pathology of prostate gland
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/74
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 12:04 PM on 12/11/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
1
New cards
2
New cards
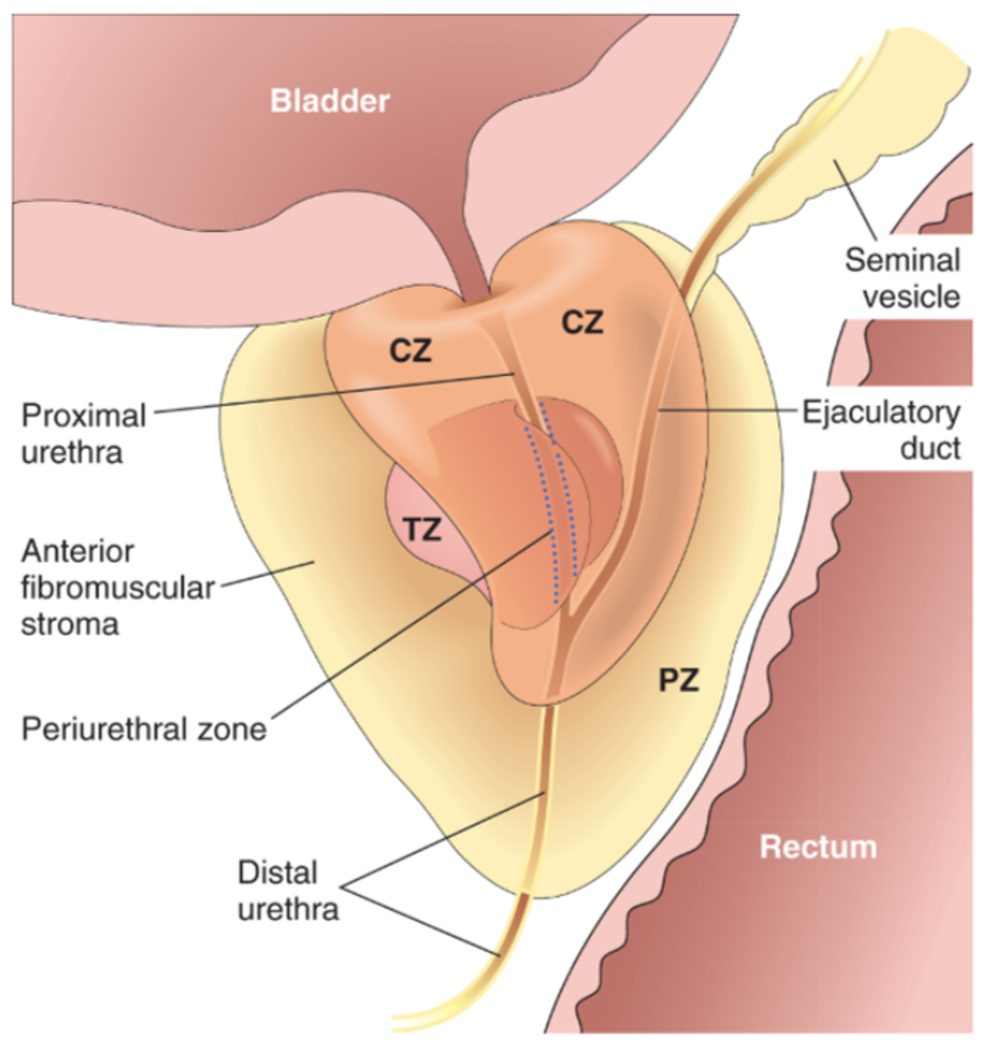
peripheral glands (peripheral zone) therefore palpable on examination
carcinomas arise from
3
New cards
central glands (central zone), non palpable and more likely to produce URINARY obstruction (obstructs the urethra) earlier than carcinoma
nodular hyperplasia arises
4
New cards
1) INNER epithelial cells --> under androgenic control and secrete prostate specific antigen (PAS)
2) OUTER/underlying basal cells --> lost in carcinoma (malignancy)
2) OUTER/underlying basal cells --> lost in carcinoma (malignancy)
glands bilayered
5
New cards
- either acute (UTI: e.coli) or chronic
- chronic abacterial
- granulomatous
- chronic abacterial
- granulomatous
prostatitis causes
6
New cards
aka nodular hyperplasia of prostate
- ages 40 and above, a lot around 60, mainly around 80 y/o
- urinary frequency, nocturia, difficulty in starting/stopping urine, overflow dribbling and dysuria
- ages 40 and above, a lot around 60, mainly around 80 y/o
- urinary frequency, nocturia, difficulty in starting/stopping urine, overflow dribbling and dysuria
benign prostatic hyperplasia presentation
7
New cards
hyperplasia of prostatic stromal/epithelial cells = nodules around periutethral region of prostate
- role of androgens (inner epithelia regulated by it)
- influence cell proliferation and apoptosis
- role of androgens (inner epithelia regulated by it)
- influence cell proliferation and apoptosis
BPH aetiopathogenesis
8
New cards
1. medical:
alpha blockers - A1 receptors decreasing muscle tone
or
inhibit synthesis of DHT: inhibitors of 5-alpha-reductase shrinks prostate
2. surgical
resection of prostate
alpha blockers - A1 receptors decreasing muscle tone
or
inhibit synthesis of DHT: inhibitors of 5-alpha-reductase shrinks prostate
2. surgical
resection of prostate
BPH treatment
9
New cards
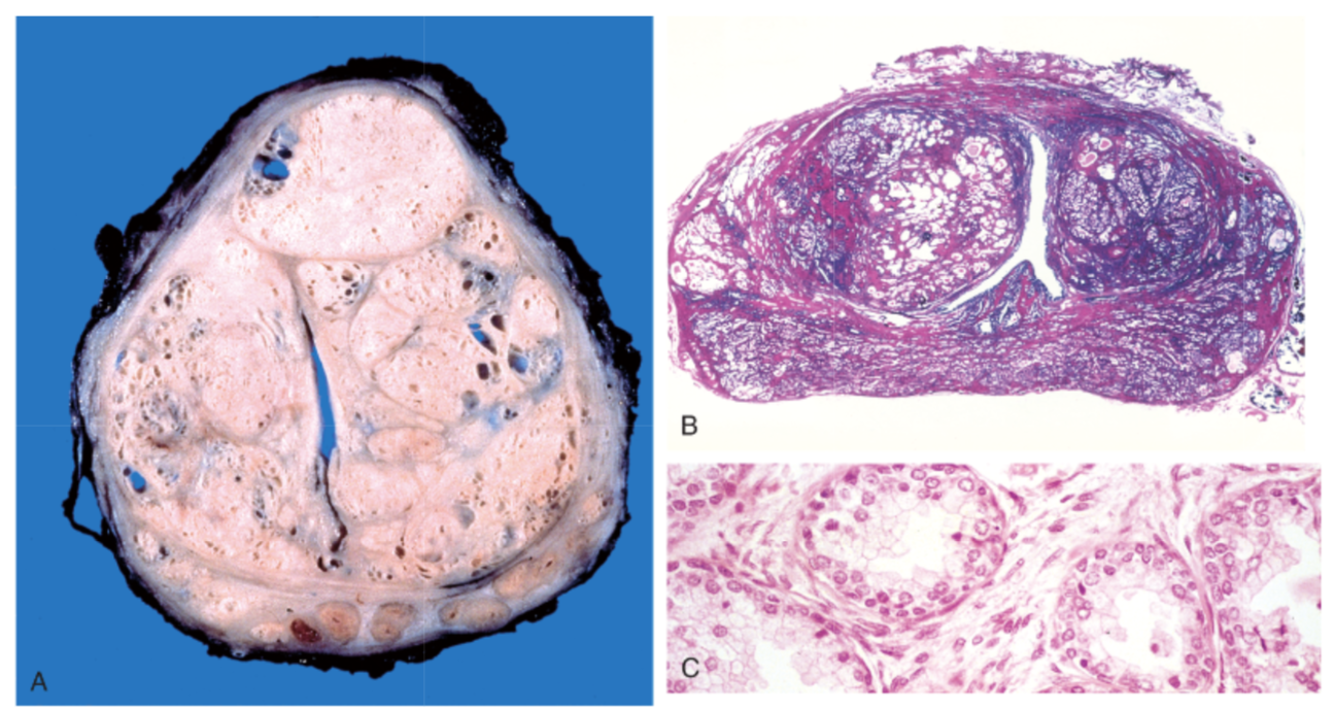
A. central portion separated by urethral slit = obstruction
B. nodules formation
C. dual cell population: inner columnar epithelial and outer flattened basal cells (not lost)
B. nodules formation
C. dual cell population: inner columnar epithelial and outer flattened basal cells (not lost)
describe images
10
New cards
- occurs in same age population but detected later as the obstruciton occurs later on
- glands in peripheral zone
- symptoms are same of BPH
- glands in peripheral zone
- symptoms are same of BPH
adenocarcinoma of prostate
11
New cards
- OSTEOBLASTIC metastasis especially in vertebra
adenocarcinoma of prostate metastasis
12
New cards
prostate specific antigen
- can occur in cancer elevated levels
- can occur in cancer elevated levels
PSA
13
New cards
prostate carcinoma has perineural invasion of malignant glands
adenocarcinoma of prostate invasion
14
New cards
- poor differentiated = less glands, forms sheets of malignant cells + irregular branches
- lower grade cancer = presence of crystalloids around glands
- lower grade cancer = presence of crystalloids around glands
GLEASON GRADING
15
New cards
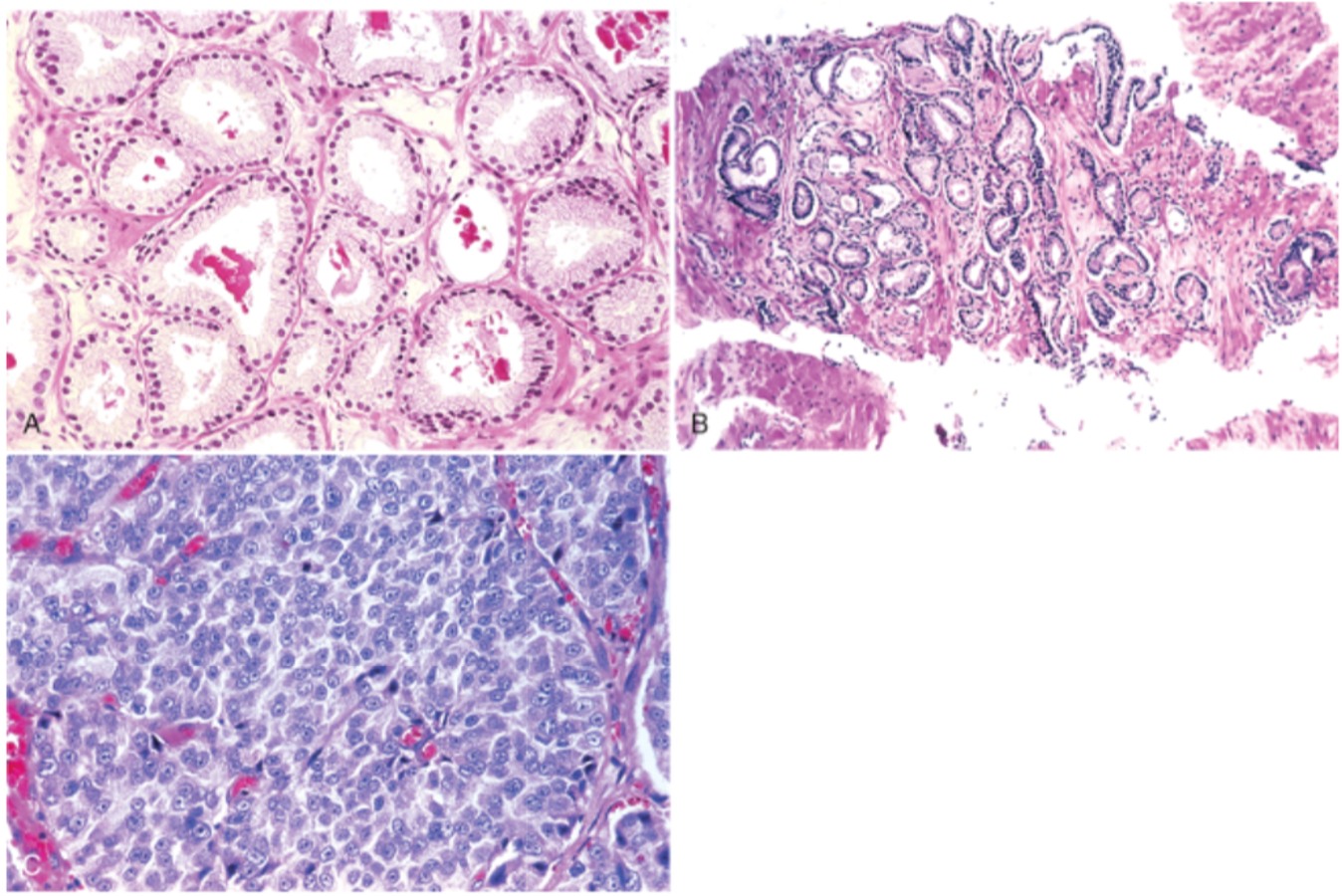
A. well differentiated = lower gleason score, glands contain crystalloids around
B. variably sized, moderately differentiated, still forming glands tho
C. no gland formation, high grade cancer
B. variably sized, moderately differentiated, still forming glands tho
C. no gland formation, high grade cancer
c
16
New cards
- local expansion = periprostatic tissue
- metastasis = lympatics + blood
- metastasis = lympatics + blood
adenocarcinoma spread besides bone
17
New cards
most common is UROTHELIAL (transitional) tumors
CIS (not spreading but very dangerous)
CIS (not spreading but very dangerous)
bladder neoplasms types
18
New cards
hematuria, irritiative symptoms, obstructive symptoms,
bladder cancer features
19
New cards
- smokers
- exposure to arylamines industrial arylamines
- schistosoma hematobium
- long term use of analgesics
- exposure to cyclophosphamide (immunosuppressant)
- preior exposure to bladder radiation
- exposure to arylamines industrial arylamines
- schistosoma hematobium
- long term use of analgesics
- exposure to cyclophosphamide (immunosuppressant)
- preior exposure to bladder radiation
bladder cancer causes
20
New cards
1) non invasive papillary tumor of bladder
2) flat non invasive or invasive carcinoma aka carcinoma is situ CIS (basement membrane invasion = malignancy)
- invasion to lamina propria and MUSCULARIS PROPRIA = worse prognosis
2) flat non invasive or invasive carcinoma aka carcinoma is situ CIS (basement membrane invasion = malignancy)
- invasion to lamina propria and MUSCULARIS PROPRIA = worse prognosis
precursors to invasive UROTHELIAL carcinoma
21
New cards
high grade papillary urothelial carcinoma (atypia)
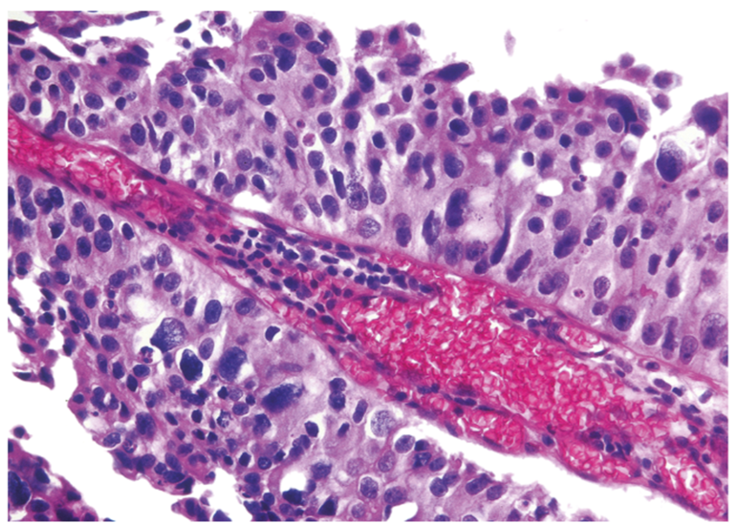
22
New cards
- if non-muscle invasive cancer = treatment is prevention to MIBC so transurethral resection of blasser
- if MICB = radial cystectomy
- if MICB = radial cystectomy
treatment of urinary bladder cancer
23
New cards
- metabolic factors = obesity
- beverage consumption - caffeine/alcohol beneficial as they reduce androgen
- intake of vitamin A beta carotene is beneficial, reduce Vitamin C
- beverage consumption - caffeine/alcohol beneficial as they reduce androgen
- intake of vitamin A beta carotene is beneficial, reduce Vitamin C
modifiable risks of BPH
24
New cards
- CV risk
- neurologic factors (detrusor function and stability)
- diabetes - decrease bladder sensitivity, detrusor contractility, incomplete emptying, polyuria
- neurologic factors (detrusor function and stability)
- diabetes - decrease bladder sensitivity, detrusor contractility, incomplete emptying, polyuria
conditions exacerbating LUTS/BPH
25
New cards
1) mediated by dihydrotestosterone produced by 5 alpha reductase conversion from testosterone. Inhibition of 5alpha = treat overflow incontinence
2) muscle tone prostate mediated by alpha 1 adrenergic receptors
2) muscle tone prostate mediated by alpha 1 adrenergic receptors
pathophysiology of BPH
26
New cards
upreglated in BPH
blocks alpha1 receptors in internal sphincter --> relax smooth muscle of bladder --> increase urethral flow = helps in overflow incontinence
ends with zosins
blocks alpha1 receptors in internal sphincter --> relax smooth muscle of bladder --> increase urethral flow = helps in overflow incontinence
ends with zosins
alpha 1 adrenergic receptors antagonist
27
New cards
alpha 1 receptor antagonist
useful in BPH
postural hypotension/dizziness/headache (occurs in alpha blockers), sexual adverse effects
do not use with viagra (PDE-5) sildenafil/talanafil
do not use during cataract surgery
useful in BPH
postural hypotension/dizziness/headache (occurs in alpha blockers), sexual adverse effects
do not use with viagra (PDE-5) sildenafil/talanafil
do not use during cataract surgery
tamzulosin
28
New cards
e.g. tadalafin/sidalafil
used in BPH + erectile dysfunction
do not use with alpha 1 blocker or postural hypotension increases
used in BPH + erectile dysfunction
do not use with alpha 1 blocker or postural hypotension increases
PDE 5 inhibitors
29
New cards
- blocks conversion b/w testosterone to dihydrotestosterone
- effective in LUTS rather than in BPH (prevention cure)
- reduce prostate size (shrinks) - PSA used to measure prostate volume
- can be used in hair loss for men
e.g dutasteride = do not use in PREGNANCY (accidental)
- effective in LUTS rather than in BPH (prevention cure)
- reduce prostate size (shrinks) - PSA used to measure prostate volume
- can be used in hair loss for men
e.g dutasteride = do not use in PREGNANCY (accidental)
5 alpha reductase inhibitors
30
New cards
1) anticholinergic agents = ach muscarinic atagonists - increase bladder size + decrease contraction (dry mouth, constipation...)
2) beta 3 adrenergic agonists = stimulate detrusor to promote relaxation + less side effects
2) beta 3 adrenergic agonists = stimulate detrusor to promote relaxation + less side effects
overactive bladder (urge continence)
31
New cards
1) alpha1 antagonists + 5 alpha reductase (dutasteride + tasmulosin) = overflow incontinence improved + shrinks prostate = DUODART)
2) beta 3 agonists + alpha 1 blockers = OAB + relaxation muscles but side effects
2) beta 3 agonists + alpha 1 blockers = OAB + relaxation muscles but side effects
combination therapy
32
New cards
acts like 5 alpha reductase inhibitors + anti inflammatory
herbal saw palmetto
33
New cards
herbal
hypoxis rooperi
34
New cards
herbal
pygeum africanum
35
New cards
e.g. goserelin
gonadotrophin releasing hormone analog, increase of FSH and LH to decrease testosterone
- QT prolongation effects
gonadotrophin releasing hormone analog, increase of FSH and LH to decrease testosterone
- QT prolongation effects
androgen deprivation therapy
36
New cards
more than 25mL
size prostate to be enlarged
37
New cards
- acute urinary retention
- increase UTI risk
- bladder stones
- formation of diverticuli (no epmtying so the bladder expands, more pressure, herniation)
- renal damage
- increase UTI risk
- bladder stones
- formation of diverticuli (no epmtying so the bladder expands, more pressure, herniation)
- renal damage
complications of BPH
38
New cards
- urine retention
- UTI recurrency
- stones
- diverticuli
- UTI recurrency
- stones
- diverticuli
when to go for surgery in BPH
39
New cards
- start on alpha blockers (stop priot to surgery)
- do US KUB
- if high bladder volume
- insert catheter
- start on duodart (combination alpha 1 blocker and 5-alpha-reductase)
- if after removing catheter, still high then think surgery
- do US KUB
- if high bladder volume
- insert catheter
- start on duodart (combination alpha 1 blocker and 5-alpha-reductase)
- if after removing catheter, still high then think surgery
steps for BPH
40
New cards
- stress incontinence: stress situation like lifting, squeezing, sneezing = leak (occurs in pregnancy, pelvic floor therapy needed)
- urge incontinence: patients with OAB (detrusor contracted) --> give medication (anticholingergic/beta 3) or botox to paralyze detrusor
- mix of both
- urge incontinence: patients with OAB (detrusor contracted) --> give medication (anticholingergic/beta 3) or botox to paralyze detrusor
- mix of both
types of incontinence
41
New cards
below 15ml/second is LOW
uro-flow study Q max value
42
New cards
- most common benign renal tumor
- cannot metastasize
- papillomatous structures
- do not differ from low grade papillary renal cell CARCINOMA
- both contain 7 and 17 trisomies
- treat like its cancer
- cannot metastasize
- papillomatous structures
- do not differ from low grade papillary renal cell CARCINOMA
- both contain 7 and 17 trisomies
- treat like its cancer
renal papillary adenoma
43
New cards
- benign tumor composed of vessels, fat and muscle
- found in people with tuberous sclerosis (loss of function in TSC1 and 2)
- can hemorrhage
- found in people with tuberous sclerosis (loss of function in TSC1 and 2)
- can hemorrhage
angiomyolipoma
44
New cards
- condition leading to angiomyolipoma (sometimes multiple lesions)
- triangular lesions in brain
- ash leaf macule on skin
- angiofibroma on skin (bumps)
- triangular lesions in brain
- ash leaf macule on skin
- angiofibroma on skin (bumps)
tuberous sclerosis
45
New cards
angiomyolipoma
vessels, fat, muscle containing spindle cells
vessels, fat, muscle containing spindle cells
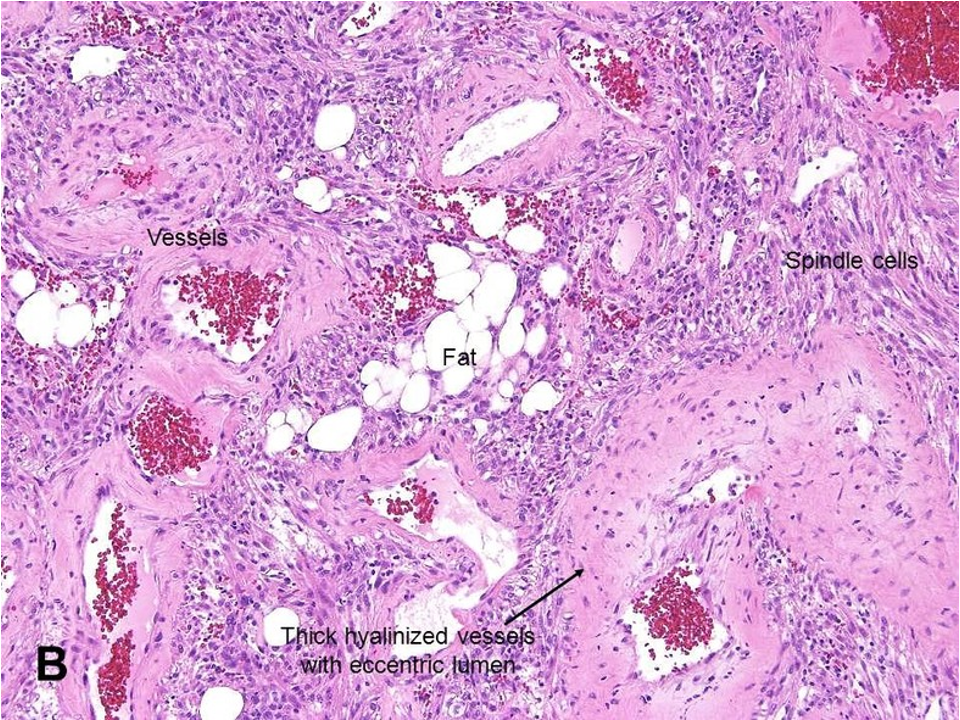
46
New cards
renal papillary adenoma papillary architecture
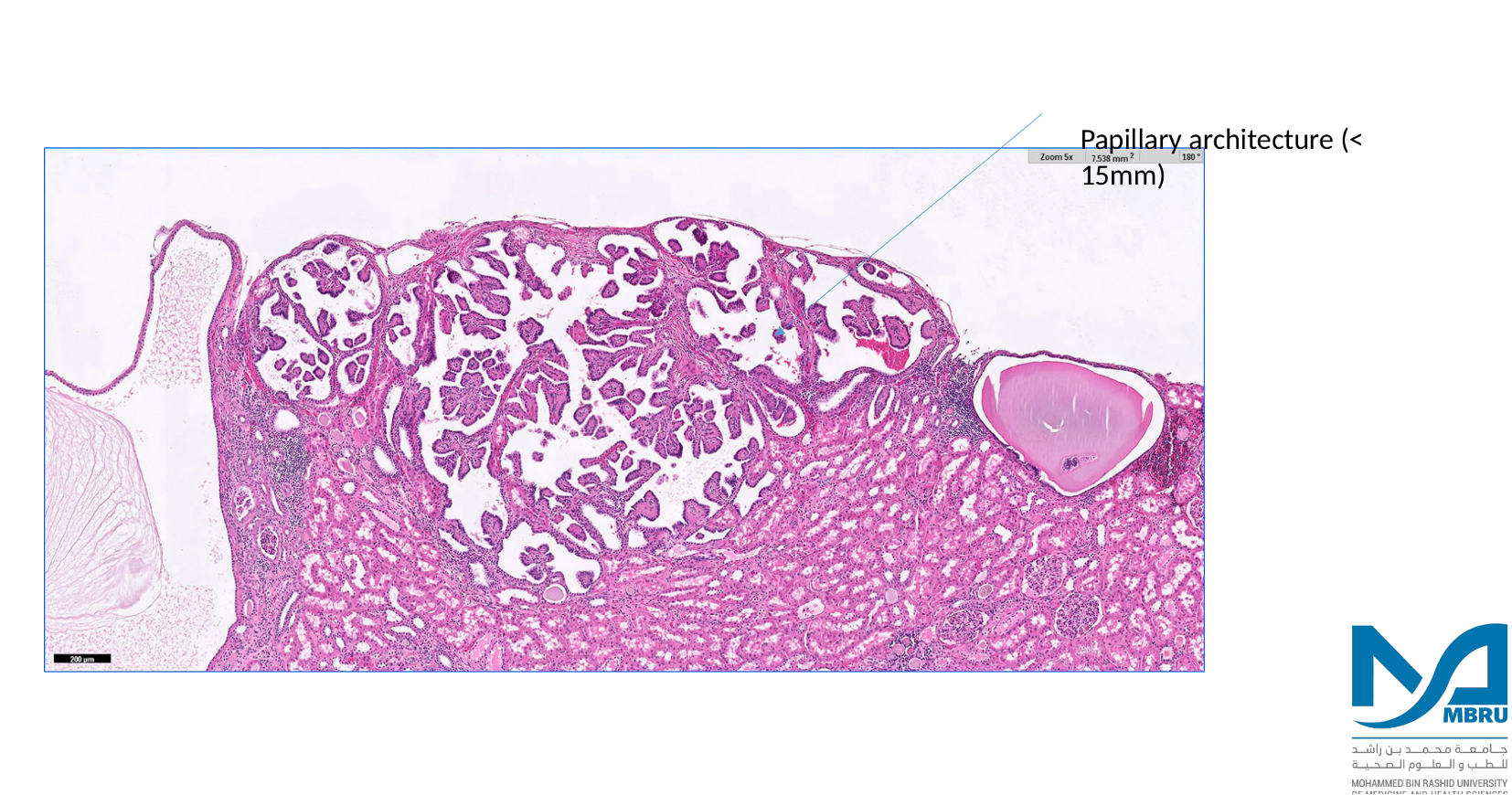
47
New cards
aka benign oxophilic adenoma
- encapsulated, tan, mohogany brown with central scar
- contains oncocytic cells (eosinophilic)
- encapsulated, tan, mohogany brown with central scar
- contains oncocytic cells (eosinophilic)
oncocytoma
48
New cards
oncocytoma
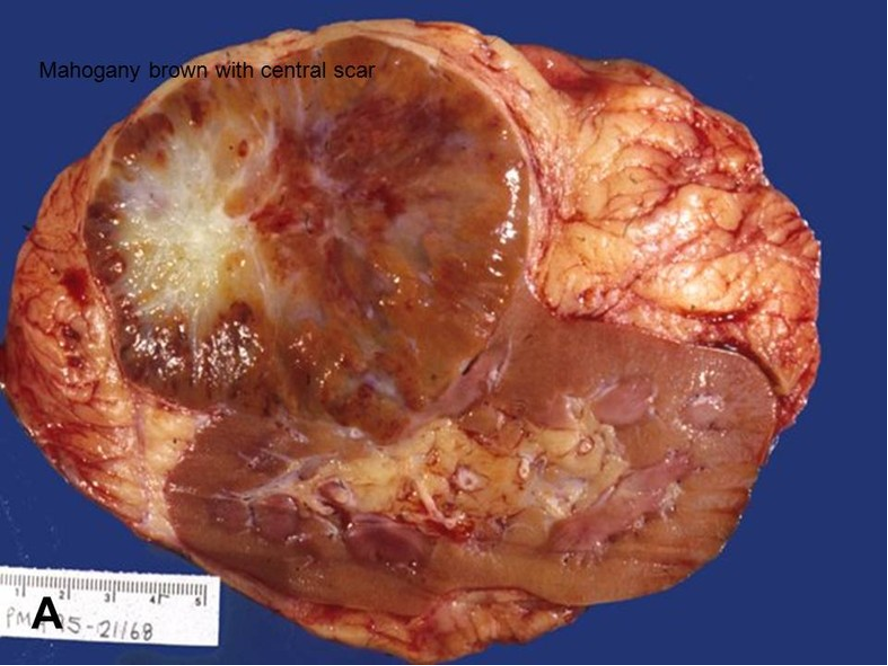
49
New cards
- most common malignant tumor
- arise from tubular epithelium = renal adenocarcinomas
- arise from tubular epithelium = renal adenocarcinomas
renal cell carcinoma
50
New cards
- smoking, obesity, hypertension, renal failure, tuberous sclerosis
- inherited: sporadic
1. von hippellindau: hemangioblastomas, renal cysts and RCC
2. hereditary clear cell carcinoma
3. hereditary papillary carcinoma
- inherited: sporadic
1. von hippellindau: hemangioblastomas, renal cysts and RCC
2. hereditary clear cell carcinoma
3. hereditary papillary carcinoma
epidemiology of RCC
51
New cards
if present: costovertebral pain, palpable mass and hematuria
- metastasize widely (lungs ad bones)
- metastasize widely (lungs ad bones)
renal cell carcinoma diagnostic features
52
New cards
- common: clear cell carcinoma
- papillary carcinoma (7,17 trisomies)
- chromophobe renal - good prognosis + raisinoid nuclei
- collecting duct (bellini) carcinoma - medullary location
- papillary carcinoma (7,17 trisomies)
- chromophobe renal - good prognosis + raisinoid nuclei
- collecting duct (bellini) carcinoma - medullary location
types of RCC
53
New cards
clear cell carcinoma
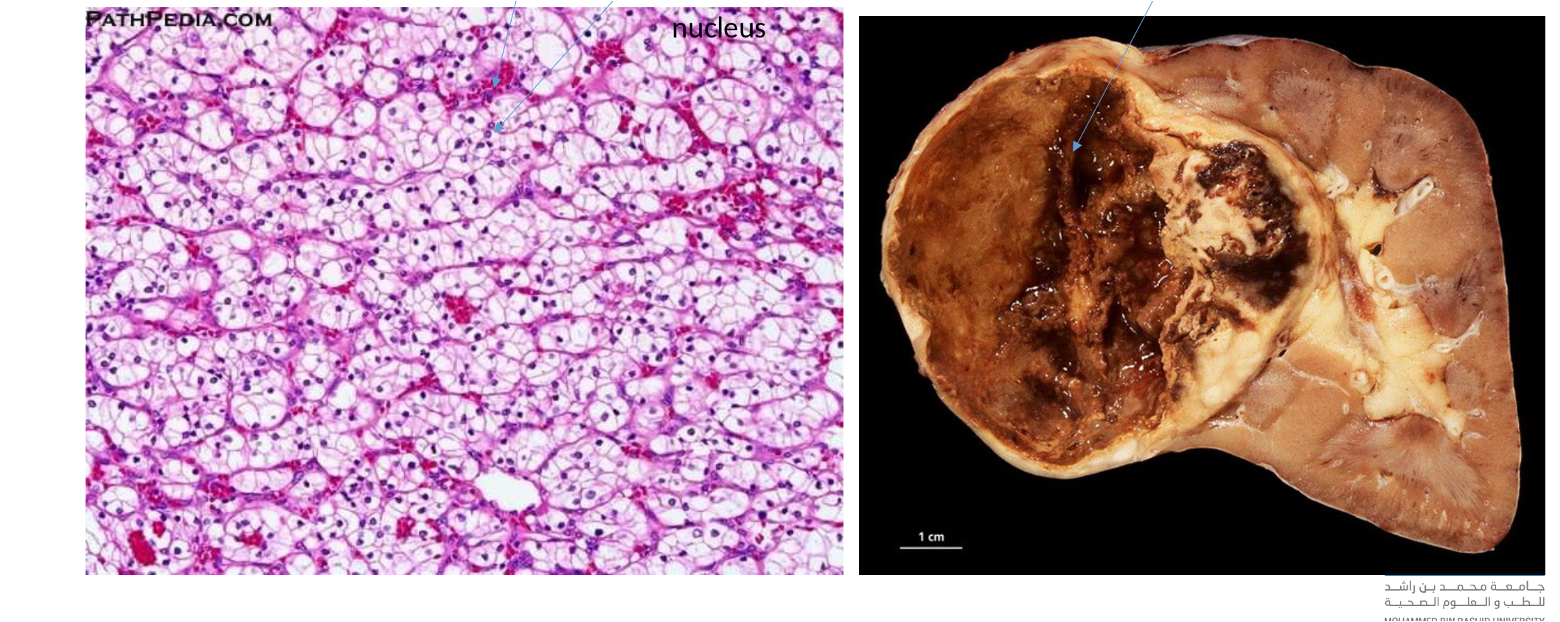
54
New cards
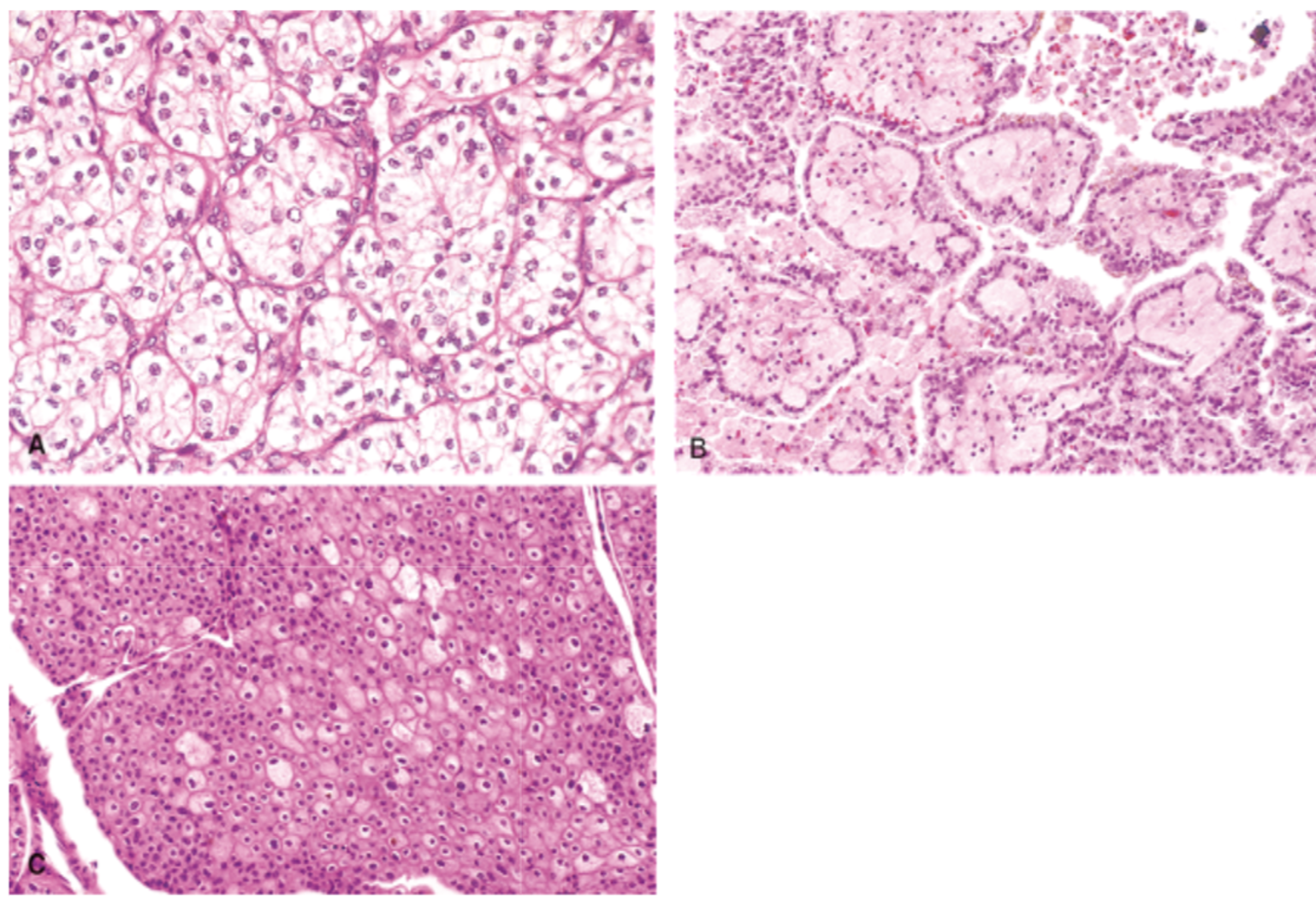
A. clear cell carcinoma
B. papillary
C. chromophobe = raisinoid nuclei
B. papillary
C. chromophobe = raisinoid nuclei
55
New cards
collecting duct (bellini) carcinoma - rare + aggressive form
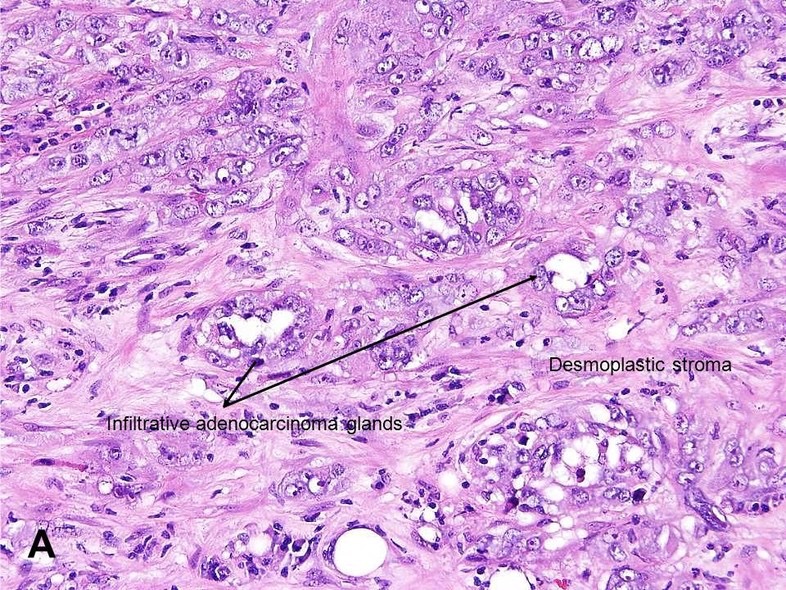
56
New cards
usually w/ immunotherapy + tyrosine kinase inhibitors
treatment of RCC
57
New cards
aka wilms tumor
-affects children
- lobulated lesion can be seen
- involves both kidneys
-affects children
- lobulated lesion can be seen
- involves both kidneys
nephroblastoma
58
New cards
- tumor suppressor gene in kidney and gonads
- wilms tumor can have mutation in this gene
- wilms tumor can have mutation in this gene
WT 1 gene
59
New cards
- WAGR syndrome: aniridia, genital anomalies, retardation
- Denys drash syndrome: dysgenesis gonads, renal failure
- BWS syndrome: hemihypertrophy, omphalocele.
- Denys drash syndrome: dysgenesis gonads, renal failure
- BWS syndrome: hemihypertrophy, omphalocele.
nephroblastoma associations
60
New cards
1) blastemal component (purple cells)
2) epithelial = primitive tubules
3) mesenchymal
2) epithelial = primitive tubules
3) mesenchymal
triphasic histology of nephroblastoma
61
New cards
A. 3 components of nephroblastoma
B. anaplasia nephroblastoma
B. anaplasia nephroblastoma
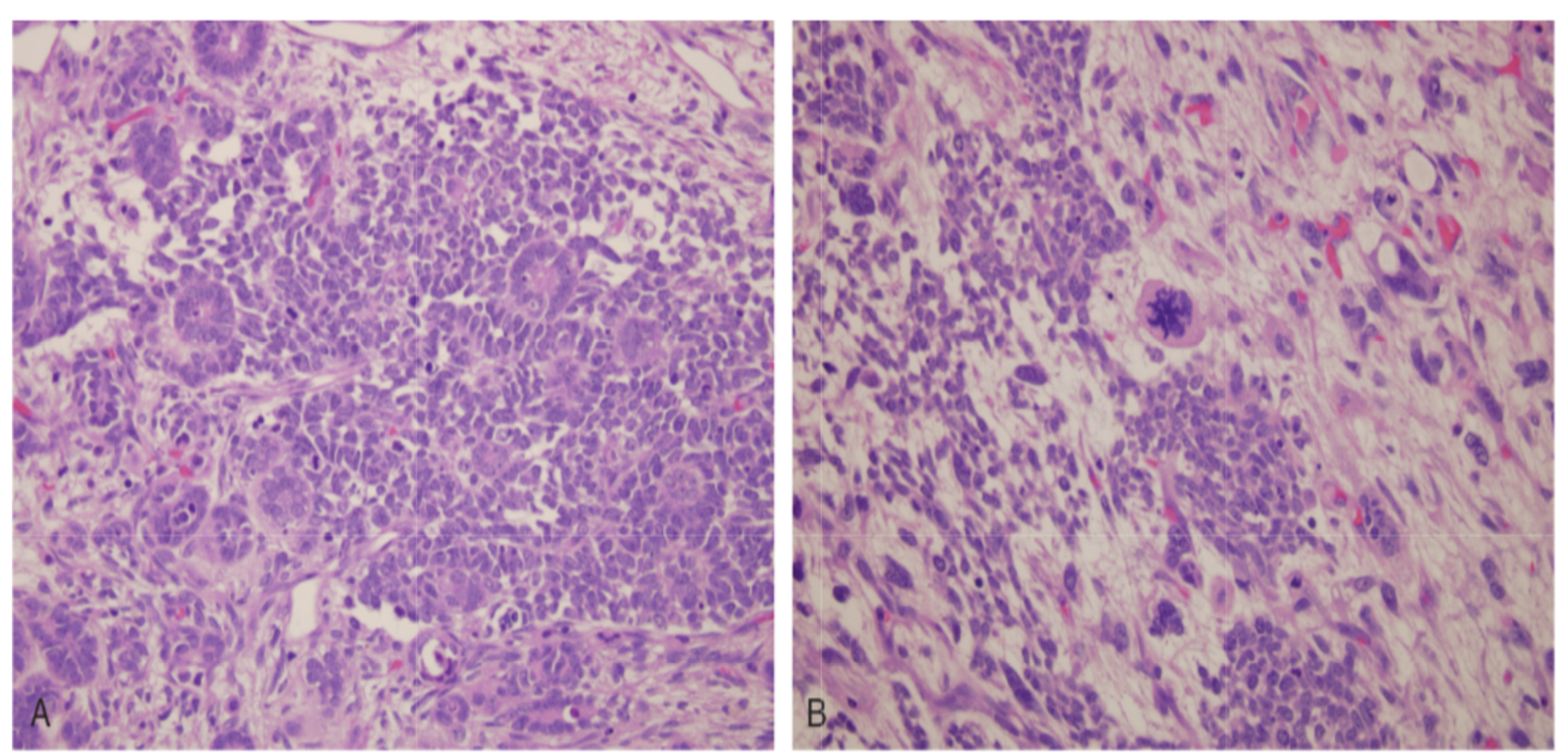
62
New cards
collecting duct, as reabsoprtion is load dependent
region where calculi most likely to form
63
New cards
occur in collecting duct, load dependent --> depends on saturation and pH
precipitation location
64
New cards
urine saturation --> supersaturation --> nucleation of crystals --> aggregation = stone formation
steps to stone formation
65
New cards
promoters: high urinary excretion of calcium, oxalate and urate
inhibitors: high rate of citrate excretion, potassium and magnesium as they dilute urine
inhibitors: high rate of citrate excretion, potassium and magnesium as they dilute urine
promoters and inhibitors of stones
66
New cards
- male gender
- low fluid intake
- high salt intake (na)
- low fluid intake
- high salt intake (na)
general risk factors for stones
67
New cards
- iodiopathic
- hyperparathyroidism
- hypercalcemia
- supplements
- hyperparathyroidism
- hypercalcemia
- supplements
hypercalciuria and stones
68
New cards
1)enteric hyperoxaluria: short bowel, fatty acids bind to calcium and oxalate is free to be reabsorbed in gut, or oxalate is not secreted through colon therefore enters urine (associated w/chrons and celiac disease)
ileum resection: malabosprtion of bile salts, increases permeability to oxalate
2) primary hyperoxaluria
genetic disorders PH1 and 2
ileum resection: malabosprtion of bile salts, increases permeability to oxalate
2) primary hyperoxaluria
genetic disorders PH1 and 2
high urinary oxalate
69
New cards
- hypokalemia
- chronic acidosis
- distal renal tubular acidosis - genetic loss of bicarbonate
- chronic acidosis
- distal renal tubular acidosis - genetic loss of bicarbonate
hypocitraturia
70
New cards
metabolized to oxalate or uric acid
decreases pH
decreases pH
high animal protein intake in stones
71
New cards
- composed: potassium, ammonium, phosphate
- due to UTI urease +ve e.g. proteus
- due to UTI urease +ve e.g. proteus
struvite stones
72
New cards
- increase fluid intake - nocturia
- decrease salt use
- decrease animal products
- decrease vit c supplement and calcium
- decrease salt use
- decrease animal products
- decrease vit c supplement and calcium
principles of management stones
73
New cards
- recurrent stones: give thiazide diuretics that reduce calcium excretion in urine and promote hyperkalemia
- hypocitraturia: potassium citrate supplements
- enteric hyperoxaluria: stop eating oxalate food
- primary hyperoxaluria: pyridozine supplements
- hypocitraturia: potassium citrate supplements
- enteric hyperoxaluria: stop eating oxalate food
- primary hyperoxaluria: pyridozine supplements
specific management stones
74
New cards
calcium oxalate
low pH stones
75
New cards
calcium phosphate
high pH stone