4.3 - CompTIA A+ Core 2
Backup
Backup: An extra copy of data from a computer/device.
Full
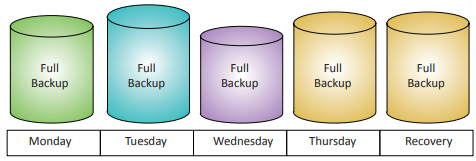
Full backup: A backup of everything - all the operating system and user files. Usually the longest backup method, and may be impractical every day.
Incremental
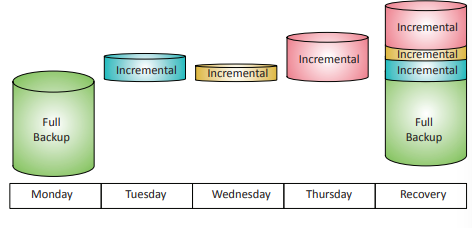
Incremental backup: Backup implementation that saves a full backup, and all new files and files modified since the last backup was performed. Saves time compared to a full backup, but data restoration requires the full backup and all incremental backups.
Differential
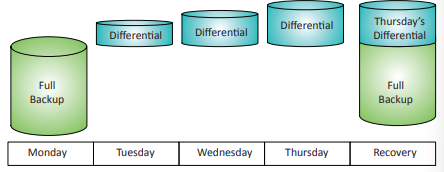
Differential backup: Backup type that saves a full backup first, then subsequent backups include all data modified since the last full backup. Data restoration involves retrieving the last full backup and the latest differential backup - more efficient than full/incremental backups.
Synthetic full
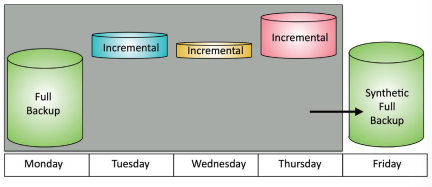
Synthetic backup: Backup type that contains the latest full backup with subsequent incremental backups to create a new, up-to-date full backup. Faster and less bandwidth-intensive compared to full/incremental backups.
Recovery
In-place/overwrite
In-place/overwrite: Recovery type that replaces the files on the original system with a backup (original files aren’t visible). Often used when reimaging OSes.
Alternative location
Alternative location: Backup/recovery type that restores systems to a separate system/drive - no data is lost on the original system.
Backup testing
Backup testing: This process involves verifying the integrity of backups to ensure data can be successfully restored in case of hardware failure or data loss. (It’s not enough to perform the backup; you have to be able to restore data from it.)
Frequency
Backup frequency: Refers to how often backups are conducted on a system - this can be weekly, monthly, quarterly, etc.
Backup rotation schemes
On-site vs. off-site
On-site backups: Backups are performed at an organization’s location using available infrastructure (e.g., servers, on-premise data centers). No WAN/Internet link required, data is immediately available, and generally less expensive than off-site backups.
Off-site backups: Data stored in a different geographical location/over the internet. This allows data to be available after a local disaster, and the backup could be stored anywhere.
Grandfather-father-son (GFS)
Grandfather-father-son (GFS): Refers to three separate, hierarchical backup rotations (e.g., monthly - grandfather, weekly - father, daily - son).
3-2-1 backup rule
3-2-1 backup rule: Popular backup strategy that involves having 3 backup copies available, 2 different media types for backups, and 1 off-site backup to ensure data redundancy.