Chem 1010- Exam 2 Study Guide
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
A gas consists of small particles that
move rapidly in straight lines
have essentially no attractive (or
repulsive) forcesare very far apart
have very small volumes
compared to the volume of the container they occupyhave kinetic energies that
increase with an increase in temperature
The volume of a gas…
is the same as the volume of the container it occupies
is usually measured in liters or milliliters
increases with an increase in temperature at a constant pressure
The temperature of a gas relates to the
average kinetic energy of the molecules and is measured in the Kelvin (K) temperature scale
Pressure is a measure of the gas particle collisions with sides of a container and is measured in units of
millimeters of mercury (mmHg) or Torr
atmospheres (atm)
pascals (Pa) or kilopascals (kPa)
pounds per square inch (psi)
Gas particles in the air exert
pressure on us. It is called
atmospheric pressure
A barometer…
measures the pressure exerted by the gases in the atmosphere
indicates atmospheric pressure as the height in millimeters of the mercury column
760 mmHg = 1 atm = 760 Torr
Atmospheric pressure
is the pressure exerted by a column of air from the top of the atmosphere to the surface of Earth
decreases as altitude increases
is 1 atm at sea level
Atmospheric pressure changes with variations in weather
and altitude.
On a hot, sunny day, the mercury column _____, indicating a higher atmospheric pressure.
On a rainy day, the atmosphere exerts less pressure, which causes the mercury column to ____.
rises; fall
What is 475 mmHg expressed in atmospheres?
0.625 atm
The pressure in a tire is 2.00 atm. What is this pressure
in millimeters of mercury?
1520 mmHg
The downward pressure on the Hg in a barometer is _____ the pressure of the atmosphere.
the same as
A water barometer is 13.6 times taller than a Hg barometer (dHg = 13.6 g/mL) because
H2O is less dense than mercury
According to the Kinetic Molecular Theory, what happens to the kinetic energy of gas particles when the temperature of the gas increases?
The inverse relationship between the pressure and volume of a gas is known as
Boyle’s Law
Boyle’s Law
Changes occur in opposite directions. When volume increases, the pressure decreases provided the temperature and moles of the gas remain constant.
Boyle’s law states that
the pressure of a gas is inversely related to its
volume when T is constantthe product P × V is
constant when temperature and amount of a gas are
held constantif volume decreases,
the pressure increases
P1V1 = P2V2
In Boyle’s Law, what is constant?
temperature
During an inhalation,
the lungs expand
the pressure in the
lungs decreasesair flows toward the lower pressure in the lungs
During an exhalation,
lung volume decreases
pressure within the lungs increases
air flows from the higher pressure in the lungs to
the outside
Freon-12, CCl2F2, was used in refrigeration systems. What is
the new volume of an 8.0-L sample of Freon gas initially at
550 mmHg after its pressure is changed to 2200 mmHg at
constant temperature and moles?
2.0 L
A sample of oxygen gas has a volume of 12.0 L at 600 mmHg. What is the new pressure when the volume changes to 36.0 L at a constant T and n?
200 mmHg
For a cylinder containing helium gas, indicate whether cylinder A or cylinder B represents the new volume for the following
changes. (n and T are constant.)
If a sample of helium gas has a volume of 120 mL and a
pressure of 850 mmHg, what is the new volume if the pressure
is changed to 425 mmHg at a constant T and n?
240 mL
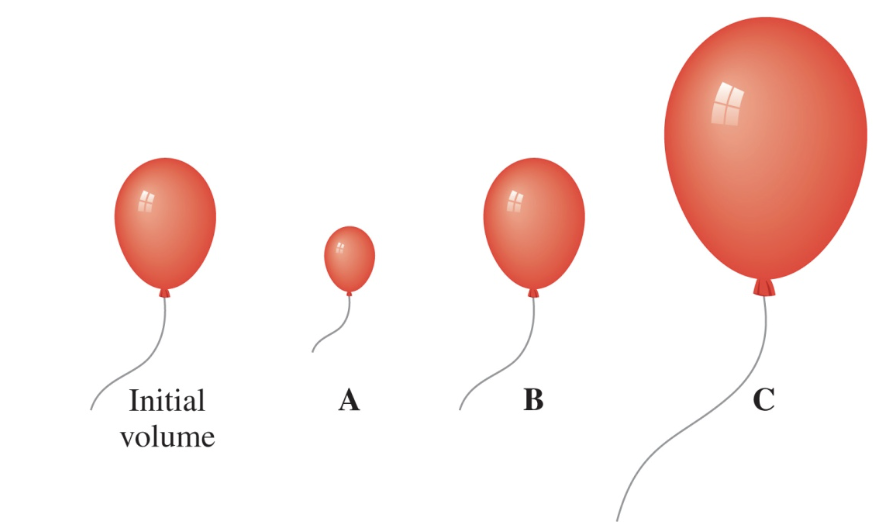
A sample of helium gas in a balloon has a volume of 6.4 L at a pressure of 0.70 atm. At 1.40 atm (T and n are constant), is the new volume represented by A, B, or C?
If we increase the temperature of a gas sample, kinetic molecular theory states that the motion (kinetic energy) of the gas particles will ___________.
also increase
If the amount and pressure of the gas is held constant, the volume of the container will _______.
increase
In Charles’s law,
the Kelvin temperature of a gas is directly related to the volume
pressure and moles of gas are constant
when the temperature of a sample of gas increases, its volume increases at a constant pressure
What is constant in Charle’s Law?
P and n
A balloon has a volume of 785 mL at 21 °C. If the temperature drops to 0 °C, what is the new volume of the balloon at constant pressure and moles?
729 mL
A sample of oxygen gas has a volume of 420 mL at a temperature of 18 °C. At what temperature (in degrees Celsius) will the volume of the oxygen be 640 mL? (P and n are constant.)
170 °C
Use the gas laws to complete each sentence with increases
or decreases.
A. Pressure _______ when V decreases at a constant temperature and moles.
B. When T decreases, V _______ at constant pressure and moles.
C. Pressure _______ when V changes from 12 L to 24 L at constant temperature and moles.
D. Volume _______when T changes from 15 °C to 45 °C at constant pressure and moles.
According to Charles’s Law, if the temperature of a gas is doubled (while keeping pressure and the amount of gas constant), what happens to the volume?
Gay-Lussac’s law
when the Kelvin temperature of a gas is doubled and the volume and amount of gas do not change, the pressure also doubles.
In Gay-Lussac’s law,
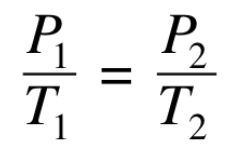
the pressure exerted by a gas is directly related to the Kelvin temperature of the gas
What is constant in Gay-Lussac’s law?
volume and amount of gas
A gas has a pressure at 2.0 atm at 18 °C. What is the new pressure when the temperature is 62 °C? (Volume and moles remain constant.)
2.3 atm
A gas has a pressure of 645 Torr at 128 °C. What is the temperature in degrees Celsius if the pressure increases to 824 Torr? (V and n remain constant.)
239°C
Explain why water boils at a lower temperature in the mountains than at sea level.
Atmospheric pressure in the mountains is less than at sea level. The vapor pressure of the water reaches the atmospheric pressure at a lower temperature.
The combined gas law uses the pressure–volume–temperature relationships from Boyle’s law, Charles’s law, and Gay-Lussac’s law where n is constant.
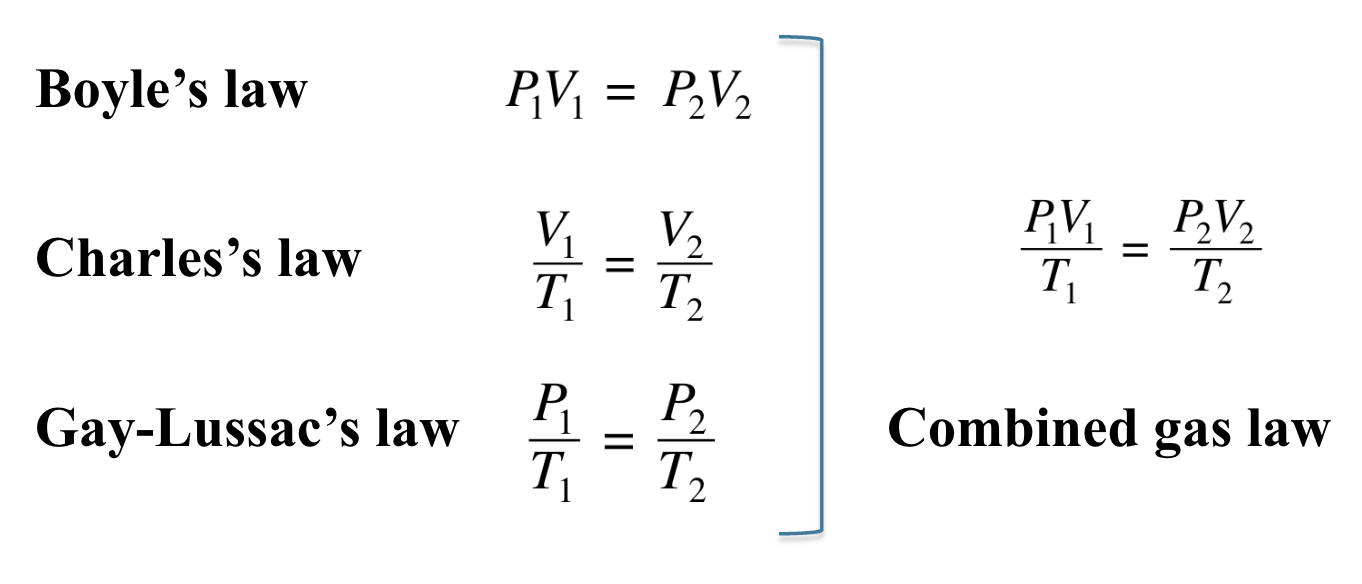
A gas has a volume of 675 mL at 35 °C and 646 mmHg pressure. What is the volume (in milliliters) of the gas at −95 °C and a pressure of 802 mmHg? (n is constant.)
314 mL
A sample of helium gas has a volume of 0.180 L, a pressure of 0.800 atm, and a temperature of 29 °C. At what temperature (in degrees Celsius) will the helium have a volume of 90.0 mL and a pressure of 3.20 atm? (n remains constant.)
604 K
In Avogadro’s law,
the volume of a gas is directly related to the number of moles (n) of gas
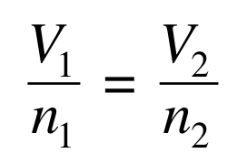
What is constant in Avogadro’s law?
T and P
If 0.75 mole of helium gas occupies a volume of 1.5 L, what volume (in liters) will 1.2 moles of helium occupy at the
same temperature and pressure?
2.4 L
The volumes of gases can be compared at STP, Standard Temperature and Pressure, when they have
the same temperature
standard temperature (T )
0 °C or 273 K
the same pressure
standard pressure (P )
1 atm (760 mmHg)
At standard temperature and pressure (STP), 1 mole of a gas occupies a volume of 22.4 L, which is called its ____________.
molar volume
What is the volume occupied by 2.75 moles of N2 gas at STP?
61.6 L N2
What is the volume at STP of 4.00 g of CH4?
5.60 L
How many grams of He are present in 8.00 L of gas at STP?
1.43 g
The ____________ of a
gas is the pressure that each
gas in a mixture would exert if it were by itself in the container.
partial pressure
Dalton’s law of partial pressures indicates that
pressure depends on the total number of gas particles, not on the types of particles
the total pressure exerted by gases in a mixture is the sum of the partial pressures of those gases
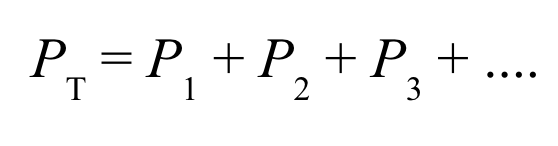
The air we breathe
is a mixture of
different gasescontains mostly N2 and
O2, and small amounts
of other gases
A scuba tank contains O2 with a pressure of 0.450 atm and He at 855 mmHg. What is the total pressure, in millimeters of mercury, in the tank? (Volume and temperature are constant.)
1.20 × 103 mmHg
For a deep dive, a scuba diver uses a mixture of helium and oxygen with a pressure of 8.00 atm. If the oxygen has a partial pressure of 1280 mmHg, what is the partial pressure of the helium? (Volume and temperature are constant.)
4800 mm Hg
A gas mixture contains Nitrogen at a partial pressure of 400 mmHg and Oxygen at a partial pressure of 300 mmHg. What is the total pressure of the mixture?