Plant Physiology 3
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Cellular Respiration
Reduced carbon is oxidized to carbon dioxide and water
glycolysis, oxidative pentose phosphate pathway, citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation
C12H22O11 + 12O2 → 12CO2 + 11H2O
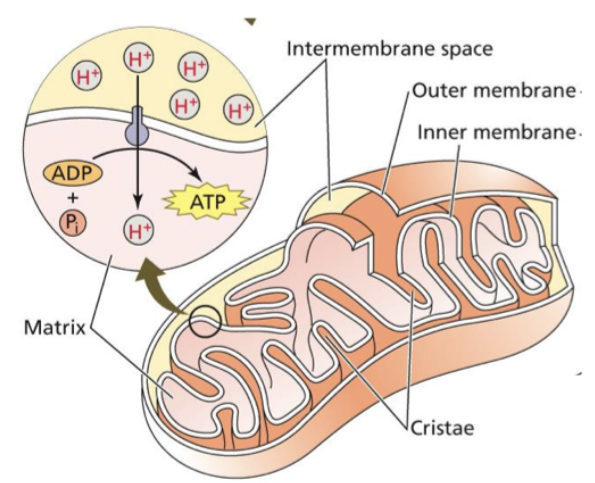
Mitochondria
Place where the citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation occur. Proton gradient uses energy of oxidation-reduction.
Acetyl CoA
Serving as an intermediate between glycolysis and the citric acid cycle. It's produced by oxidizing pyruvate, a product of glycolysis, and then enters the citric acid cycle, where it's broken down to generate ATP and other energy-carrying molecules.
Cytosol and plastids
Where glycolysis and oxidate pentose phosphate pathways occur.
Convert sugars into organic acids such as pyruvate, generating NADH and ATP.
Glycolysis
Carbohydrates are converted into hexose phosphates, each of which is then split into two triose phosphates. In a subsequent energy-conserving phase, each triose phosphate is oxidized and rearranged to yield one molecule of pyruvate, an organic acid.
Besides preparing the substrate for oxidation in the citric acid cycle, glycolysis yields some ATP and NADH.
Fermentation
In the absence of oxygen, NAD+ is regenerated and needed for glycolysis. With ethanol or lactate as the final product, the efficiency of is about 4%.
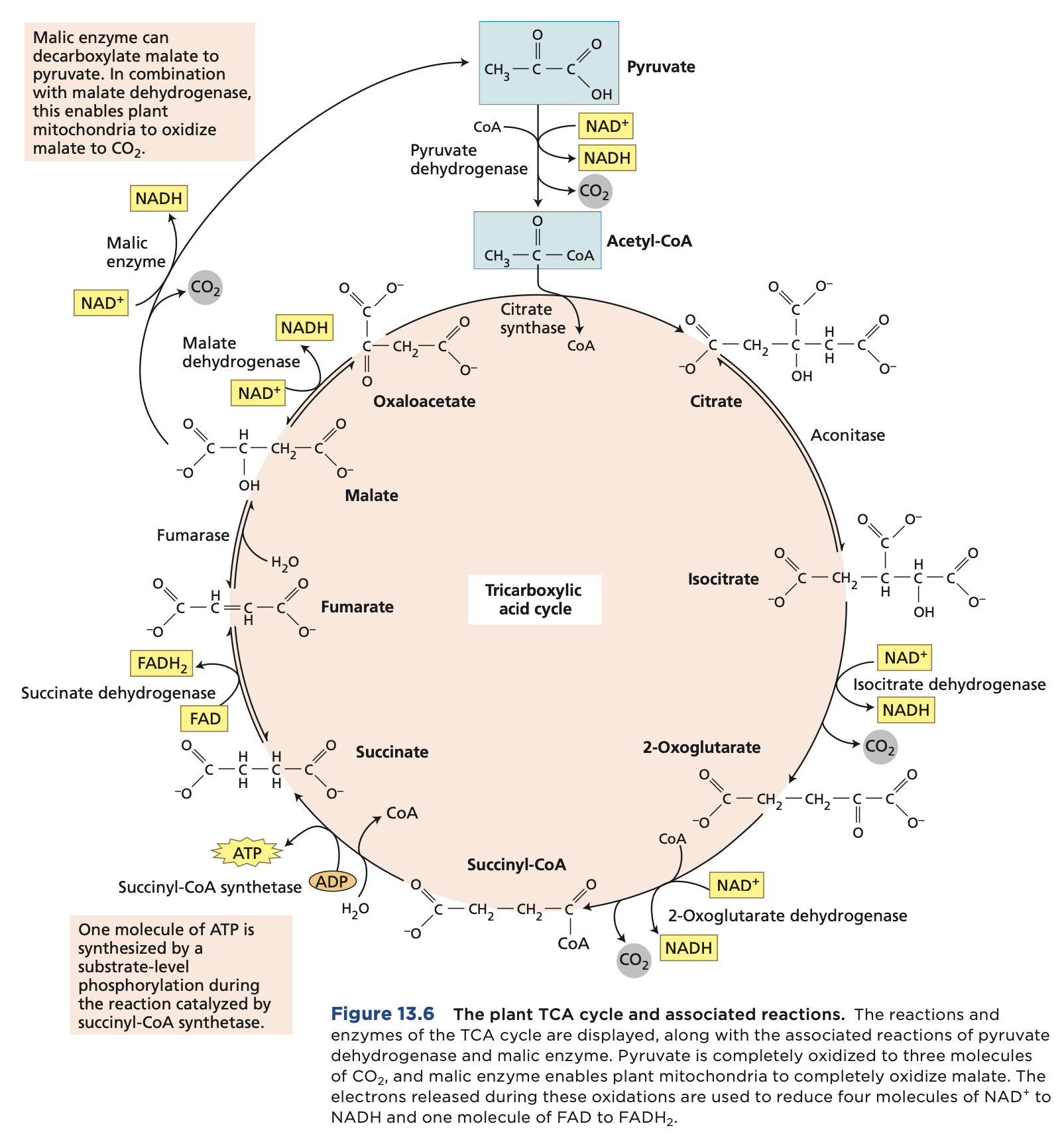
Citric Acid Cycle
Pyruvate is oxidized to CO2 within the mitochondrial matrix through the ____, generating a large number of reducing equivalents in the form of NADH and FADH2 and a small amount of ATP. One molecule of pyruvate gives rise to three molecules of CO2
Mitochondria Image
Citric Acid Cycle Image
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Electron transport from NADH and FADH2 to oxygen is coupled by enzyme complexes to proton transport across the inner mitochondrial membrane. This generates an electrochemical proton gradient used for powering synthesis and export of ATP. The ETC catalyzes a lot number of electrons from NADH to O2. Adenosine triphosphate is the major product.
Oxidative Phosphorylation Image
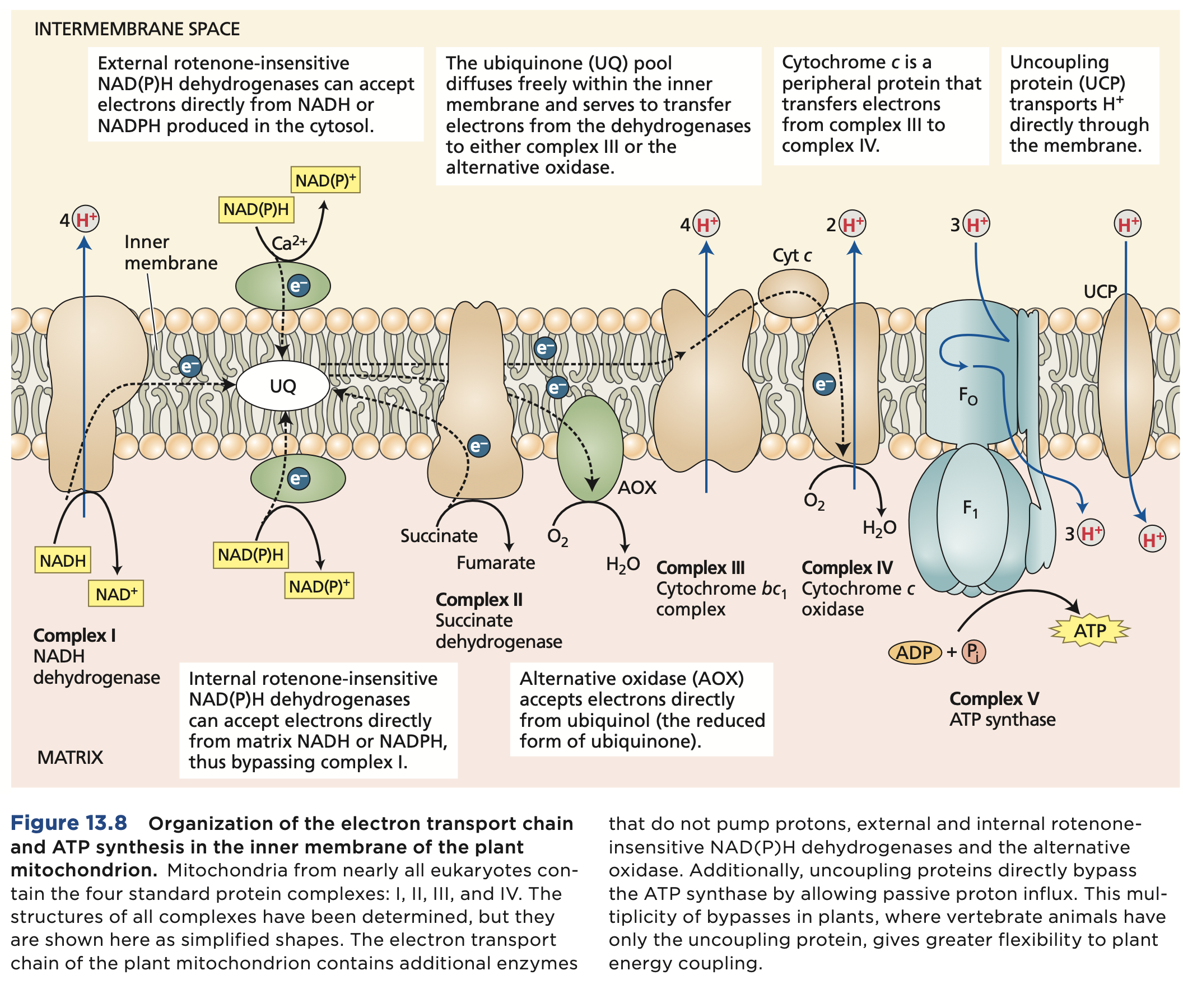
Complex 2
Does not engage in proton pumping.
Complex 5
ATP synthesis in oxidative phosphorylation.
Order of development in plant cells
Sclerenchyma → phloem → cortex → xylem
Middle Lamella
Forms during cell division, rich in pectin
Primary cell wall
After cell division and during cell growth it is created on either side of the middle lamella. A more flexible cell wall. 25% cellulose, 35% hemicellulose, 35% pectin, 2-5% protein. Ratios vary greatly, as do specifics.
Secondary cell wall
After cell growth, it is deposited inside primary cell wall. More rigid due to components. Rigidity is why it comes in after cell growth - too rigid for cell to grow. Typically more cellulose and less pectin. Can contain lignin. Great diversity in specific chemical composition of plant cell walls. Chemical diversity leads to physical diversity.
Scaffolding of cell wall
Cellulose (microfibrils)
Hydrated matrix of the wall
Pectins, xyloglucan, non enzymatic proteins, lignin. Polysaccharide components. Outside of cell, within the cellulose.
Cellulose microfibrils
Very strong physical strength. Glucan chain varies in length, and is not strong. High tensile strength (steel), chemical stability, and resistant to enzymatic attacks. 18-36 glucan chains within, extensive hydrogen bonding within and between glucan chains. Linear chains of 1-4 linked beta-D-glucose individual glucose per chain. Made by rosettes.
Cellulose synthase
Synthesizes the individual glucan chains. CESA units together make up a rosette subunit (3 to 6 units). Six rosette subunits together make up the particle rosette. If a rosette has 3 subunits it has 18 glucan chains total. It is embedded in the plasma membrane. As soon as CESA synthesizes, it leaves the cell.
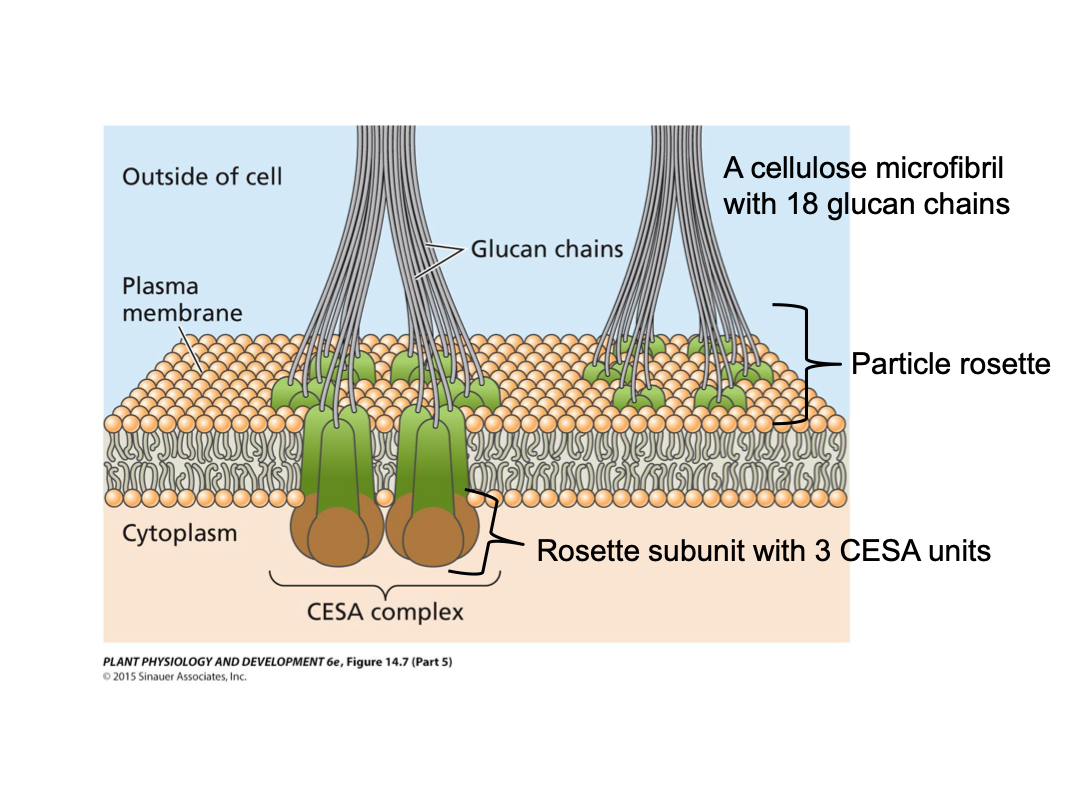
UDP-glucose
CESA may be complexed with sucrose synthase → cleaves intracellular sucrose to ____ and fructose → ____ is then used for synthesis of the glucan chain, which is being released into the cell wall space
Hemicellulose and pectin
Complex polysaccharides that are the flexible hydrated matrix into which cellulose microfibrils are embedded. Wide variety of monosaccharide building blocks. Polysaccharides synthesized in Golgi apparatus. Delivered to cell wall via exocytosis (vesicle).
Hemicellulose
Tightly bound polysaccharides of the wall, long chains often with short side branches, bind to surface of microfibrils, form tethers between microfibrils. Commonly xyloglucan.
Commonly Xyloglucan. Xylose sticks out of glucan chain (characterization). Xylose and glucose are two basic subunits, very simple structure.
Pectins
Highly hydrated gel phase of the wall (more easily extracted), complex polysaccharides, typically containing galacturonic acid. Methyl esters can be removed, exposing carboxyl groups. Can get ionic bridging of the carboxyl groups of adjacent chains by Ca2+. This can generate large pectin networks.
Lignin
In secondary cell wall as an aromatic ring with hydroxyl group (phenol). Secreted into the wall where oxidation by cell wall peroxidase cross-links.
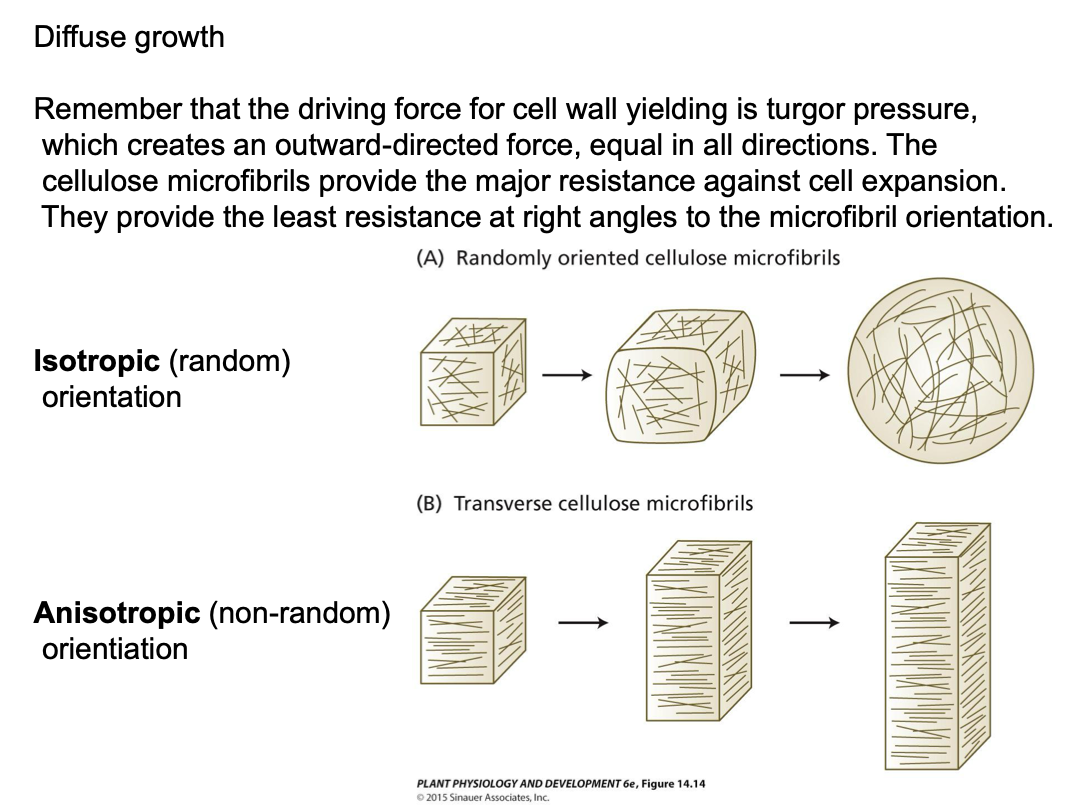
Diffuse growth
expansion distributed over cell surface and due to both wall yielding and new wall synthesis. Expansion can still be directional. Most plant cells expand by diffuse growth.
Tip growth
localized cell expansion due to localized (polar) new wall synthesis. Root hairs and pollen tubes expand by this.
Cell expansion factors
Direction - tip growth and diffuse growth
Rate - turgor pressure, cell wall structure, cell wall loosening.
Cell wall growth
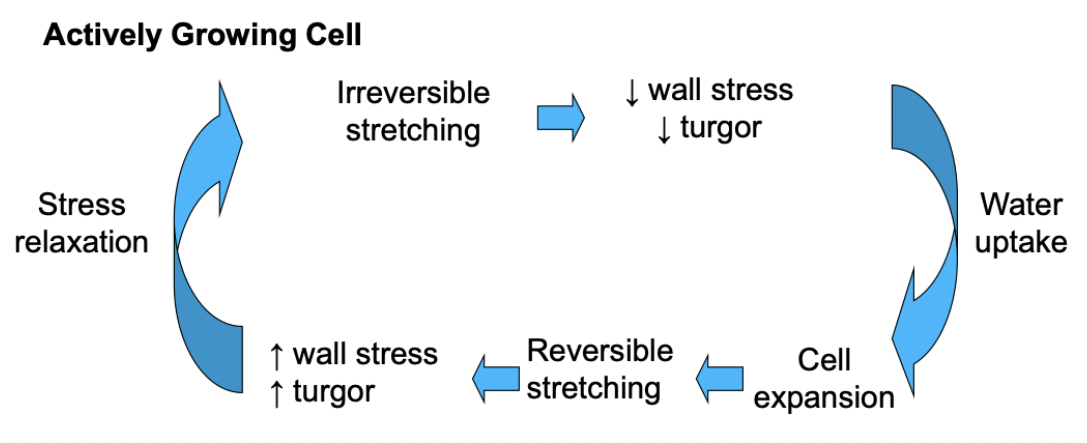
Stress relaxation
stem section → isolate cell walls → use extensometer for tension (turgor pressure) → measure wall extension (creep) under different conditions
wall creep enhanced at lower pH
Acid growth response is prevalent in young expanding cells, but not mature ones
Pre-treated with heat or protease denaturation - acid growth response not active
Changes in mature cell wall
Leads to cessation of cell expansion
Reduction in stress relaxation processes
Increased cross-linking of wall components
New matrix polysaccharides that associate more strongly with each other and/or the cellulose microfibrils.
Enzymes, pectin esterase makes cell walls more rigid. Expose carboxyl groups in pectin.
Lignification.
Expansins
Family of proteins added to heat-treated cell walls, acid growth is restored. While their mode-of-action is not yet completely understood, they may loosen the association between cellulose microfibrils and hemicellulose.
Acid growth hypothesis
Plant hormone auxin stimulates cell expansion by inducing acidification of the cell wall, which in turn activates enzymes that loosen the cell wall, allowing it to expand. A stimulation of plasma membrane H+-ATPase activity by auxin increases rate of cell expansion.
Wall extensibility
Cell wall properties that determine the rate of cell expansion at a given turgor pressure