AP Psychology Unit 9A: Social
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
1
New cards
attribution theory
theory that describes how people explain their own and others' behavior
2
New cards
fundamental attribution error
the tendency for observers, when analyzing another’s behavior, to underestimate the impact of the situation and to overestimate the impact of personal disposition
3
New cards
just world phenomenon
people get what they deserve
4
New cards
saliency bias
focusing on the most noticeable (salient) factors when explaining the causes of behavior
5
New cards
self-serving bias
tendency to credit oneself for positive consequences and avoid blame for negative consequences
6
New cards
dispositional vs. situational vs. self-serving
dispo - someone is blamed
situation - environment is blamed
self - someone avoids blame
situation - environment is blamed
self - someone avoids blame
7
New cards
… and … effect our behavior/social thinking
internal attitudes and external influences
8
New cards
compliance
changing one’s behavior as a result of someone directing/asking for the change
9
New cards
compliance: foot in the door
tendency for someone to comply with a big request after complying with a smaller one
10
New cards
compliance: door in the face
when a large request is made so that they will agree with a smaller request
11
New cards
compliance: lowballing
to induce someone to agree to something with a low ‘cost’ and then adding on to the original product
12
New cards
compliance: reciprocity
people are socialized into returning favors (favor for favor)
13
New cards
role
set of expectations about a social position
14
New cards
example of a role
stanford prison experiment
15
New cards
cognitive dissonance theory
an uncomfortable state of mind arising when our attitude and actions are inconsistent; we then seek to resolve/reduce dissonance by changing our attitude
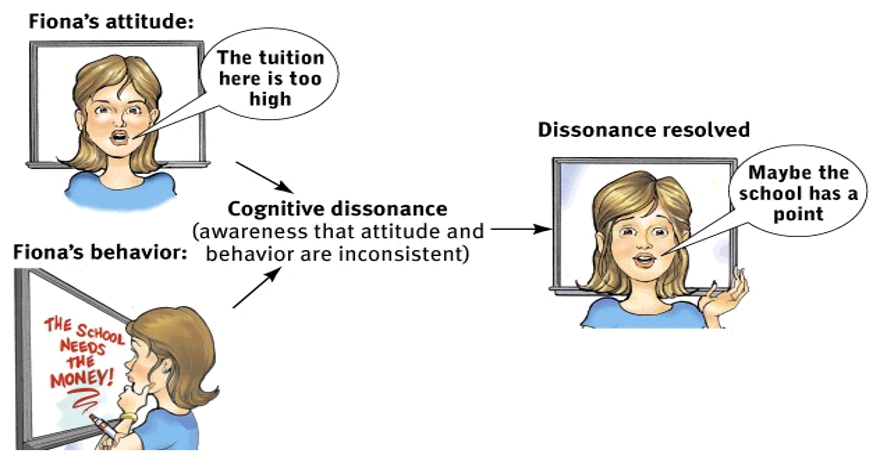
16
New cards
persuasion: central route of persuasion
focuses on facts and the message in order to convince
(logos)
(logos)
17
New cards
persuasion: peripheral route of persuasion
focuses on feelings in order to convince
(personality of speaker, how the message was delivered)
(ethos, pathos)
(personality of speaker, how the message was delivered)
(ethos, pathos)
18
New cards
conformity
compliance with standards, rules, laws
19
New cards
norm
something that is usual, typical, standard
20
New cards
normative social influence
changing behavior to fit into the norms/gain approval/avoid disapproval
21
New cards
informational social influence
following the behavior of others because you think they are ‘right’
22
New cards
the asch effect
a form of conformity in which a group majority influences individual judgements

23
New cards
asch effect: 3 factors that influence conformity
1. size of the majority
2. presence of a partner
3. size of discrepancy between opinions
24
New cards
milgram’s obedience experiment
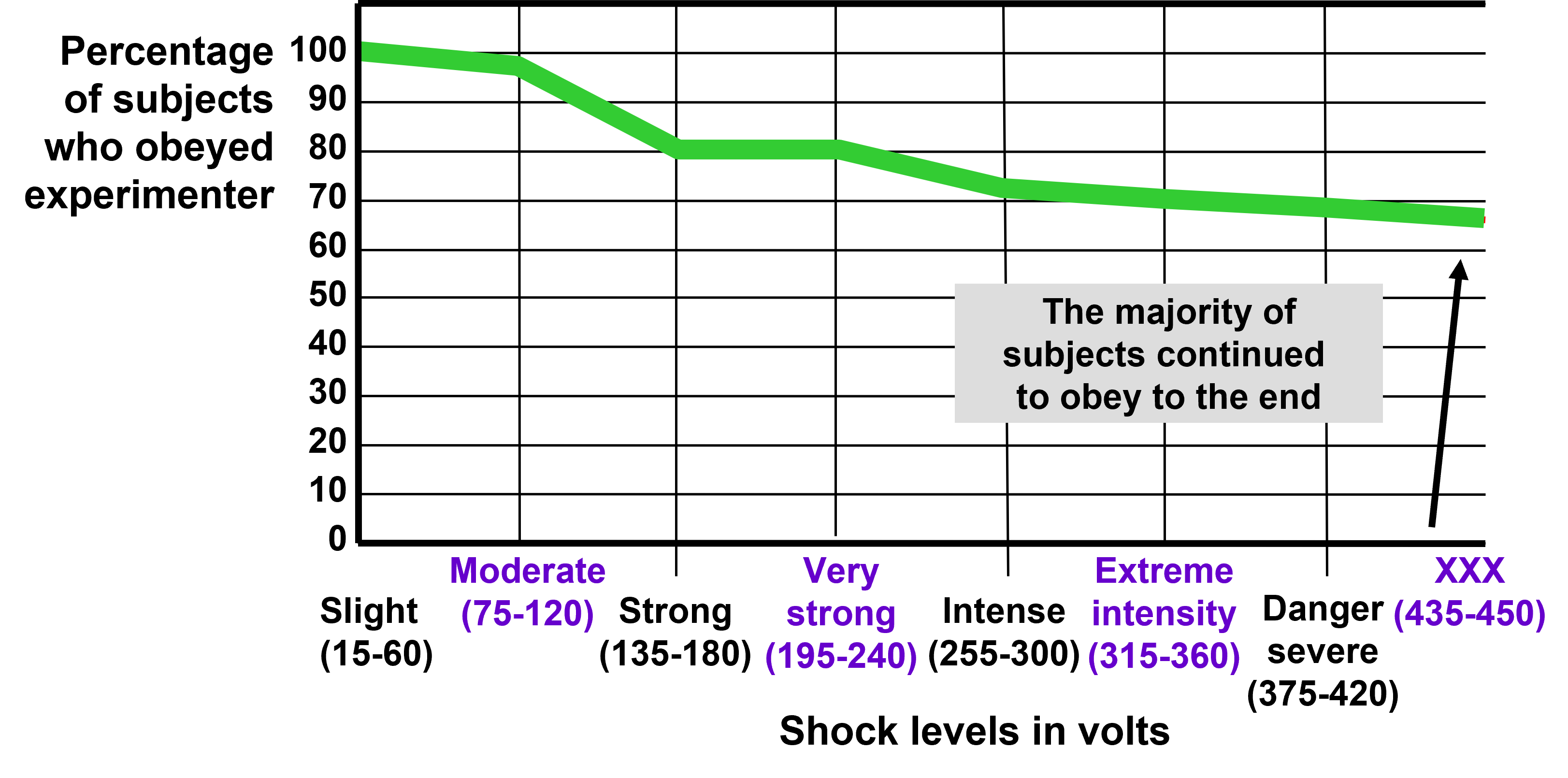
25
New cards
social facilitation
improved performance of tasks in the presence of others
26
New cards
social loafing
tendency for people in a group to exert less effort than when they are individual
27
New cards
deindividuation
loss of self-awareness and self-restraint in groups
(ie. internet trolling/negative comments when posting anonymously)
(ie. internet trolling/negative comments when posting anonymously)
28
New cards
group polarization
tendency for members of a group discussing an issue to move toward a more extreme version of the positions they held before the discussion began
29
New cards
groupthink
when a group makes irrational/unrealistic decisions spurred by the urge to conform
30
New cards
self-fulfilling prophecy
one tends to behave in ways that reinforce beliefs and actions, thus causing them to come true
31
New cards
prejudice
negative/unjustifiable attitude toward a group
32
New cards
stereotype
overgeneralization about a group
33
New cards
ingroup vs. outgroup
i - people who share a common identity
o - those perceived as different from the ingroup
o - those perceived as different from the ingroup
34
New cards
ingroup bias
tendency to favor one’s own group
35
New cards
scapegoat theory
theory that prejudice provides outlet for anger and blame
36
New cards
5 causes for discrimination
1. dissimilarity and social distance
2. economic competition
3. scapegoating
4. conformity to social norms
5. media stereotypes
37
New cards
halo effect
cognitive bias in which an someone’s overall impression of something/someone influences their thoughts about their character
(ie. assuming something good because they seem good)
(ie. assuming something good because they seem good)
38
New cards
aggression
any physical/verbal behavior intended to hurt/destroy
39
New cards
frustration-aggression principle
principle that frustration creates anger, which generates aggression
(ie. hot weather and crime rates)
(ie. hot weather and crime rates)
40
New cards
social trap
a situation where conflicting groups each pursue their self-interest and end up in a mutually destructive behavior
we harm out collective well-being by pursuing personal interests
we harm out collective well-being by pursuing personal interests
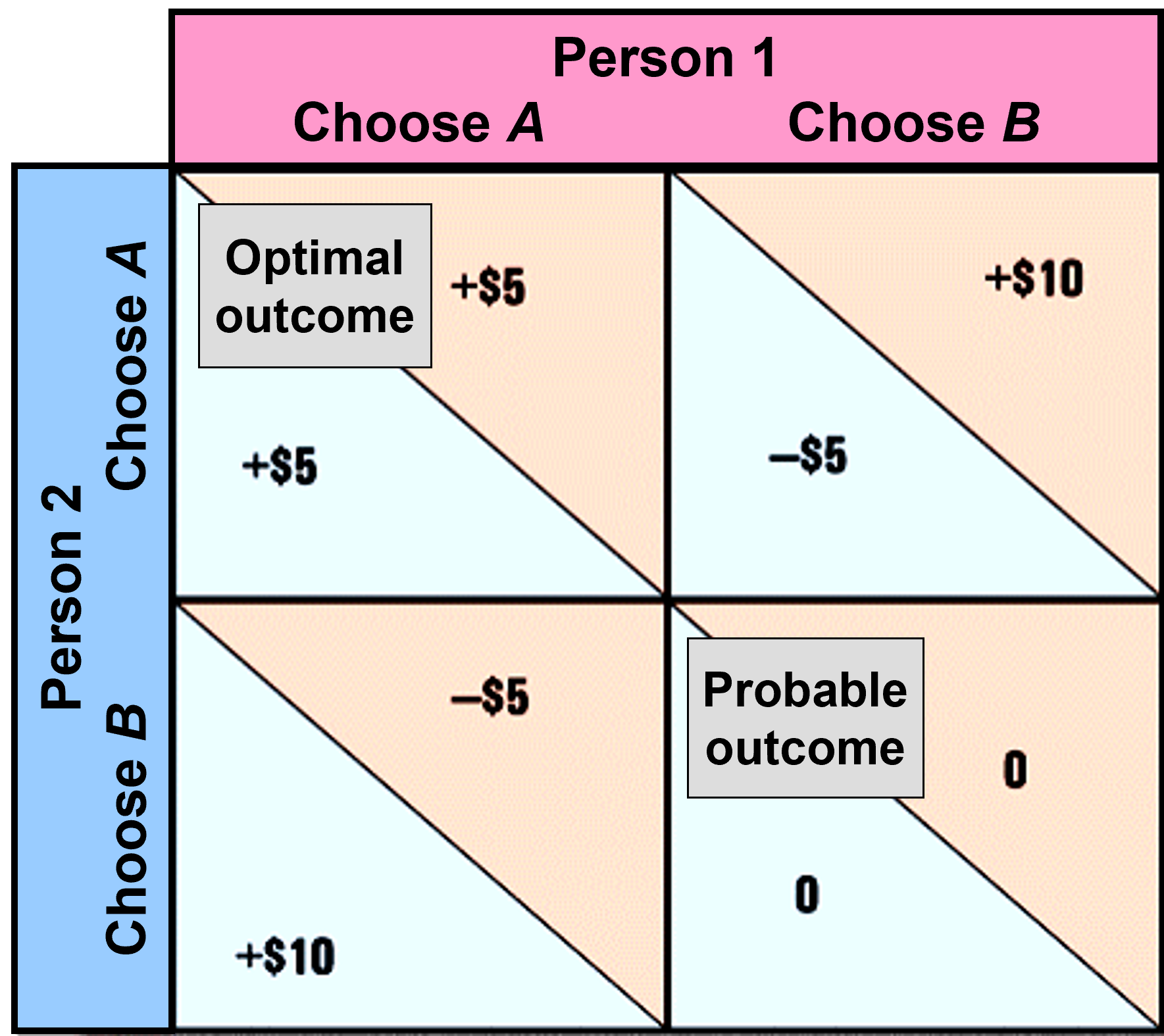
41
New cards
social relations: types
(+/+) approach-approach
(-/-) avoidance-avoidance
(+/-) approach-avoidance
(-/-) avoidance-avoidance
(+/-) approach-avoidance
42
New cards
4 sources of attraction
1. proximity
2. similarity
3. self-disclosure (trust)
4. physical attractiveness (average=beautiful, beautiful=unapproachable)
43
New cards
matching hypothesis
prediction that people will find friends/mates that are perceived to be about their same level of attractiveness
44
New cards
expectancy value theory
theory that people decide to pursue relationships based on the minimal risk of failure
(trying to find best chance at success)
(trying to find best chance at success)
45
New cards
5 forms of love
1. empty love (commitment)
2. infatuation (passion)
3. romantic love/passionate love (intimacy and passion)
4. companionate love (commitment and intimacy)
5. consummate love (commitment, intimacy, and passion)
46
New cards
equity
what people receive in proportion to what they give to it
47
New cards
self-disclosure
revealing intimate aspects of oneself to others
48
New cards
altruism
unselfish regard for welfare of others
49
New cards
bystander effect
tendency to be less likely to help when other bystanders are present
50
New cards
social exchange theory
theory that our social behavior is an exchange process (maximize benefits, minimize costs)
51
New cards
superordinate goals
shared goals override differences
52
New cards
prosocial behavior
behavior that is intended to help
53
New cards
antisocial behavior
behavior that is intended to hurt