Topic 6 Human Physiology Review
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
P1+P2, from MaritNy on Quizlet
Last updated 3:22 PM on 3/16/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
1
New cards
List and describe the functions of the salivary glands, esophagus, and stomach involved in digestion and absorption of food.
* Salivary glands - moisten food into a bolus and begin chemical digestion (saliva contains lubricants and enzymes \[salivary amylase\] that start starch digestion
* Esophagus - movement of food by peristalsis from the mouth to the stomach
* Stomach - stores and churns food, mixing it with water and acid secreted by the gastric pits lining the stomach that kills foreign bacteria and other pathogens in food. Initial stages of protein digestion by protease
* Esophagus - movement of food by peristalsis from the mouth to the stomach
* Stomach - stores and churns food, mixing it with water and acid secreted by the gastric pits lining the stomach that kills foreign bacteria and other pathogens in food. Initial stages of protein digestion by protease
2
New cards
List and describe the functions of the liver, gallbladder, and pancreas involved in digestion and absorption of food.
* Liver - Takes raw materials absorbed by the small intestine and uses them to make key chemicals. Involved in detoxification, storage of vitamins, metabolism, bile production (secretion of surfactants in bile break up lipid droplets), hemoglobin breakdown
* Gallbladder- stores/concentrates bile which is used to emulsify fats, bile is released into the small intestine via the common bile duct
* Pancreas - Releases digestive enzymes and hormones (insulin, glucagon) into the small intestine via the duodenum
* Gallbladder- stores/concentrates bile which is used to emulsify fats, bile is released into the small intestine via the common bile duct
* Pancreas - Releases digestive enzymes and hormones (insulin, glucagon) into the small intestine via the duodenum
3
New cards
List and describe the functions of the small intestine, large intestine, rectum/anus
* Small intestine - absorbs nutrients from food (three sections - duodenum, jejunum, ileum)
* Large intestine - Final section of the alimentary canal, water and minerals are absorbed
* Rectum/anus - stores and expels feces
* Large intestine - Final section of the alimentary canal, water and minerals are absorbed
* Rectum/anus - stores and expels feces
4
New cards
Describe the function of the left atrium, right atrium, left ventricle, and right ventricle.
* Left atrium: receives oxygenated blood from the pulmonary veins
* Right atrium: receives deoxygenated blood from the body
* Left ventricle: pumps blood into the aorta
* Right ventricle: pumps deoxygenated blood into the pulmonary artery
* Right atrium: receives deoxygenated blood from the body
* Left ventricle: pumps blood into the aorta
* Right ventricle: pumps deoxygenated blood into the pulmonary artery
5
New cards
Describe the function of the pulmonary vein, pulmonary artery, atrioventricular valve, semilunar valve
* Pulmonary vein: takes oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium
* Pulmonary artery: carries deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs
* Atrioventricular valves: opens up to allow oxygenated blood to flow into the ventricles
* Semilunar valves: opens up to allow deoxygenated blood into the pulmonary artery/aorta
* Aorta: takes oxygenated blood from the left ventricle to the body
* Pulmonary artery: carries deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs
* Atrioventricular valves: opens up to allow oxygenated blood to flow into the ventricles
* Semilunar valves: opens up to allow deoxygenated blood into the pulmonary artery/aorta
* Aorta: takes oxygenated blood from the left ventricle to the body
6
New cards
Describe the function of the coronary arteries, the superior vena cava, and the inferior vena cava
* Coronary arteries: supply the heart muscle with oxygen and nutrients
* Superior and inferior vena cava: carries deoxygenated blood from the body back to the heart (right atrium)
* Superior and inferior vena cava: carries deoxygenated blood from the body back to the heart (right atrium)
7
New cards
Compare/distinguish between type I and type II diabetes.
* Type I
* An inability to produce sufficient quantities of insulin due to the destruction of beta cell
* Usually occurs during childhood
* Requires insulin injections to regulate blood glucose
* Type II
* An inability to process or respond to insulin because of a deficiency of insulin receptors or glucose transporters on target cells/down-regulation of insulin receptors
* Usually occurs during adulthood
* Controlled by managing diet and lifestyle
* An inability to produce sufficient quantities of insulin due to the destruction of beta cell
* Usually occurs during childhood
* Requires insulin injections to regulate blood glucose
* Type II
* An inability to process or respond to insulin because of a deficiency of insulin receptors or glucose transporters on target cells/down-regulation of insulin receptors
* Usually occurs during adulthood
* Controlled by managing diet and lifestyle
8
New cards
Explain the process of ventilation.
* Air is inhaled into the lungs via the trachea/bronchi/and bronchioles, and is exhaled using the same route
* Exchanges stale air with fresh air from the environment
* Inhaling: the external intercostal muscle contract and move the ribcage up and out
* The diaphragm contracts, move down and flattens
* The volume of the thorax then increases as pressure drops below atmospheric pressure
* This allows air to flow into the lungs until the pressure rises to atmospheric pressure
* Exhaling:
* The internal intercostal muscles contract
* The ribcage moves down
* The diaphragm moves upwards, becoming more domed
* The volume of the thorax then decreases as the pressure increases (to a level above atmospheric pressure)
* This allows air to flow out of the lung, and air pressure returns below atmospheric levels
* Exchanges stale air with fresh air from the environment
* Inhaling: the external intercostal muscle contract and move the ribcage up and out
* The diaphragm contracts, move down and flattens
* The volume of the thorax then increases as pressure drops below atmospheric pressure
* This allows air to flow into the lungs until the pressure rises to atmospheric pressure
* Exhaling:
* The internal intercostal muscles contract
* The ribcage moves down
* The diaphragm moves upwards, becoming more domed
* The volume of the thorax then decreases as the pressure increases (to a level above atmospheric pressure)
* This allows air to flow out of the lung, and air pressure returns below atmospheric levels
9
New cards
Outline the state of the different valves of the heart during contraction of different parts of the heart.
**When the atria contracts:**
* Atrioventricular valves open (then blood is pumped through atria):
* Semilunar valves close
\
**When the ventricles contract:**
* Atrioventricular valves close (blood is not being pumped into the heart but it continues to flow in)
* Semilunar valves are still closed
\
**When ventricle pressure is greater than arterial pressure:**
* Semilunar valves open (blood is pumped from the ventricles to the arteries
* Pressure in atria rises as veins drain blood into them
\
**When the ventricles stop contracting/ventricle pressure is lower than arterial pressure:**
* semilunar valves close
\
**When ventricular pressure drops below atrial pressure**
* Atrioventricular valves open
* Blood from veins drains into the atria and the ventricles, and the pressure slowly increases
* Atrioventricular valves open (then blood is pumped through atria):
* Semilunar valves close
\
**When the ventricles contract:**
* Atrioventricular valves close (blood is not being pumped into the heart but it continues to flow in)
* Semilunar valves are still closed
\
**When ventricle pressure is greater than arterial pressure:**
* Semilunar valves open (blood is pumped from the ventricles to the arteries
* Pressure in atria rises as veins drain blood into them
\
**When the ventricles stop contracting/ventricle pressure is lower than arterial pressure:**
* semilunar valves close
\
**When ventricular pressure drops below atrial pressure**
* Atrioventricular valves open
* Blood from veins drains into the atria and the ventricles, and the pressure slowly increases
10
New cards
Oral contraceptives contain progesterone. How does that stop pregnancy?
**The simple answer:** Inhibits the secretion of FSH
\
**The longer answer that also illustrates the process of menstruation:**
* Oral contraceptives contain estrogen and progestin/progesterone which limit the secretion of FSH.
* FSH stimulates the development of follicles, which contain follicular fluid and an oocyte (immature female gametes sex cell).
* At high levels, estrogen inhibits FSH and stimulates LH.
* LH both triggers ovulation and promotes the development of the follicular wall (the follicular wall secretes estrogen and progesterone).
* Progesterone promotes the thickening and maintenance of the endometrium.
* Eventually the extended and increased release of estrogen and progestin/progesterone prevents ovulation
\
**The longer answer that also illustrates the process of menstruation:**
* Oral contraceptives contain estrogen and progestin/progesterone which limit the secretion of FSH.
* FSH stimulates the development of follicles, which contain follicular fluid and an oocyte (immature female gametes sex cell).
* At high levels, estrogen inhibits FSH and stimulates LH.
* LH both triggers ovulation and promotes the development of the follicular wall (the follicular wall secretes estrogen and progesterone).
* Progesterone promotes the thickening and maintenance of the endometrium.
* Eventually the extended and increased release of estrogen and progestin/progesterone prevents ovulation
11
New cards
Describe the negative feedback loop involved in regulating blood glucose levels.
**Negative feedback loops:**
* increase or decrease a stimulus/level constancy
* Blood glucose can be increased by glucose absorption by the small intestine (digestion) and productive of new glucose cells by the liver
* High glucose levels are detected by beta cells of the pancreas, with secrete insulin
* Insulin stimulates the uptake of glucose in the liver, skeletal muscles, and adipose tissue (meaning more glucose is used up) and store glucose in the form of glycogen, reducing blood glucose levels
* Low glucose levels are detected by the alpha cells of the pancreas, which secrete glucagon
* Glucagon inhibits insulin production, accelerates the production of glycogen to glucose in skeletal muscle, adipose tissue, and the liver, and stimulates the synthesis and release of glucose into the blood
* increase or decrease a stimulus/level constancy
* Blood glucose can be increased by glucose absorption by the small intestine (digestion) and productive of new glucose cells by the liver
* High glucose levels are detected by beta cells of the pancreas, with secrete insulin
* Insulin stimulates the uptake of glucose in the liver, skeletal muscles, and adipose tissue (meaning more glucose is used up) and store glucose in the form of glycogen, reducing blood glucose levels
* Low glucose levels are detected by the alpha cells of the pancreas, which secrete glucagon
* Glucagon inhibits insulin production, accelerates the production of glycogen to glucose in skeletal muscle, adipose tissue, and the liver, and stimulates the synthesis and release of glucose into the blood
12
New cards
Draw an annotated diagram of the male reproductive system.
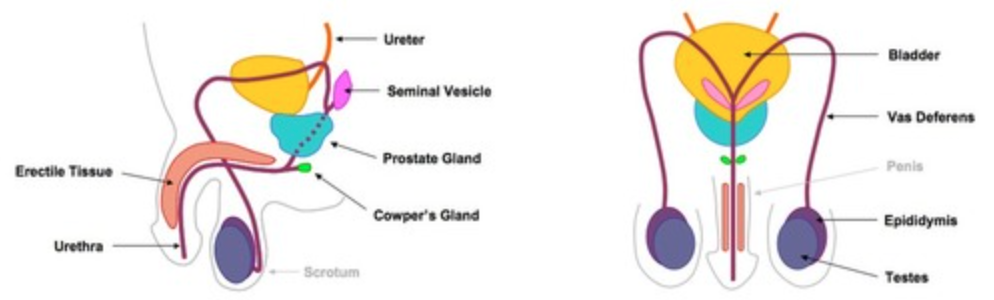
13
New cards
Draw an annotated diagram of the female reproductive system.
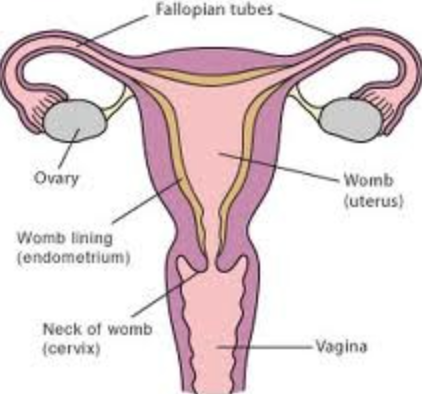
14
New cards
Describe what would happen if villi cells were destroyed.
* Villi cells increase the surface area over which absorption takes place.
* They absorb monosaccharides such as glucose, fructose, galactose, amino acids, fatty acids, glycerol, vitamins and minerals, and nucleotide bases.
* The lack of surface area of volume ratio for absorption will lead to decreased absorption of nutrients into the bloodstream.
* This can result in malnourishment of the body
* They absorb monosaccharides such as glucose, fructose, galactose, amino acids, fatty acids, glycerol, vitamins and minerals, and nucleotide bases.
* The lack of surface area of volume ratio for absorption will lead to decreased absorption of nutrients into the bloodstream.
* This can result in malnourishment of the body
15
New cards
Describe the cause and transmission of AIDS.
* AIDS is the result of HIV, and it is categorized as the variety of systems and infections that occur are a result of HIV.
* HIV is a retrovirus that targets and infects helper-T cells (lymphocytes) and disabled the immune system.
* The virus reproduces silently, then actively attacks T-lymphocytes, thus preventing the production of antibodies and lowering immunity.
* AIDS is the period of constitutional symptoms and opportunistic infections. It is transmitted by the exchange of bodily fluids, blood transfusions, breastfeeding, etc.
* HIV is a retrovirus that targets and infects helper-T cells (lymphocytes) and disabled the immune system.
* The virus reproduces silently, then actively attacks T-lymphocytes, thus preventing the production of antibodies and lowering immunity.
* AIDS is the period of constitutional symptoms and opportunistic infections. It is transmitted by the exchange of bodily fluids, blood transfusions, breastfeeding, etc.
16
New cards
Describe the social implications of AIDS.
* Families and friends suffer grief from prolonged sickness that can last decades, then eventually death.
* Families become poorer if the individual with AIDS was the wage earner and is refused life insurance, or if that person has no medical insurance to pay for the medicine to prolong their life.
* Individuals infected with HIV may become stigmatized and not find partners, housing, or employment.
* Sexual activity in a population may be reduced to the fear of AIDS.
* Families become poorer if the individual with AIDS was the wage earner and is refused life insurance, or if that person has no medical insurance to pay for the medicine to prolong their life.
* Individuals infected with HIV may become stigmatized and not find partners, housing, or employment.
* Sexual activity in a population may be reduced to the fear of AIDS.
17
New cards
Distinguish between and describe the structures & function of different blood vessels.
**Arteries:** take (high pressure) blood away from the heart
* Narrow lumen to maintain high blood pressure
* Thick muscle layers/elastic fibers to help pump blood;
* Thick collagen/fibers to avoid bursting/withstand high pressure
\
**Capillaries:** exchange materials between cells in tissues and blood
* Thin permeable walls
* Branch to form a capillary network
* One layer thick
* Coated by protein gel with pores between the cells
* Pores between cells so phagocytes can squeeze out
* Narrow lumen to fit into small spaces
* Large number resulting in increased surface area
\
**Veins:** collect (low pressure) blood and delivers it to the heart
* Wide lumen to maximize blood flow
* Thin muscle layers with few fibers because blood is not under high
* Thin so they are able to be pressed by muscles to pump blood;
* Wide lumen relative to overall diameter
* Wide lumen to maintain blood flow / decrease resistance to flow
* Have valves to maintain circulation of blood/prevent backflow
* Narrow lumen to maintain high blood pressure
* Thick muscle layers/elastic fibers to help pump blood;
* Thick collagen/fibers to avoid bursting/withstand high pressure
\
**Capillaries:** exchange materials between cells in tissues and blood
* Thin permeable walls
* Branch to form a capillary network
* One layer thick
* Coated by protein gel with pores between the cells
* Pores between cells so phagocytes can squeeze out
* Narrow lumen to fit into small spaces
* Large number resulting in increased surface area
\
**Veins:** collect (low pressure) blood and delivers it to the heart
* Wide lumen to maximize blood flow
* Thin muscle layers with few fibers because blood is not under high
* Thin so they are able to be pressed by muscles to pump blood;
* Wide lumen relative to overall diameter
* Wide lumen to maintain blood flow / decrease resistance to flow
* Have valves to maintain circulation of blood/prevent backflow
18
New cards
Outline the pathway that a nerve impulse follows.
(Background information: Nerve impulse = action potentials that move along the length of an axon as a wave of )
* Nerves transmit electrochemical signals between points in the body
* The event in this sequence is some external stimulus.
* A stimulus is something that human sensory receptors are able to detect.
* Examples may include: Sounds, physical contact, tastes, visual stimuli, etc.
* This triggers the "Sensory Receptors".
* These receptors are located all over the body.
* Sensory neuron(s) then transmit information from the sensory receptor(s) to the Central Nervous System
* (i.e. the brain and spinal cord, sometimes referred to in the abbreviated form: C.N.S.).
* This happens because peripheral nerves all connect to the spinal cord via the network of nerves within the nervous system.
* The information so received by the C.N.S. is further transmitted by relay neuron (s) with the C.N.S. (Spinal Cord)
* Nerves transmit electrochemical signals between points in the body
* The event in this sequence is some external stimulus.
* A stimulus is something that human sensory receptors are able to detect.
* Examples may include: Sounds, physical contact, tastes, visual stimuli, etc.
* This triggers the "Sensory Receptors".
* These receptors are located all over the body.
* Sensory neuron(s) then transmit information from the sensory receptor(s) to the Central Nervous System
* (i.e. the brain and spinal cord, sometimes referred to in the abbreviated form: C.N.S.).
* This happens because peripheral nerves all connect to the spinal cord via the network of nerves within the nervous system.
* The information so received by the C.N.S. is further transmitted by relay neuron (s) with the C.N.S. (Spinal Cord)
19
New cards
Compare the state (oxygenated/deoxygenated) of blood in different parts of the heart.
* **Deoxygenated blood:**
* Enters the right atrium (through the superior vena cava and the inferior vena cava)
* Drains into the right ventricle
* Leaves the right ventricle and is pumped into the pulmonary artery
* From the pulmonary artery blood is carried to the lungs and gets oxygenated
* **Oxygenated blood:**
* Oxygenated blood is taken to the heart by the pulmonary veins
* Enters the left atrium and is drained into the left ventricle
* The blood is pumped to the aorta as the left ventricle contracts
* Aorta branches into arteries that branch into arterioles and capillaries which exchange oxygen for carbon dioxide
* Enters the right atrium (through the superior vena cava and the inferior vena cava)
* Drains into the right ventricle
* Leaves the right ventricle and is pumped into the pulmonary artery
* From the pulmonary artery blood is carried to the lungs and gets oxygenated
* **Oxygenated blood:**
* Oxygenated blood is taken to the heart by the pulmonary veins
* Enters the left atrium and is drained into the left ventricle
* The blood is pumped to the aorta as the left ventricle contracts
* Aorta branches into arteries that branch into arterioles and capillaries which exchange oxygen for carbon dioxide
20
New cards
Describe antibodies and how they are produced.
**Antibodies are:**
* Globular proteins that recognize an antigen and attach to its surface, forming an antibody-antigen complex that macrophages can recognize and ingest through phagocytosis.
\
Antibody production:
* Lymphocytes are a type of white blood cell (leucocyte) that makes antibodies.
* Each lymphocyte makes one specific antibody.
* Antibodies are formed on the surface of the lymphocyte's plasma membrane.
* When the antigen of a foreign pathogen binds with the antibody of the lymphocyte, it activates and divides by mitosis (makes "clones") which produces large amounts of the specific antibody needed to defend against this specific pathogen
* Globular proteins that recognize an antigen and attach to its surface, forming an antibody-antigen complex that macrophages can recognize and ingest through phagocytosis.
\
Antibody production:
* Lymphocytes are a type of white blood cell (leucocyte) that makes antibodies.
* Each lymphocyte makes one specific antibody.
* Antibodies are formed on the surface of the lymphocyte's plasma membrane.
* When the antigen of a foreign pathogen binds with the antibody of the lymphocyte, it activates and divides by mitosis (makes "clones") which produces large amounts of the specific antibody needed to defend against this specific pathogen
21
New cards
Explain the structures and adaptations of alveoli.
**Adaptations/structures:**
* Walls are close to dense network of capillaries for gas exchange between air and blood
* Millions of small alveoli, folded provide large total surface area for large total gas exchange
* Moist walls to speed up diffusion of dissolved O2 and CO2
* Thin walls (a single layer of flattened cells) for rapid diffusion
* Elastic walls to allow increased ventilation and thinner walls during exercise
* Walls are close to dense network of capillaries for gas exchange between air and blood
* Millions of small alveoli, folded provide large total surface area for large total gas exchange
* Moist walls to speed up diffusion of dissolved O2 and CO2
* Thin walls (a single layer of flattened cells) for rapid diffusion
* Elastic walls to allow increased ventilation and thinner walls during exercise
22
New cards
State the source, substrate, products and optimal pH conditions of the different enzymes produced in the accessory organs of the digestive system.
**Amylase:** found in the salivary glands, small intestine, pancreas, substrate is starch, optimal pH is 7-7.8
\n **Protease:** found in the stomach, pancreas, and small intestine, substrate is protein, optimal pH is 2
\n **Lipase:** pancreas, small intestine, stomach, substrate is lipid, pH is 7.2-7.5
\n **Protease:** found in the stomach, pancreas, and small intestine, substrate is protein, optimal pH is 2
\n **Lipase:** pancreas, small intestine, stomach, substrate is lipid, pH is 7.2-7.5
23
New cards
State the steps involved in IVF.
1. For a period of three weeks, the woman has to have a drug injected to stop her normal menstrual cycle.
2. After these three weeks, high doses of FSH are injected once a day for 10-12 days so that many follicles develop in the ovaries of the women.
3. HCG (another hormone) is injected 36 hours before the collection of the eggs. HCG loosens the eggs in the follicles and makes them mature.
4. The man needs to ejaculate into a jar so that sperm can be collected from the semen. The sperm is processed to concentrate the healthiest ones.
5. A device that is inserted through the wall of the vagina is used to extract the eggs from the follicles.
6. Each egg is then mixed with sperm in a shallow dish. The dishes are then put into an incubator overnight.
7. The next day the dishes are looked at to see if fertilization has happened.
8. If fertilization has been successful, two or three of the embryos are chosen to be placed in the uterus by the use of a long plastic tube.
9. A pregnancy test is done a few weeks later to find out if any of the embryos have been implanted.
10. A scan is done a few weeks later to find out if the pregnancy is progressing normally.
24
New cards
Describe the process of transmission across a synapse.
Synaptic transmission
1. Action potential reaches the end of a presynaptic neuron.
2. Voltage gated calcium channels open.
3. Calcium ions flow into the presynaptic neuron.
4. Vesicles with neurotransmitters inside the presynaptic neuron fuse with the plasma membrane.
5. Neurotransmitters diffuse in the synaptic cleft and bind to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron.
6. The receptors are channels which open and let sodium ions into the postsynaptic neuron.
7. The sodium ions cause the postsynaptic membrane to depolarize.
8. This causes an action potential which passes down the postsynaptic neuron.
9. Neurotransmitters in the synaptic cleft are degraded and the calcium ions are pumped back into the synaptic cleft.
1. Action potential reaches the end of a presynaptic neuron.
2. Voltage gated calcium channels open.
3. Calcium ions flow into the presynaptic neuron.
4. Vesicles with neurotransmitters inside the presynaptic neuron fuse with the plasma membrane.
5. Neurotransmitters diffuse in the synaptic cleft and bind to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron.
6. The receptors are channels which open and let sodium ions into the postsynaptic neuron.
7. The sodium ions cause the postsynaptic membrane to depolarize.
8. This causes an action potential which passes down the postsynaptic neuron.
9. Neurotransmitters in the synaptic cleft are degraded and the calcium ions are pumped back into the synaptic cleft.
25
New cards
Describe the process of neural transmission.
Nerve impulse:
* action potentials that move along the length of an axon as a wave of depolarization
* neural transmission occurs when a neuron is activated, or fired (sends out an electrical impulse)
* activation (firing) of the neuron takes place when the neuron is stimulated by pressure, heat, light, or chemical information from other cells
* when a neuron is sufficiently stimulated to reach the neural threshold (a level of stimulation below which the cell does not fire), depolarization, or a change in cell potential, occurs.
\
How a transmission of a signal within a neuron (in one direction only, from dendrite to axon terminal) is carried out:
* by the opening and closing of voltage-gated ion channels, which cause a brief reversal of the resting membrane potential to create an action potential.
* as an action potential travels down the axon, the polarity changes across the membrane.
* the dendrites of a neuron pick up nerve impulses and conduct them toward the cell body.
* through the cell body, the impulse is conducted down the axon, which transmits impulses for long distances to effectors on muscle cells
* the axon is separated into segments of nerve fibers, some of which are myelinated
* Gaps between myelinated cells are called nodes of Ranvier
* Nerve impulses jump from one node to another (saltatory conduction = regenerating the action potential at each node of Ranvier)
* action potentials that move along the length of an axon as a wave of depolarization
* neural transmission occurs when a neuron is activated, or fired (sends out an electrical impulse)
* activation (firing) of the neuron takes place when the neuron is stimulated by pressure, heat, light, or chemical information from other cells
* when a neuron is sufficiently stimulated to reach the neural threshold (a level of stimulation below which the cell does not fire), depolarization, or a change in cell potential, occurs.
\
How a transmission of a signal within a neuron (in one direction only, from dendrite to axon terminal) is carried out:
* by the opening and closing of voltage-gated ion channels, which cause a brief reversal of the resting membrane potential to create an action potential.
* as an action potential travels down the axon, the polarity changes across the membrane.
* the dendrites of a neuron pick up nerve impulses and conduct them toward the cell body.
* through the cell body, the impulse is conducted down the axon, which transmits impulses for long distances to effectors on muscle cells
* the axon is separated into segments of nerve fibers, some of which are myelinated
* Gaps between myelinated cells are called nodes of Ranvier
* Nerve impulses jump from one node to another (saltatory conduction = regenerating the action potential at each node of Ranvier)
26
New cards
Distinguish between antigen and antibody.
Antibodies are proteins that defend the body against pathogens by binding to antigens on the surface of these pathogens and stimulating their destruction
\n Antigens are foreign substances which stimulate the production of antibodies. Antibodies usually only bind to one specific antigen.
\n Antigens are foreign substances which stimulate the production of antibodies. Antibodies usually only bind to one specific antigen.
27
New cards
Explain the process of lipid assimilation and absorption.
* Absorption occurs when the food enters the body as the food molecules pass through a layer of cells and into the body’s tissues.
* This occurs in the small intestine which has many villi that are specialized for absorption.
* Assimilation occurs when the food molecules become part of the body’s tissue.
* Therefore, absorption is followed by assimilation.
* **Lipid Absorption:**
* enzymes digest macromolecules (lipids) into monomers
* lipids pass into the villi to be absorbed
* **Lipid Assimilation:**
* lipids are incorporated into new membranes
* (brought to a body cell and then used)
* This occurs in the small intestine which has many villi that are specialized for absorption.
* Assimilation occurs when the food molecules become part of the body’s tissue.
* Therefore, absorption is followed by assimilation.
* **Lipid Absorption:**
* enzymes digest macromolecules (lipids) into monomers
* lipids pass into the villi to be absorbed
* **Lipid Assimilation:**
* lipids are incorporated into new membranes
* (brought to a body cell and then used)
28
New cards
Describe the effects of HIV on the immune system.
* Without a functioning immune system, the body is vulnerable to pathogens that normally would be controlled easily
* Individuals with HIV/AIDS have a low number of lymphocytes, antibodies, weight loss, and other diseases caused by viruses/bacteria
* This is what leads to death
* Individuals with HIV/AIDS have a low number of lymphocytes, antibodies, weight loss, and other diseases caused by viruses/bacteria
* This is what leads to death
29
New cards
Annotate a diagram of the respiratory system.
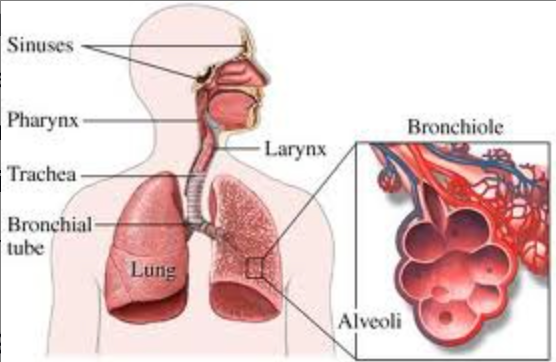
30
New cards
List and describe several adaptations of the small intestine.
* Microvilli
* Ruffling of the epithelial membrane further increases the surface area
* Rich blood supply
* Dense capillary network rapidly transports absorbed products
* Single layer epithelium
* Minimizes diffusion distance between lumen and blood
* Lacteals
* Absorbs lipids from the intestine into the lymphatic system
* Intestinal glands
* Exocrine pits (crypts of Lieberkuhn) release digestive juices
* Membrane proteins
* Facilitate transport of digested materials into epithelial cells
* Ruffling of the epithelial membrane further increases the surface area
* Rich blood supply
* Dense capillary network rapidly transports absorbed products
* Single layer epithelium
* Minimizes diffusion distance between lumen and blood
* Lacteals
* Absorbs lipids from the intestine into the lymphatic system
* Intestinal glands
* Exocrine pits (crypts of Lieberkuhn) release digestive juices
* Membrane proteins
* Facilitate transport of digested materials into epithelial cells
31
New cards
State the definition of pathogen.
Any living organism or virus that is capable of causing a disease.
32
New cards
Describe the effects of antibiotics on bacteria and viruses.
* Antibiotics are produced by microorganisms to kill or control the growth of other microorganisms by blocking specific metabolic pathways within the cell
* Since bacteria are so different from human cells, antibiotics can be taken by humans to kill bacteria without harming the human cells
* Viruses on the other hand are different as they do not carry out many metabolic processes themselves.
* Instead they rely on a host cell (a human cell) to carry out these processes for them.
* Therefore, viruses cannot be treated with antibiotics as it is impossible to harm the virus without harming the human cells.
* Since bacteria are so different from human cells, antibiotics can be taken by humans to kill bacteria without harming the human cells
* Viruses on the other hand are different as they do not carry out many metabolic processes themselves.
* Instead they rely on a host cell (a human cell) to carry out these processes for them.
* Therefore, viruses cannot be treated with antibiotics as it is impossible to harm the virus without harming the human cells.
33
New cards
List several molecules transported in blood.
* Nutrients
* Oxygen
* Carbon dioxide
* Hormones
* Antibodies
* Urea
* Heat
* Oxygen
* Carbon dioxide
* Hormones
* Antibodies
* Urea
* Heat
34
New cards
Draw the human digestive system.
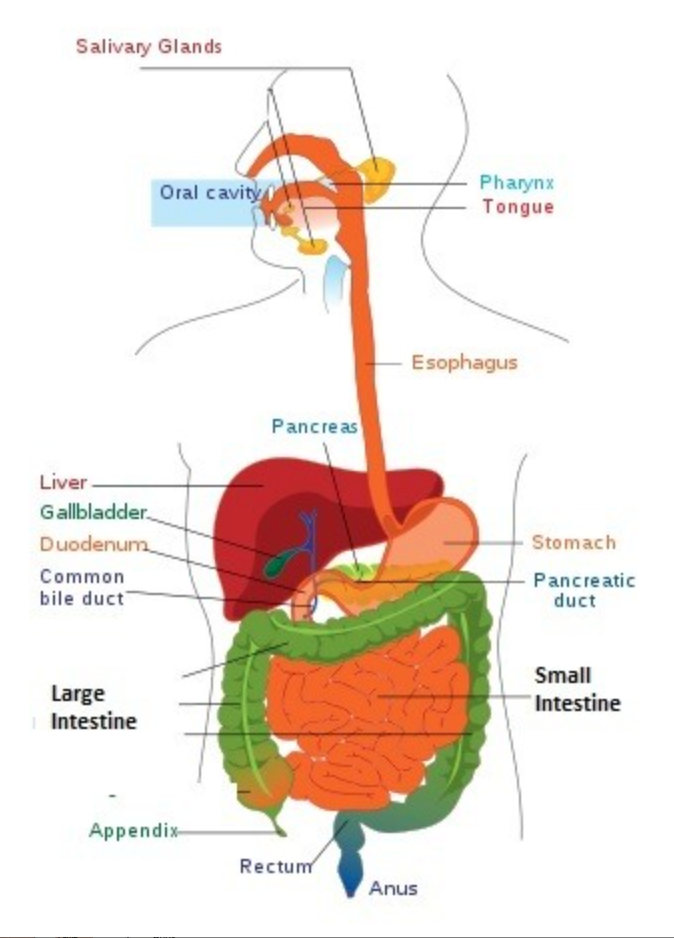
35
New cards
What sequence of organs do substances pass through, as they move through the human digestive system?
Mouth-> esophagus -> stomach -> small intestine -> large intestine
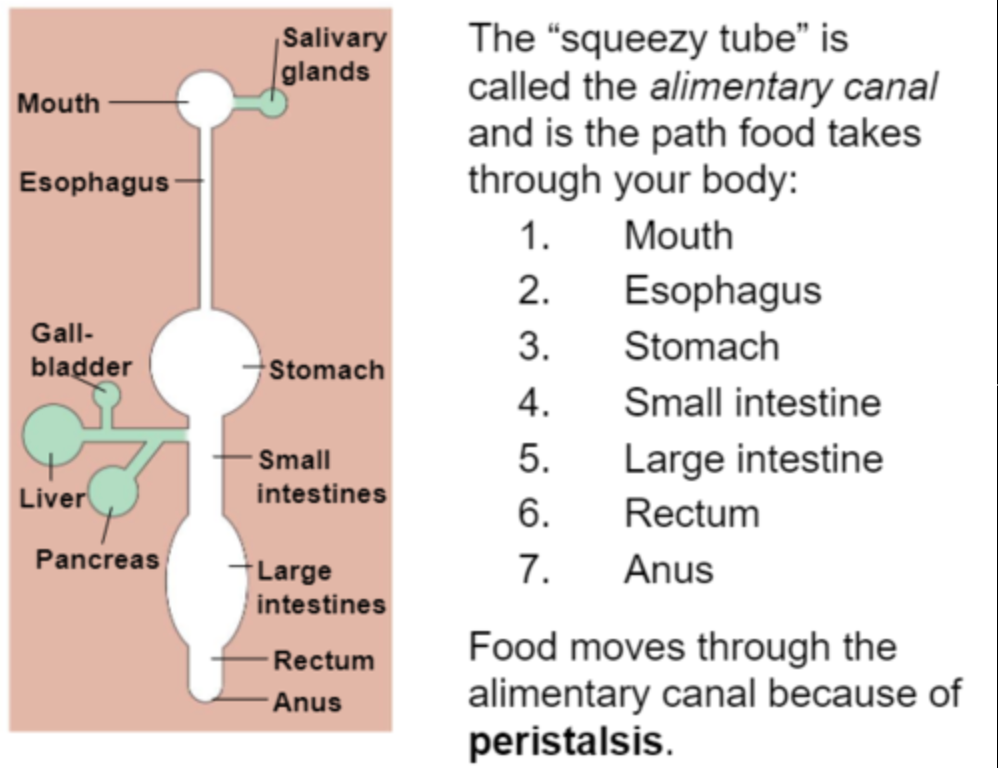
36
New cards
Arterioles in the skin contain muscle fibers which contract. What is the function of these fibers?
To reduce blood flow to the skin when the body is too cold
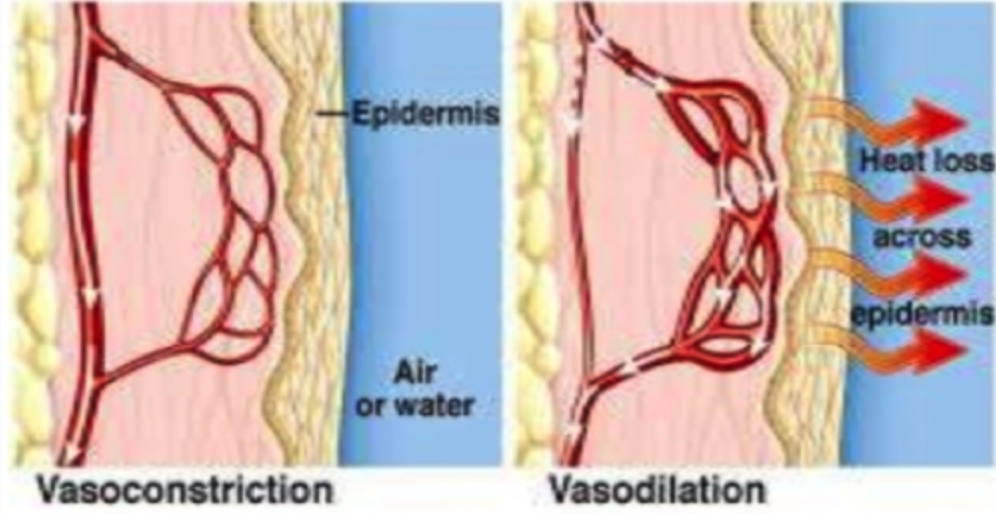
37
New cards
What sequence of events correctly describes the destruction of pathogens in body tissue?
Chemical recognition -> amoeboid motion -> endocytosis -> enzymatic digestion
38
New cards
What is happening to the heart when the semi-lunar valves are closed?
Blood is entering the ventricles
39
New cards
Diagram of the heart
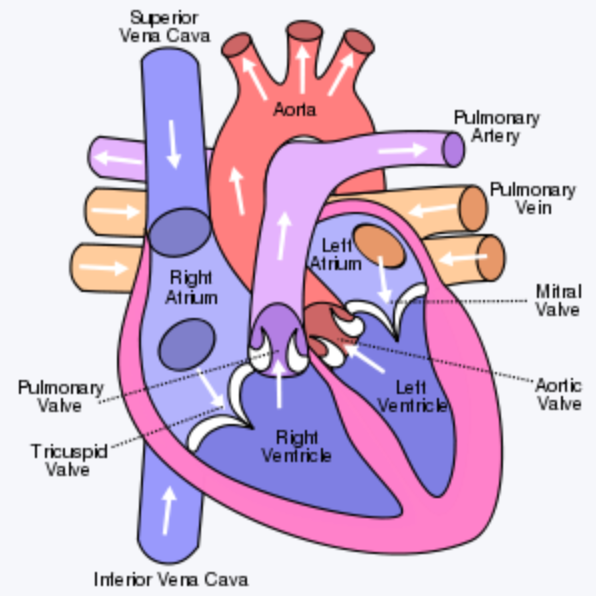
40
New cards
In the digestive system, enzyme A has an optimum pH of 1.5 and enzyme B an optimum pH of 7. What are the possible substrates?
Enzyme A: Proteins \n Enzyme B: Lipids
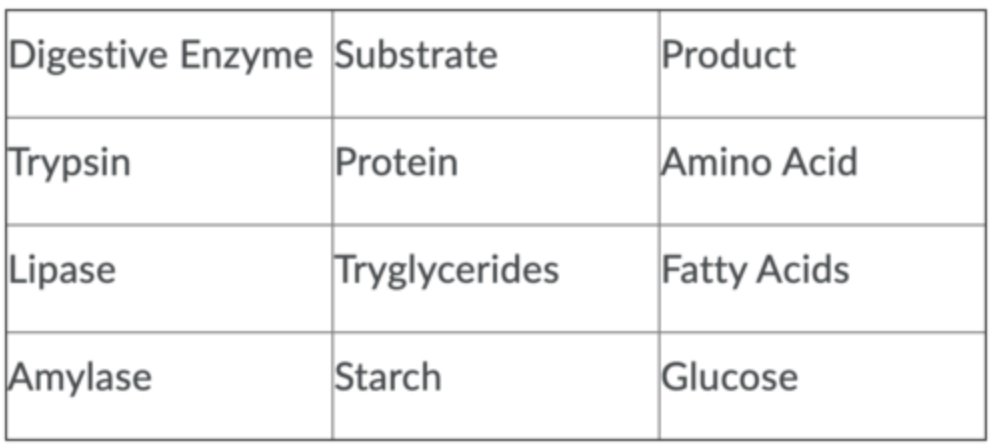
41
New cards
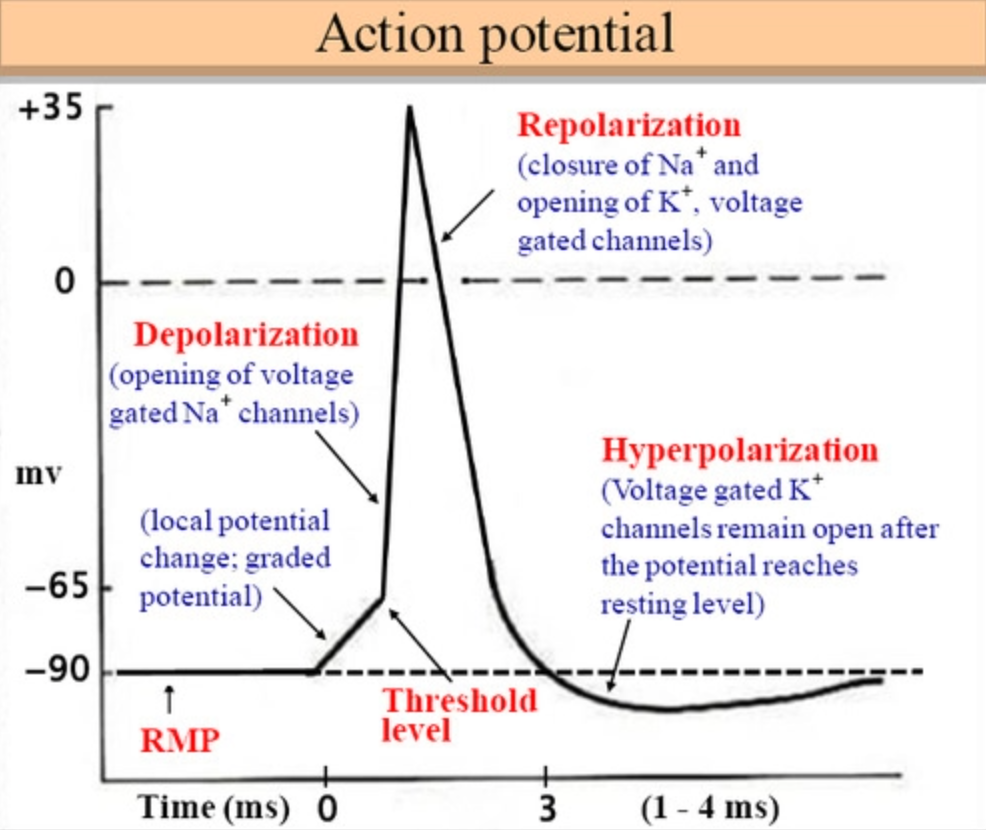
After depolarization, what happens to restore resting potential?
Potassium channels open and potassium ions diffuse out of the neuron
42
New cards
Capillaries surround the alveoli in the lungs. Which pair of statements correctly describes the concentrations of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the lungs?
Oxygen = higher in the alveoli \n Carbon dioxide = higher in the capillaries
43
New cards
Functions of the stomach, small intestine, large intestine
Stomach: digest proteins \n Small intestine: absorb glucose \n Large intestine: absorb water

44
New cards
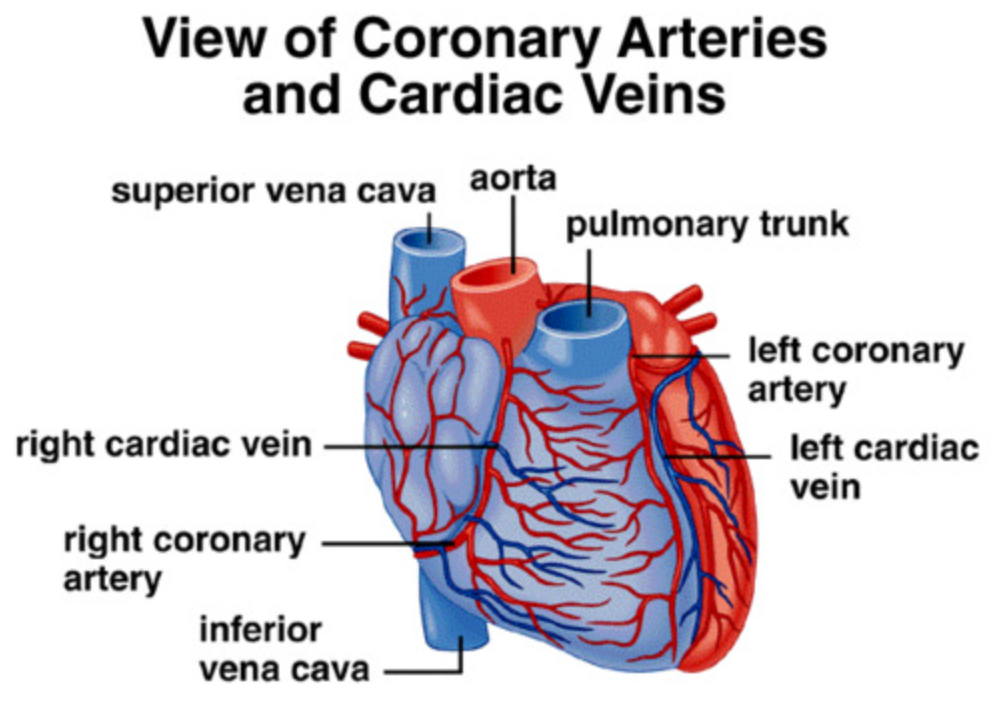
Role of the coronary arteries
Supply the heart muscle w/ oxygen and nutrients
45
New cards
When human body temperature rises during exercise…
The water from sweat evaporates to cool the body
46
New cards
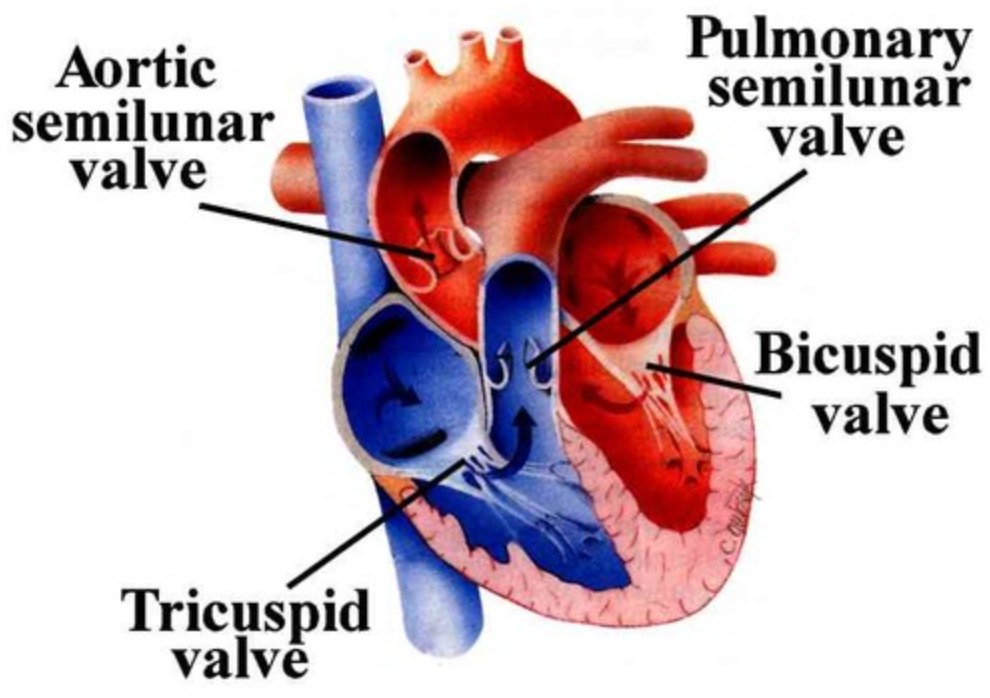
When the left ventricle contracts…
Atrioventricular valves = closed \n Semi lunar valves = open
47
New cards
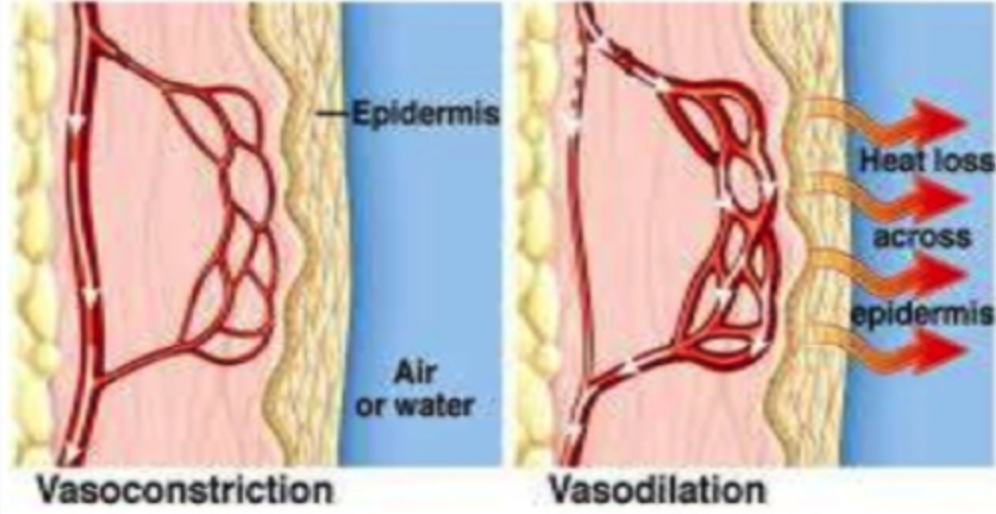
How does the body respond to an increase in body temperature?
Vasodilation of skin arterioles
48
New cards
Diagram of a villi
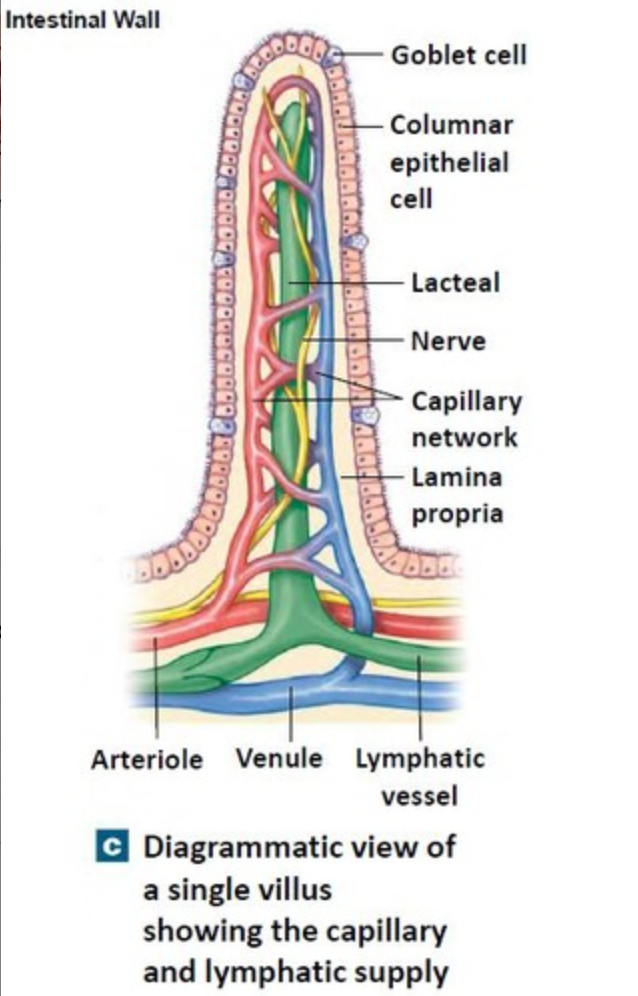
49
New cards
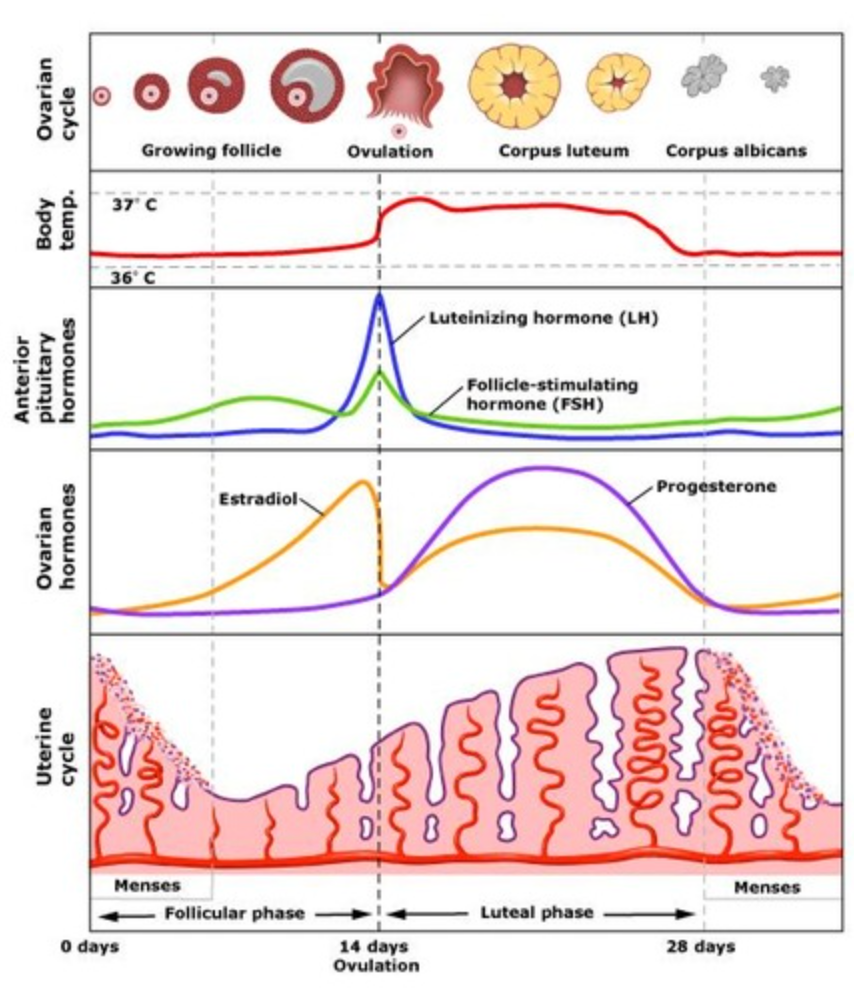
LH causes the rupture of a follicle and release of an egg cell. This process is called…
Ovulation
50
New cards
Celiac disease causes the destruction of villi cells. Which of the following is most likely to happen to someone with Celiac disease?
Poor absorption of calcium
51
New cards
Between which structures do sensory neurons carry nerve impulses?
From receptors to the central nervous system
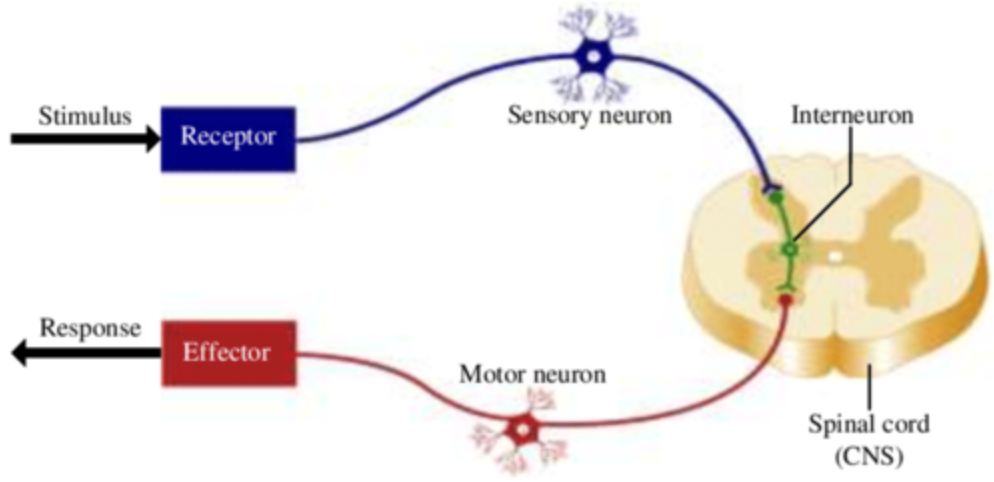
52
New cards
Is the blood in the aorta, left ventricle, and pulmonary artery oxygenated or deoxygenated?
**Aorta:** oxygenated \n **Left ventricle:** oxygenated \n **Pulmonary artery:** deoxygenated
53
New cards
What is the substrate, source, and optimum pH of lipase?
**Substrate:** triglycerides
**Source:** pancrease
**Optimum pH:** 7
**Source:** pancrease
**Optimum pH:** 7
54
New cards
In the diagram of synaptic transmission below, what is indicated by the letter X and Y?
**X:** Ca2+ ions diffuse into synaptic knob \n **Y:** neurotransmitter
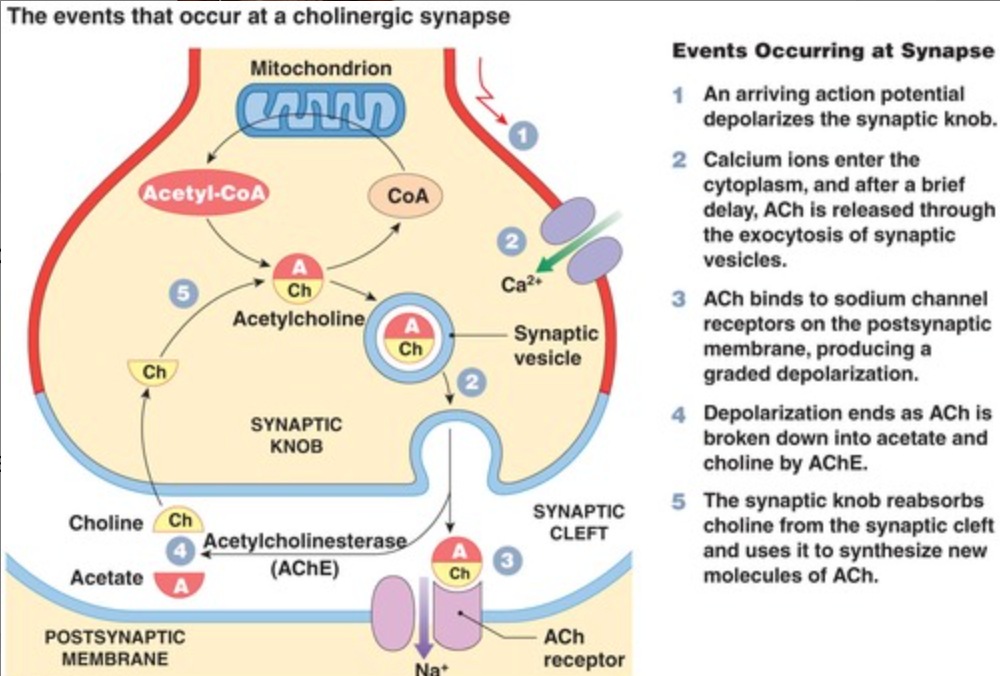
55
New cards
Pathway for the blood flowing through the heart
Right atrium, tricuspid valve, right ventricle, pulmonary artery
56
New cards
Explain the roles of hormones involved in the menstrual cycle and pregnancy.
1. FSH and LH are produced by the pituitary gland
2. Estrogen and progestin are produced by the ovary
3. FSH stimulates the ovary to promote the development of a follicle
4. The developing follicles secrete estrogen, which inhibits FSH (negative feedback)
5. Estrogen stimulates the growth of the endometrium
6. Estrogen stimulates LH secretion (positive feedback)
7. LH stimulates follicle growth and triggers ovulation
8. (The secondary oocyte leaves the ovary and) the follicle becomes corpus luteum
9. The corpus luteum secretes estrogen and progesterone
10. Estrogen and progesterone maintain the endometrium
11. Estrogen and progesterone inhibit LH and FSH (negative feedback)
12. After (two weeks) the corpus luteum degenerates progesterone and estrogen levels fall
13. This triggers menstrual bleeding, the loss of endometrium
14. The pituitary gland secreted FSH and LH, as they are no longer inhibited (and the menstrual cycle continues)