Rabies Virus
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Rabies Virus
Rhabdoviridae
Lyssavirus
unsegmented -ssRNA
Bullet shaped
7 distinct genotypes
Phylogroup 1
Classical Rabies Virus (RV-genotype 1)
Most commonly known rabies virus
Rabies Transmission
Mesocarnivores
Dogs
Foxes
Raccoon dogs
Raccoon
Mongooses
Skunks
Other mammals
Humans, Catles, Equids
Spillover
Dead end hosts
Urban Cycle
Community strays
Sylvatic Cycle
Wild mammals as reservoir
Distribution
Asia, America, Africa, Europe (sporadic)
Transmission
Saliva and broken skin (bites, scratches, licks)
Sylvatic and Urban
Cycles of RABV
Chiropteran (Bats)
Hosts of most Lyssavirus
Mesocarnivores
Hosts of RABV
Saliva and broken skin (bites, scratches, licks)
How is rabies virus transmitted?
Dead End Hosts
Other mammals can serve as hosts for RABV but they are considered what?
Epidemiology of RABV
Dogs as main source
Asia, Africa, America, Europe (sporadic)
Neglected Tropical Disease
Children as frequent victimes
September 28 World Rabies Day
RA 9482 The Anti-Rabies Act of 2007
Pathogenesis of RABV
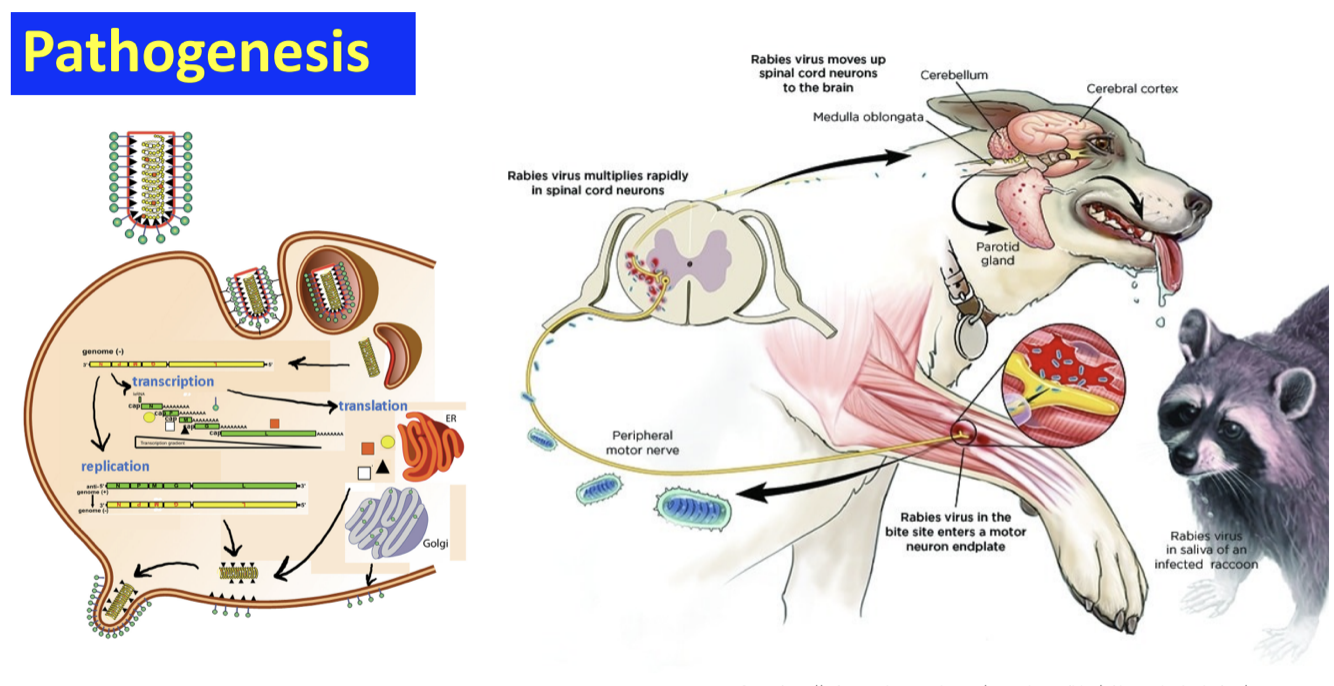
Clinicopathological feature in animals of RABV
Incubation period
3 to 12 weeks
Rarely exceeding 6 months
Phases / Stages:
PRODROMAL
2 to 3 days
Various behaviors and symptoms
FURIOUS (excitement)
Up to a week
Suddenly becomes vicious and behaves erratically
PARALYTIC
Paralysis, first in the wounded limb and then in the neck and head
3-12 weeks
incubation period of RABV generally
6 months
RABV incubation period can range from days to months but it rarely exceeds ____?
Phases or Stages of RABV Disease
Prodromal
Furious
Paralytic stage
2-3 days
How long is prodromal period
Prodromal in Animals
2-3 days
May show various behaviors and symptoms
1 week
Furious stage can last up to ____
Furious in Animals
Can last up to 1 week
Suddenly becomes vicious and behaves erratically
Paralytic in Animals
Develops paralysis
Wounded limb → Neck → Head
RABV Cases
Suspected Case
Hypersalivation
Paralysis
Lethargy
Abnormal aggression
Abnormal vocalization
Diurnal (if nocturnal)
Probable Case
History of bite by another animal
Suspect animal died within 4-5 days
Confirmed Case
Via diagnostic tests
Not a case
Ruled out
Clinicopathological feature in humans of RABV
Incubation Period: 2-3 months, up to 1 year
Viral replication in dorsal root ganglia
Pain, Paranesthesia and Pruritus
Short prodromal phase → Neurological
Exposure → Incubation 20-90D → Prodromal 1-2D → Neurologic 1-4D → Death (1-7D)
2-3 months, up to 1 year
Incubation period of RABV in humans
Dorsal root ganglia
Viral replication of RABV in humans
1-2 days
Prodromal stage in humans
1-4 days
Acute neurological phase in humans by RABV
1-7 days
Death in humans by RABV
Diagnosis of RABV in Animals
Pre-exposure
PPE
Samples transported in cold chain
Frozen cold packs
Triple packaging
Brain
Thalamus
Pons
Medula
Structure of Choice - Thalamus
Pool of brain tissues including brainstem
Detection of viral Ag
Fluiorescent Antibody Tests (FAT)
Direct Rapid Immunohistochemical Test (dRIT)
Ag ELISA
Detection of viral replication
Cell culture test (RTCIT)
Mouse inoculation test (MIT)
Molecular techniques
RT-PCR
Serology tests
Virus Neutralization: FAVN and RFFIT
Ab ELISA
Field Surveillance
Rapid Immunodiagnostic Tests (RIDT)
Rapid Immunochromatographic Tests (RICT),
Lateral Flow Devices (LFD)
Thalamus
Structure of choice in brain
Diagnosis of RABV in humans
Ag Detection
Virus Isolation
Neutralizing Ab Test
RT-PCR
IFA
Prevention and Control of RABV
STOP-R
Socio-cultural
Responsible dog ownership
Technical
Strengthen animal health and public health systems
Organizational
Ensure sufficient supply of vaccines
Political
Promote One Health
Investments in rabies elimination strategies
Resources
Create sustainable human and funding resources
Vaccinate Program for Animals
Animal Birth Control
Promotion of responsible ownership
Education Campaign
Expansion of human
PEP (post exposure prophylaxis)
PEP (Post Exposure Prophylaxis
Emergency response to a rabies exposure.
Prevents the virus from entering the central nervous system, which would invariably result in death
Consists of:
Extensive washing with water and soap for at least 15 minutes
and local treatment of the wound as soon as possible after a
suspected exposure
A course of potent and effective rabies vaccine that meets WHO
standards
Administration of rabies immunoglobulin or monoclonal
antibodies into the wound, if indicated.
Categories of contact and recommend PEP

II and III
Categories requiring PEP
Rabies-Suspect Submission Flow
Owner, Barangay, Private Animal Clinic, ABTC
→ TAHOA (Temporary Animal Holding and Observational Area)
→ TAHOF (Temporary Animal Holding and Observational Facility - IMPOUND)
Freedom from Rabies
The World Organization for Animal Health has established standards for surveillance systems used to declare an area free from disease
Disease is notifiable
An ongoing system of effective disease surveillance has been in operation for at least 2 years without any case detection, with a minimum requirement being an ongoing early detection program to ensure investigation and reporting of rabies-suspect animals.
Post-disease elimination infrastructure is maintained to enable detection of disease recursion and any disease presence is reported to national and international agencies.
Regulatory measures for the prevention of rabies are implemented, particularly restrictions on the importation of high-risk animals from rabies-endemic countries.
National Rabies Prevention and Control Program Strategic Plan 2020-2025
Vision
Rabies Free Philippines by 2030
Goal
To end human deaths from dog-mediated rabies by 2027
Activities
Mass vaccination of Dogs
Establishment of a central database system for registered and vaccinated Dogs
Impounding, field control and disposition of unregistered, Stray and unvaccinated Dog
Conduct of information and education campaign on the prevention and control of Rabies
Provision on pre-exposure treatment to high risk personnel and Post Exposure Treatment to animal bite victims
Provision of free routine immunization or Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis (P.E.P.) of schoolchildren aged five to fourteen in areas where there is high incidence of rabies as well as the encouragement of the practice of responsible pet ownership
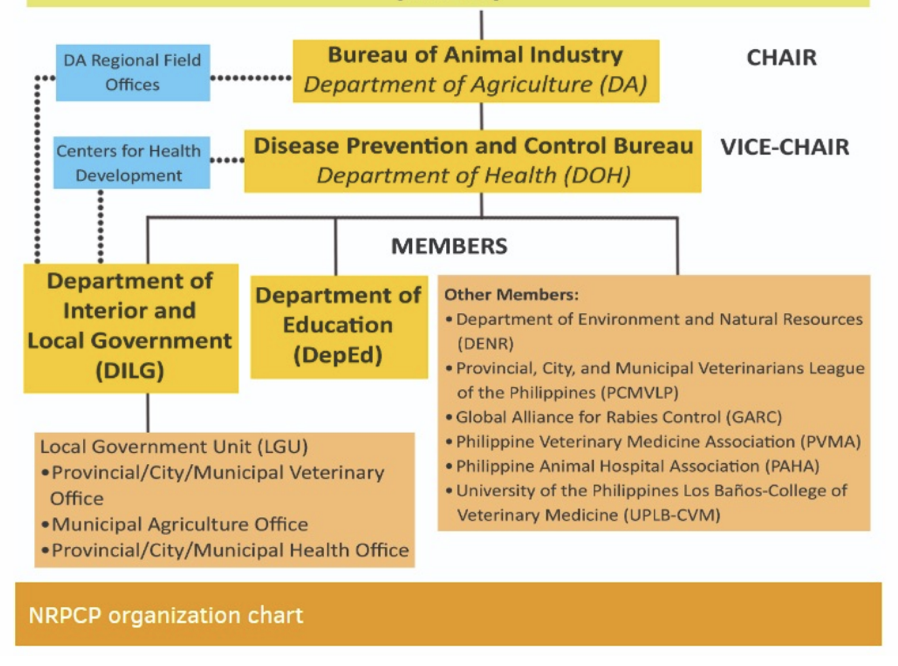
National Rabies Prevention and Control Committee (NRPCC)
Challenges of Rabies Control in the Philippines
Low canine vaccination coverage
Lack of reliable estimates of the dog population
Lack of education particularly about pet ownership
Poor mechanism for canine rabies surveillance.
Poor surveillance and lack of outbreak response activities
May lead to failure in promptly removing the source of infection for both humans and other animals
Poor rabies surveillance factors
The number of diagnostic facilities are limited
Long distance from the diagnostic facility and inadequate transportation system make it difficult for owners or bite victims to submit samples
The current current reporting system is not streamlined, which prevents real-time sharing of information
There are no guidelines or manuals for case investigation and
response
No existing case management system involving human and animal sectors upon identification of a laboratory confirmed animal rabies (LCAR) case