Lecture 22 Chemotaxis Sensing and Adaptation
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Tasks of chemotaxis sensory pathway
react to changes in stimulant concentrations on a sub second time scale
compare levels of stimulant at a given time with that 1-2 seconds earlier (short term memory)
continually refresh memory (adaptation)
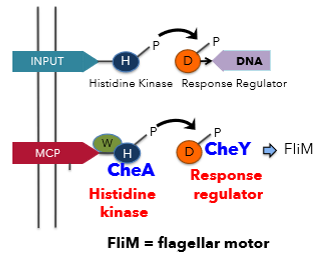
is chemotaxis a 2-component system
Yes, it involves a sensor kinase (histidine kinase, CheA) and a response regulator (CheY). Regulates direction of flagellar rotation (CW = tumble, CCW = run)
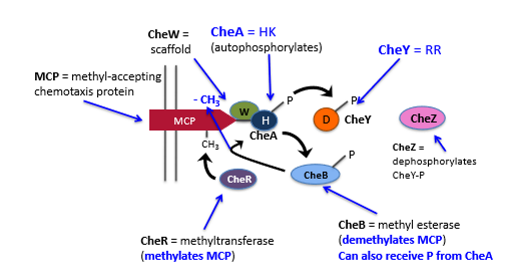
Key players in Chemotaxis
MCP = methyl accepting chemotaxis proteins
CheA (histidine kinase) = autophosphorylates
CheW = scaffold protein, ancours MCP with CheA.
CheY (response regulator) = governs direction of flagellar rotation. P transferred from Histidine residue in CheA to aspartate residue in CheY. When phosphorylated binds to FliM in flagellar motor and induces CW tumbling.
CheZ = phosphatase that dephosphorylates CheY, promoting a switch back to CCW rotation.
CheR = methyl transferase (methylates MCPs)
CheB = methyl esterase (demethylates MCPs)
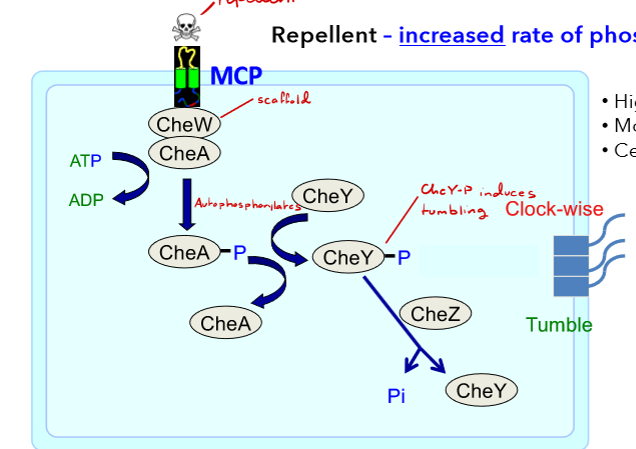
Chemotaxis Sequence of events
MCP binds chemical signal
conformational change in CheA with help from CheW causing autophosphorylation (CheA-P).
Attractants = decrease phosphorylation, CCW =run
Repellents = increase phosphorylation, CW = tumble
CheY-P interacts with flagellar motor (FliM).
CheZ dephosphorylates CheY to allow for continued runs
Repellent Present
Increase in phosphorylation
higher CheY-P, more binding to FliM, CW =tumbles
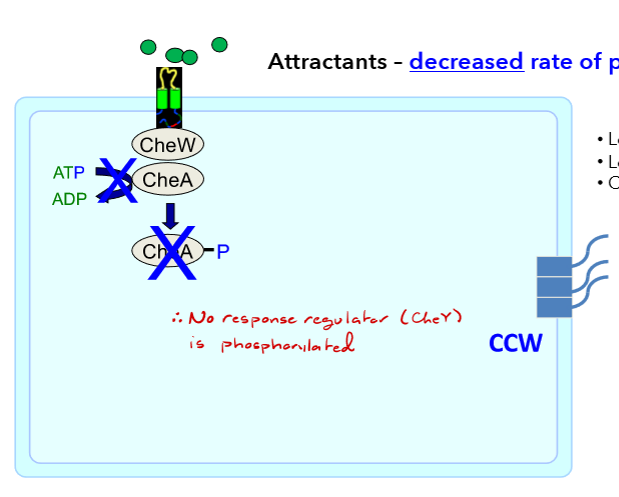
Attractant present
decrease rate of phosphorylation
lower CheY-P, less binding to FliM, CCW =cell continues to run
What determines direction of flagellar rotation
level of phosphorylation of CheY
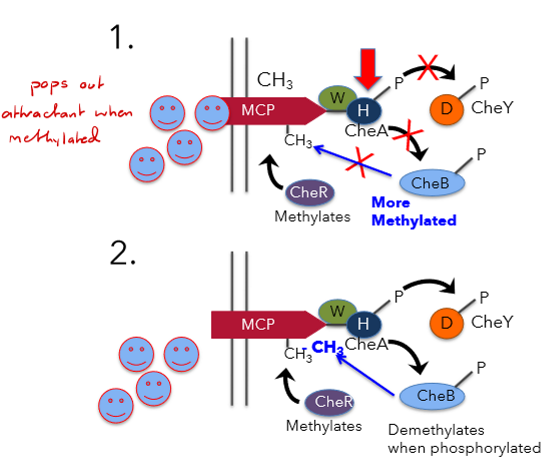
Adaptation
Sensing system is frequently reset allowing cells to respond to small changes in attractant concentrations. (attractant is ejected so the cell, can sense again). Involves modification of the MCPs
Key proteins in Adaptation
Methylating and demethylating MCPs changes the 3D structure, ejecting attractant or repellant.
CheB (methyl esterase); demethylates MCPs adn is a receptor for phosphorylation from CheA. CheB-P removes methyl groups from MCPs.
CheR (methyl transferase); methylates MCPs. continually adds methyl groups to MCPs at a slow rate.
If attractant concentration is high what happens in terms of adaptation
CheA-P low, CheY-P low, CheB-P low = less demethylation of MCPs.
Methylated MCPs no longer respond well to attractant when fulkly methylated = attractant unbinds.
Now CheA-P high, CheY-P high (tumble), MCPs demethylated by CheB-P and are ready to respond to attractants again.