Cell biology lecture 17
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Signal pathway regulation
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Learning objectives
How different cells respond differently to the same signal
How signalling pathways interact in a coordinated way
How signalling pathways are switched off
How some drugs act by interfering with the “on/off” switch
Coordination of signalling pathways
Different cells can respond differently to the same signal:
By using different receptors
By activating different intracellular machinery
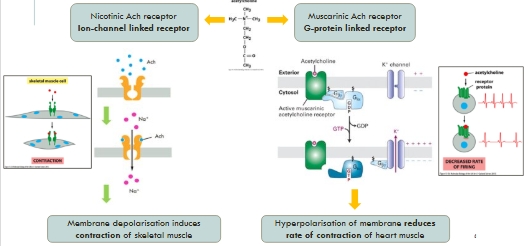
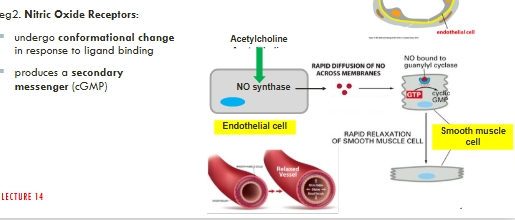
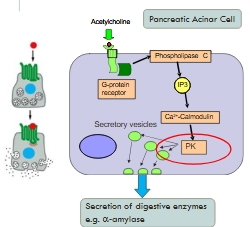
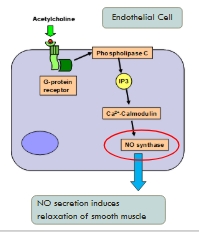
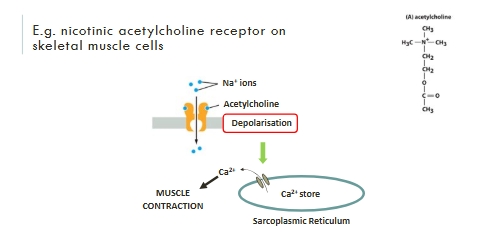
E.g. Acetylcholine receptors
- Skeletal muscle cells (L15)
- Heart muscle cells
- Endothelial cells (L14)
- Pancreatic acinar cells
Nicotinic Ach receptor vs muscarinic Ach receptor
NO and intracellular receptors
Activating different intracellular machinery: Pancreatic acinar cell
GPCR
Activating different intracellular machinery: Endothelial cell
GPCR
What can signalling pathways do?
They can interact and different responses need diff combinations of signal
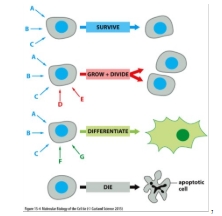
Signals may combine to alter the activity of signalling protein
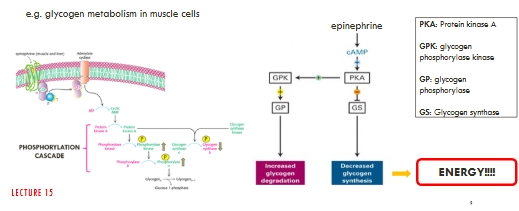
Signals may combine to alter the activity of signalling protein
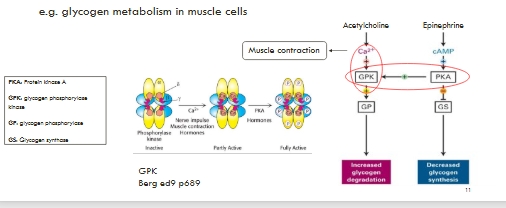
Signals may combine to alter the level of active signalling protein
what is overlap between signalling pathways known as?
Cross talk
Common 2nd messengers are shared by many different pathways
Some signalling proteins are shared by different pathways
Ad:
allows fine-tuning of response – different signals can act together to control levels of a 2nd messenger or activity of a signalling protein
Dis:
means that there is a risk of a signal producing the wrong response
Signalling complexes 1
1) Stable: components of the signalling pathway are linked by a scaffold protein
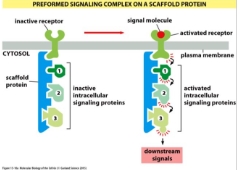
Signalling complex
2) Transient: the signalling complex assembles after the receptor is activated
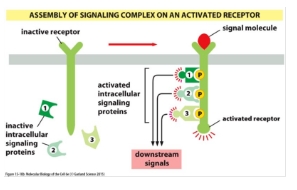
Signalling complex 3
3) Transient: modification of plasma phospholipid molecules
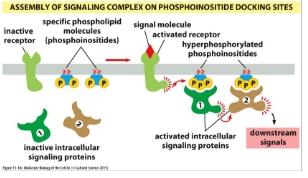
Switching the signal off
Failure to do so can lead to cancer (Ras pathway) or cholera toxin (GPCR)
Need to be switched off to prevent this
Many drugs use this process to solve diseases/dysfunctions
Switching signal off 1
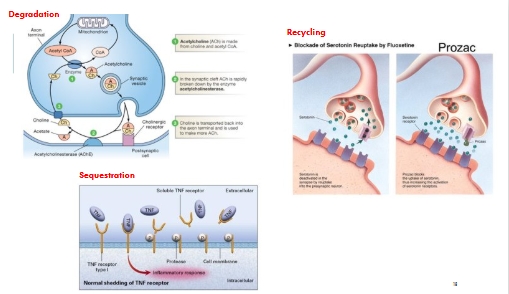
Removal/ inactivation of signal
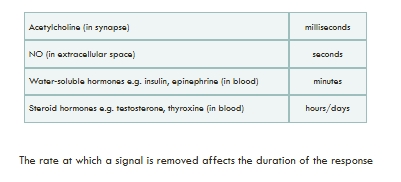
By degradation e.g. hydrolysis of acetylcholine by acetylcholinesterase
By recycling of signalling molecule e.g. neurotransmitters: serotonin,dopamine
By sequestration by other proteins e.g. soluble TNF receptor
Speed of inactivation
Switching off 2
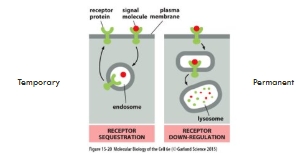
Removal of receptors
Allows cells to become adapted to a constant signal – desensitization
A common mechanism is ligand-dependent receptor-mediated endocytosis
Switching off 3
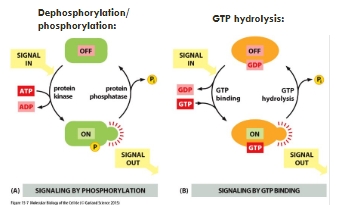
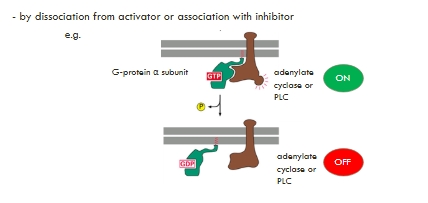
Inactivation of activated proteins - molecular switches
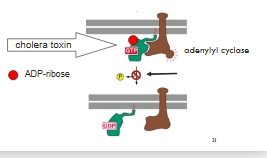
Cholera toxin
Interferes with G protein hydrolysis
ADP-ribosylation of Gα prevents hydrolysis of GTP
Locks G-protein in an active state
Adenylyl cyclase remains activated
Increase in cAMP leads to loss of Cl- and water into intestinal lumen
Severe watery diarrhoea > dehydration > death
Allosteric Inactivation
Switching off 4
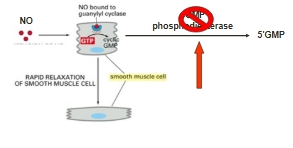
Degradation/removal of second messengers
E.g. Removal of cAMP and cGMP by hydrolysis
Catalysed by phosphodiesterase
Summary
How different cells respond differently to the same signal
How signalling pathways interact in a coordinated way
How signalling pathways are switched off
How some drugs act by interfering with the “on/off” switch
Lecture series summary
L14: Principles of cell signalling. Local and distant signalling. Intracellular receptorsignalling. Androgen insensitivity. NO signalling and blood flow.
L15: Ion gated receptors, muscle contraction and Myasthenia gravis. GPCR, trimericG-proteins as transducers. cAMP as second messenger and amplification.
L16: IP3, DAG, Ca2+ and calmodulin. Enzyme-linked receptors, receptor tyrosinekinases, monomeric G proteins, the RAS-MAPK cascades and cancer.
L17: Coordination, cross talk and switching signalling off. Cholera, Prozac andViagra.
Lecture series LOs
Understand the important principles of cell signalling
Understand how cells can send signals to each other over short and long distances
Describe the differences between intracellular and extracellular receptors
Be able to describe some common signalling pathways
Be able to use the pathways you know to illustrate the key principles of cell signalling