PD E3- OB Exam
1/89
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
What is a glycoprotein produced by the developing placenta shortly after implantation that is found in urine and plasma; often used to test for pregnancy?
Beta subunit of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)
Would you obtain a urine hCG or plasma hCG for the following?
diagnosing ectopic pregnancy
monitoring trophoblastic tumors
screening fetal abnormalities
serial levels to r/o spontaneous abortions
Plasma hCG
When does a home urine pregnancy test become positive?
4 wks LMP
*low false positive / high false negative rate
What is the most accurate way to diagnose pregnancy, and is accurate before missed menses?
Serum beta hCG
When do you start obtaining transabdominal US?
≥ 6 wks (once gestational sac is present)
When can you start to detect fetal heart tones with electronic doppler device?
8-14 weeks
What is hegar’s sign?
Softening of isthmus of uterus
What is Chadwick’s sign?
Increased vascularity throughout pelvic region → bluish discoloration of vagina and cervix
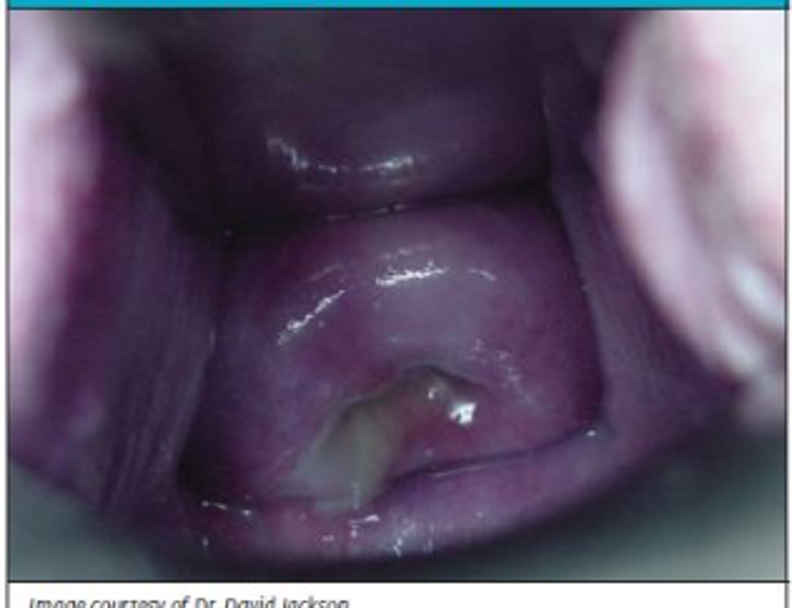
When does nausea / “morning sickness” usually improve?
After 12-16 wks
What causes heartburn in pregnancy?
Progesterone causes GE sphincter to relax → enlarged uterus presses upward pressure on the stomach → decreases gastric motility & acid secretion → delayed digestion
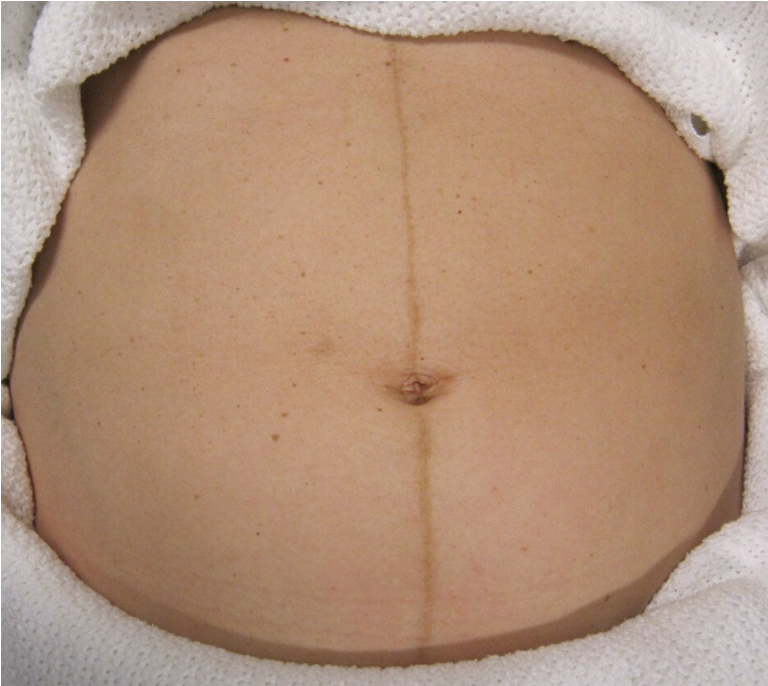
What is brownish-black pigment along the midline of the abdomen?
Linea nigra
What is diastasis recti?
Rectus abdominis muscles separate at midline (noticeable in later trimesters)
How does the abdomen enlarge throughout pregnancy?
Uterus rises out of pelvis into abdomen by 12th week → inc in abdominal girth apparent by 15th week
*enlargement may appear earlier if multiparous female
What causes backaches during pregnancy?
Estrogen & progesterone relax pelvic joints, increased uterine weight increases lumbar lordosis, & abdominal muscles stretch and lose tone
What urinary changes occur during pregnancy?
Inc frequency around the 6th week, inc vascularity & pressure from uterus, & symptoms improve when uterus rises above pelvis until fetal head settles into maternal pelvis near term
What is the sensation of fetal movement that usually begins at 20 wks in primigravida or 17-18 wks in multipara?
Quickening
What is “dropping” late in pregnancy (3rd trimester) when the fetus descends into the lower pelvis?
Lightening
How often should prenatal visits occur?
≤ 28 wks: every month
28-36 wks: every 2-3 wks
≥ 36 wks: once per wk until delivery
What is performed at the 10-13 week prenatal visit?
Nuchal translucency screen, mother’s lab work, UA & culture
What is performed at the 16-18 week prenatal visit?
1st sonogram, UA & culture, amniocentesis / CVS (if indicated), & triple screen (trisomy 16, 18, 21)
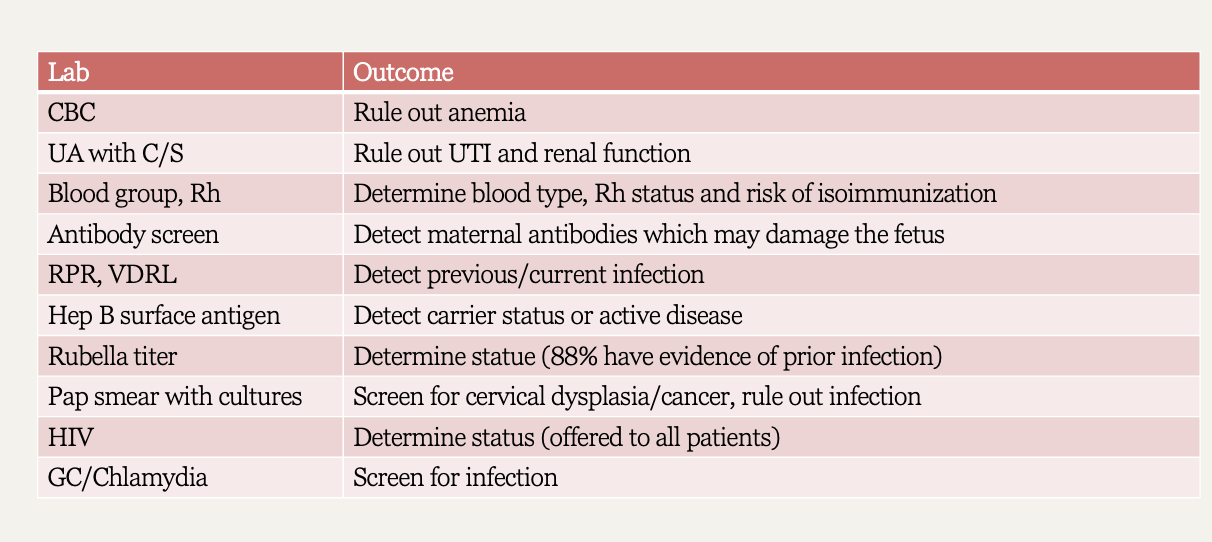
What is performed at the first prenatal visit?
Pap smear, Rh w/ blood type, STI screen- GC/ chlamydia, HIV, rubella, syphillis, HBV, TB, labs- H&H, UA & culture
What is performed at the 26-28 week prenatal visit?
Fetal: FHT, fundal height, position
Labs: DM, CBC, Ab screen, GC/chlamydia, UA & C, syphilis (optional)
Give rhogam if indicated
What is performed at the 36 week prenatal visit?
GBS culture
What is performed at the 40 week prenatal visit?
Focused fetal exam, UA & C, fetoplacental function tests (PRN)
WHa tis the time of pregnancy counting from the first day of LMP?
Gestational age
What is the time of pregnancy counting from fertilization?
Developmental age
What is the first trimester?
0-14 wks
What is the second trimester?
14-28 wks
What is the third trimester?
28 wks - birth
What is fertilization to 8 wks?
Embryo
What is 8 wks to birth?
Fetus
What is pre viable?
Before 24 wks (trending towards 20 wks)
What is preterm?
24-26 wks
What is term?
37-42 wks
What is the total number of pregnancies?
Gravity (G)
What is the number of deliveries > 500g or ≥ 20 wks GA?
Parity (P)
What is GP status if a patient has twins?
G1P2
What is the number of pregnancies lost before 20 wks or fetus < 500 g?
Abortus (Ab)
What is the number of successful pregnancy outcomes?
Living children (LC)
What is “painless” uterine contractions occurring after the 28th week?
Braxton-hicks contractions
What is pelvic pain occurring at mid cycle and related to ovulation?
Mittelschmerz
The following signs are associated with what condition?
uterus increases rapidly in size shortly after implantation
persistent vaginal bleeding, no fetal movement, no FHT by 12 weeks
N/V more intense
grape like clusters of tissues may be expelled through vagina
Hydatidiform mole / molar pregnancy
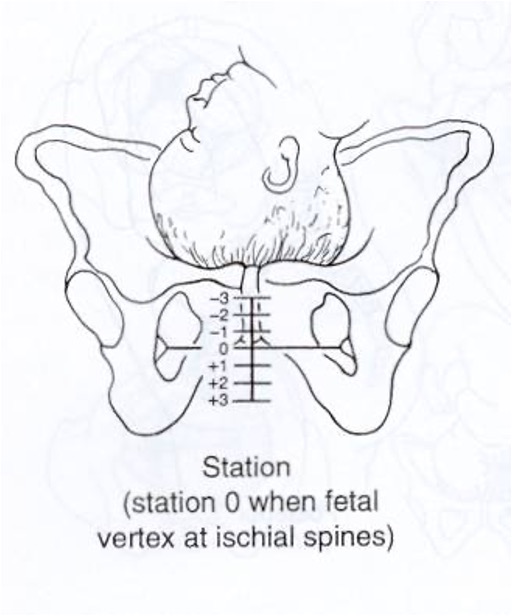
What characterizes the level of descent of the presenting part of the fetus?
0 = fetal occiput (vertex presentation) has reached level of maternal ischial spines (engagement)
-1 = 1 cm above
+1 = 1 cm below
Station
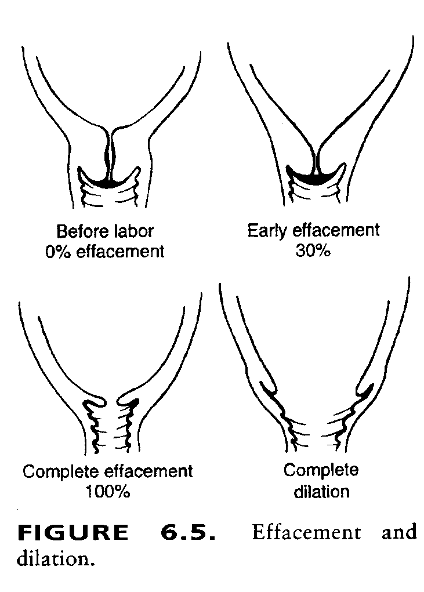
What is the degree to which the cervix has thinned, expressed as a number of cm in which cervix has changed?
also expressed as percentage
determined by digital exam
4 cm = is unchanged
Effacement
What is the number of cm of the opening of the internal os, determined on exam with 1-2 fingers?
Dilation
What is calculated with GaPbcde?
a: total # of pregnancies
b: full term ≥ 37 wks
c: preterm 20-36 wks
d: abortions & ectopic < 20 wks
e: living children
What rule is used to calculate estimated date of confinement (EDC)?
Naegele’s rule → first day of LMP - 3 months + 1 year & 7 days
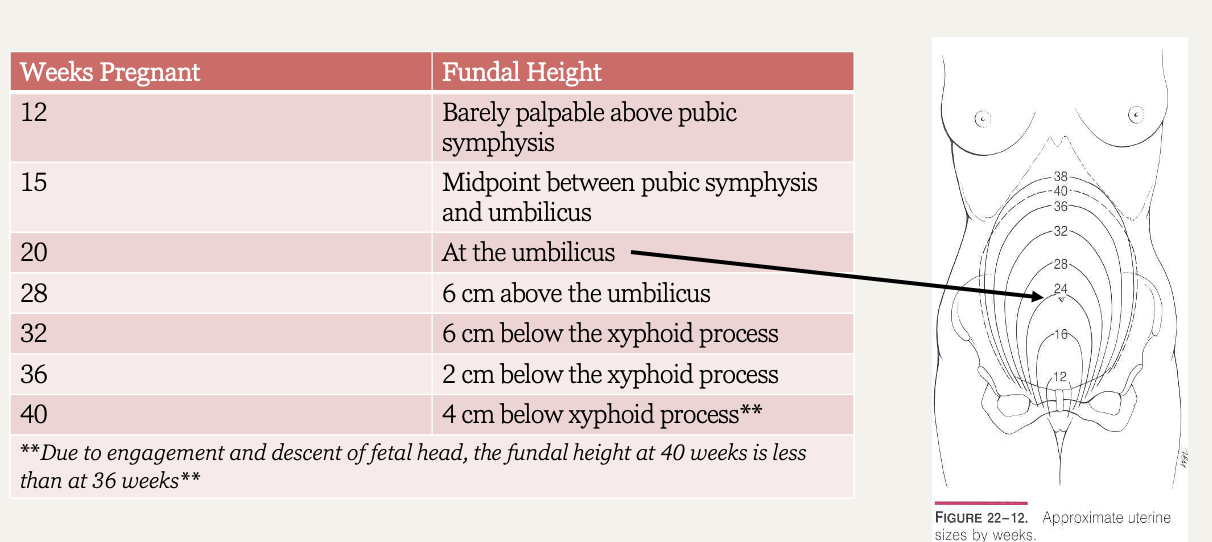
What is the fundal height at 12 weeks?
Uterus at level of pubic symphysis
What is the fundal height at 16 weeks?
Uterus between pubic symphysis and umbilicus
What is the fundal height at 20 weeks?
Uterus at the level of umbilicus
What can compression of the descending aorta and IVC during the OB exam cause (patient should sit briefly before proceeding to pelvic exam to avoid- semi-sitting position with knees bent)?
Supine hypotensive syndrome
What is considered gestational HTN?
≥ 140/90 after week 20 without proteinuria
What is chronic HTN in pregnancy?
≥ 140/90 before pregnancy, before week 20 and after 12 weeks PP
What is pre-eclampsia?
≥ 140/90 after week 20 with proteinuria
Mid pregnancy blood pressure is normally ______ than in the non-pregnant state
Lower
First trimester weightless should NOT exceed what amount of prepartum weight?
5%
What is mammary soufflé?
Increased blood flow through dilated internal mammary artery → easily heard in 2nd & 3rd interspace in parasternal areas
Which murmurs, if heard in pregnancy, may accompany anemia & should be investigated?
Diastolic murmurs & dyspnea
Regular uterine contractions +/- pain or bleeding occurring is considered abnormal (preterm labor) before what timeframe?
Before 37 wks
What should you consider if the fundal height is > 4 cm than expected?
Large fetus, extra amniotic fluid, uterine leiomyoma
What should you consider if the fundal height is < 4 cm than expected?
Missed abortion, transverse lie, growth restriction or false pregnancy
What might a lack of audible FHR indicate?
Fetal demise or false pregnancy
Fundal height chart
What does a pink cervix indicate?
Non-pregnant state
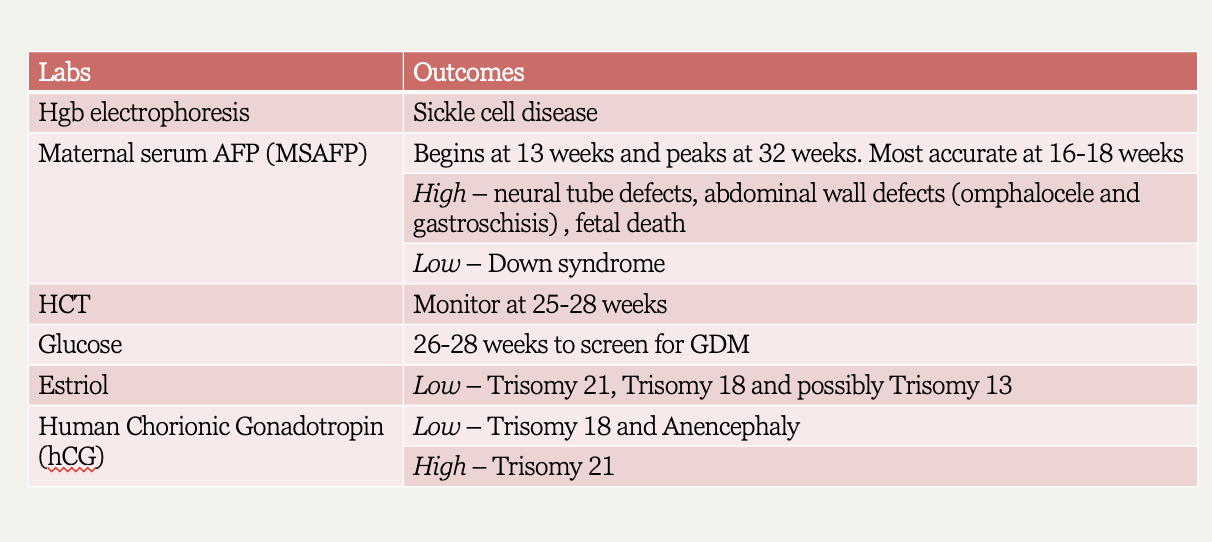
Routine labs / diagnostics chart
How can pregnancy be diagnosed with US?
Once yolk sac is present, easier with TVUS than pelvic
*excludes ectopic pregnancy except in rare instance of heterotopic
What is a blighted ovum or an embryonic pregnancy?
GS > 10 mm and no yolk sac is identified
What is a normal FHR?
120-160 bpm
*higher earlier in pregnancy
When should FHR increase with movement?
after 32-34 weeks
What is the best place to auscultate FHR if breech (back on right)?
RUQ
What is the best place to auscultate FHR if head is down?
LLQ
When can FHR be heard without doppler amplification (US), using a fetoscope instead?
20 weeks
What is the relationship of the long axis of the fetus to the mother?
*99% vertex (head first) or breech (buttocks first)
Lie
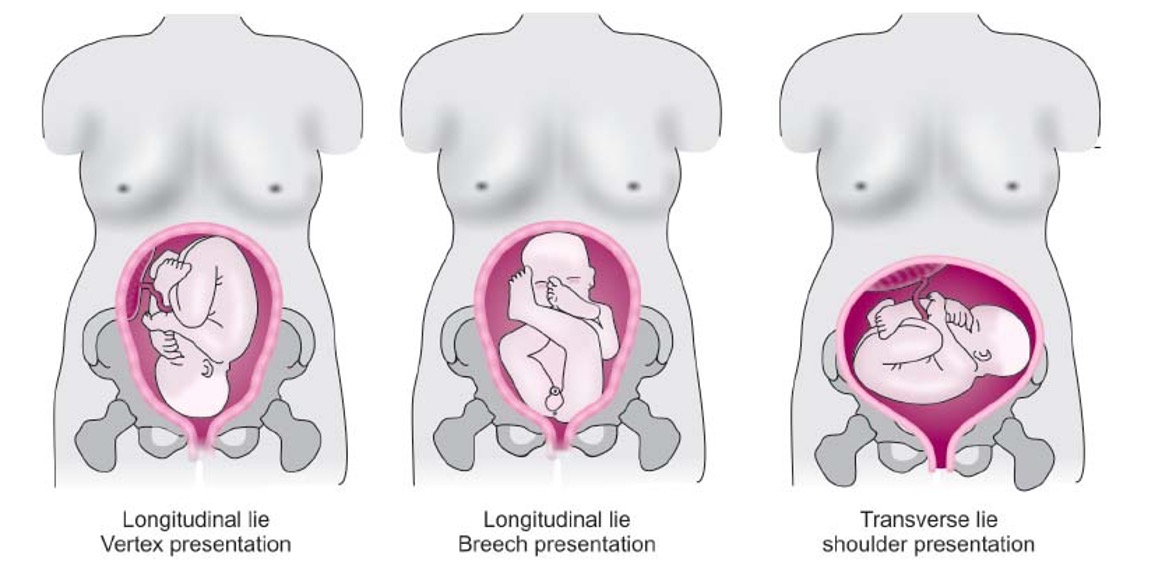
What is the lowest part of the fetus in the birth canal, palpated through the cervix?
Presentation
What is the relation of the presenting part of the fetus to maternal R or L side of birth canal, anteriorly (A), transversely (T), or posteriorly (P)?
Position
What term describes the position of the arms, legs, spine, neck and face?
Attiude / posture / habitus
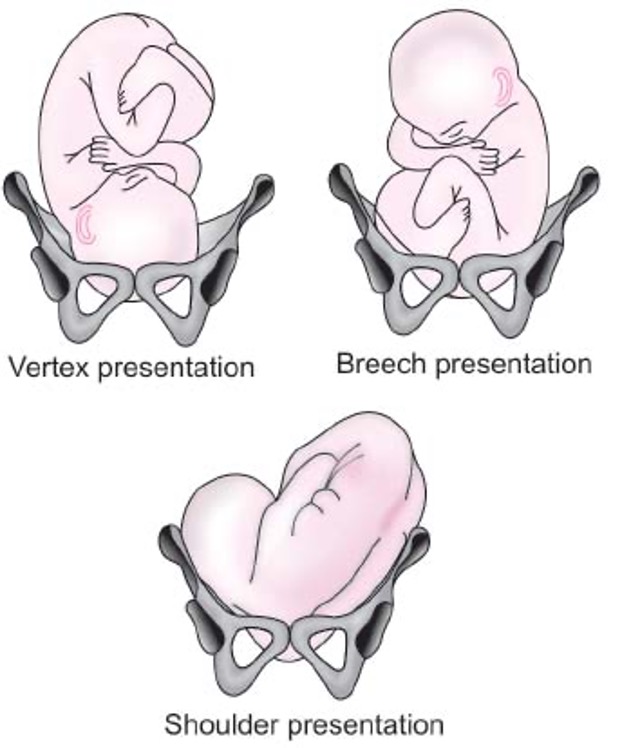
What is the normal presentation?
Head flexed w/ chin on chest, posterior fontanel is the presenting part
What is shoulder dystocia/
Fetal head delivered, shoulder is impacted behind pubic symphysis
What is face presentation?
Neck is extended, sinciput presentation, anterior fontanel presents first
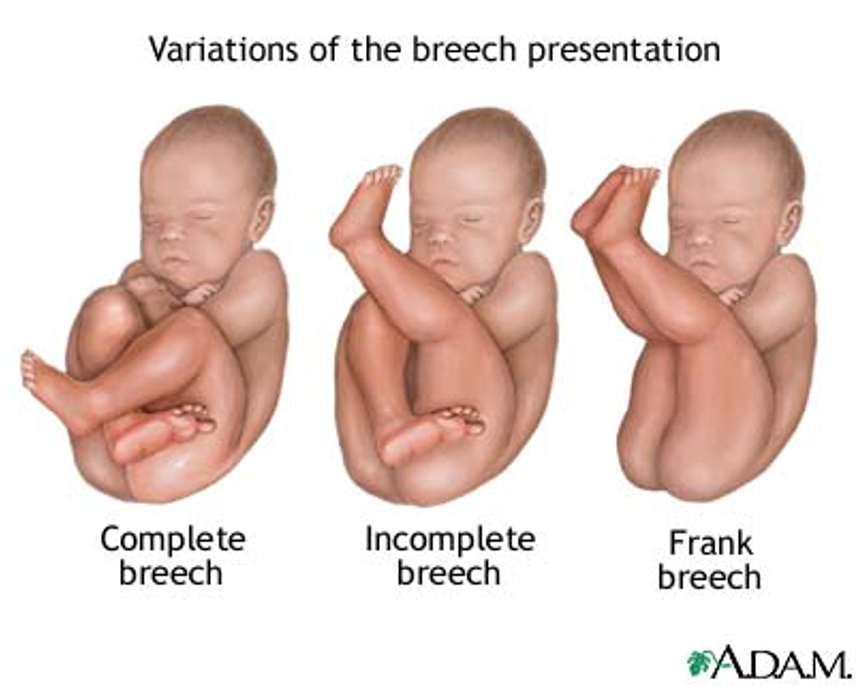
What is breech presentation?
Buttocks presents first (frank MC)
What is brow presentation?
Eyebrow presents first
What is maneuvers provide useful information to assess the lie and presentation of the fetus from the 28th week & on?
Leopold’s maneuvers
What are the 4 parts of Leopold’s maneuvers?
Determine what fetal part occupies fundus: buttocks feels firm but irregular, head feels hard & moveable
Determine what side is fetal back: one side rounded but firm, other is irregular, lumpy, & moves
Identify descent of presenting part: if lower pole not engage, moveable part will be felt
Identify cephalic prominence: confirm presentation part & locate side of cephalic prominence
What should a prenatal multivitamin contain?
Atleast 400 mcg folic acid
What food / nutrition should be a voided in pregnancy?
Unpasteurized dairy products, undercooked meats, excess vitamin A, shark, swordfish, king mackerel, canned tuna
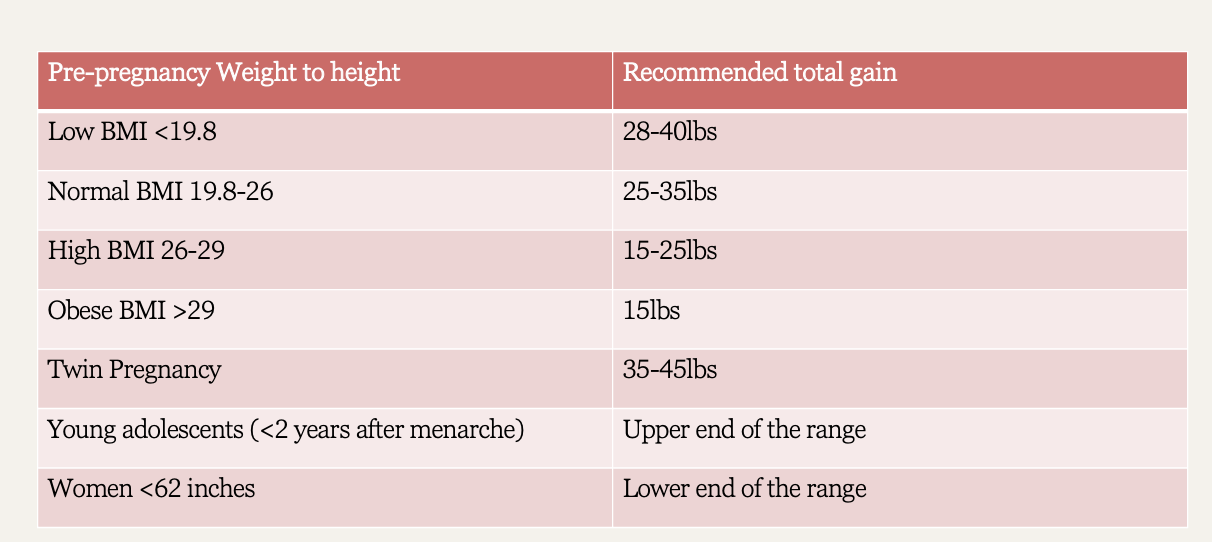
pregnancy weight chart
What exercise should patient avoid after first trimester?
Anything in supine position → compresses IVC and decreases blood flow to placenta
What vaccines should be avoided in pregnancy?
Live vaccines (VZV, MMR)
What vaccines can be given in pregnancy?
Tetanus, influenza, pneumococcal, meningococcal, HBV
What is a typical meal plan recommendation for pregnancy?
3 meals per day → additional 300 kcal