Anatomy and Physiology- The Peripheral Nervous System
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
The Peripheral Nervous System
the sensory and motor neurons that connect the central nervous system to the rest of the body
Somatic Nervous System
the division of the peripheral nervous system that is under conscious control. Connects the CNS to the body's skeletal muscles and skin
The Autonomic Nervous system
the division of the peripheral nervous system that is not under conscious control. Connects the body's organs to the central nervous system
Endoneurium
delicate connective tissue around individual nerve fibers in nerve
Perineurium
Thick sheet of connective tissue that holds many nerve fibers together.
Epineurium
Dense connective tissue that surrounds entire nerve including fascicles and blood vessels.
Sensory Nerve
carries messages toward the brain and spinal cord from a receptor; afferent nerve
Motor nerves
Efferent nerves, Nerves that carry information from the central nervous system to the muscles or glands of the body.
Mixed Nerves
nerves carrying both sensory and motor fibers
olfactory nerve (I)
Sensory nerve only
Associated with sense of smell
Optic Nerve (II)
sensory only nerve, Associated with sense of vision
Oculomotor Nerve (III)
Primarily motor nerve, moves the eyes and eyelids, adjusts the amount of light entering the eye.(autonomic)
Small sensory component (proprioceptive fibers)
Trochlear Nerve (IV)
Smallest pair of cranial nerves
Primarily motor nerve
Motor impulses to one pair of muscles that move the eyes
Trigeminal Nerve (V)
Mixed nerve with three branches; Opthalmic, Maxillary, and Mandibular. All three branches provide sensory information. Also controls muscles of mastication (Chewing)
Abducens Nerve (VI)
Primarily motor nerve
Motor impulses to one pair
of muscles that move the eyes
Some sensory (proprioceptive
fibers)
Facial Nerve (VII)
a mixed nerve. Sensory from taste receptors Motor to muscles of facial expression, tear glands, and salivary glands
vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII)
Acoustic or auditory nerve
Sensory nerve only made of 2 branches:
Vestibular and Cochlear branches
Vestibular branch of CN VIII
Sensory from equilibrium receptors of ear
Cochlear Branch of CN VIII
Sensory from hearing receptors
Glossopharyngeal Nerve (IX)
Mixed nerve
Sensory from pharynx, tonsils, part of tongue
Motor to salivary glands and muscles of pharynx (for swallowing)
Vagus Nerve (X)
Mixed nerve,
*Somatic motor to muscles of speech and swallowing
*Autonomic motor to heart,
other viscera of thorax and abdomen
*Sensory from pharynx, larynx, esophagus, and viscera of thorax and abdomen
Accessory Nerve (XI)
Primarily a motor cranial nerve; innervates muscles to control swallowing and innervates other muscles to move head, neck, and shoulders
Hypoglossal Nerve (XII)
Primarily motor
Motor to muscles of the tongue for speaking, chewing, swallowing
spinal nerves
31 pairs of nerves arising from the spinal cord
number of cervical spinal nerves
8 pairs
number of thoracic spinal nerves
12 pairs
number of lumbar spinal nerves
5 pairs
number of sacral spinal nerves
5 pairs
number of coccygeal spinal nerves
1 pair
dermatome
Area of skin supplied by a single spinal nerve
cervical plexus
C1-C4; innervates superficial neck structures, skin of neck, posterior portion of head
brachial plexus
C5-T1
innervates the pectoral girdle and upper limbs
musculocutaneous nerve
Supply muscles of anterior arms and skin of forearms
ulnar and median nerves
Supply muscles of forearms and hands, skin of hands
radial nerve
Supply posterior muscles of arms and skin of forearms and hands.
Axillary Nerve
Supply muscles and skin of anterior, lateral, and posterior arms.
lumbosacral plexus
Formed of L2-S2 rami. Supplies the lower limb.
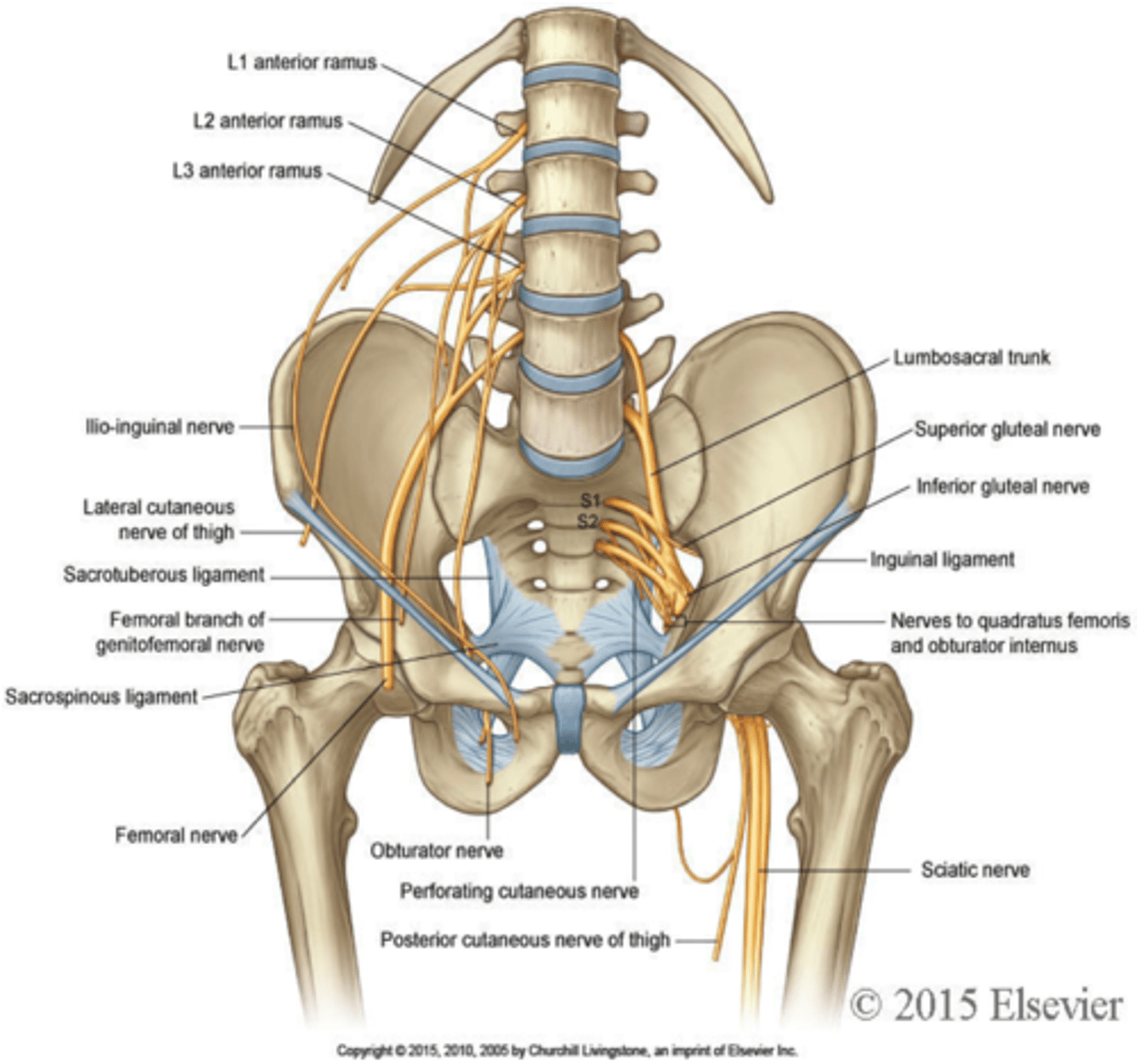
obturator nerve
passes through obturator foramen to innervate adductor muscles
femoral nerve
innervates quadriceps and skin of anterior thigh and medial surface of leg
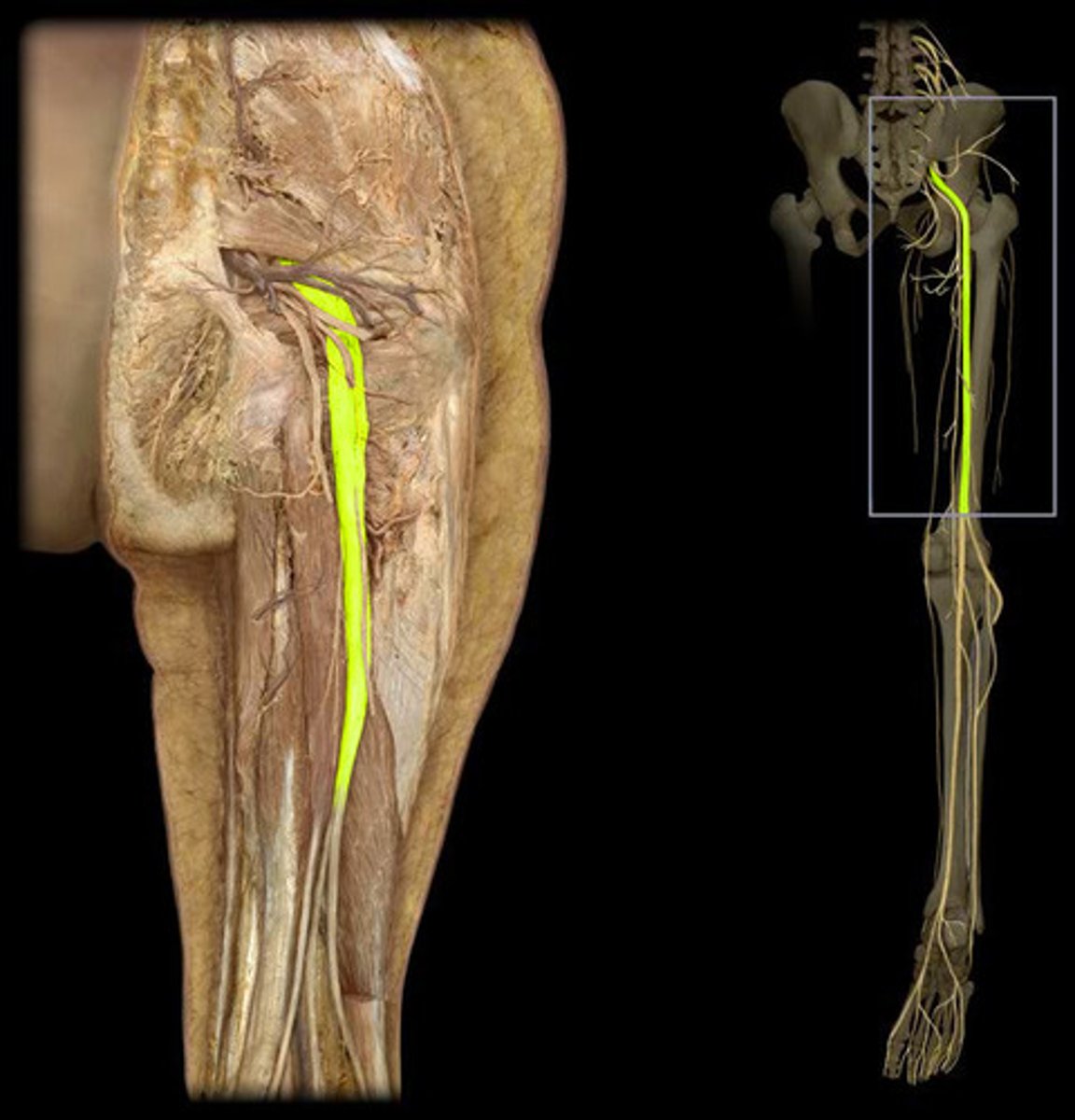
sciatic nerve
Supply muscles and skin of thighs, legs and feet; largest and longest nerve in the body