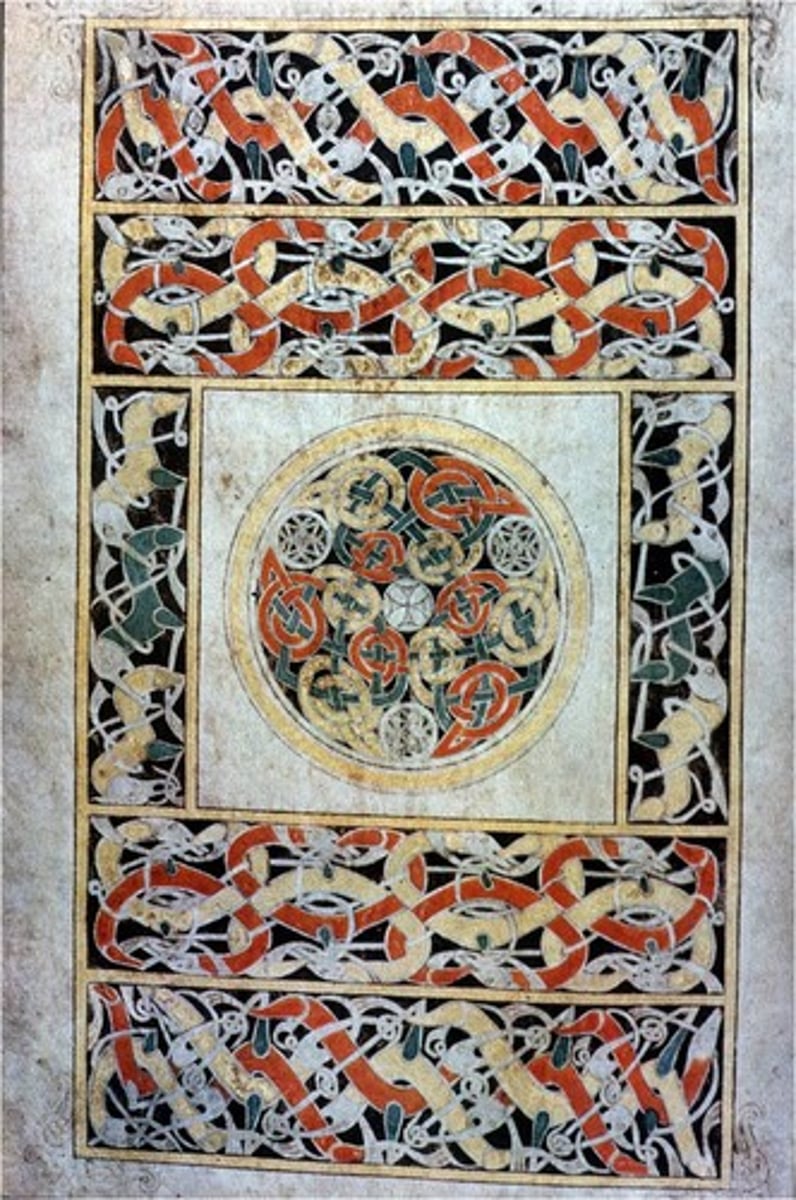
Book of Durrow, Carpet Page, late 7th cent.
-same interlacing abstract design
-manuscript page
-Migration Art (Ireland)

Interlace
cross or be crossed intricately together, interweave
Book of Durrow, Symbols of SS. Matthew and Mark
-Matthew: human figure, Mark: lion (Evangelistic symbols)
-cloisonne in the garments
-abstract representation
-interlace
-Migration Art (Ireland)
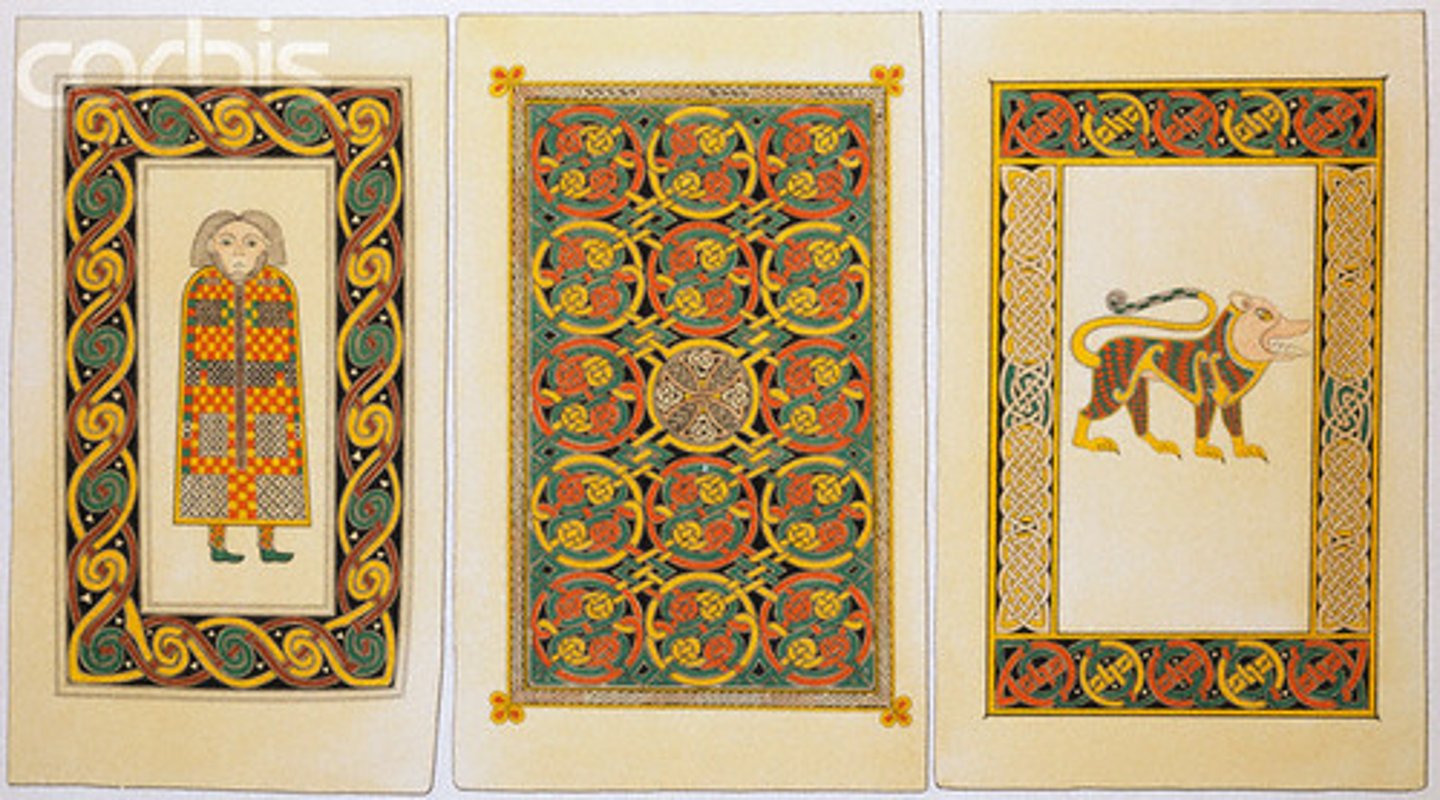

Book of Kells, St. John, late 7th cent.
-4 Evangelist symbols
-St. John: eagle
-abstract form
-individual cloissane compartments
-Migration Art (Ireland)

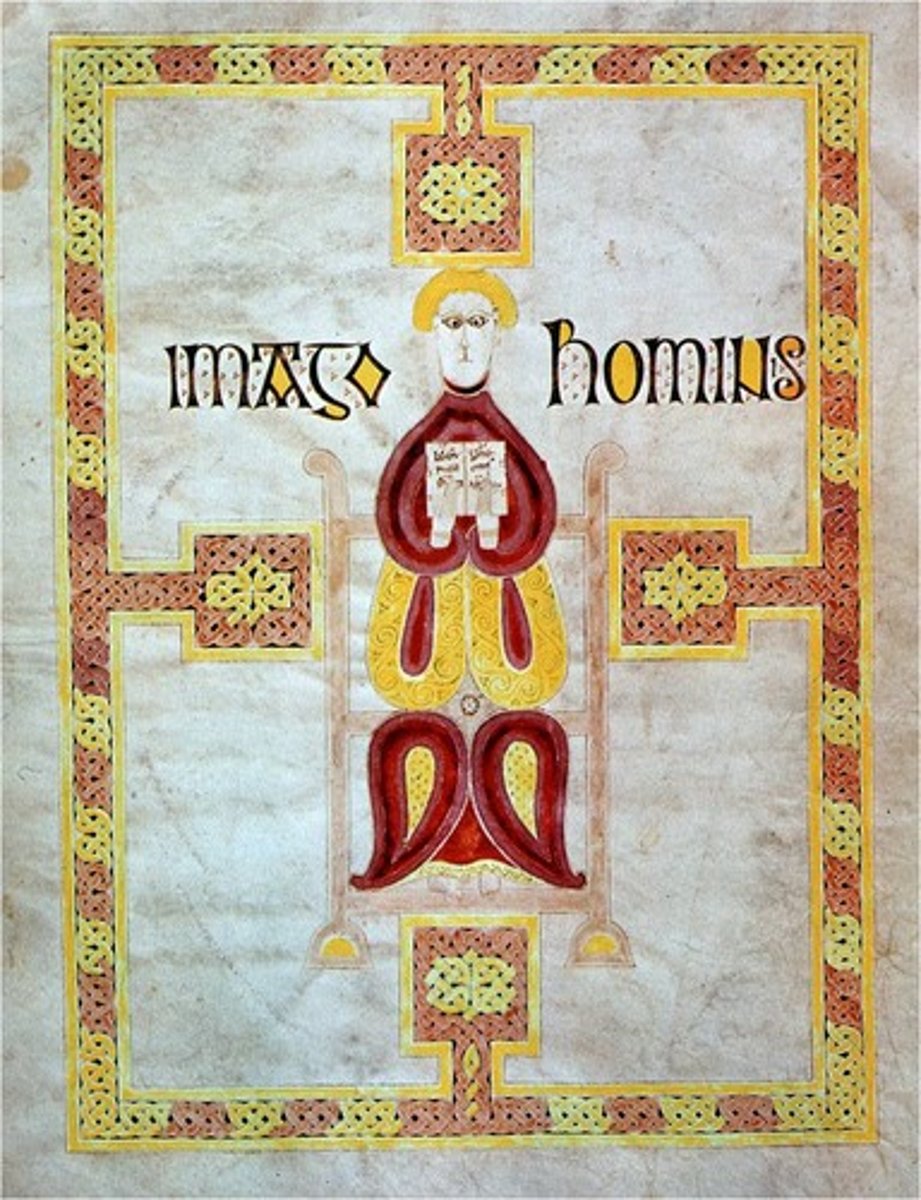
Echternach Gospels, St. Matthew, late 7th cent.
-reads "Image of Man"
-shown as elongated cloisonne compartments
-ambigous chair
-Migration Art (Ireland)

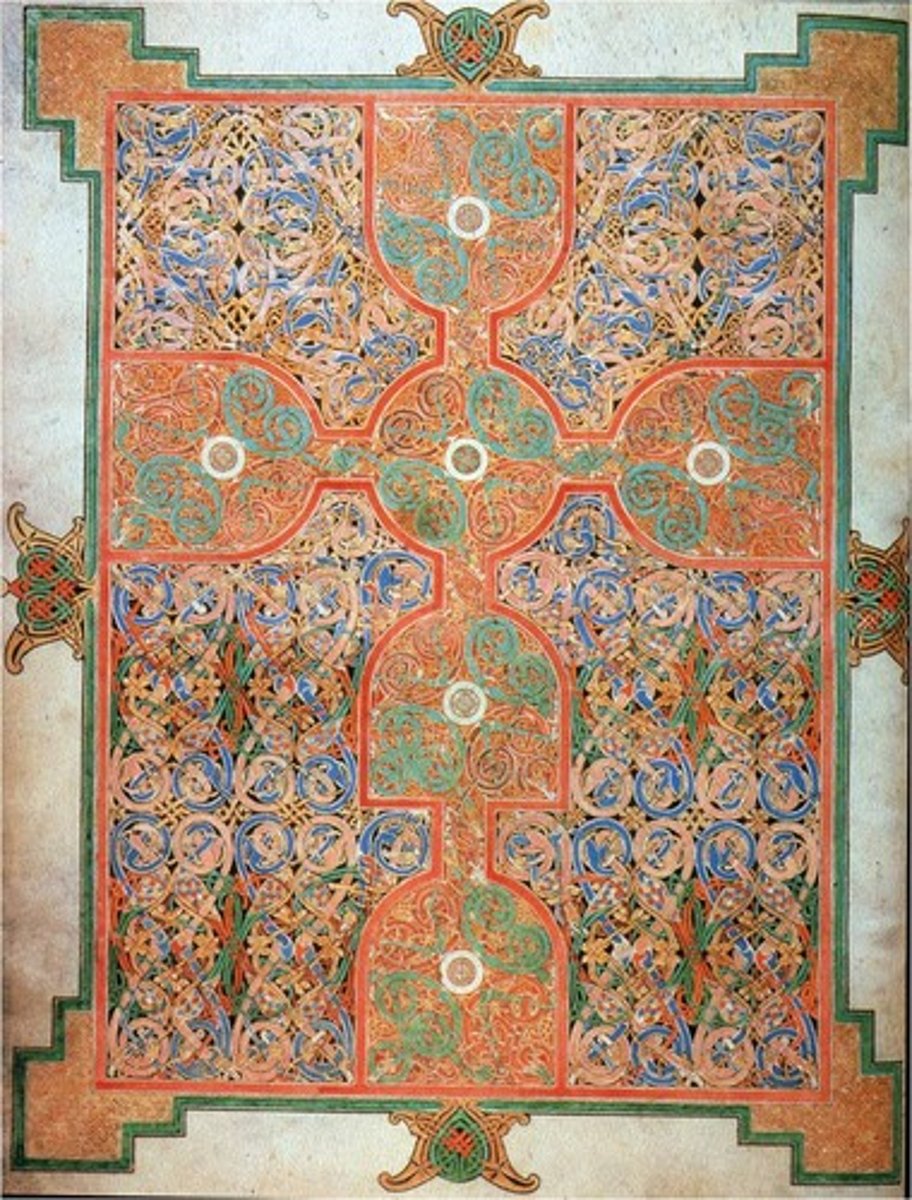
Lindesfarne Gospels, Carpet Page, early 8th cent.
-manuscript illumination
-Migration Art (Ireland)

Lindesfarne Gospels, St. Matthew, early 8th cent.
-naturalistic representation of figure
-composing gospel with an angel
-Migration Art (Ireland)

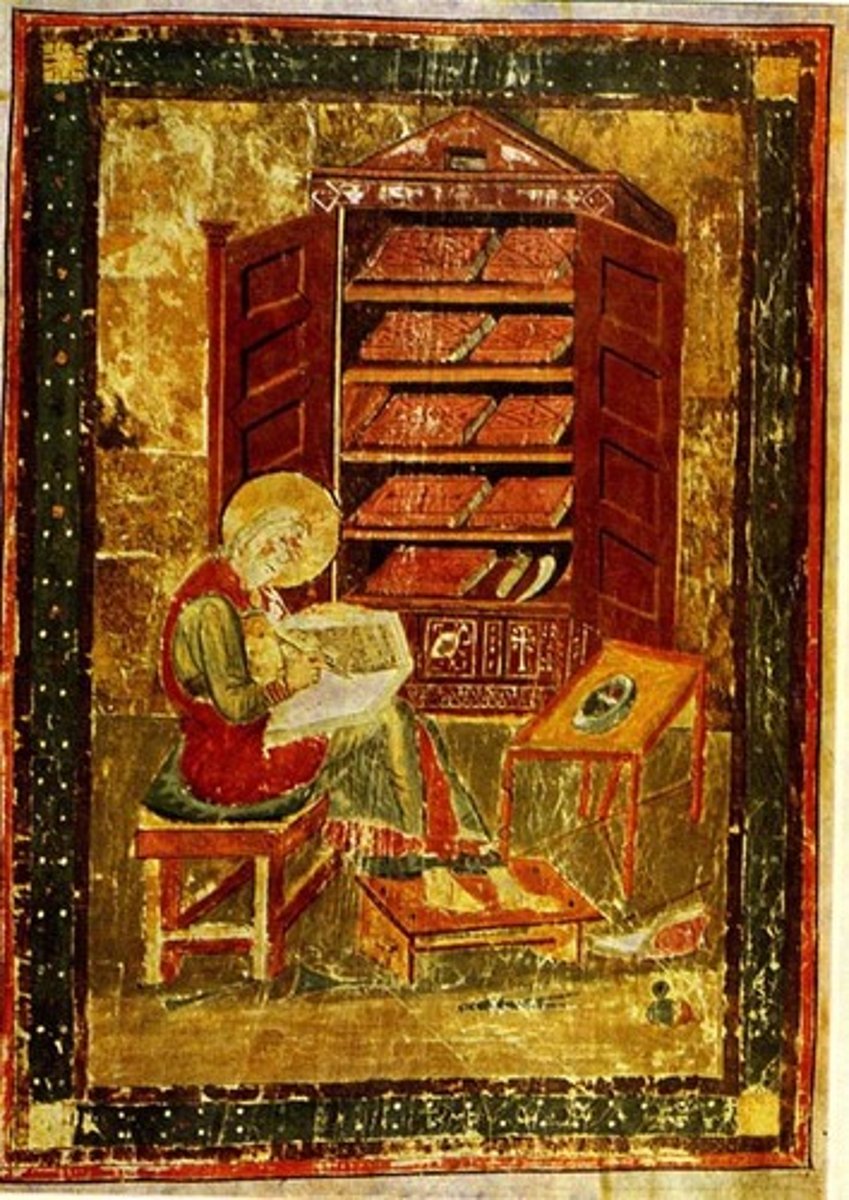
Codex Amiatinus, Ezra, from Jarrow Monastery (England), early 8th cent.
-similar style as Lindesfarne Gospels St. Matthew
-illusionism in bookshelf (Romanism)
-Migration Art (Ireland)

Monastery
building(s) occupied by monks, become a place of learning and safe haven
Illusionism
principle or technique by which artistic representations are made to resemble real objects or to give an appearance of space by the use of perspective
Oseberg Ship Burial, 825
-Migration Art (Vikings)
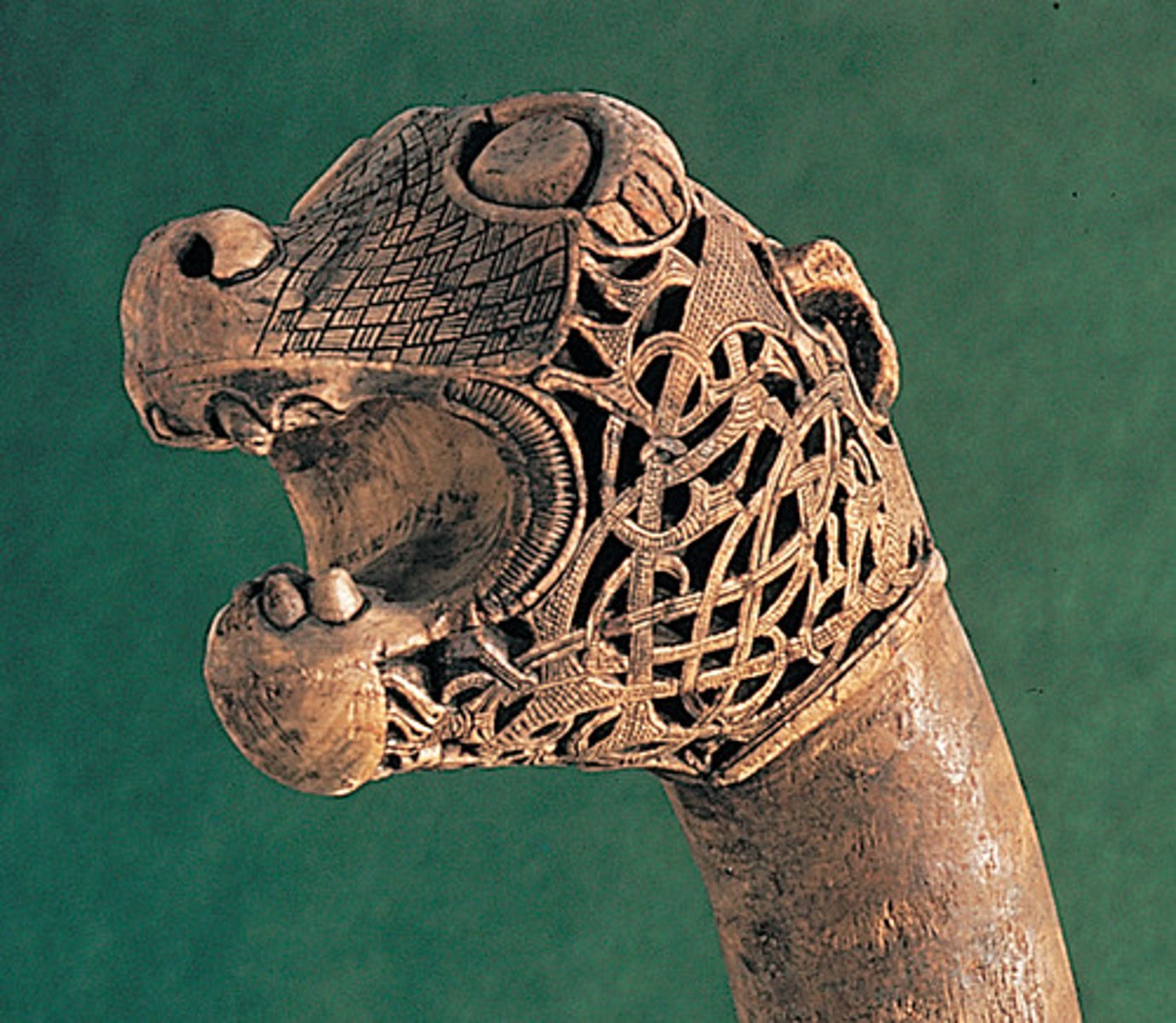

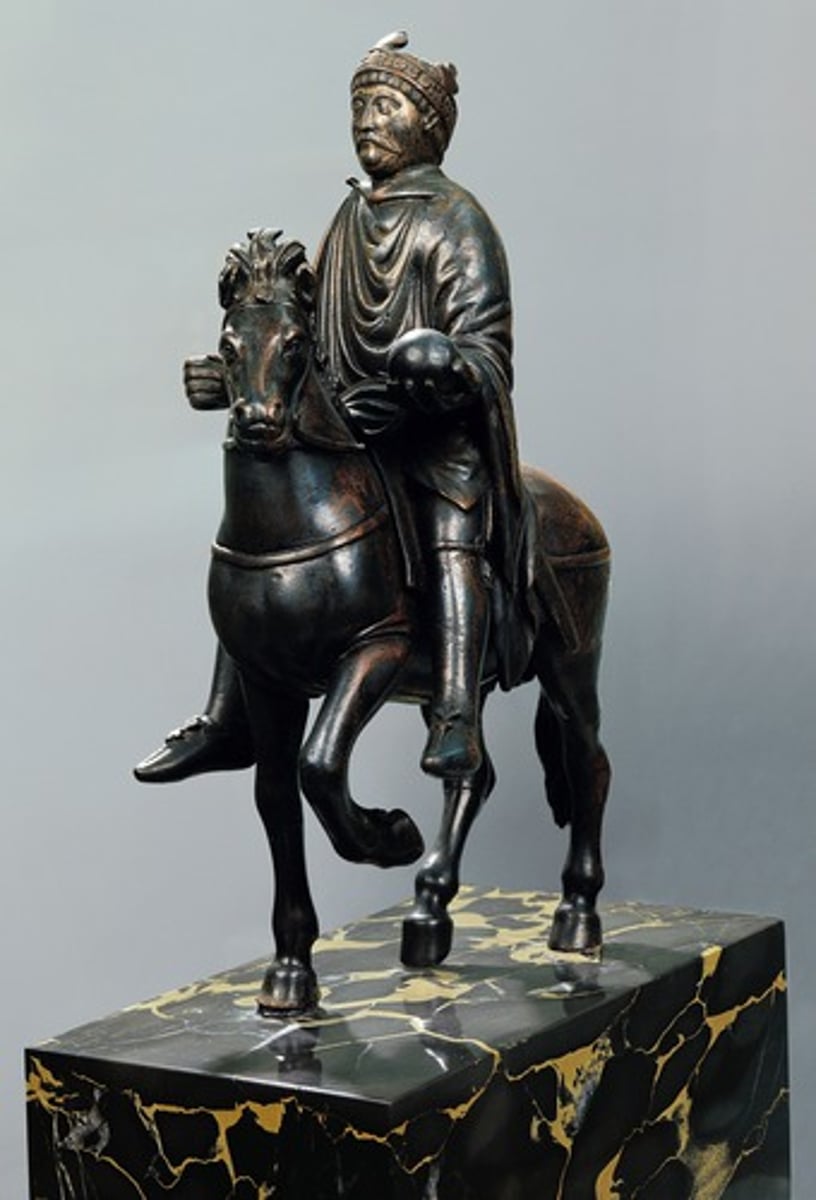
Equestrian Portrait of Charlemagne, from Metz (France), 9th cent.
-proclaimed emperor of the Holy Roman Emperor
-Recalls the equestrians statues of the Roman Empire
-Carolingian Renasissance

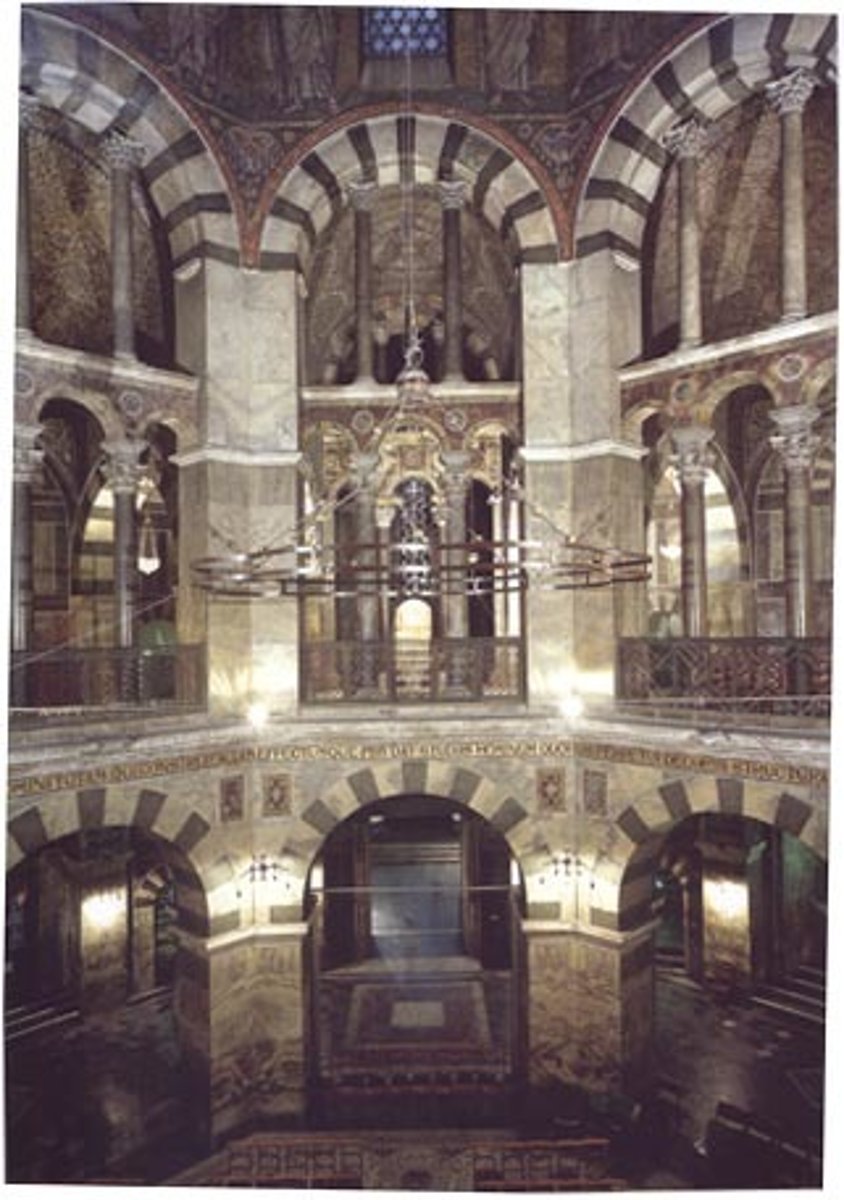
Palatine Chapel of Charlemagne, Odo of Metz, Aachen (Germany), 792-805
-basilica plan
-similar to layout of St. Vitale (classical elements)
-Carolingian Renaissance

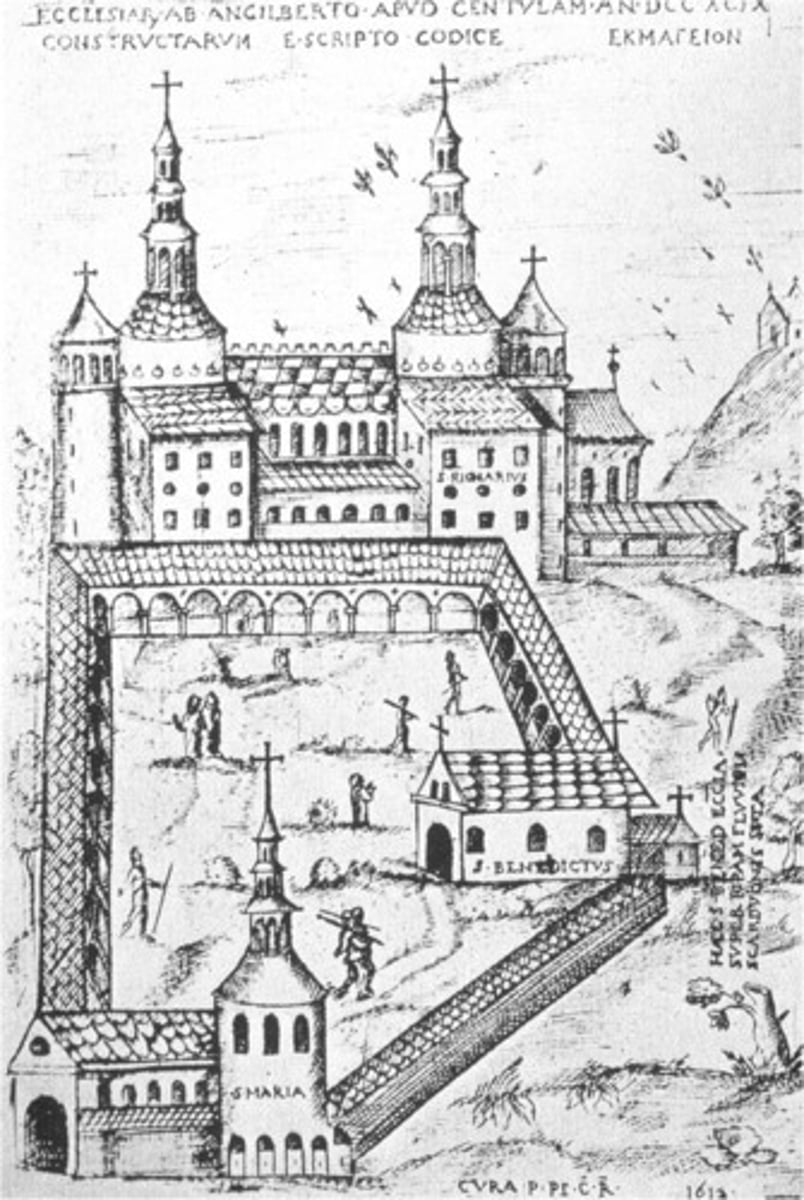
St. Riquier, Centula (France), late 8th cent.
-no longer standing
-Westwork: the monumental, west-facing entrance section of a church, the exterior consists of multiple stories between two towers
-Carolingian Renaissance

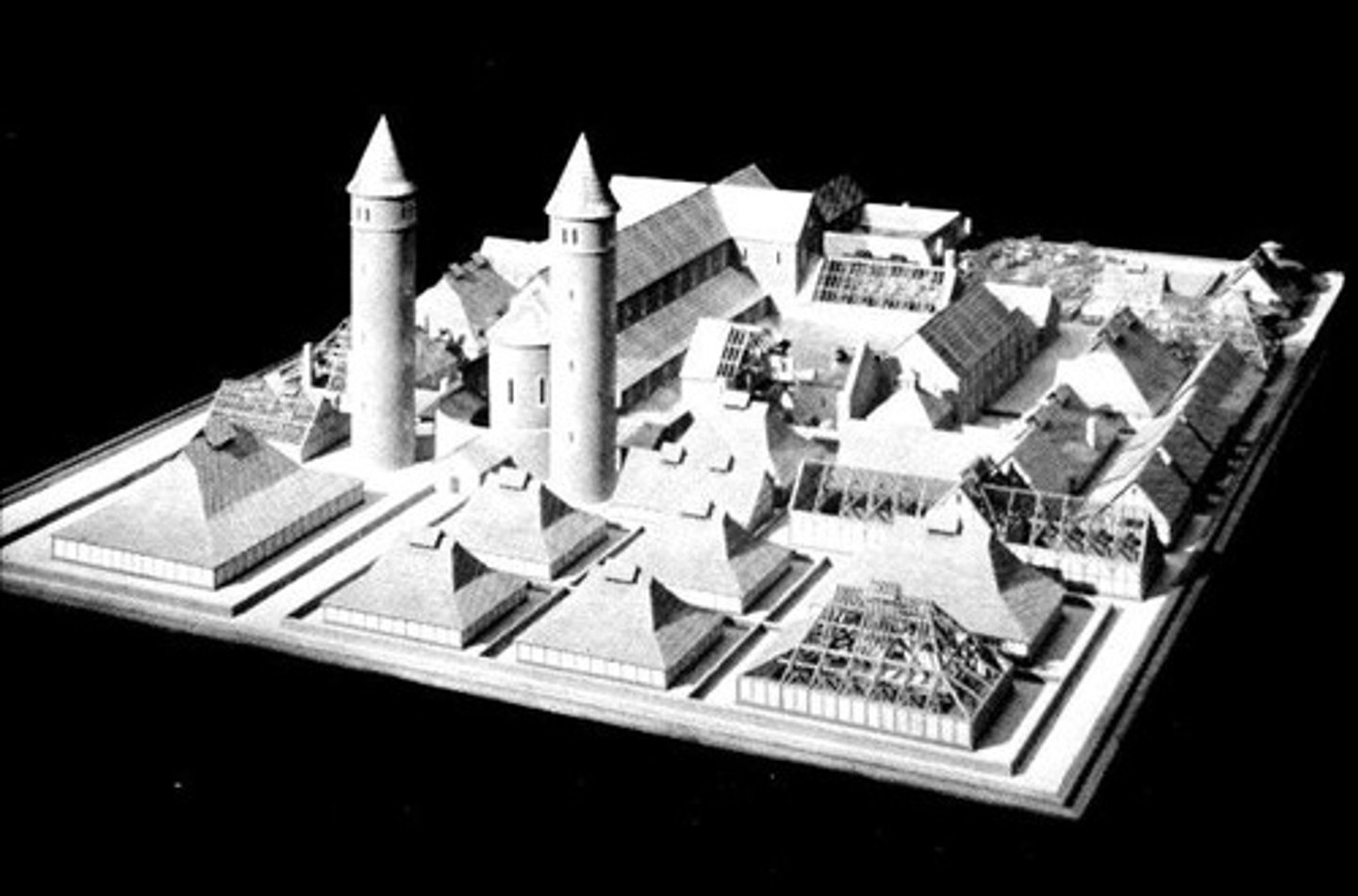
St. Gall Monastery, Switzerland, 819
-no longer standing
-Modular construction, done by using basic units of which the dimensions of the major parts of a work are multiples
-Cloister: colonnaded courtyard (much like the atrium)

Lorsh Gateway, Torhall (Germany), 9th cent.
-similar style as Arch of Constantine
-classical elements
-Carolingian Renaissance

Coronation Gospels of Charlemagne, early 9th cent.
-similar to migration art from Ireland
-nimbus
-Carolingian Renaissance

Gospels of Archbishop Ebbo, near Reims (France), 816-35
-similiar to Gospels of Charlemagne (and other manuscripts from Ireland)
-abstract representation
-Carolingian Renaissance

Utrecht Psalter, from Reims, 830
-pen illustrations
-Carolingian Renaissance
Codex Aureus of St. Emmeram (cover), 870
-Medorla: enclosure containing Holy figures
-Carolingian Renaissance

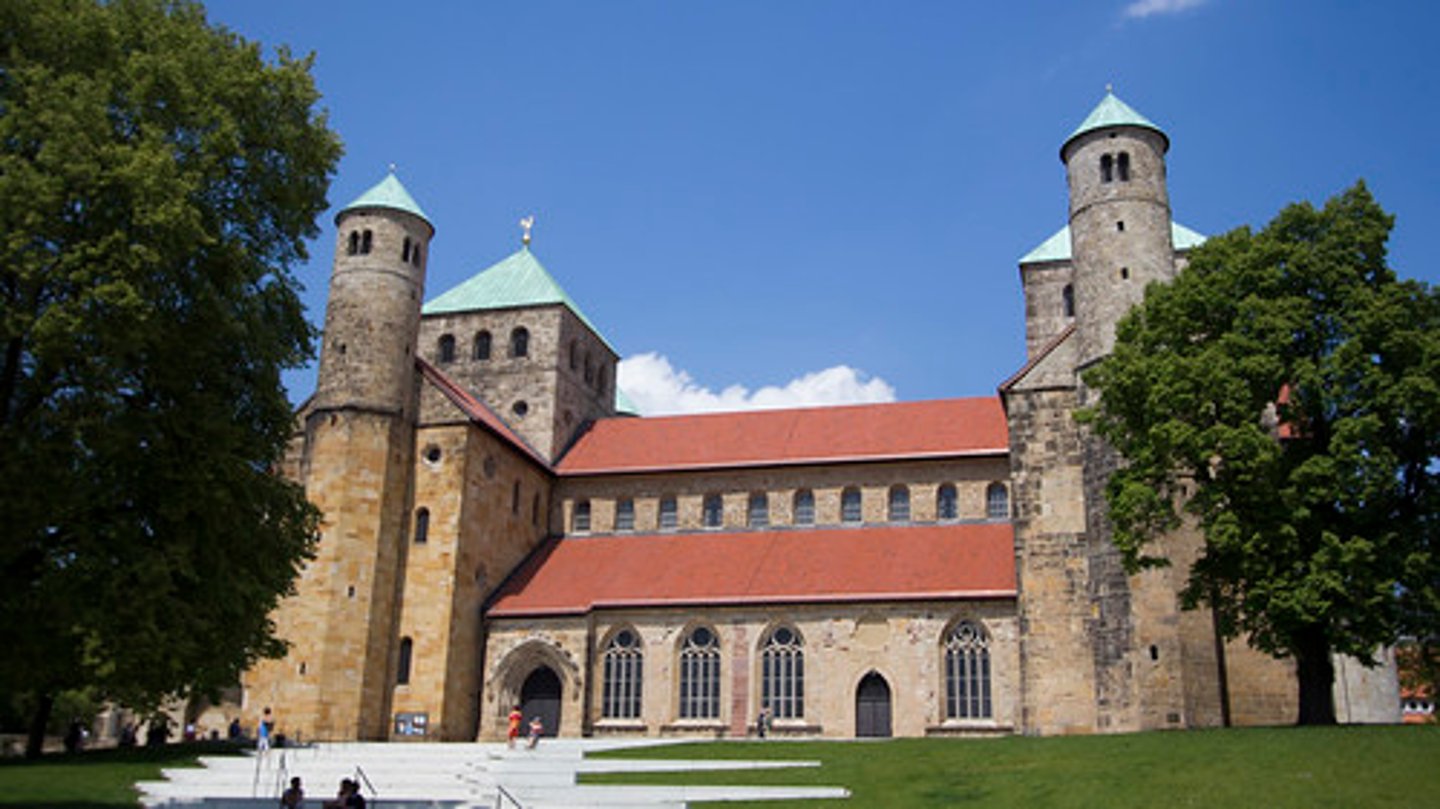
St. Michael's, Hildesheim (Germany), 1001-31
-Bishop Bernward: responsible for the decoration of the interior
-Theological symbols: 3 bays for the Holy Trinity, 4 piers for Evangelists, 12 columns for apostles
-no narthex, entrances on both sides instead
-Ottonian Art

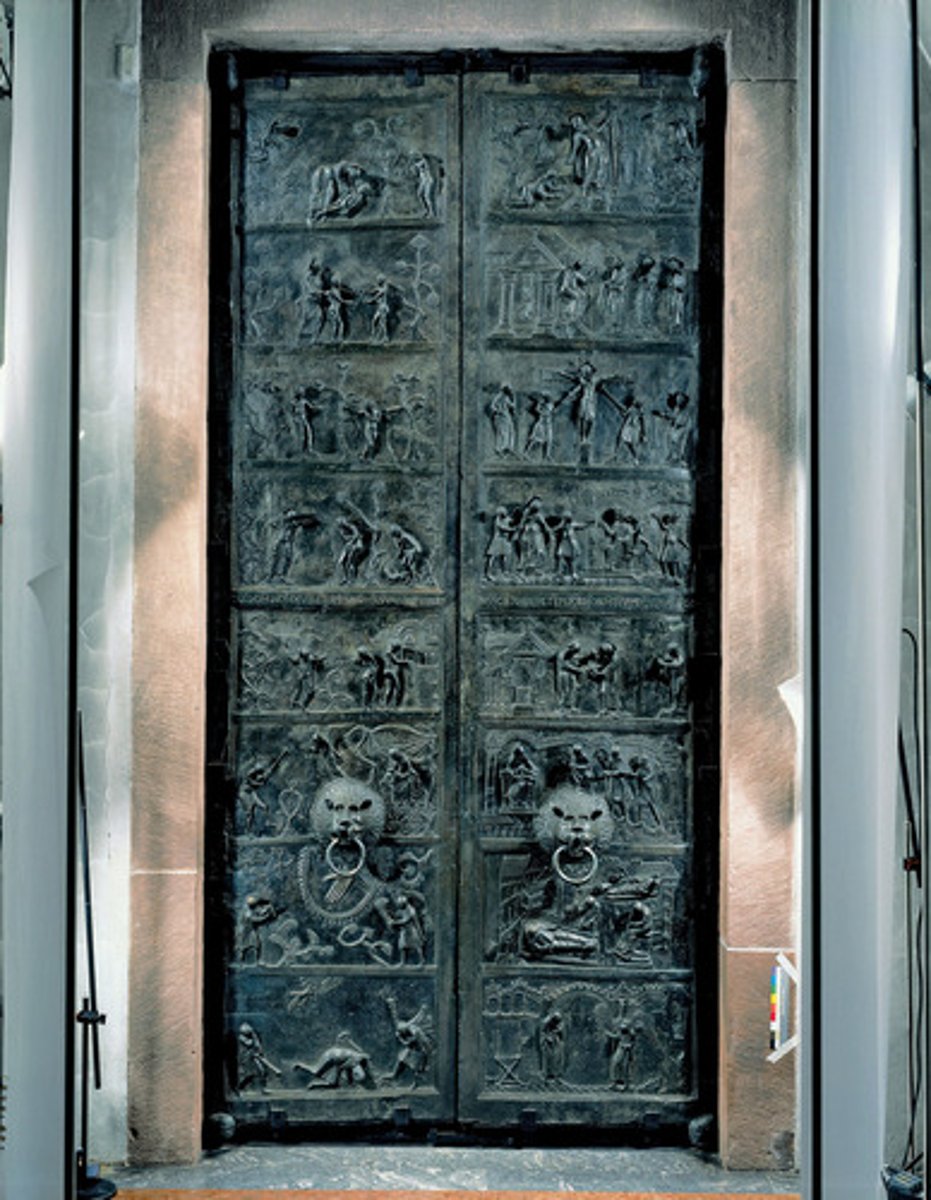
Bronze Doors, St. Michael's
-Creation of Eve (left door), Life of Jesus (right door)
-"Bernward Doors"
-Ottonian Art

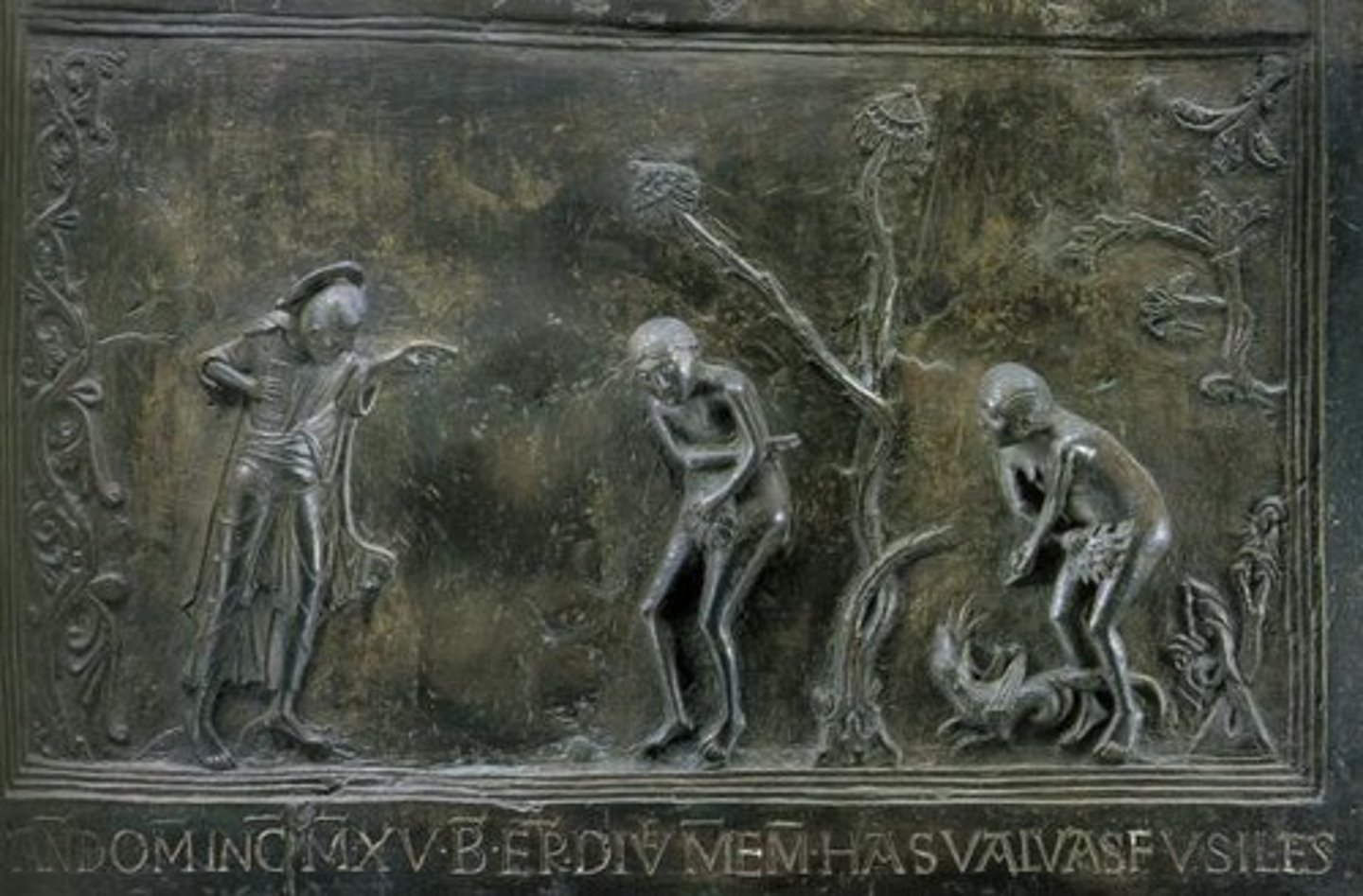
Fall of Man, Bronze Doors, St. Michael's
-show origin of sin
-left door
-Ottonian Art

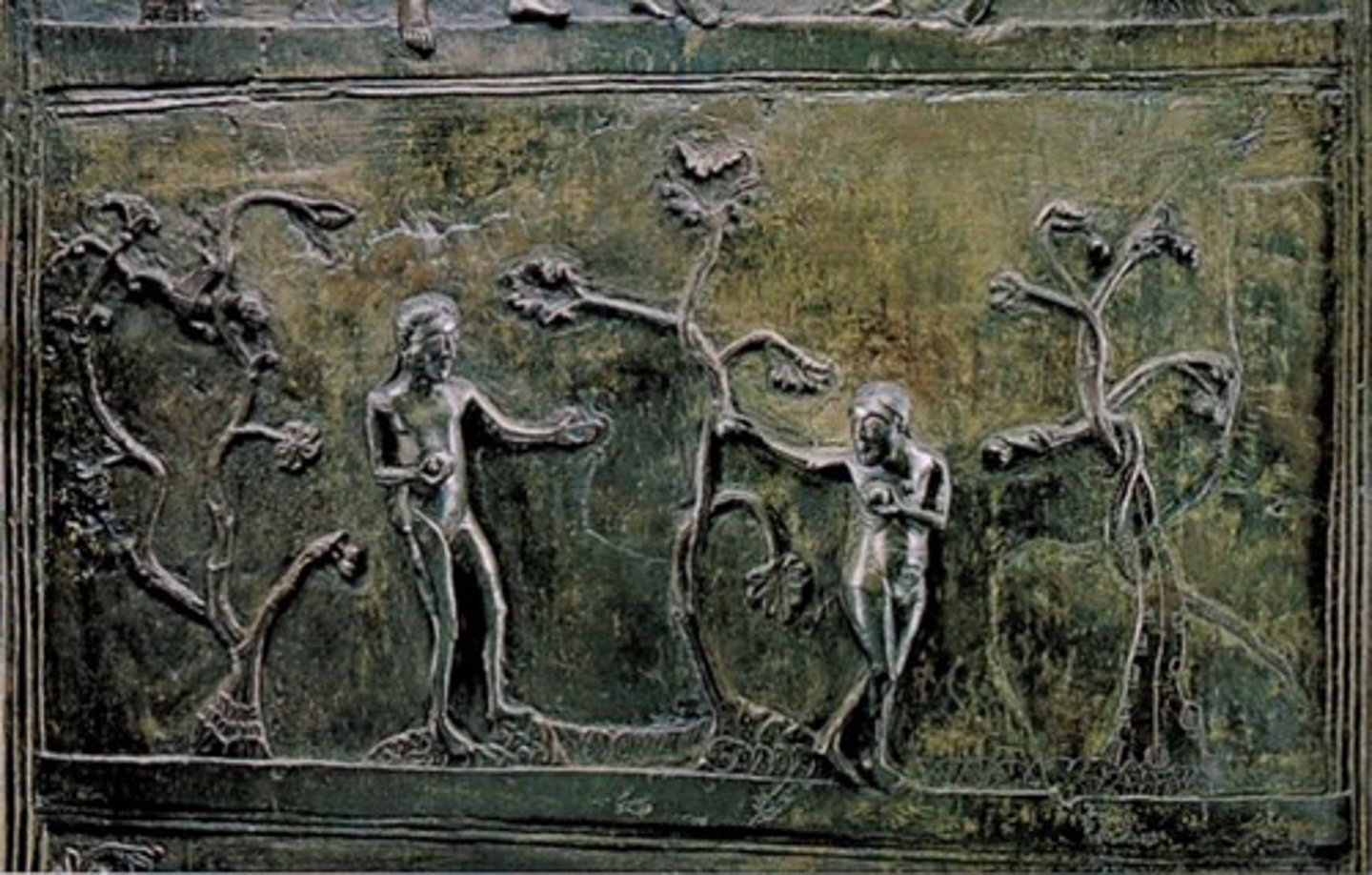
Expulsion from Eden, Bronze Doors, St. Michael's
-banished from Eden
-left door
-Ottonian Art

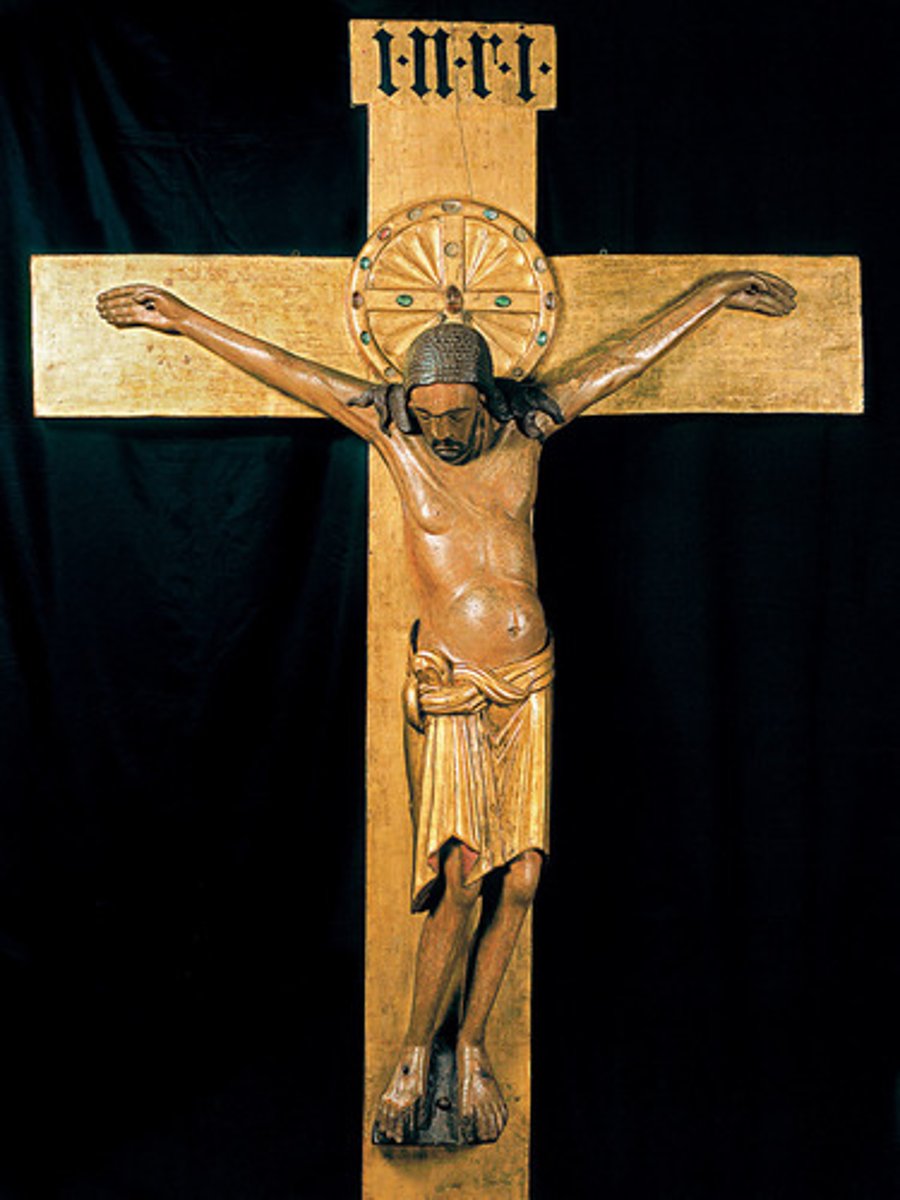
Crucifix of Archbishop Gero, Cologne Cathedral (Germany), 970
-carved from wood and painted
-life size (6 ft tall)
-naturalistic
-Ottonian Art

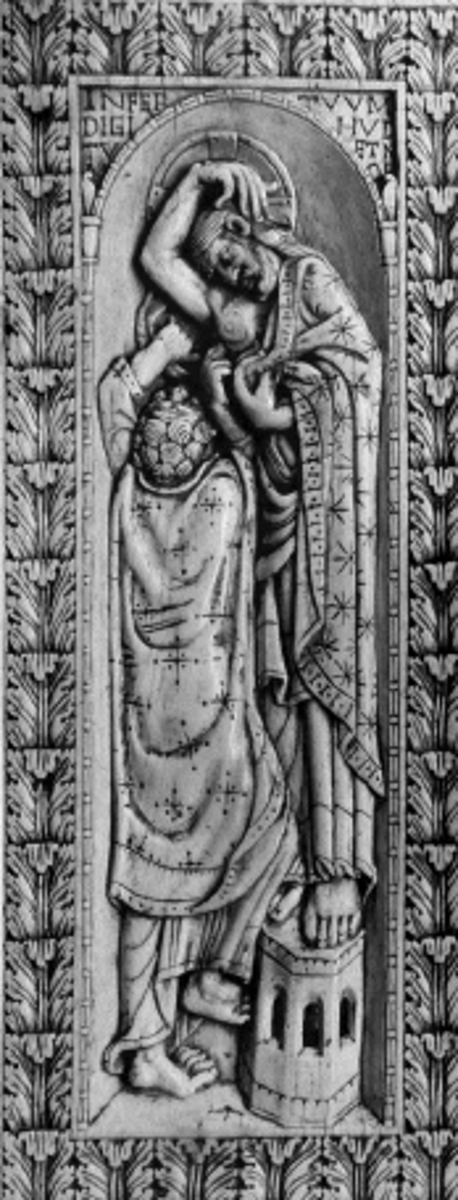
"Doubting Thomas" Ivory Plaque, 1000
-Ottonian Art

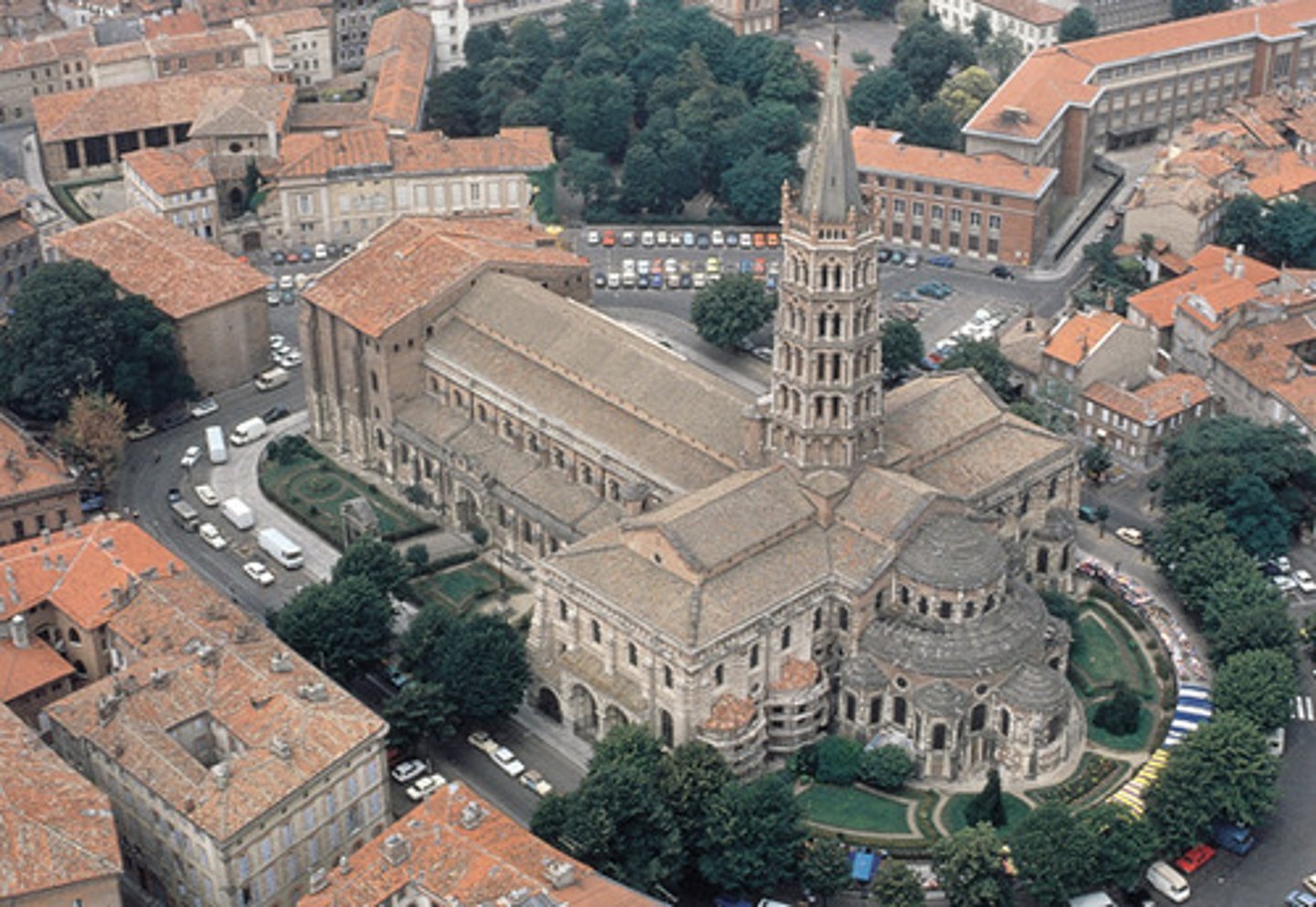
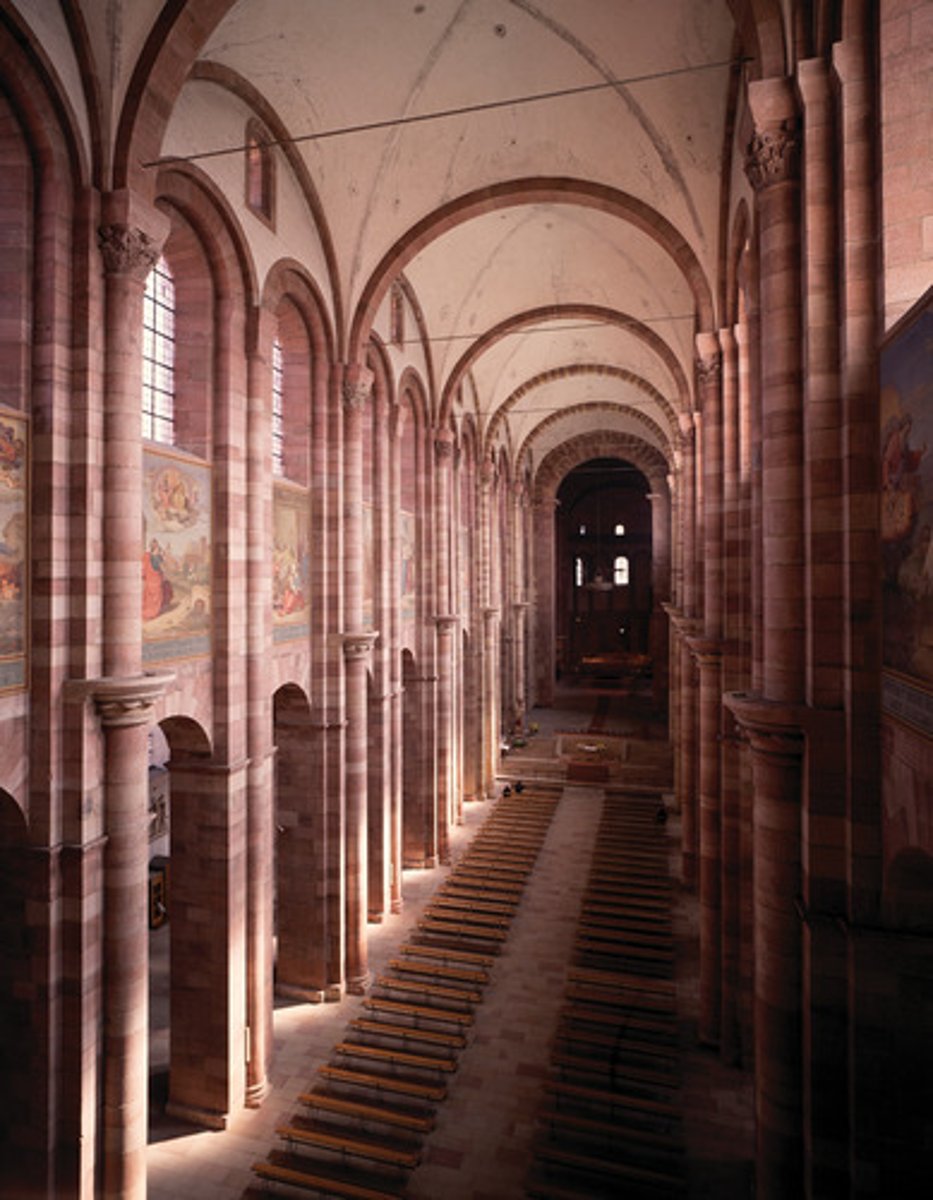
St. Sernin, Toulouse (France), 1070-1120
-desire for height
-cruciform plan: cross shaped
-bland exterior, beautiful interior
-Radiating chapels: small apses off of the main apse
-Romanesque Architecture

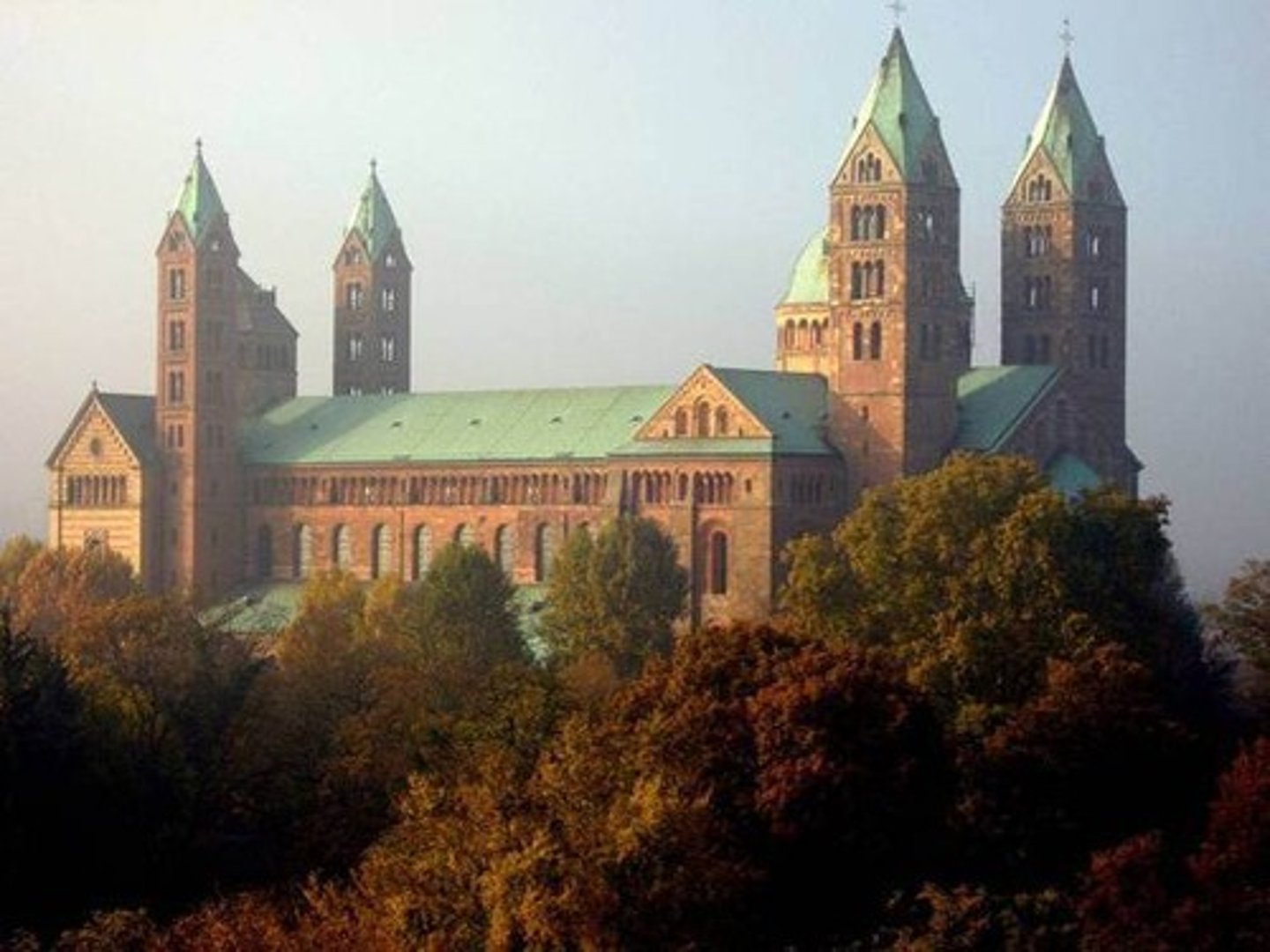
Speyer Cathedral (Germany), 1030, revaulted 1082
-same sturdy and plain exterior
-Romanesque Architecture

St. Sernin, Toulouse (France), Interior
-barrel vaults
-Transverse arch: an arch separating one vaulted bay from another
-2 aisles, 1 as an ambulatory: aisle that has no beginning or end
-very dark
-Romanesque Architecture
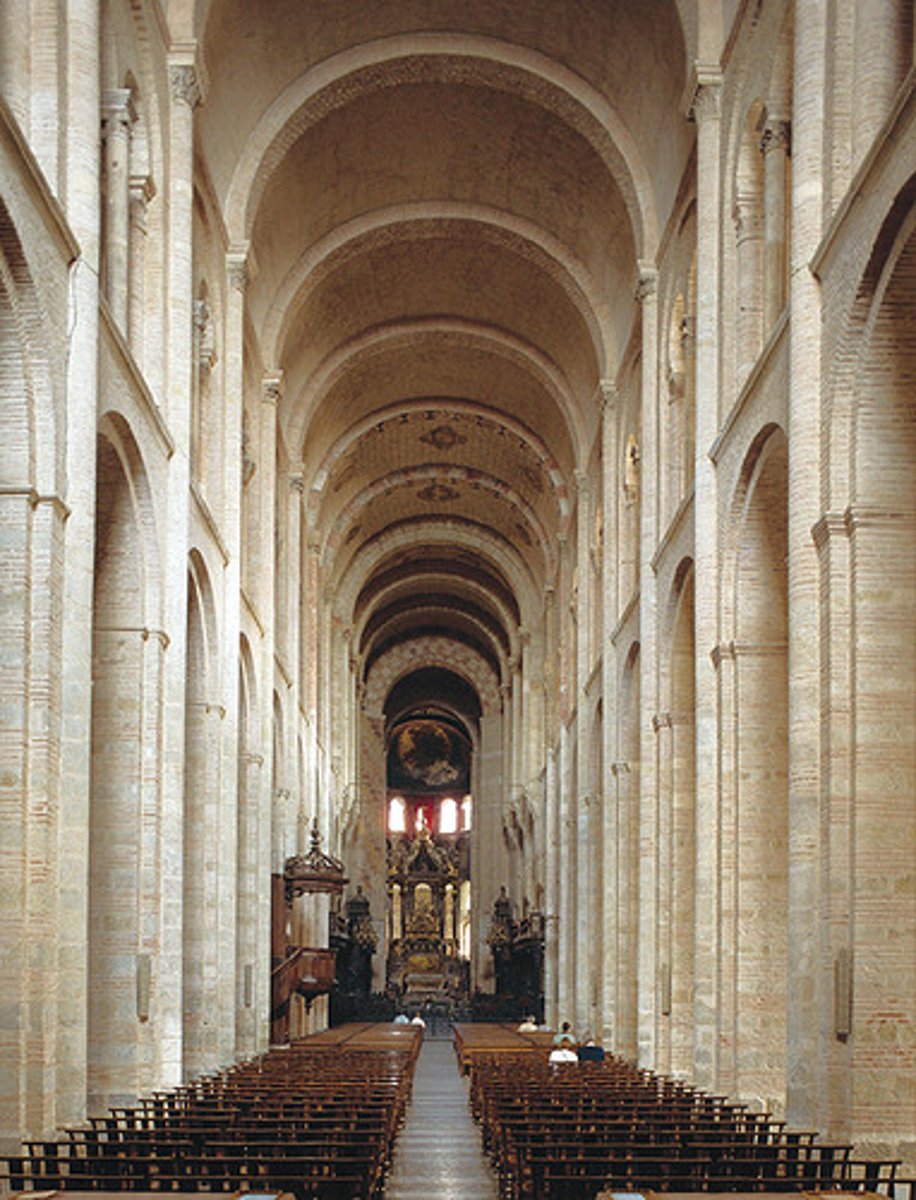

Speyer Cathedral (Germany), Interior
-groin vault
-alternate support system (A, B)
-very dark
-Romanesque Architecture

Reasons for Vaulting During Romanesque Period
1. Fire proofing
2. Music (Acoustics)
Groin Vault
intersection of two barrel vaults
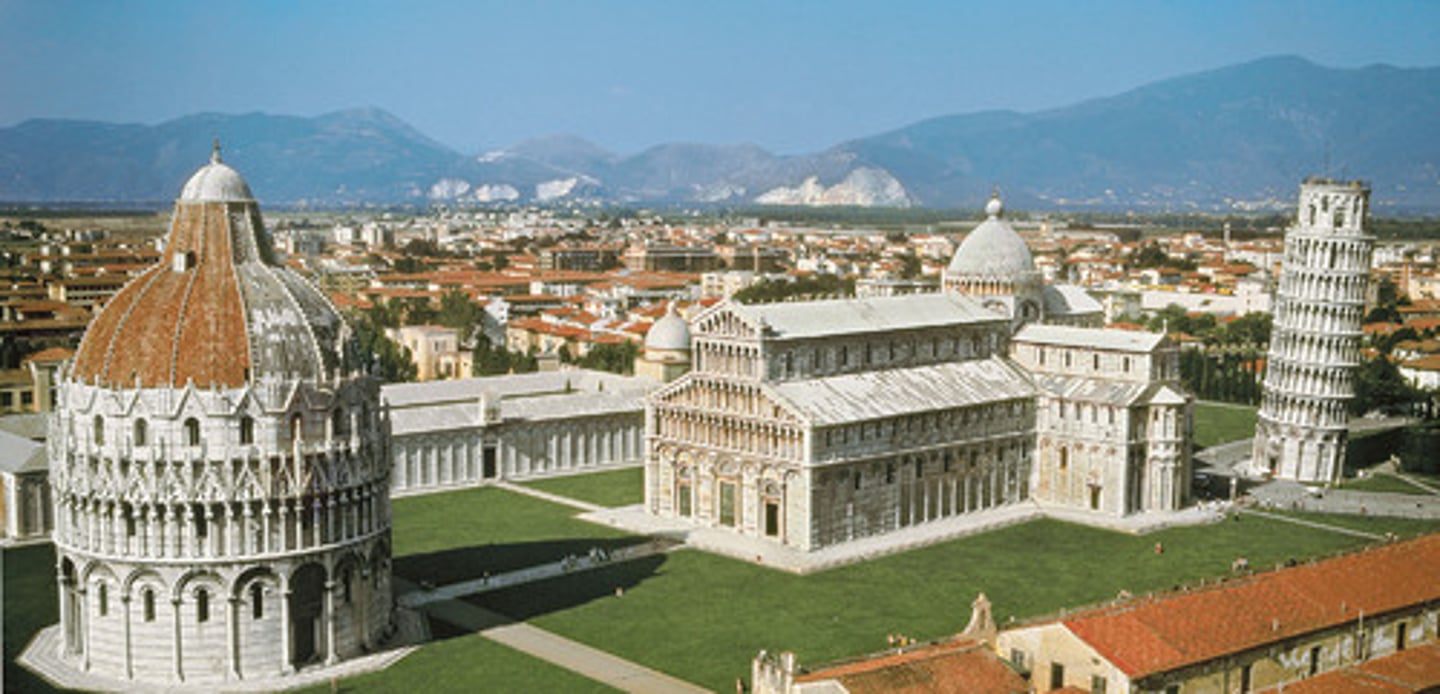
Pisa Cathedral (Italy), begun 1063, campanile begun 1174
-Classical facade
-reminiscent of old Roman buildings
-mosaics above the doorways
-Romanesque Architecture

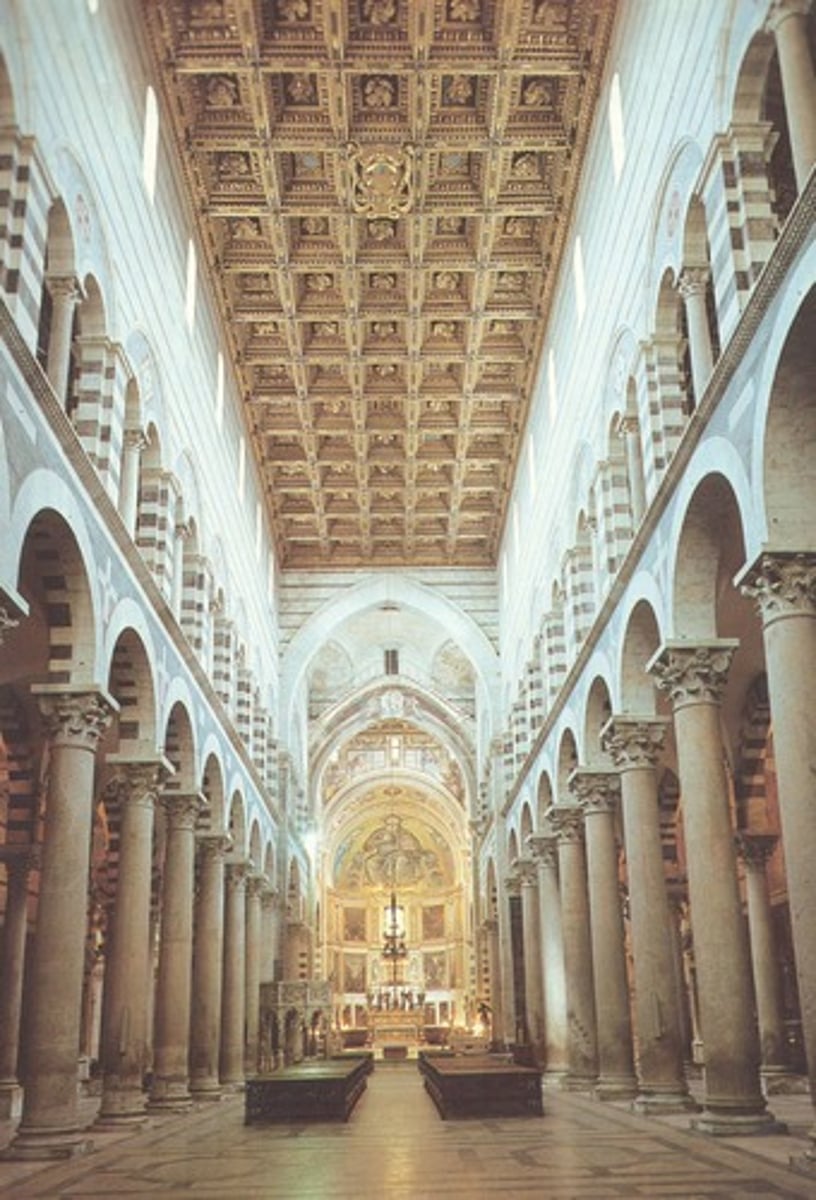
Pisa Cathedral (Italy), Interior
-very dark
-columns derived from old Roman buildings
-wooden roof (unlike stone used in North)
-use of pointed arches (derived from Islamic style)
-coffering
-Romanesque Architecture

Pisa Cathedral (Italy), Campanile
-belltower for Pisa Cathedral
-"Leaning Tower of Pisa"
-was not anchored into solid base, started to lean
-Romanesque Architecture

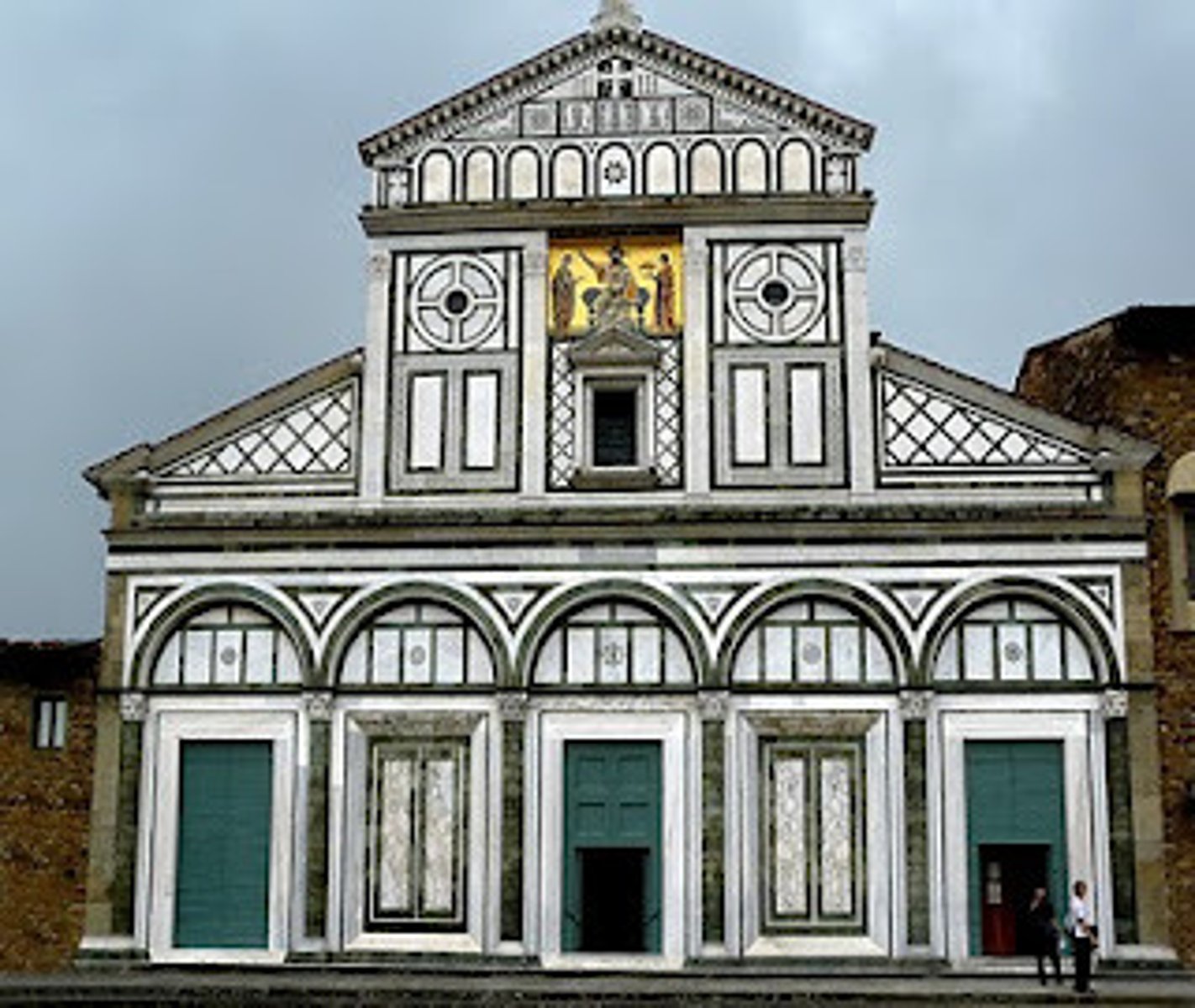
San Miniato al Monte, Florence (Italy), completed 1062
-building materials: tuffa, marble, mosaic (looks more Roman)
-Byzantine mosaic
-corinthian columns
-false facade (higher than actual building)
-Romanesque Architecture

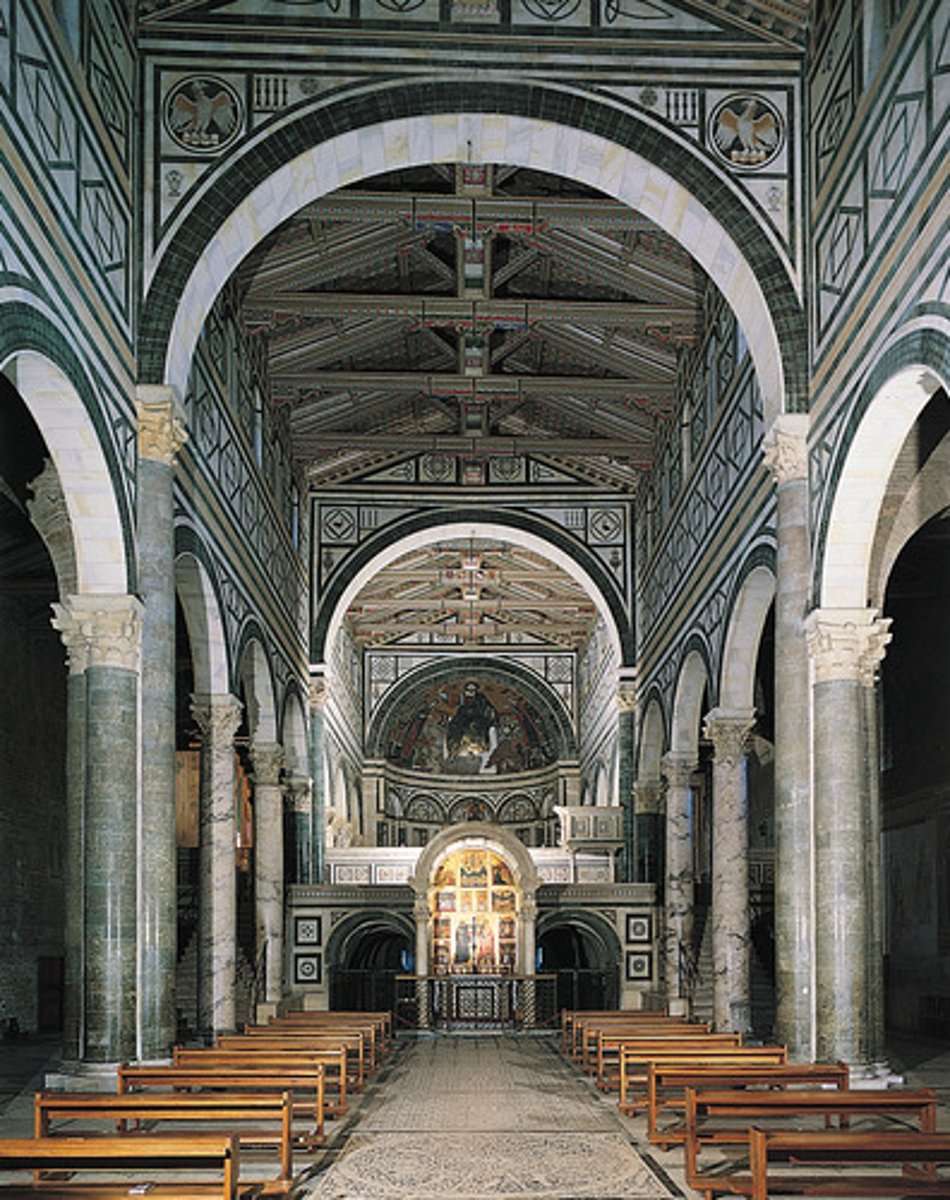
San Miniato al Monte, Florence (Italy), interior
-alternate support system (A, B, B, A)
-elements of early basilica and Romanesque North
-diagraphm arches made of stone
-marlbe panels placed on arches
-Romanesque Architecture

Diagraphm Arch
a transverse, wall-bearing arch that divides a vault or a ceiling into compartments, provides a fire break
Sant'Ambrogio, Milan (Italy), 1100
-german inspired
-Romanesque Architecture

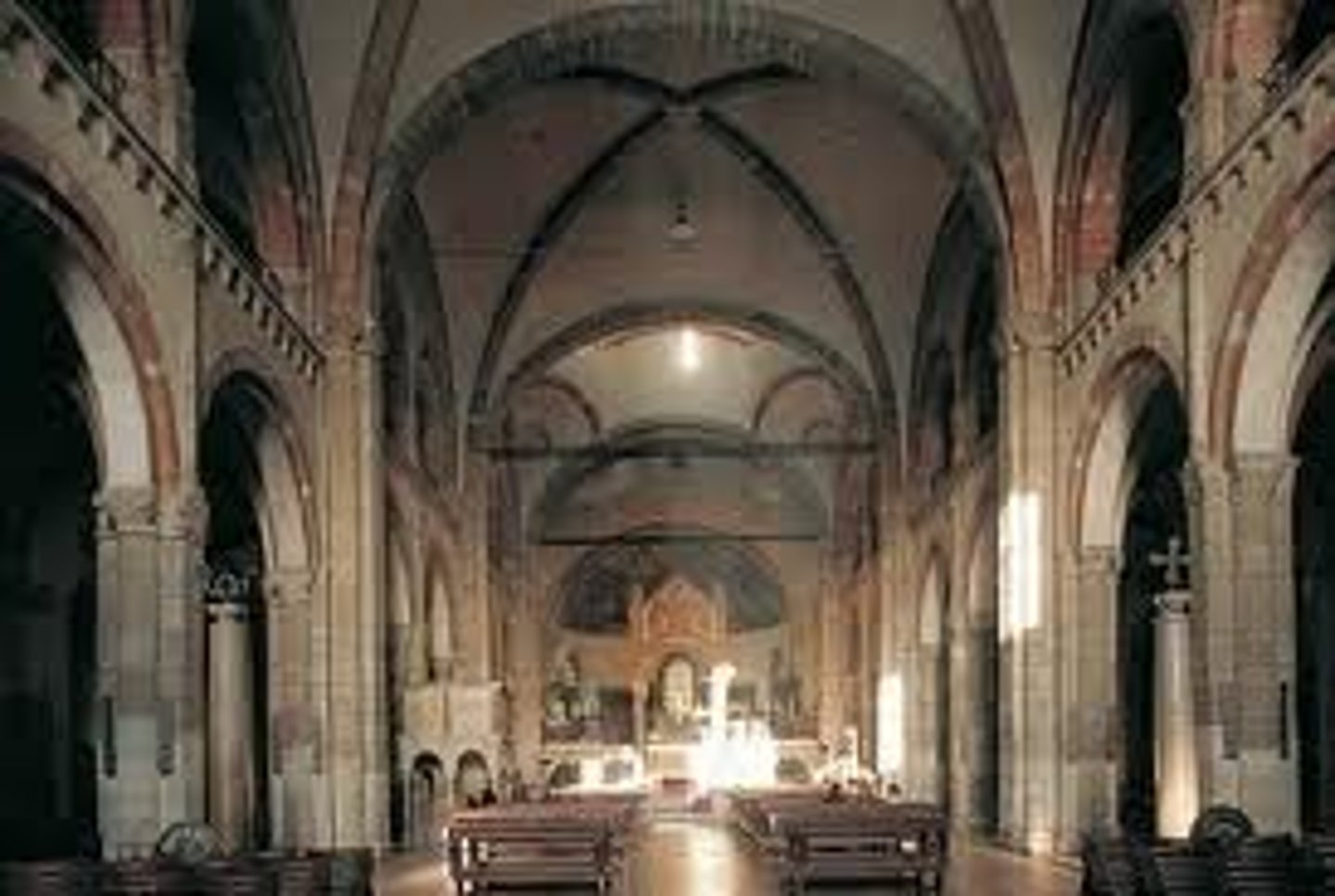
Sant'Ambrogio, Milan (Italy), Interior
-gallery but no clerestory
-used rib vaults
-no narthex
-Romanesque Architecture

Rib Vault
a vault where the diagonal and transverse ribs compose a structural skeleton that partially supports the masonry web between them, were not confident with this building style at the time
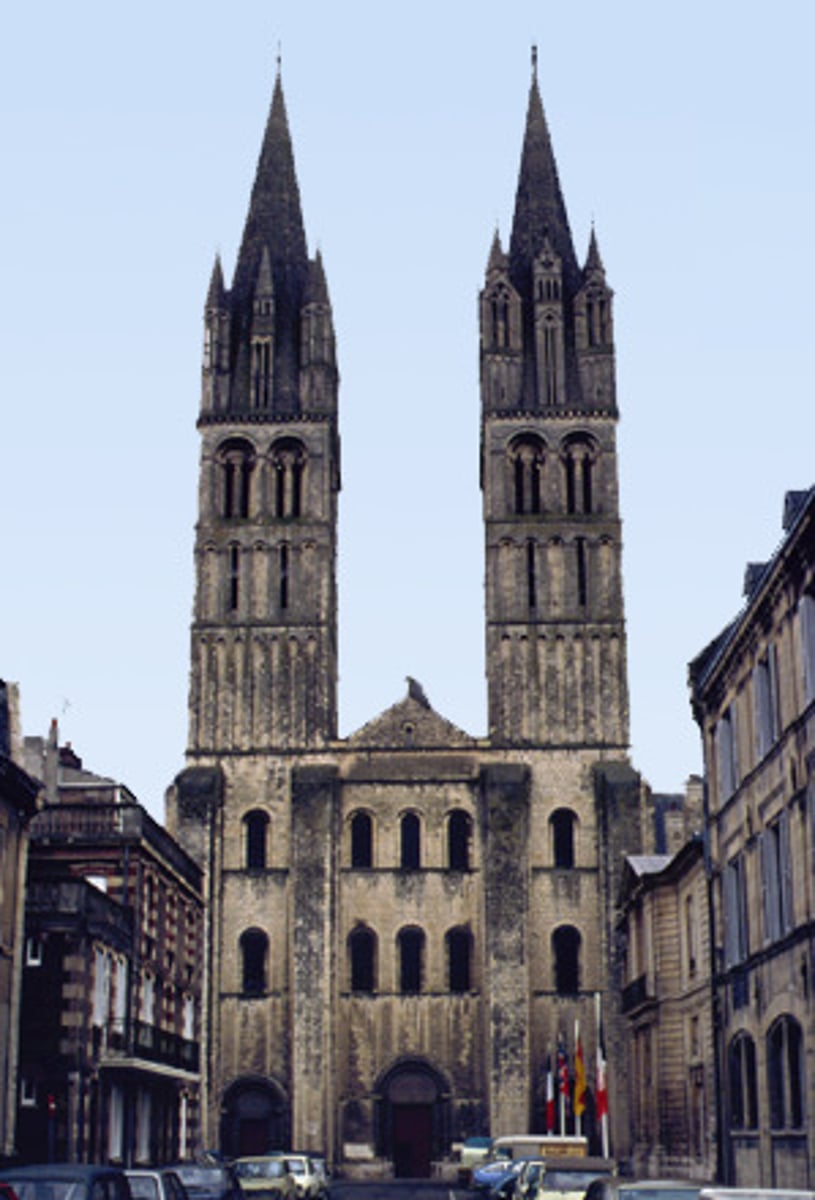
St. Etienne, Caen (France), begun 1067, vaulted in early 12th cent.
-germanic church
-bland exterior
-Romanesque Architecture

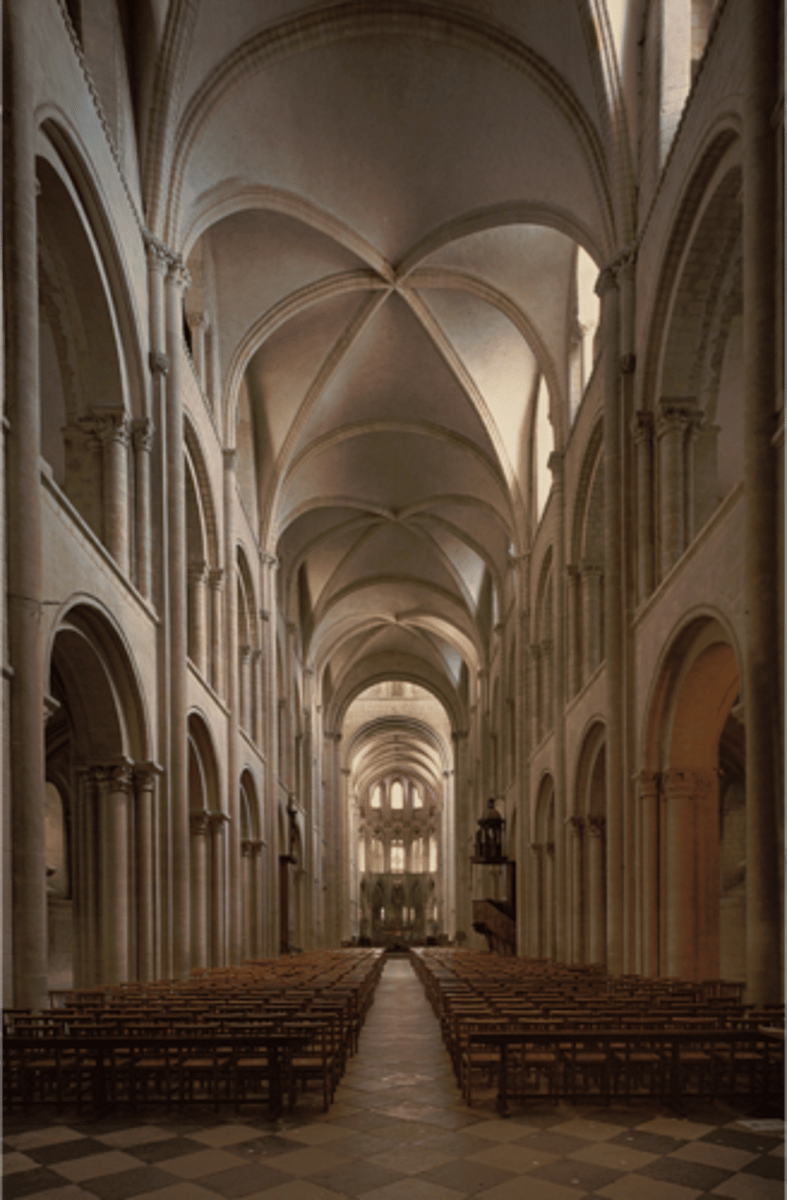
St. Etienne, Caen (France), Interior
-rib vaults
-more light (rib vaults allowed this, made higher ceiling)
-alternate support system (A, B)
-Romanesque Architecture

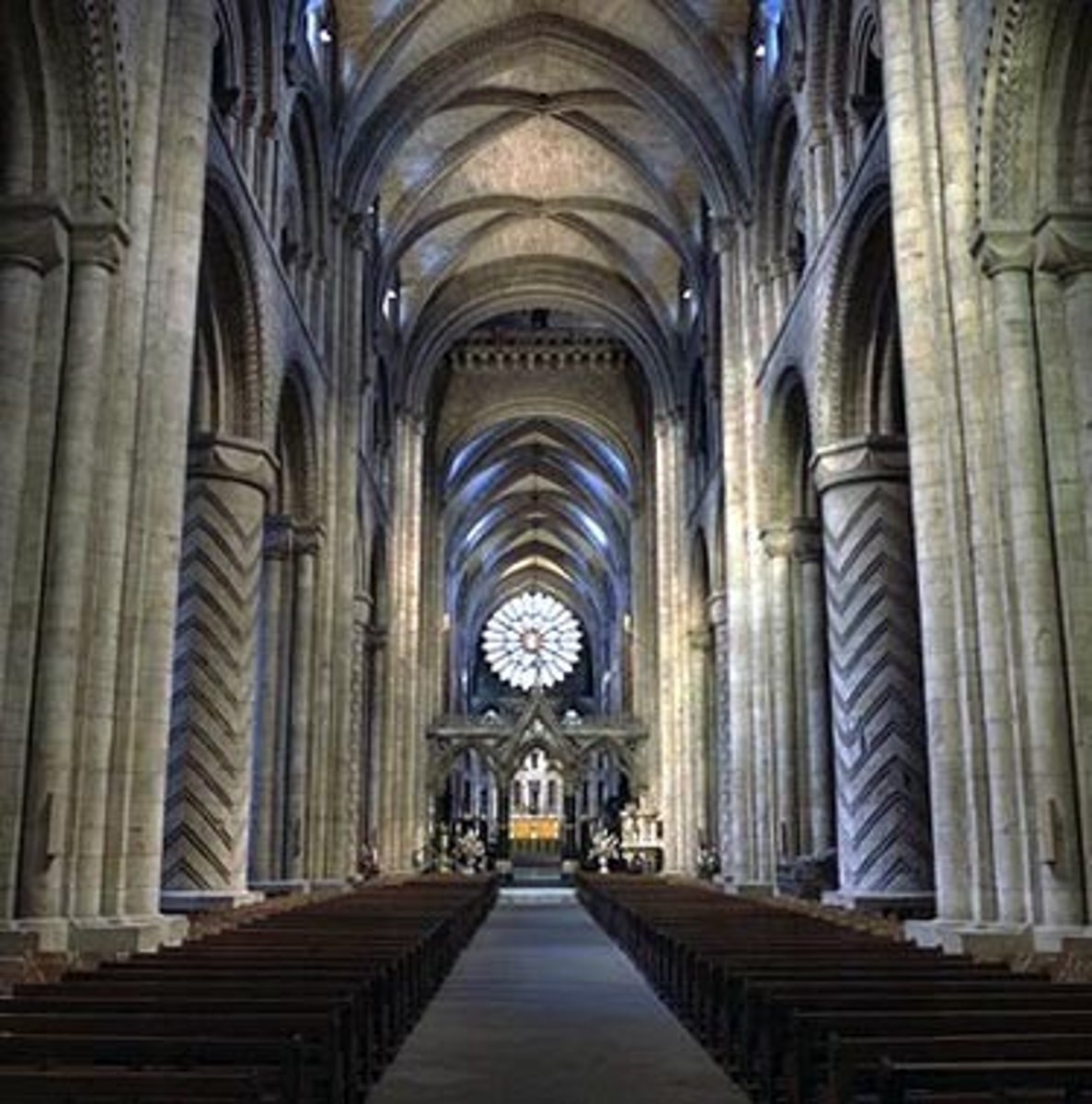
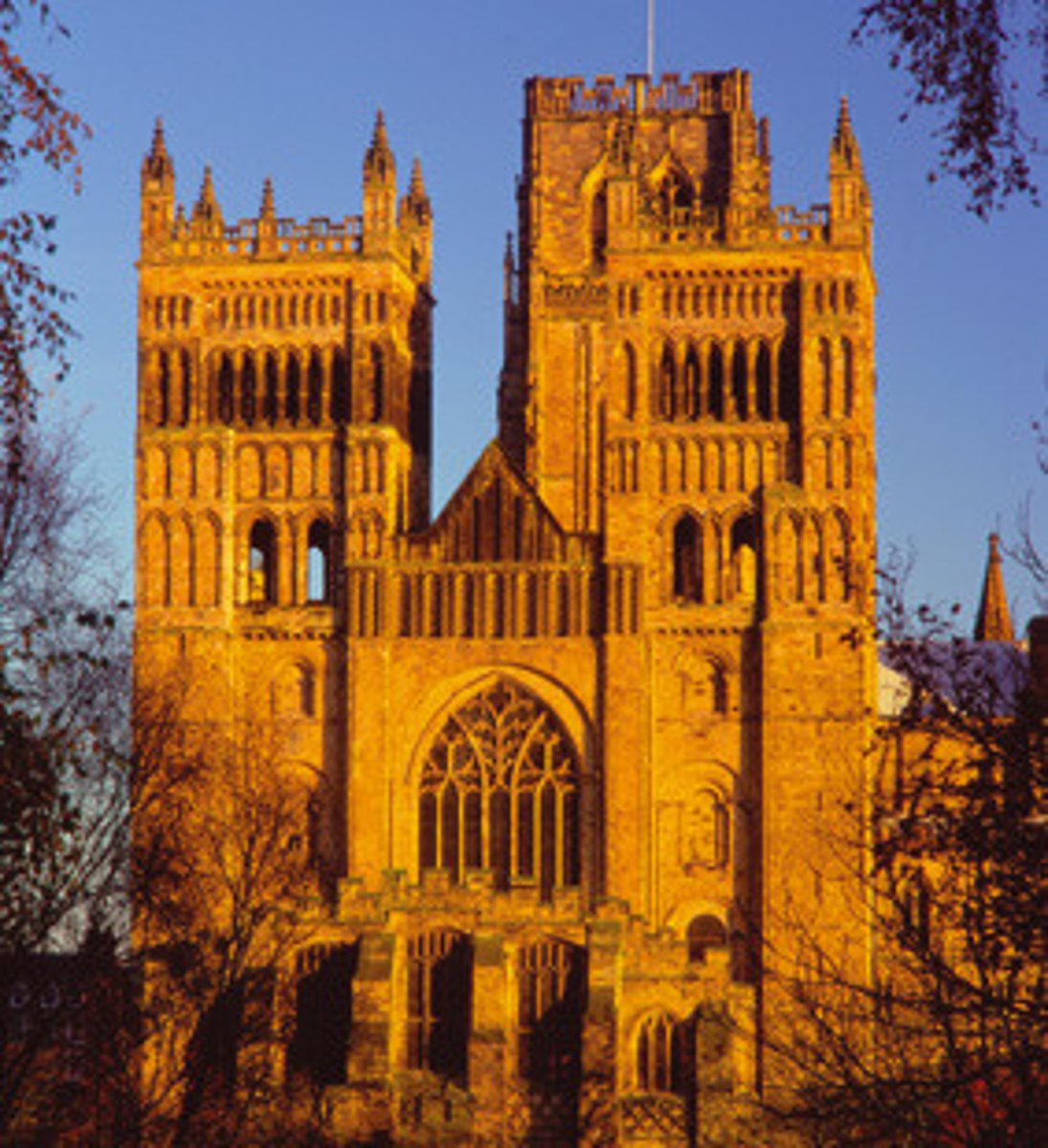
Durham Cathedral (England), 1093-1130
-first church built for rib vaults from the start
-Romanesque Architecture

Durham Cathedral (England), Interior
-alternate support system using cluster piers (A, B)
-very dark
-not very tall
-Romanesque Architecture
