Vet Anatomy 2 Quiz 2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/165
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:46 AM on 1/12/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
166 Terms
1
New cards
what nerve innervates trapezius, omotransversarius, and brachiocephalicus
accessory n & cervical spinal n
2
New cards
what nerve innervates rhomboideus
dorsal rami cerival spinal n
3
New cards
what nerve innervates latissimus dorsi
thoracodorsal n.
4
New cards
what nerve innervates serratus ventralis
long thoracic n
5
New cards
what nerve innervates pectoralis superficialis
cranial pectoral n
6
New cards
what nerve innervates pectoralis profundus
caudal pectoral n
7
New cards
what nerve innervates deltoid, teres major, teres minor
axillary n
8
New cards
what nerve innervates infraspinatus and supraspinatus
suprascapular n
9
New cards
what nerve innervates subscapularis
subscapular n
10
New cards
what nerve innervates coracobrachialis
musculocutaneous n
11
New cards
what muscles elevate the scapula
trapezius and rhomboid
12
New cards
what muscles depress the scapula
serratus ventralis
13
New cards
what muscles advance/move forward/move glenoid cranially (of scapula)
trapzeius, brachiocephalicus, omotransversarius
14
New cards
what muscles retract/move back/ move glenoid caudally (of scapula)
trapezius, latissimus dorsi, pectoralis profundus
15
New cards
what muscles extend the glenohumeral joint
supraspinatus and brachiocephalicus
16
New cards
what muscles flex the glenohumeral joint
deltoid, teres minor, teres major, latissimus dorsi, pectoralis profundus, long head of triceps brachii
17
New cards
what muscles ABduct the glenohumeral joint
infraspinatus
18
New cards
what muscles ADduct the glenohumeral joint
pectoralis profundus, pectoralis superficialis, subscapularis, coracobrachialis
19
New cards
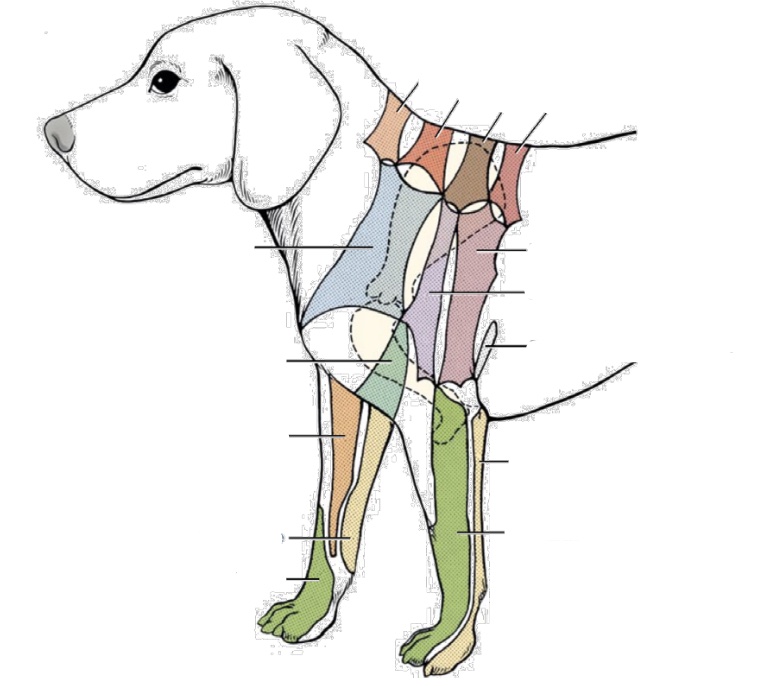
what nerve innervates yellow area on forelimb
ulnar nerve
20
New cards
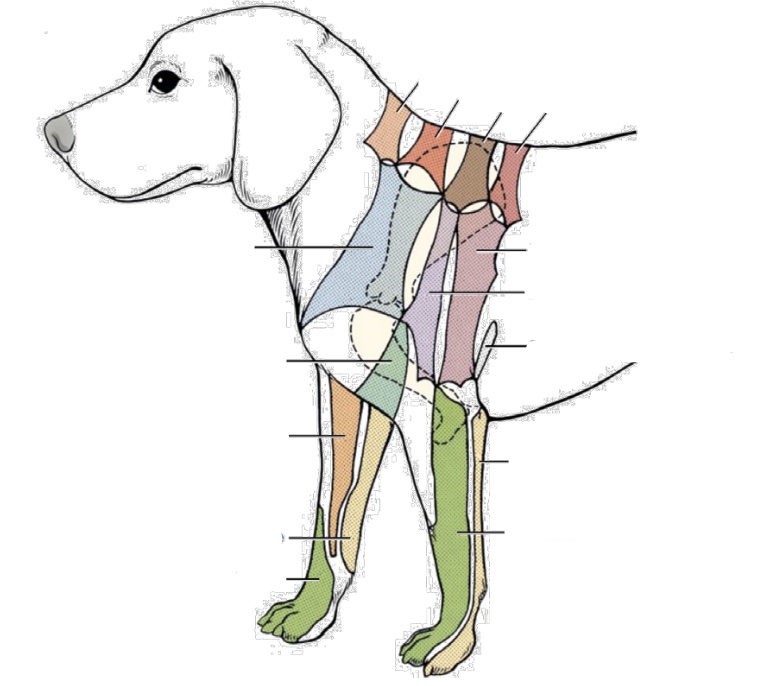
what nerve innervates green area on forelimb
radial nerve
21
New cards
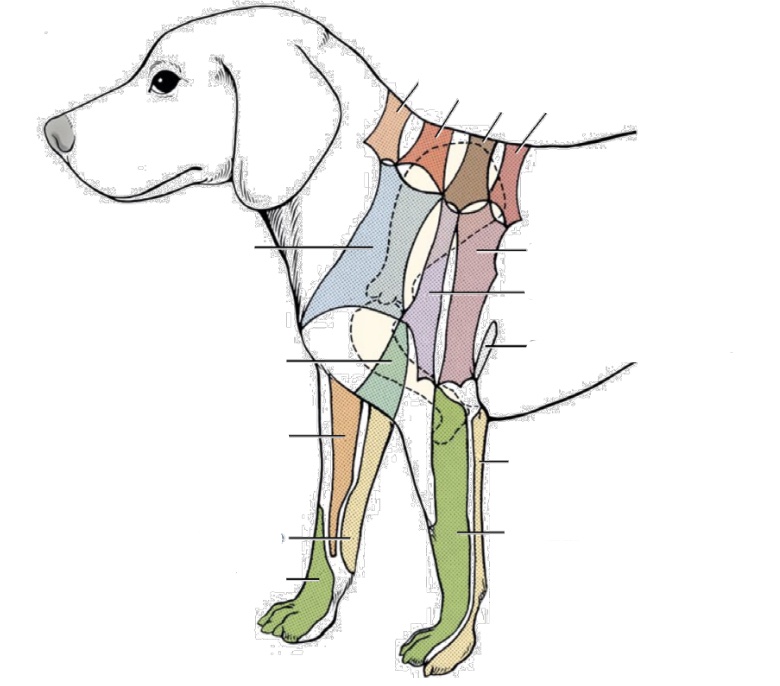
what nerve innervates orange area on forelimb
musculocutaneous
22
New cards
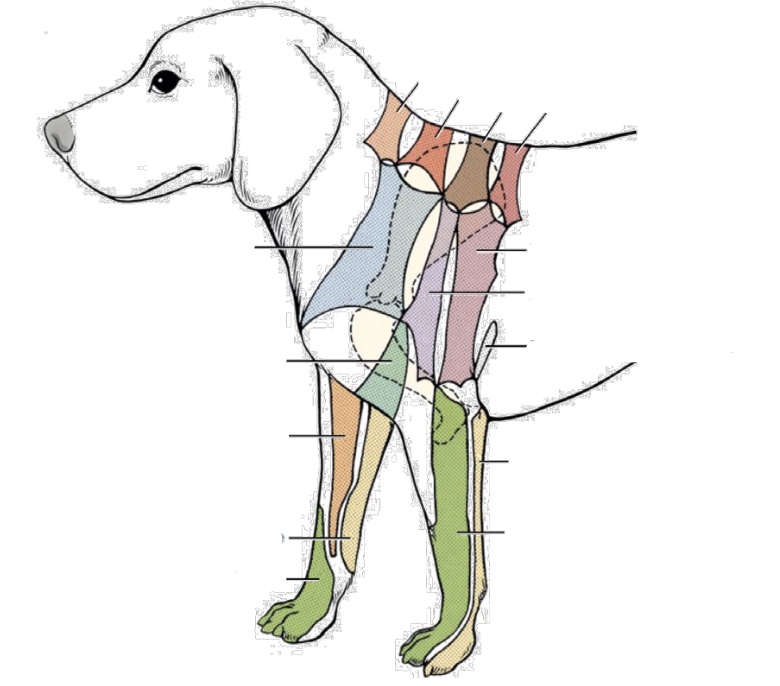
what nerve innervates teal area on chest
brachiocephalic nerve
23
New cards
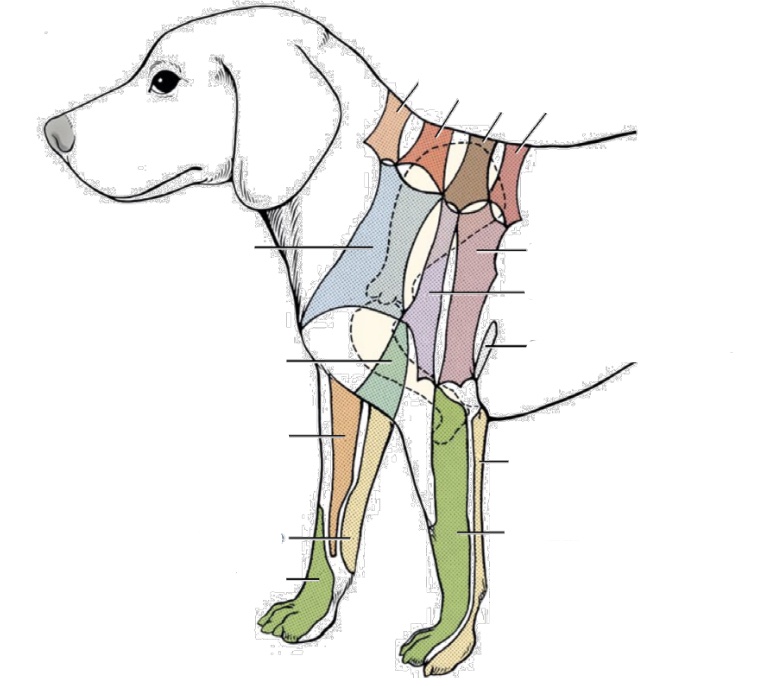
what nerve innervates blue area on chest
C5 ventral cutaneous branch
24
New cards
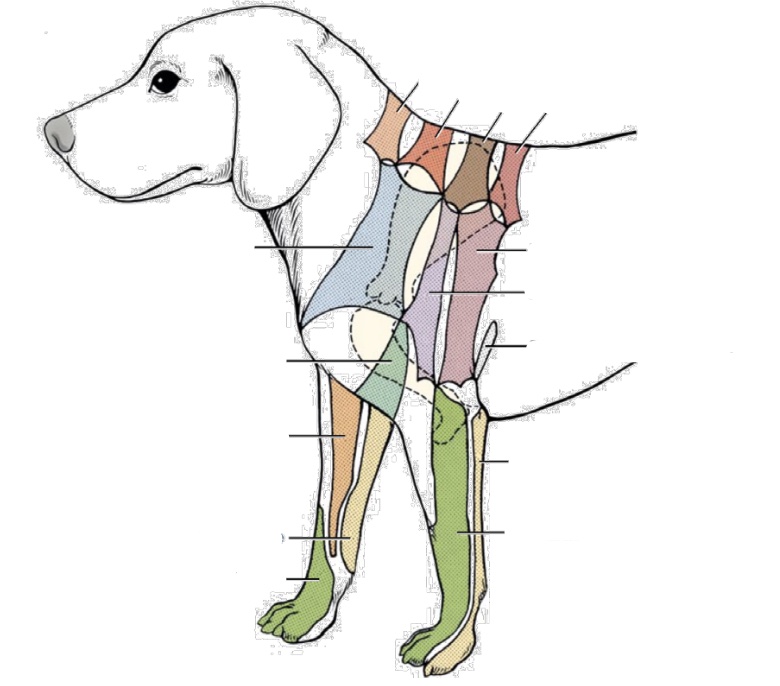
what nerve innervates purple area on chest
axillary nerve
25
New cards
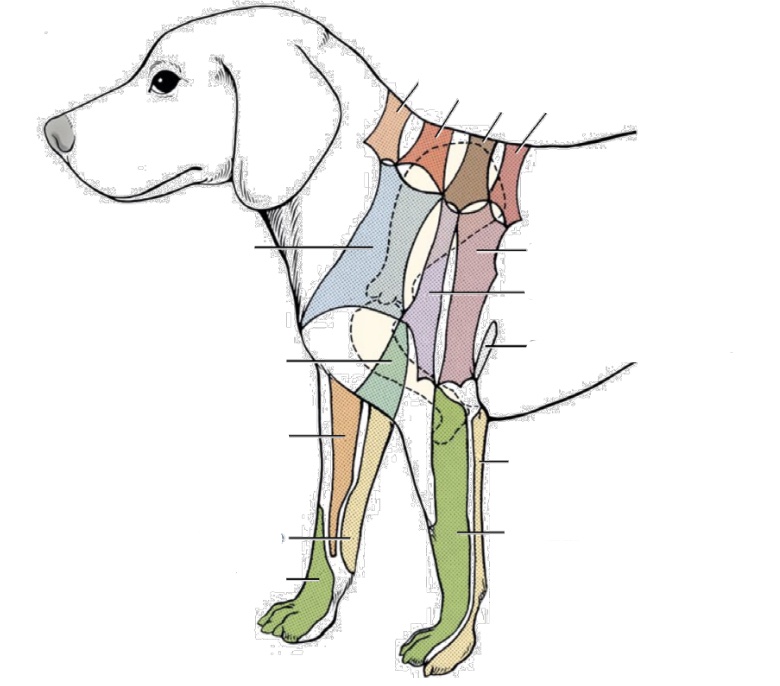
what nerve innervates pink area (next to purple) on chest
T2 lateral cutaneous branch
26
New cards
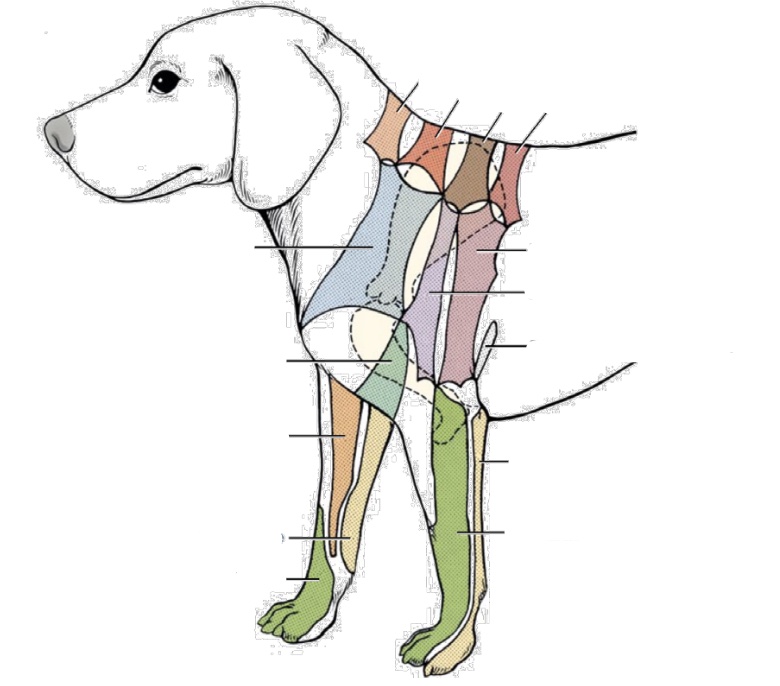
what nerve innervates light orange (cranial one along dorsal spine)
C5 dorsal cutaneous branches
27
New cards
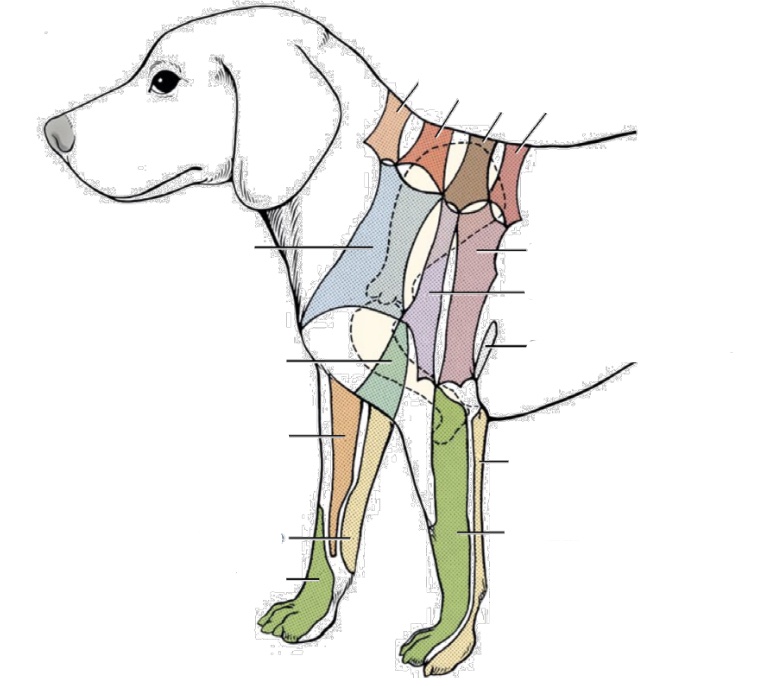
what nerve innervates dark orange (next to light orange, along dorsal spine)
C6 dorsal cutaneous branches
28
New cards
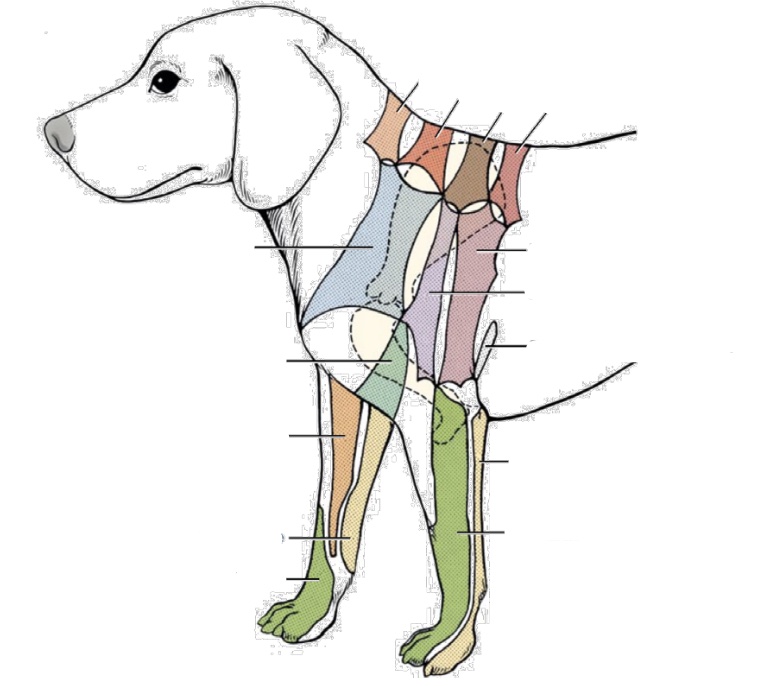
what nerve innervates brown area
T2 dorsal cutaneous branches
29
New cards
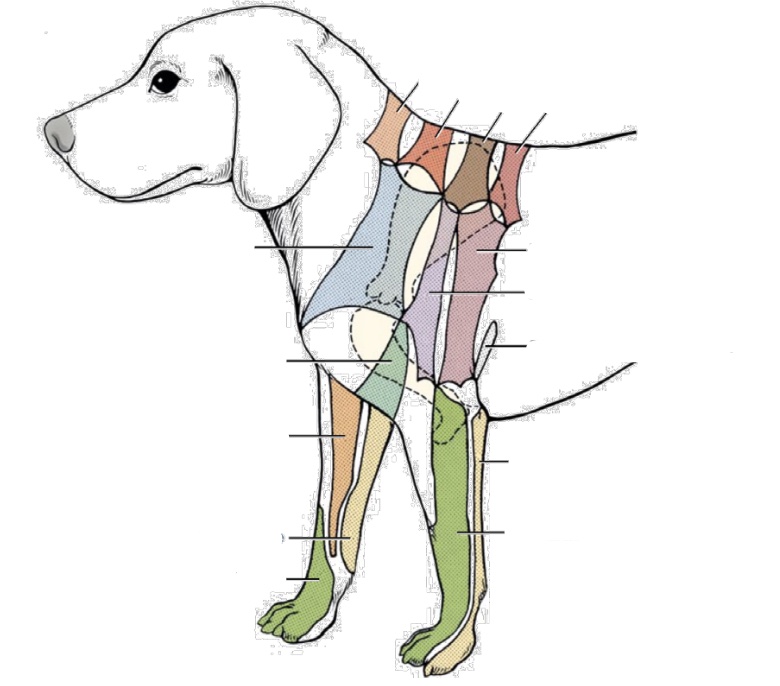
what nerve innervates salmon area (along dorsal spine)
T3 dorsal cutaneous branches
30
New cards
parts of pectoral girdle
clavicle, coracoid, scapula
31
New cards
how is the forelimb connected
via fibromuscular attachments
32
New cards
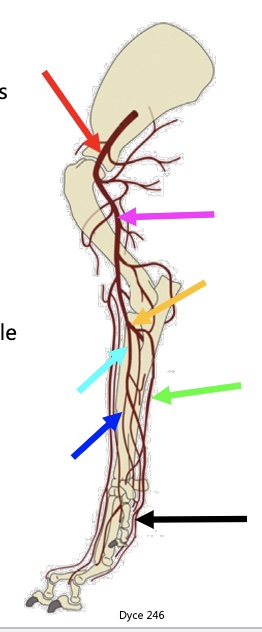
above red arrow
subclavian artery
33
New cards
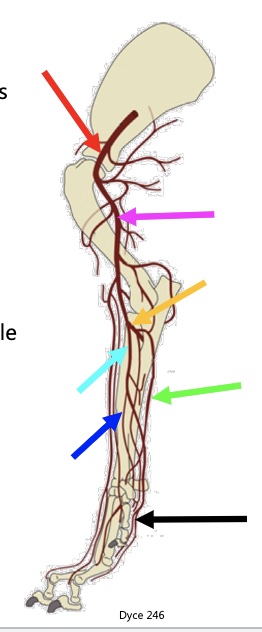
red arrow
axillary a
34
New cards
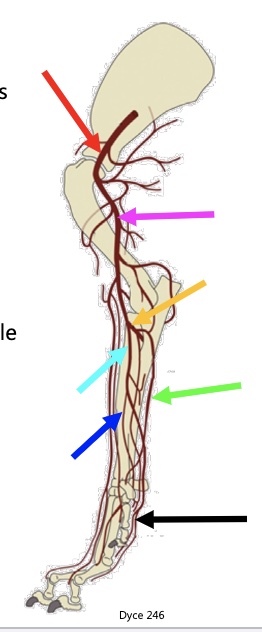
pink arrow
brachial a
35
New cards
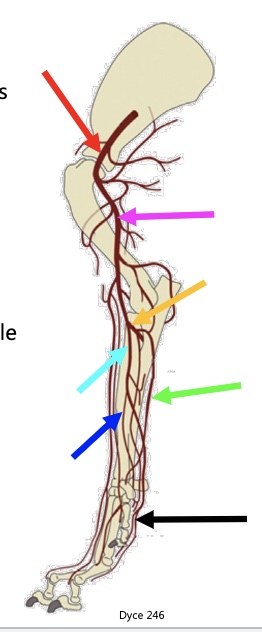
yellow arrow
common interosseous a
36
New cards
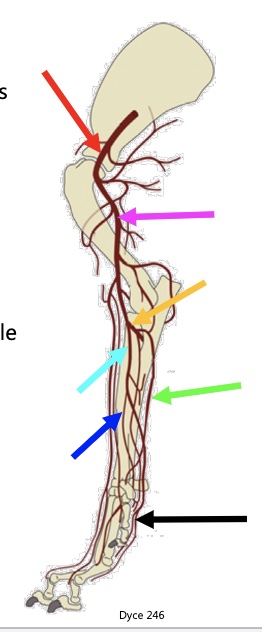
light blue arrow
median a.
37
New cards
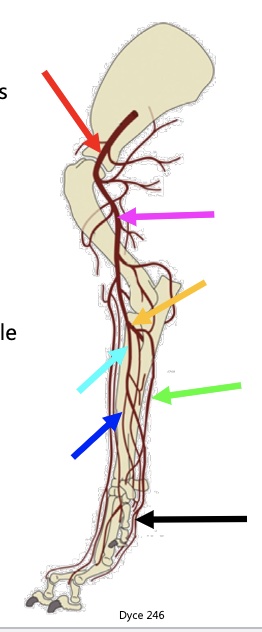
green arrow
ulnar a.
38
New cards
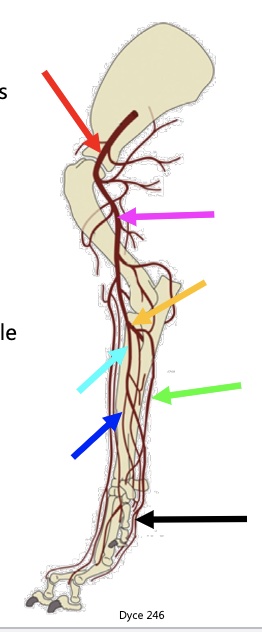
dark blue arrow
radial a.
39
New cards
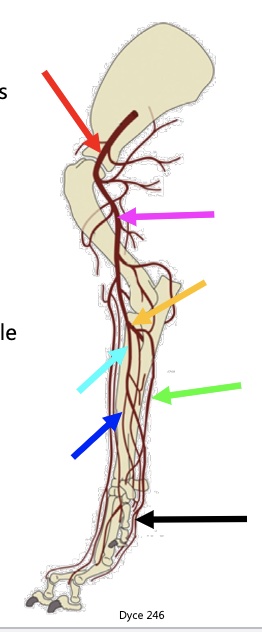
black arrow
metacarpal & carpal arteries
40
New cards
what are the 3 branches of the axillary artery
long thoracic, thoracodorsal, and subscapular arteries
41
New cards
what is the branch of the brachial artery
deep brachial a
42
New cards
where does the suprascapular artery come from
directly off subclavian artery
43
New cards
external jugular vein →
omobrachial v. → axillobrachial v. → cephalic v.
44
New cards
flexors of arm muscles (also flex forearm)
biceps brachii & brachilais
45
New cards
extensors of arm muscles (also extend forearm)
all heads of triceps brachii, tensor fascia antebrachii, anconeus
46
New cards
innervation of flexor of arm muscles
musculocutaneous n.
47
New cards
innervation of extensors of arm muscles
radial n.
48
New cards
where do all the heads of triceps brachii muscle insert
olecranon of ulna
49
New cards
what happens when there is problems/damage to olecranon of ulna “alvusion fracture”
dropped elbow apperance, loss of elbow extension, inability to support weight of limb; radial n issue; loss of triceps brachii
50
New cards
why can biceps brachii affect both the radius and ulna at the same time
bc it has 2 insertions, one deep one superficial
51
New cards
brachial v and cephalic v come together via
median cubital vein
52
New cards
what is within the cubital fossa
medial nerve, ulnar nerve, brachial artery, brachial vein, cephalic vein, median cubital vein
53
New cards
dorsal collateral lig in wrist of dogs
short; connect neighboring bones
54
New cards
medial/lateral collateral ligs in wrist of dogs
prevent excessive AB/Dduction
55
New cards
deep palmar lig in wrist of dogs
covers entire skeletal surface, hides unevenness of bones so they dont impact the limb
56
New cards
superficial transverse lig in wrist of dogs
“flexor retinacula”; encloses carpal tunnel
57
New cards
distal ligs of accessory bone in wrist of dogs
helps prevent overextension while not affecting flexion
58
New cards
craniolateral muscles of antebrachium
supinator, brachioradialis, extensor carpi radialis, common digitial extensor, lateral digital extensor, ulnaris lateralis, abductor digiti 1 longus, extensor digiti 1 and 2
59
New cards
innervation of craniolateral muscles of antebrachium
radial n
60
New cards
function of craniolateral muscles of antebrachium
extensors and supinators
61
New cards
exceptions to craniolateral muscles of antebrachium
ulnaris lateralis acts as a flexor
62
New cards
origin of craniolateral muscles of antebrachium
lateral epicondlye of humerus
63
New cards
caudal muscles of antebrachium
pronator teres, pronator quadratus (very deep), flexor carpi radialis, flexor carpi ulnaris, superficial digital flexor, deep digitial flexor
64
New cards
innervation of caudal muscles of antebrachium
median nerve
65
New cards
function of caudal muscles of antebrachium
flexion and pronation
66
New cards
origin of caudal muscles of antebrachium
medial epicondyle of humerus
67
New cards
exceptions to caudal muscles of antebrachium
flexor carpi ulnaris is innervated by ulnar n
deep digital flexor is innervated by median & ulnar n
deep digital flexor is innervated by median & ulnar n
68
New cards
cranial to caudal lateral antebrachium muscles
extensor carpi radialis → common digital extensor → lateral digital extensor → ulnaris lateralis → flexor carpi ulnaris
69
New cards
cranial to caudal medial antebrachium muscles
extensor carpi radialis→ pronator teres → flexor carpi radialis → superficial digital flexor → deep digital flexor (2 heads, below sdf) → flexor carpi ulnaris (2 heads)
70
New cards
muscles of the manus
4 interosseous muscles
71
New cards
what innervates the 4 interosseous manus muscles
ulnar n. primarily, also median n.
72
New cards
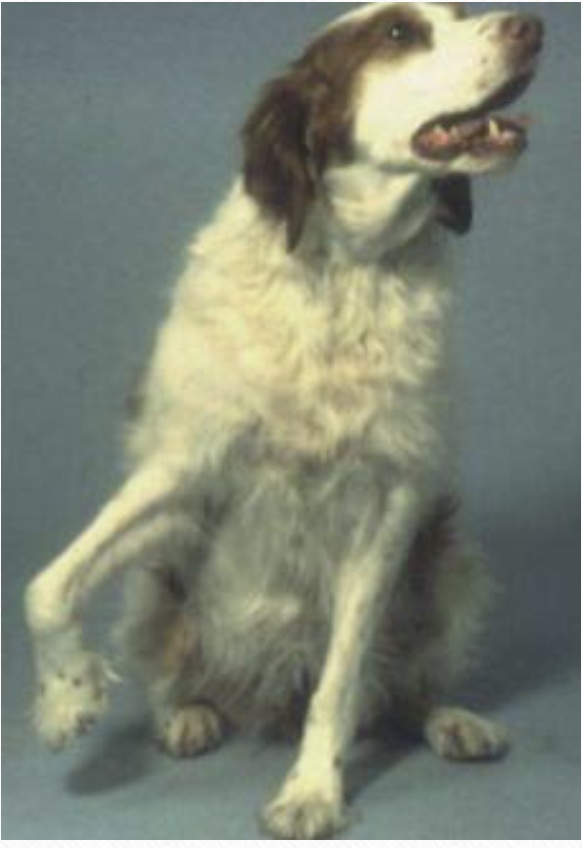

gait disorder: infraspinatus contracture
degeneration and atrophy of infraspinatus muscle fibers; unable to rotate the shoulder internally therefore circumducts limb when walking
73
New cards
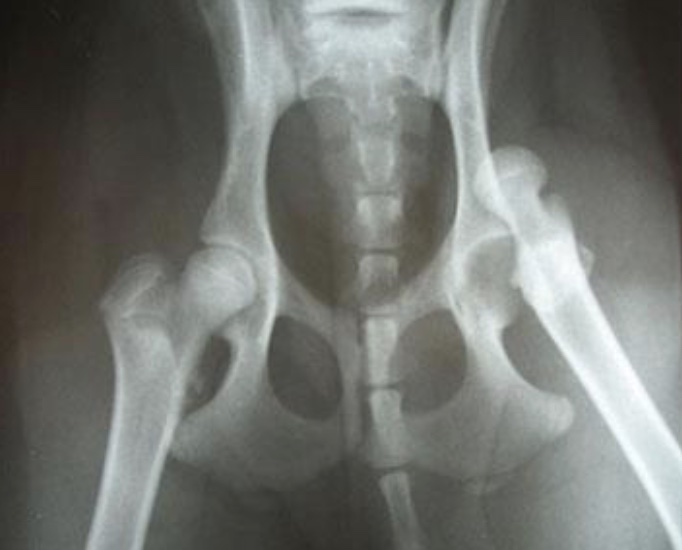
gait disorder: coxofemoral luxation
results of extreme trauma (hbc) or extreme ABduction of hip joint; limb appears shorter from behind; thigh adducted, stifle rotated outward, tarsus rotated inward
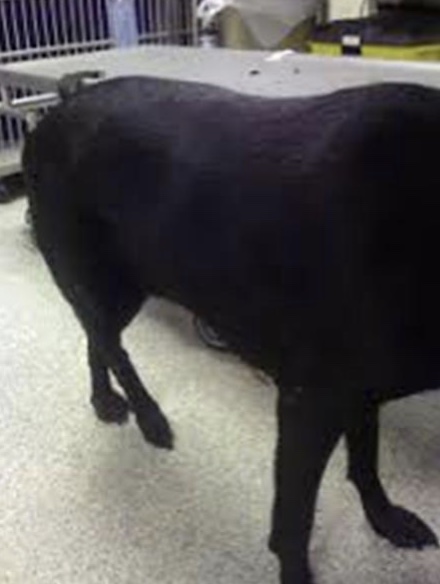
74
New cards
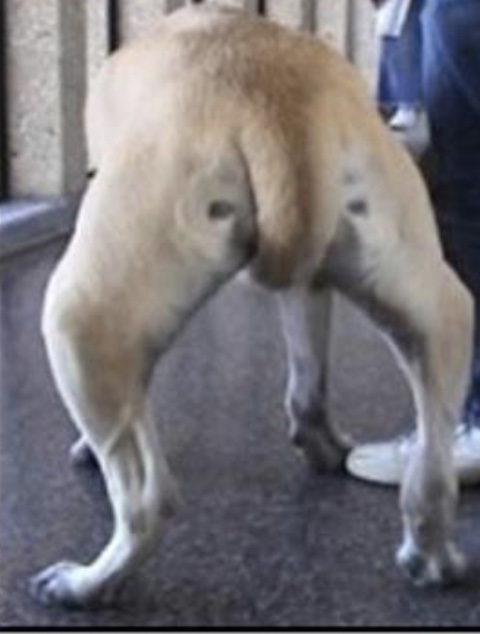
gait disorder: medial patellar luxation
bow legged stance; external rotation of hip; often asymptomatic
75
New cards
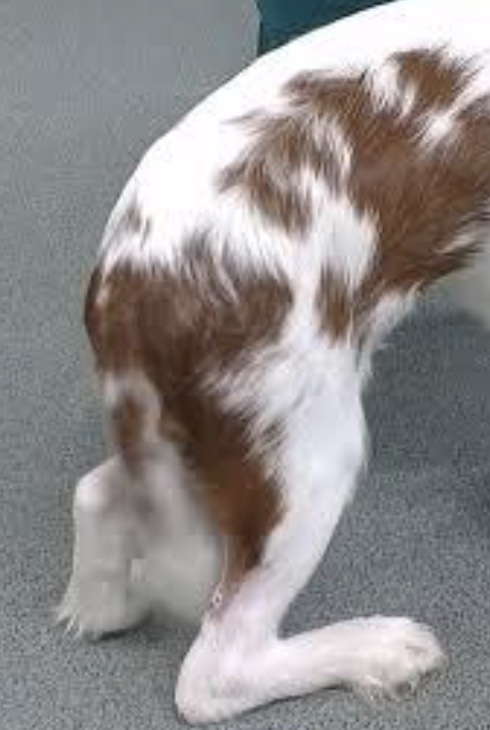

gait disorder: calcaneal tendon rupture
often traumatic; initially nonweight bearing lameness; stifle extends and tarsocrural join hyperflexes
76
New cards
gait disorder: CCL rupture
most common ortho sx; usually nonweight bearing in rear limb; can be partial weight bearing (toe touching)
77
New cards
gait disorder: “sweeney” or suprascapular nerve injury
suprascapular nerve damage via high speed collision or neck injury; muscle atrophy of supra or infraspinatus renders joint unstable; prominent scapular spine; characteristic shoulder roll during weight bearing
78
New cards
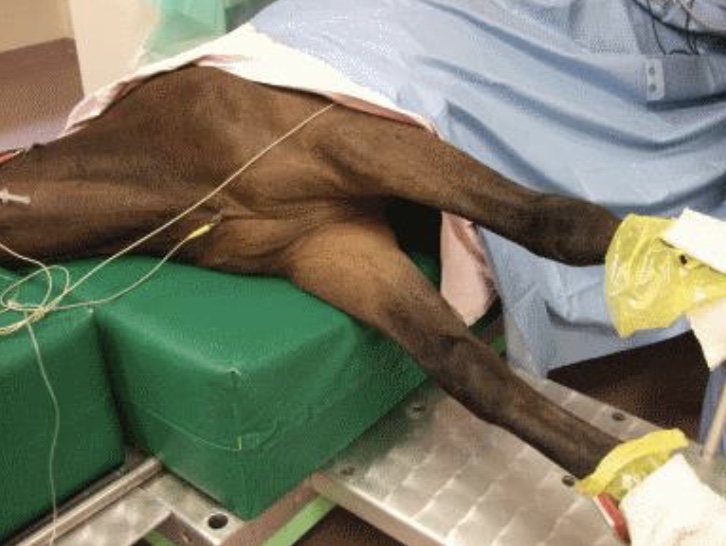
gait disorder: radial nerve injury
result of being in lateral recumbency for prolonged periods of time (ex- during anesthesia); only motor damage; 1/2 -1 hr of ischemia can cause conduction failure; 3 hrs of ischemia can cause permanent damage
79
New cards
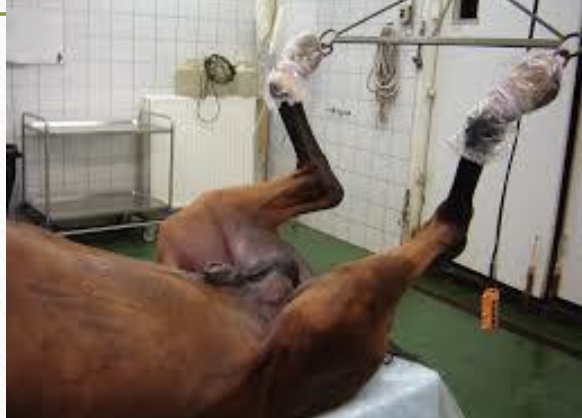
gait disorder: femoral nerve paralysis
ischemic injury; compression of nerve roots from birth canal or by prolonged rough pulling of hind limbs or prolonged stretch/increased tissue pressure during anesthesia in dorsal recumbency
80
New cards
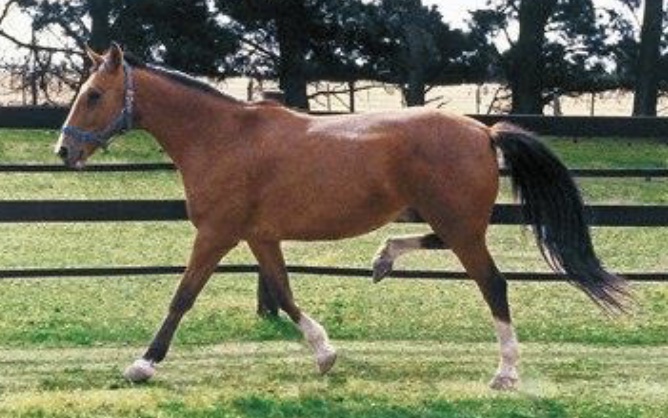

gait disorder: stringhalt
involuntary & exaggerated flexion or one or both hind limbs; limb is jerked forwards toward abdomen
conventional: in US, unknown etiology, rare, lateral digital extensor myotenectomy sx performed
outbreak: in Australia, etiology from dandelions, more freq, can also affect left recurrent laryngeal nerve
conventional: in US, unknown etiology, rare, lateral digital extensor myotenectomy sx performed
outbreak: in Australia, etiology from dandelions, more freq, can also affect left recurrent laryngeal nerve
81
New cards
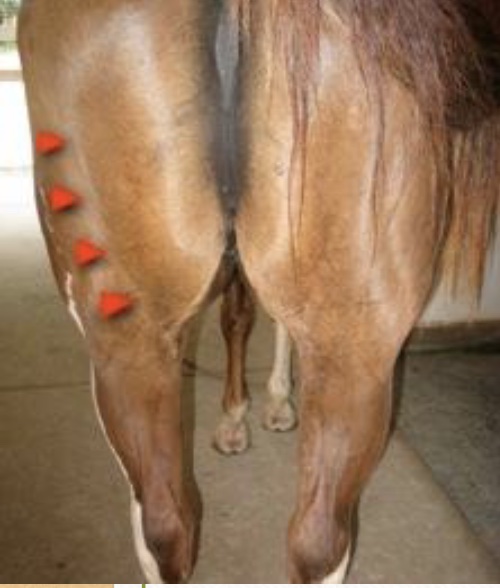
gait disorder: fibrotic myopathy
mechanical gait created when semitendonosus muscle has been injured and heals with a dense scar; fibrotic scar tissue restricts the normal elastic properties of muscle and limit the forward motion of limb; a slapping of foot to ground is evident
82
New cards
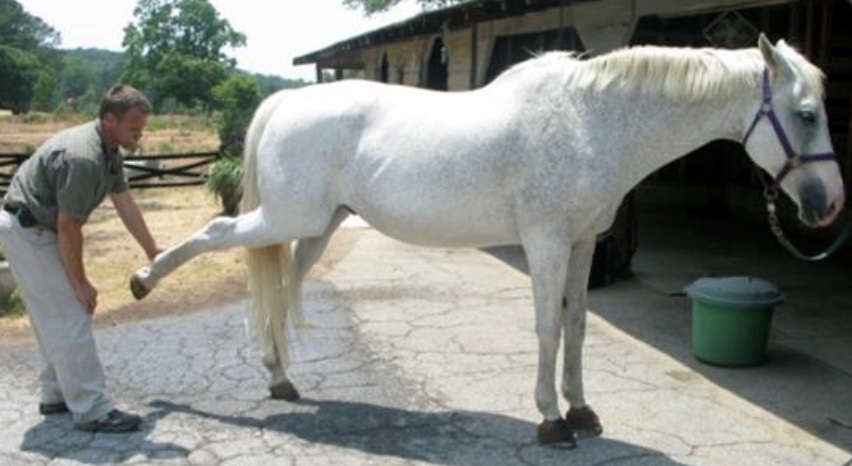

gait disorder: perneous tertius rupture
result of overextension of tarsus with normal flexed stifle; reciprocal apparatus of hind limb no longer functional (flex/flex)
83
New cards
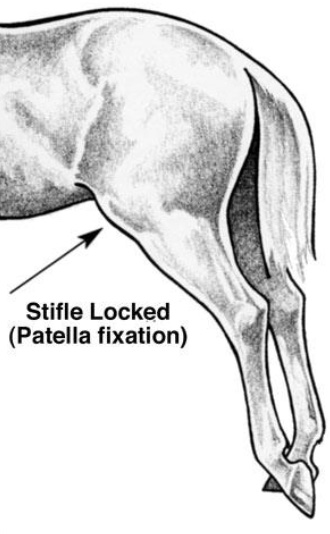
gait disorder: upward fixation of patella
patella lock mechanism is stuck; can develop bc of poor quadricep development; evident gait abnormality; leg locks in extension and is dragged behind
84
New cards
what are the muscles involved in the synsarcosis (shoulder suspension mechanism)
serratus ventralis and deep pectoral muscle primarily
85
New cards
superficial venous drainage
cephalic vein → axillobrachial vein → omobrachial vein → external jug → brachiocephalic vein → cranial vena cava
86
New cards
what do horses have on their biceps brachii that dogs dont
internal tendon
87
New cards
function of internal tendon of biceps brachii
stores kinetic energy to allow a quick “snap” of flexion during a fast gait
88
New cards
what does the internal tendon have
lacertus fibrosus
89
New cards
function of lacertus fibrosis
a thickened band that blends and extends to wrist on ECR
90
New cards
what head of triceps brachii acts on both GH and elbow joints
long head
91
New cards
brachialis inserts on
ulnar tuberosity
92
New cards
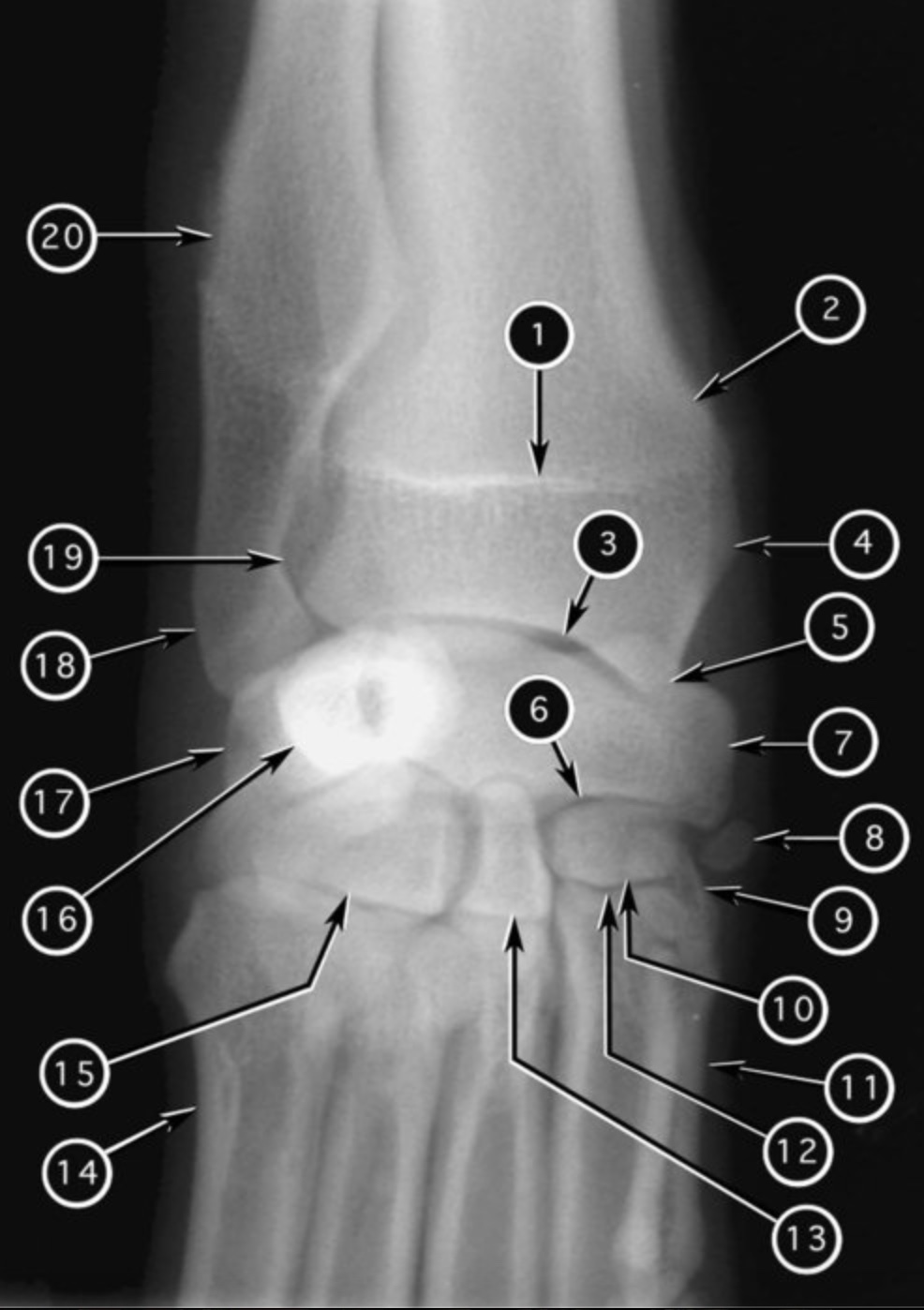
joint #3?
antebrachiocarpal joint
93
New cards
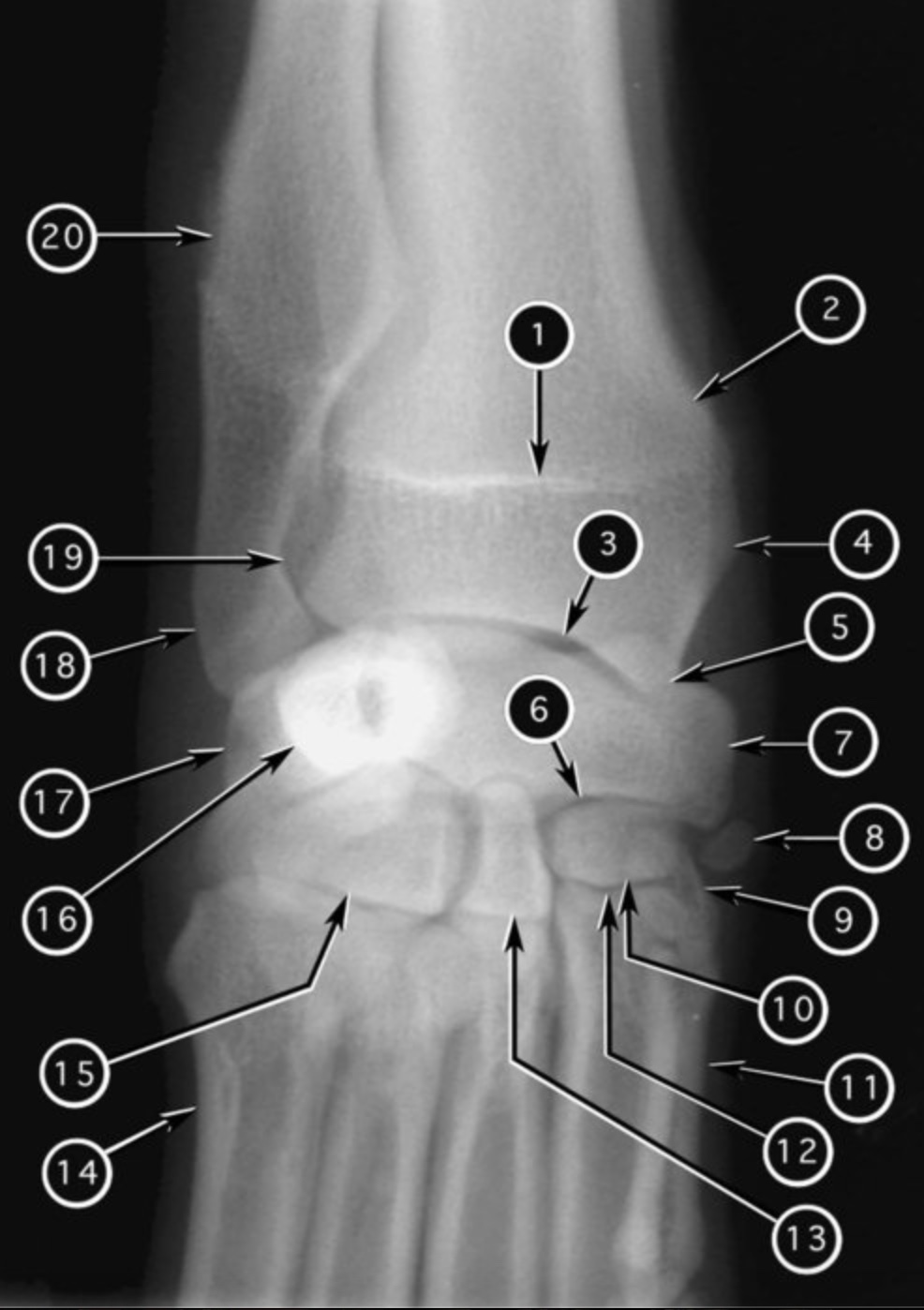
joint #19?
distal radioulnar joint
94
New cards
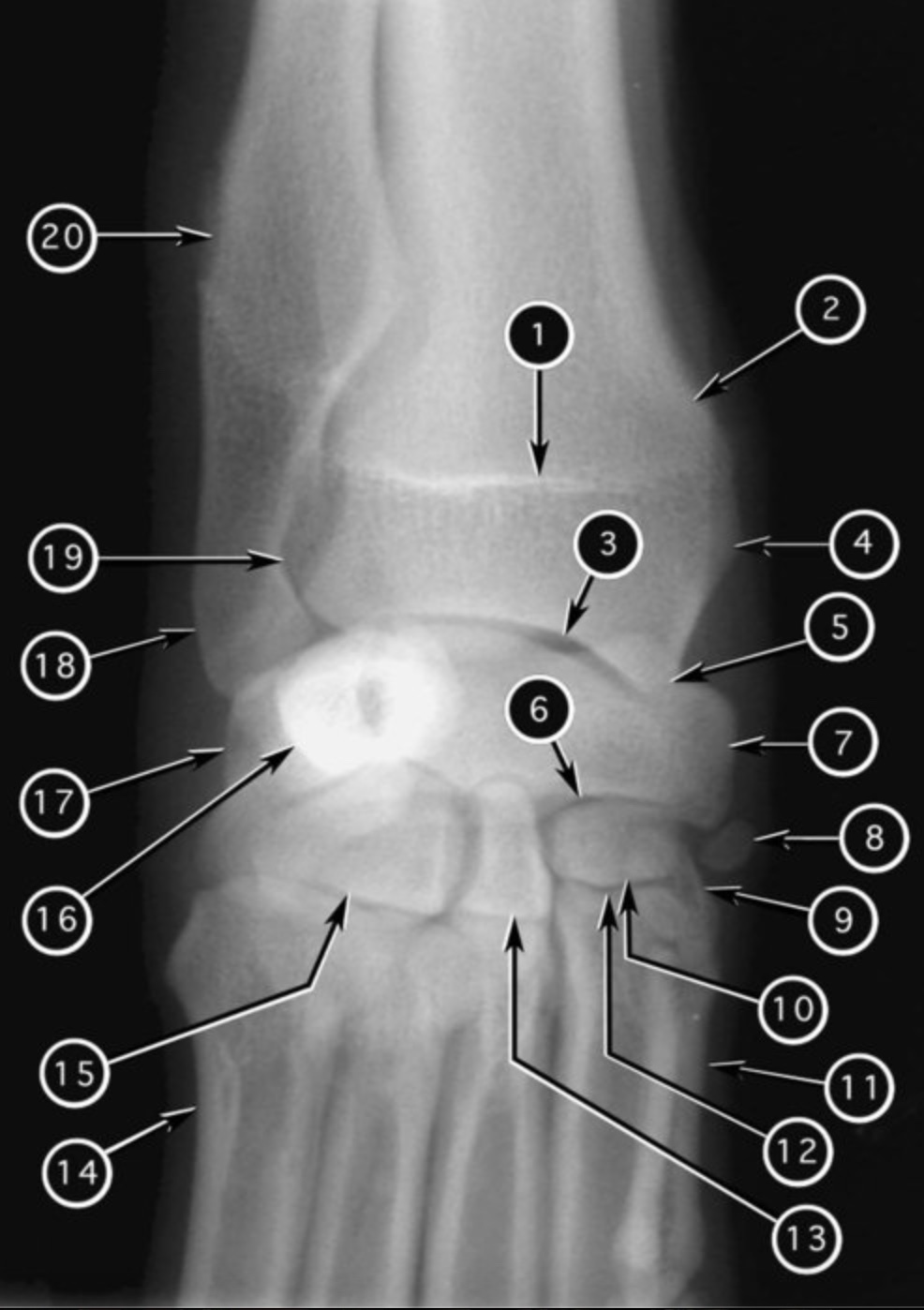
joint #6?
midcarpal joint
95
New cards
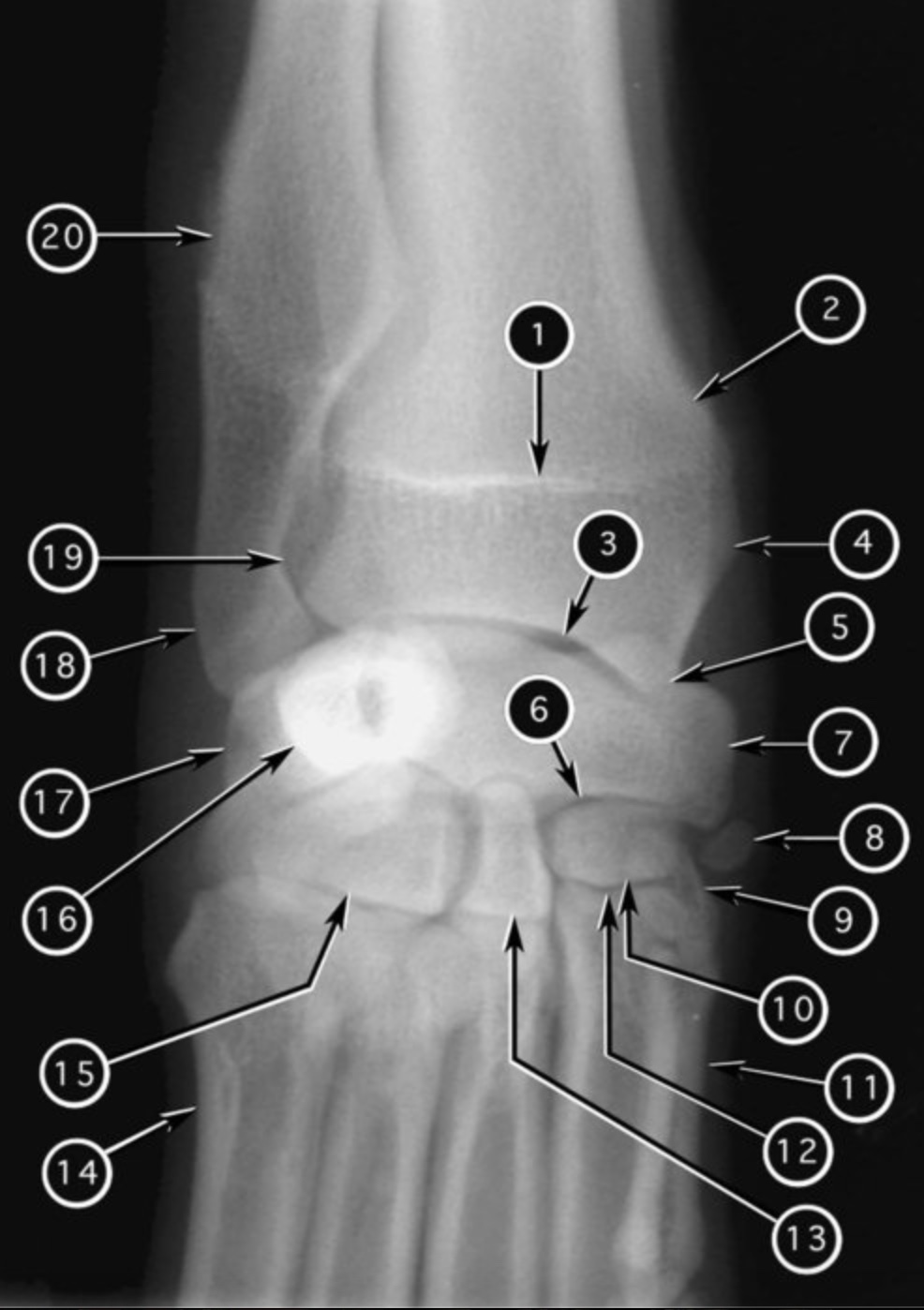
joint #12?
carpo-metacarpol joint
96
New cards
what is a ginglymus
a hinge with some lateral movement: at the joints of the wrist
97
New cards
high rise injuries
wrist ligaments cannot handle force of landing from a high surface; bc elbow is outwardly angled it creates a valgus angle; force can cause lateral condylar fractures, tendons passing through carpal tunnel cannot function normally
98
New cards
what muscles do horses have instead of abductor digiti 1 longus since they do not have a first digit
extensor carpi obliquis
99
New cards
traveling companions of forearm: brachial a. +
median n
100
New cards
traveling companions of forearm:
common interosseous a. +
common interosseous a. +
median n