Thermodynamics and KTG
1/36
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
What is Degree of freedom for matter
They’re the number of independent ways in which a molecule can move (translation motion), spin (Rotational motion), and Vibrate and produce energy
What is the formulae to calculate vibrational degree of freedom
Vibrational DOF = 3N−Translational DOF − Rotational DOF
where,
N → Number of atoms in the molecule
What is entropy
It is the measure of disorderness in the system
What is Bolt’s constant
It is the measure of energy per molecule
What is the formula for Bolt’s constant
Kb = R/NA
where,
NA → Avagadro’s number
R → Universal gas constant
What is the formula for molar heat capacity at constant volume
Cv =FR/2
where,
F → Degree of freedom
R → Universal gas constant
What is the relation between molar heat capacity at constant pressure and molar heat capacity at constant volume
n*Cp - n*Cv = R
where,
Cp → molar heat capacity at constant pressure
Cv → molar heat capacity at constant volume
R → universal gas constantn → Number of moles
Cp /Cv = γ
What is the formula for the ratio that we get between Cp and Cv? What is it called?
γ = 1 + 2/f
where,
f → Degree of freedom
γ → Coefficient of adiabatic process
What is R?
It is the universal gas constant per mole of gas
What is Cm
It is the molar heat capacity
What is the formula for the speed of gas?
√γ*R*T/m
Where,
γ → Coefficient of adiabatic process
R → Universal gas constant
T → Temperature
m → mass
What is the ideal gas equation
PV = nRT
where,
P → pressure
V → Volume
n → Number of moles
R → Universal gas constant
T → Temperature
What are the formulae for work done in an isothermal process? Why is it so?
∆W = nRT*ln(V2/V1) → ∆W = 2.303*nRT*log10(V2/V1)
And using Boyle’s Law, P ∝ 1/V
∆W = nRT*ln(P1/P2) → ∆W = 2.303*nRT*log10(P1/P2)
The reason we are doing this is that pressure isn’t constant and is rather variable
What is the formula for the fraction of heat used to increase internal energy in an isobaric process?
∆U/∆Q = 1/γ
What is the formula for the fraction of heat used to increase the work done in an isobaric process?
∆W/∆Q = 1- 1/γ
What is the ideal gas equation for adiabatic processes
PVγ = nRT
What is the formula for work done in an adiabatic process
∆W = nR∆T/1-γ
What is an adiabatic wall
It is a type of wall where there is no heat flow between 2 objects
What is a diathermal wall
It is a type of wall where there is heat flow between 2 objects
What is the ideal gas equation for polytropic processes
PVx = nRT
What is the work done in Polytropic process
∆W = nR∆T/1-x
What are the 2 formulae for Molar heat capacity in polytropic processes
Cm = Cv + R/1-x
Cm = R/1-γ + R/1-x
What are the main points in the Kinetic theory for gases
Molecules considered are large in number
No energy lost
Collisions are elastic
The distance between the molecules is > size of the molecules
Momentum is conserved
When is the Kinetic theory for gases valid for ideal gas
At high temperature and low pressure
What is the value of the universal gas constant in
SI unit
CGS unit
8.31 J/Kelvin mol (or) 25/3 J/Kelvin mol
2 calorie/kelvin mol
When does a real gas become an ideal gas
At high temperatures
What is the formula for density of a gas
Mo → Also known as Gram molecular weight

What is the formula for the pressure of an ideal gas in a container
1/3 nmv²rms
Where,
n → number of molecules per unit volume => N/V
m → Mass of 1 molecule
v → rms velocity
What is the formula for average velocity of a gas molecule present inside a container
√8RT/⊼*G.M.M
What is the formula for the Maximum Pivotal velocity of a gas molecule present inside a container
√2*R*T/G.M.M
What are the formula for the rms velocity of a gas molecule present inside a container
√PV/G.M.M
√3RT/G.M.M
Where,
What does the Boltzmann distribution curve tell us, and what is it?
It is a graphical representation of molecules in a container, having a number of molecules on the y-axis and velocity on the x-axis
The area of the graph gives us the number of molecules and does not depend on temperature, and the peak of the graph provides us with the velocity of the molecules, corresponding to which there is a larger number of molecules
As you increase the temp, the graph extends; Literally
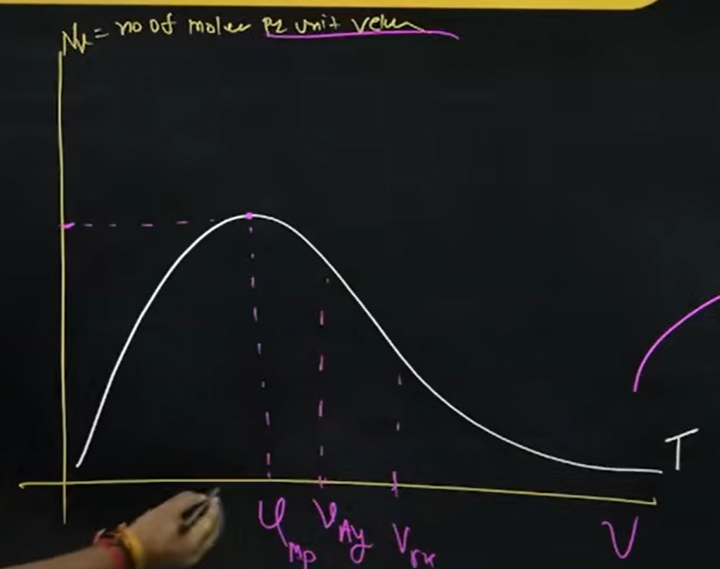
What is the Mean free path? What are its formula?
It is the distance between 2 colliding objects after a collision
S = v*t
1/ √2 ⊼ n*d²
Where,
n → Number density → Number of molecules/ volume
d → Diameter of the molecule
Whenever we write density, what do we do to the formulae
We divide the formula by volume
What is free expansion
The sudden expansion of gas into a vacuum, where,
∆U = 0
∆Q = 0
∆W = 0
The number of moles is always constant
What is the formula for the efficiency of the work done by a heat engine
Output/input => W/Q1
What does gamma show in an adiabatic process
It shows the compressibility of the gas under constant pressure and volume