Biology Discoveries and Experiments
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
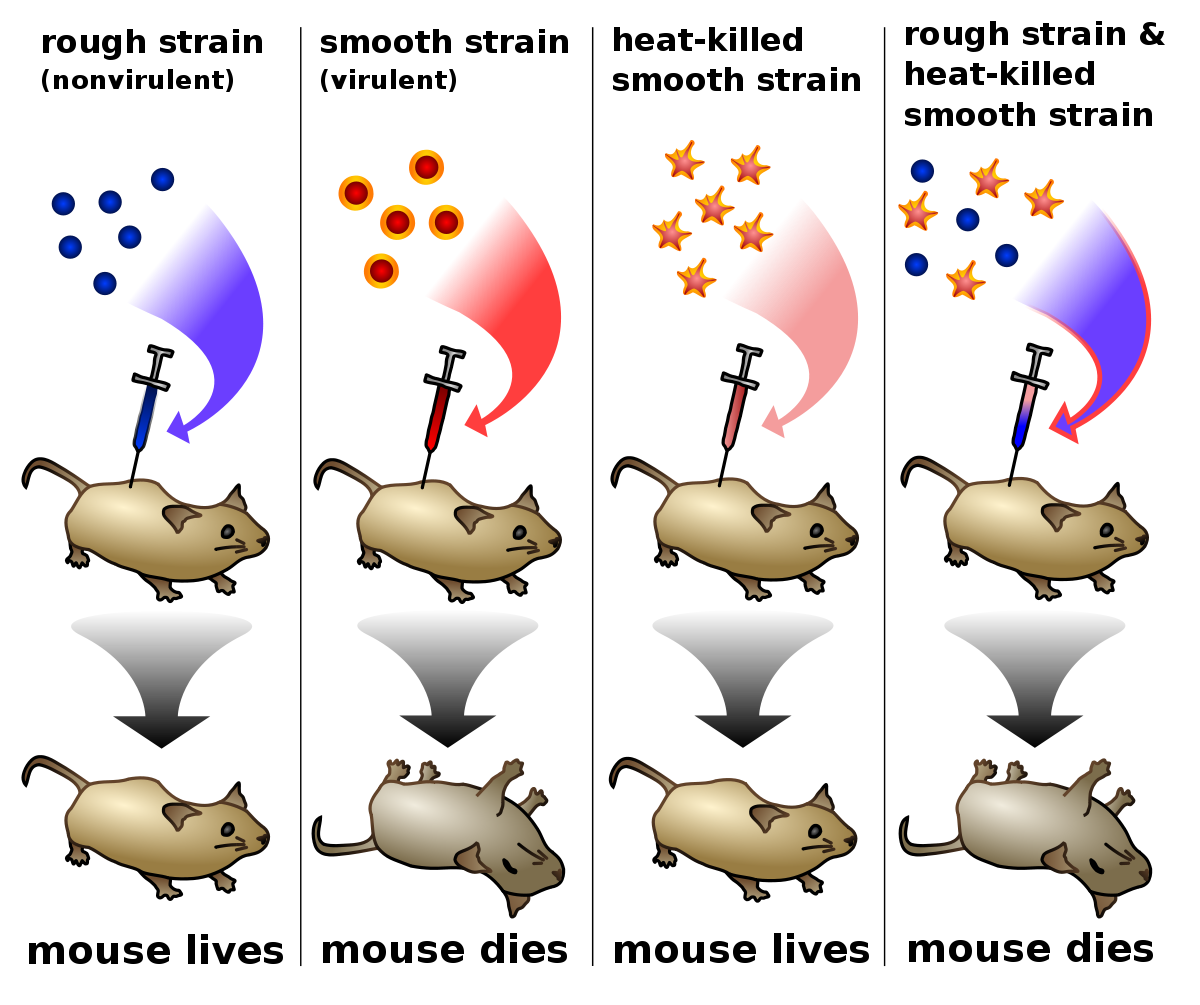
Frederick Griffith
Who, in 1928, worked with two strains of a bacterium, one pathogenic (smooth) and one harmless (rough), and injected them into mice then he mixed heat-killed remains of the smooth strain with living cells of the rough strain, some living cells became pathogenic and that mouse died?

Frederick Griffith
Who concluded there was a “transforming factor”, which is now defined as a change in genotype and phenotype due to assimilation of foreign DNA/ transformation?
Oswald Avery, Maclyn McCarty, and Colin MacLeod
Who, in 1944, isolated the molecules in the strands of the bacterium (previously used in Griffith’s experiment) into RNA, proteins, and DNA and after breaking down RNA and proteins, the heat killed smooth cells still could transfer?
Oswald Avery, Maclyn McCarty, and Colin MacLeod
Who figured that the transforming substance was DNA and left biologists skeptical and ignoring this conclusion because they thought DNA was too simple to do these processes?
Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase
Who, in 1952, grew two bacteriophages one tagged with radioactive sulfate (is found in proteins) and the other tagged with radioactive phosphorus (found in DNA), and after allowing this two viruses to infect bacteria and separating the viral protein coats from the bacterial cells using a blender and centrifugation, they found that only the radioactive phosphorus entered the bacterial cells?
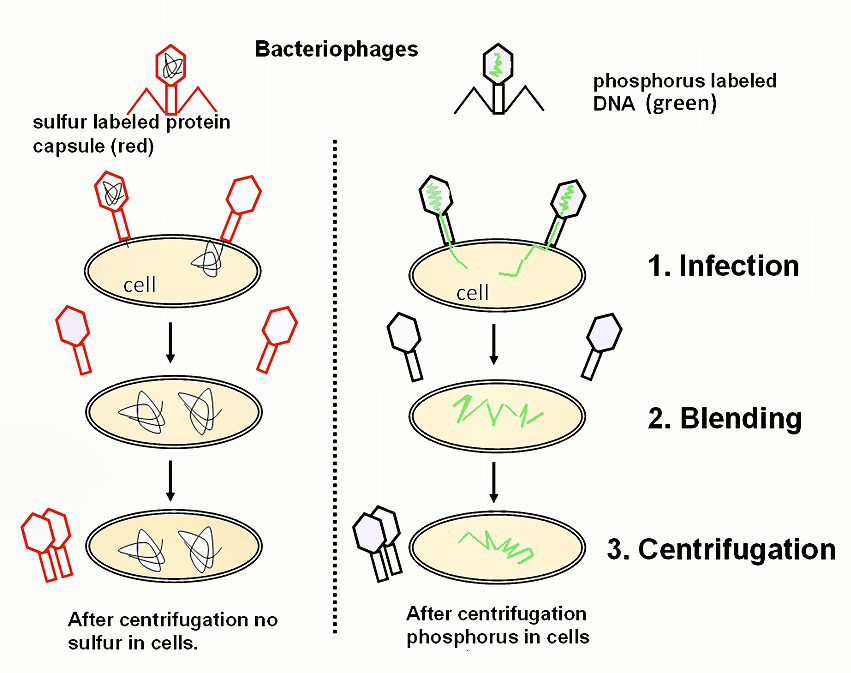
Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase
Who concluded that DNA (rather than protein) is the genetic material being transferred and inherited into other organisms?
Erwin Chargaff
Who studied and counted the different amounts of each base (A,T, C, G) in several organisms’ DNA?
Erwin Chargaff
Who concluded that in ANY species there is an equal number of A and T bases, and an equal number of G and C bases?
Rosalind Franklin and Maurice Wilkins
What two scientists, that didn’t work together, used a technique called x-ray crystallography to study molecular structure and ended up studying images of DNA fibers?
Rosalind Franklin and Maurice Wilkins
Whose credit is often forgotten when thinking of the discovery of the helix shape, but did actually discover that the DNA molecule was double stranded and twisted?
James Watson and Francis Crick
Who used x-ray crystallographic images from Franklin and Wilkins to figure that DNA was helical and calculate the width of the helix and the spacing of the nitrogenous bases which suggested that the DNA molecule was made up of two strands?
James Watson and Francis Crick
Who introduced and got credit for the double-helix for DNA?
Matthew Meselson and Franklin Stahl
Who grew E. Coli cells in the presence of nitrogen (which is found in DNA and makes DNA heavier) and then used centrifugation to separate heavy DNA from cells and then grew cells in the presence of light nitrogen which then after one cell division half of the molecule contained heavy DNA and half contained light DNA and after the second cell division in the presence of light nitrogen, the molecule would only contain light DNA?
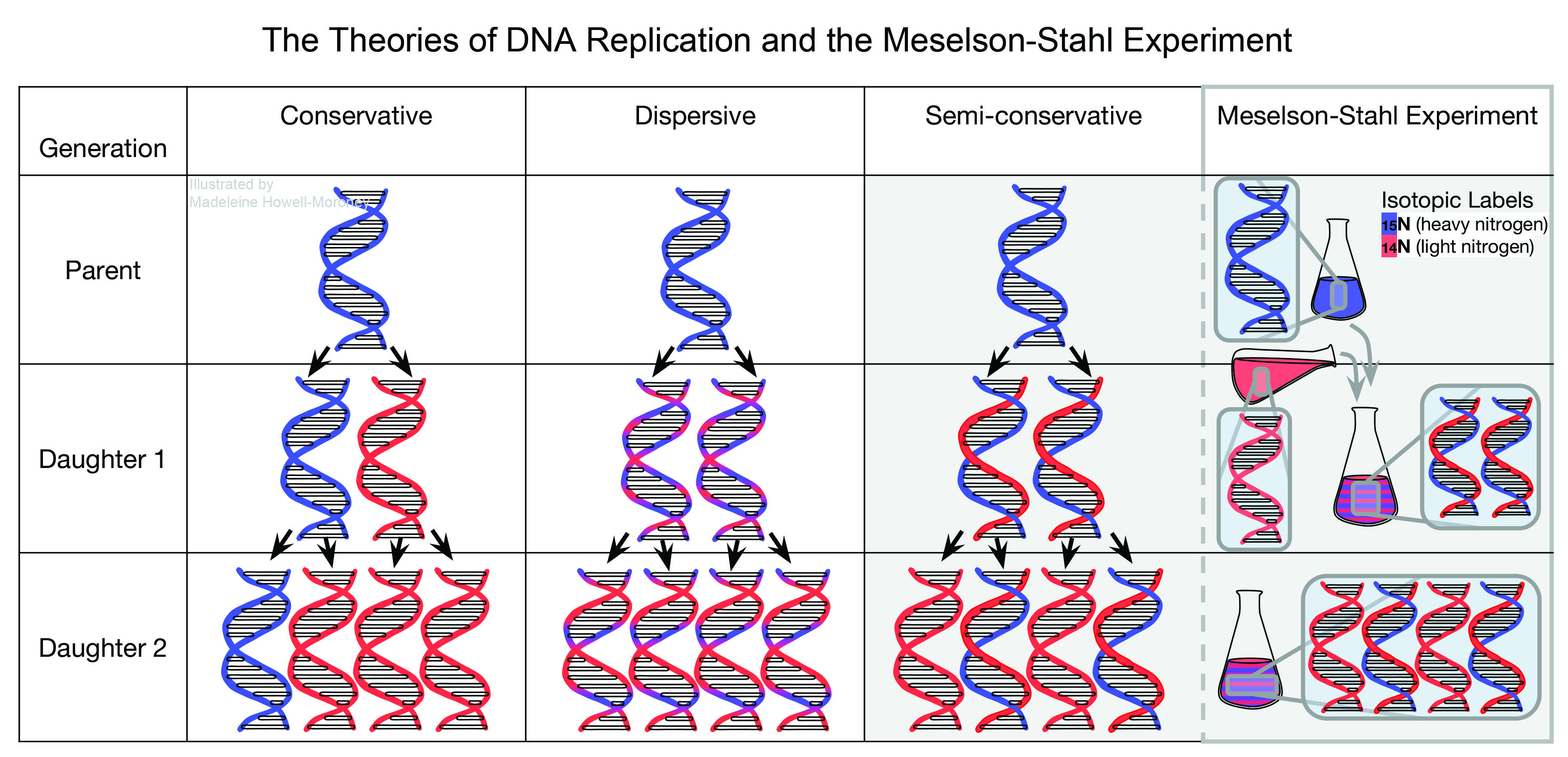
Matthew Meselson and Franklin Stahl
Who provided evidence for the Watson’s and Crick’s DNA replication was semi-conservative hypothesis and proved that when DNA replicates, each new molecule will have one old strand from the parent molecule and one newly made strand?
Archibald Garrod
Who took observations of patients with inherited disorders realizing that their genes were showing these phenotypes and their bodies were showing these symptoms because they unable to to synthesize a certain enzyme?
Archibald Garrod
Who after linking genes to enzymes, figured that cells synthesize and break down molecules in a series of steps (a metabolic pathway)?
George Beadle and Edward Tatum
Who exposed bread mold to X-rays, creating mutants that were unable to survive on a basic nutrient source, that were unable to make specific amino acids, in each one, a mutation had "broken" an enzyme needed to build a certain amino acid, and developed a one gene–one enzyme hypothesis, which states that each gene dictates production of a specific enzyme
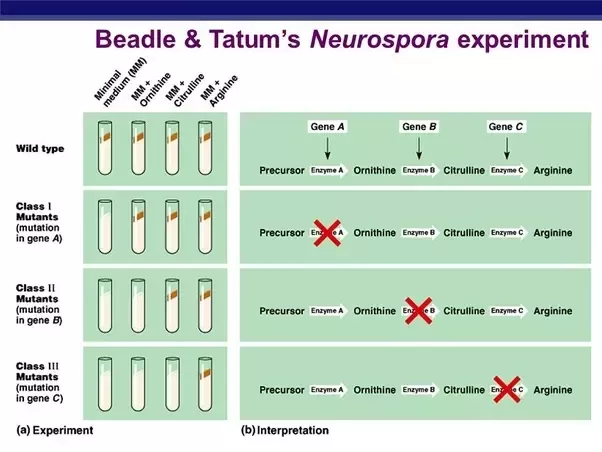
George Beadle and Edward Tatum
Who later figure out some proteins aren’t enzymes, so then edited the hypothesis to one gene–one protein, many proteins are composed of several polypeptides, each of which has its own gene, hypothesis is now the one gene–one polypeptide hypothesis?
Marshall Warren Nirenberg
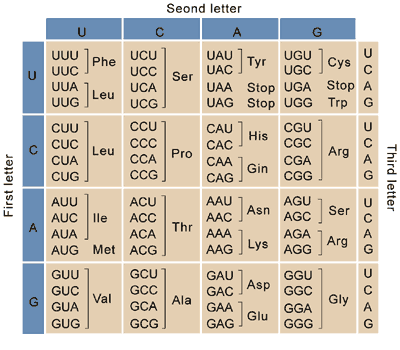
Who in 1961 took E. Coli extract and mixed that with all 20 amino acids (one being radioactive), making them all radioactive solutions poured into 20 test tubes and then added Poly U (a synthetic RNA containing only UUU), in one tube they found that an amino acid was specified by the Poly U since the mRNA transcribes genetic information from DNA, turning amino acids into proteins, they repeated this with PolyA, C, and G, discovering more codons and later identified all 64 codons?
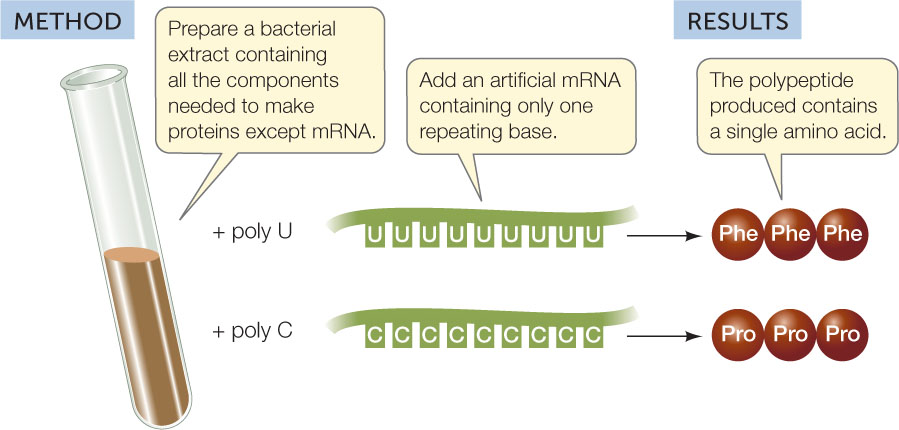
Marshall Warren Nirenberg
Who “cracked the code” and figured of the 64 triplet codons, 61 code for amino acids; 3 triplets are “stop” signals that end translation, multiple letter codes can be the same amino acid but no codon specifies more than one amino acid?