4.3 - CompTIA A+ Core 2
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
Backup
An extra copy of data from a computer/device.
Full backup
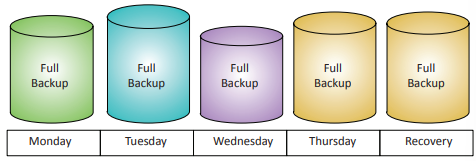
A backup of everything - all the operating system and user files, usually the longest backup method.
Incremental backup
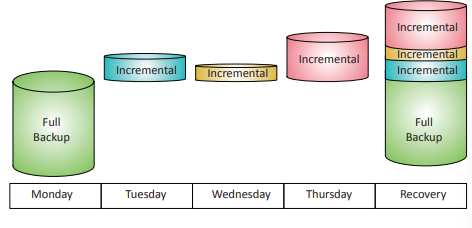
Backup implementation that saves all new or modified files since the last backup, requiring both the full backup and all subsequent backups for restoration.
Differential backup
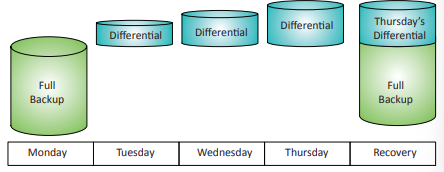
Backup type that saves a full backup and all data modified since the last full backup, requiring the last full backup and the latest backup for restoration.
Synthetic full backup
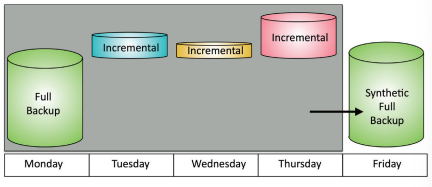
Backup type that combines the latest full backup with subsequent incremental backups to create a new, up-to-date full backup.
In-place/overwrite recovery
Recovery type that replaces files on the original system with a backup, often used when reimaging operating systems.
Alternative location recovery
Backup or recovery type that restores systems to a separate location or drive, preserving the original system's data.
Backup testing
The process of verifying the integrity of backups to ensure data can be successfully restored in case of loss.
Backup frequency
Refers to how often backups are conducted on a system, such as weekly, monthly, or quarterly.
On-site backups
Backups performed at an organization’s location using available infrastructure, generally less expensive and immediately available.
Off-site backups
Data stored in a different geographical location to ensure availability after local disasters.
Grandfather-father-son (GFS)
A hierarchical backup rotation strategy that uses three distinct tiers (e.g., monthly, weekly, and daily) for backups.
3-2-1 backup rule
Backup strategy that includes 3 copies of data, 2 different media types, and 1 off-site backup to ensure redundancy.