PTE 722: exam 3
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
109 Terms
traction therapy
applying a gentle, controlled force to the spine to reduce pressure on vertebral discs and relieve pain
list the types of lumbar traction therapies.
mechanical
positional
auto-traction
manual
inversion
gravity
list the type of cervical traction therapies.
mechanical
manual
wall mounted or “over the door” units
what are the two types of mechanical traction?
static
intermittent
what % of body weight is a good starting point for a traction weight?
7%
T or F: traction causes vertebral separation which can result in an increase in height if forces are great enough to overcome the forces of friction and gravity. (Dr. Robinson question)
T
describe the changes seen with 7%, 25%, and 50% of weight in joint distraction.
7% body weight to distract the cervical vertebrae
25% body weight to increase length of spine
50% body weight to distract lumbar zygapophyseal joints
what are the effects of spinal traction?
reduction of disc protrusion
soft tissue stretching
muscle relaxation
joint mobilization
patient immobilization
what are the five clinical indications for the use of spinal traction?
disc bulge or herniation
nerve root impingement
joint hypo-mobility
subacute joint inflammation
paraspinal muscle spasm
what are the contraindications for spinal traction?
acute injury or inflammation
joint hyper-mobility or instability
traction causes peripheralization of symptoms
uncontrolled hypertension
where motion is contraindicated
which populations should avoid using traciton?
downs syndrome, osteoporosis, rheumatoid arthritis, and pregnancy
what are the precautions for spinal traction?
structural diseases affecting the spine
when pressure from the belts may be hazardous
displacement of annular fragment
medial disc protrusion
claustrophobia
patient who cannot tolerate position
disorientation
TMJ issues or dentures
T or F: traction therapy as a single treatment for LBP will show great improvement for patients.
F; need other therapy modalities and treatments to go along with it
even for sciatic issues
symptoms generally fail to improve after traction if ____ disc herniations are present or if theres _____ of disc material
large
calcification
what type of patients may benefit from mechanical traction?
patients with leg symptoms, signs of nerve root compression, and either peripheralization with extension movements or a straight leg raise
how can a therapist mobilize a specific spinal level?
using positional traction or manual therapy techniques
what type of traction is recommended for an initial treatment ?
low-load traction
hydrotherapy
a therapeutic technique that uses water's properties like buoyancy and temperature to promote healing and well-being, often for pain relief, muscle relaxation, and improving circulation
why would a therapist use hydrotherapy?
superficial heating or cooling
water exercise
pain control
edema control
wound care
how can hydrotherapy be applied?
through immersion (whirlpool, aquatic activities, contrast bath) and/or non-immersion (pulsavac, neg pressure wound therapy)
what are the physical properties of hydrotherapy?
buoyancy
resistance
specific heat and thermal conductivity
hydrostatic pressure
buoyancy
upward force on an object immersed in a fluid that is equal to the weight of the fluid it displaces, enabling it to float or to appear ligther
resistance
a force counter to the direction of movement
T or F: the resistance to a body’s movement in water is proportional to the relative speed of the body, the water’s motion, and the frontal areas of the body in contact with the water.
T
hydrostatic pressure
pressure exerted by a fluid on a body immersed in the fluid
what is pascal’s law?
fluid exerts equal pressure on all surfaces of a body at rest at a given depth; pressure increases in proportion to the depth of the fluid
what is the mode of heat transfer when in water?
convection and conduction
T or F: when swimming, a fast moving body results in high resistance and a slow moving body results in moderate resistance.
T
what are the physiological effects of hydrotherapy?
cleansing
musculoskeletal
cardiovascular: good for venous return
respiratory: increases work of breathing
renal: increased urine production
psychological: relaxing or invigorating
buoyancy decreases weight bearing meaning the deeper you are in water, the lighter you feel. what are the percentages of body weight associated with the varying water depths?
submerged to waist level: 40-50% of BW
submerged to chest level: 25-30% of BW
submerged to neck level: ~10% of BW
what are the two musculoskeletal effects of hydrotherapy?
resistance provides force for strengthening
hydrostatic pressure increase resting muscle blood flow by 100-225%
water can simultaneously strengthen _________________ unlike many land-based exercises.
both sides of a muscle pair
what are the cardiovascular effects with immersion to the neck?
central blood volume increased by ~60%
cardiac volume and output increases by ~30%
less heart rate response to exercise
use perceived exertion to guide exercise
what are the contraindications/precautions for hydrotherapy (local immersion)?
maceration around a wound
bleeding
impaired thermal sensation in the immersed area
infection in the immersed area
confusion or impaired cognition
recent skin grafts
T or F: pregnant women can receive hydrotherapy in a full body immersion in hot water, because it’s practically like taking a bath which is okay.
F lol; also MS patients should not be immersed in hot water
what are the contraindications/precautions for hydrotherapy (full body immersion)?
cardiac instability
infections conditions
bowl incontinenece
severe epilepsy
suicidal patients
confusion or disorientation
alcohol ingestion by patient
what are the adverse effects of hydrotherapy?
drowning
burns, fainting, or bleeding
hyponatremia
infection
aggravation of edema
asthma exacerbation
hydrotherapy chart
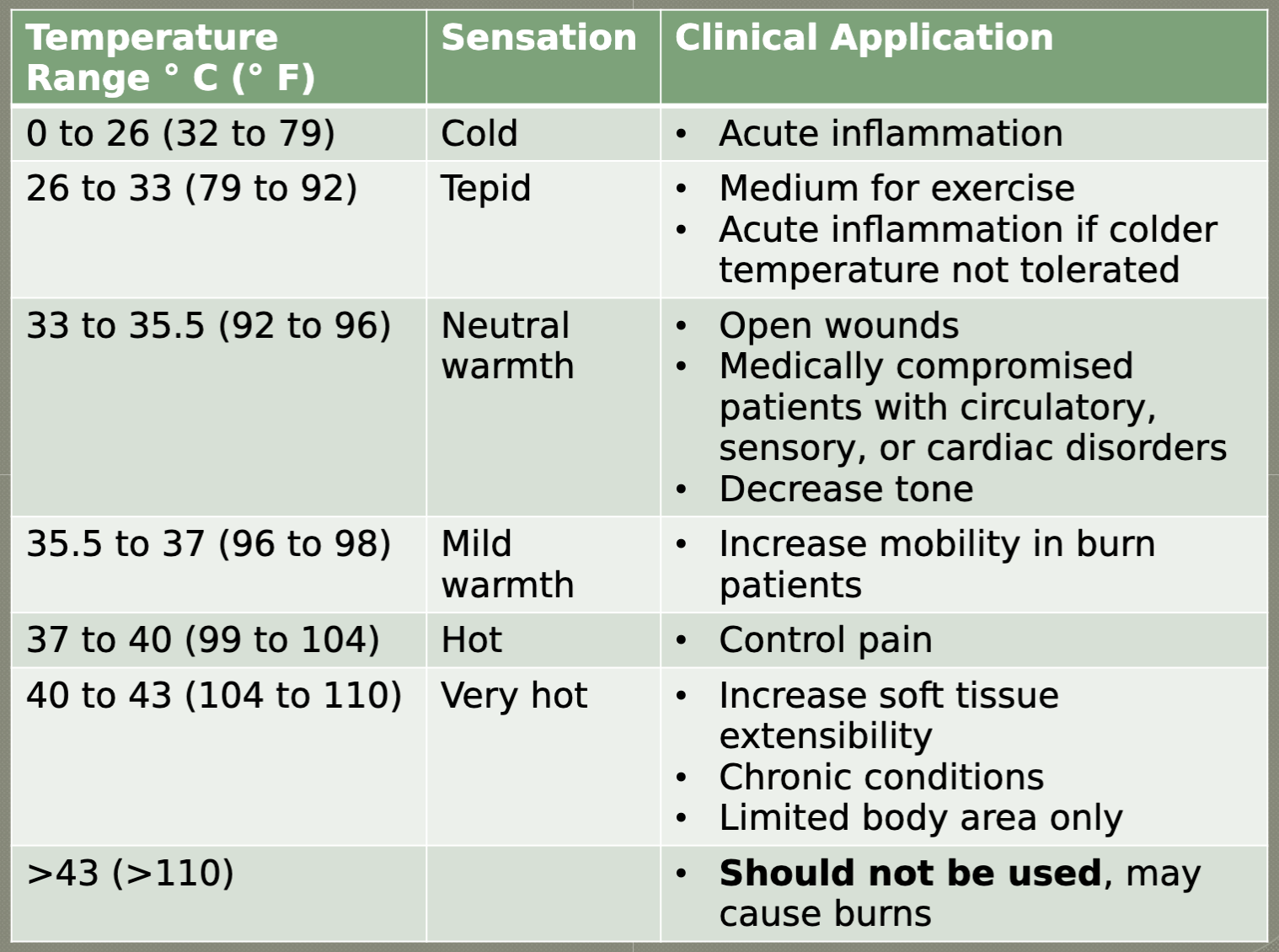
what are the steps for whirlpool applicaition?
fill the tank with appropriate temp water
allow the patient to undress the area to be treated maintaining modesty
remove wound dressings if any are present and if they are east to remove without causing pain or damaging the tissue
position the patient comfortably, with the affected area immersed in water
adjust the direction and aeration of the turbine
turn on on the turbine
stay with the patient throughout the hydrotherapy treatment and monitor the patient’s vitals before, during, and after
When the treatment is completed, remove the limb from the water, dry the intact skin thoroughly, and inspect the treated area.
Keep the patient covered or wrapped after treatment to avoid chilling.
If the whirlpool is being used for the treatment of an open wound, a clean, pressurized rinse is recommended after the whirlpool to remove bacteria more effectively.
Reapply wound dressings if open wounds are present.
Drain, rinse, and clean the whirlpool according to the directions given in the section on safety issues regarding hydrotherapy.
whirlpools are generally applied for _____ mins.
10-30 mins
water exercise/ aquatic therapy chart

compression therapy
application of a mechanical force that increases the external pressure on the body or body part
static or intermittent
T or F: intermittent compression allows for application of force sequentially (distal to proximal) or throughout the entire limb at one time.
T
edema
the accumulation of excess fluids in the spaces between cells of tissues, known as interstitial space
what are the two types of edema?
lymphatics edema: plasma proteins in the tissues stagnate owing to mechanical insufficiency of lymphatic drainage
venous edema: results from increased capillary pressure and venous obstruction
what’s the difference between hydrostatic pressure and osmotic pressure?
plasma proteins flow out of vessels due to hydrostatic pressure, but flow into vessels due to osmotic pressure
why do proteins and their products accumulate in the tissue space?
when the lymphatic system is incompetent, obstructed, or surgically obliterated
when are the two instances where edema occurs?
an imbalance of the affected pressures across the capillary membrane
obstruction to the venous or lymphatic flow
what are the effects of external compression?
improved venous and lymphatic circulation
limits the shape and size of tissues
increased tissue temp
T or F: both static and intermittent compression can increase circulation and both increase hydrostatic pressure in the interstitial space
T
what are the causes of edma?
trauma
lymphatic and/or venous compromis or insufficiency
congestive heart failure, liver failure, acute renal disease, diabetic glomerulonephritis, malnutrition, and radiation injury
infection
if a patient suffers from congestive heart failure, where might a therapist find the edema formation?
lower extremities (ankles, foot, knee)
what causes venous insufficiency?
lack of physical activity
dysfunction of venous valves due to degeneration
mechanical obstruction of the veins by a tumor or inflammation
what is the most common cause of venous insufficiency?
inflammation of the veins (phlebitis)
what type of edema results in a glossy, shiny appearance to the skin?
venous edema
lymphedema
the lymphatic system is compromised resulting in the proteins will progressively accumulate in the interstitial fluid causing an imbalance in capillary dynamics resulting edema
T or F: edema is typically characterized by a pitting quality.
F; lymphedema
what are the adverse consequences of edema?
subcutaneous tissue fibrosis
hard induration of the skin
increased risk of infection
increased risk of bacterial growth
what are the 5 protocols of the assessment of edema?
accurate baseline and follow-up girth measurements are critical in evaluating the patient with edema
same landmarks must be used each time
same person should take the measurements
measurements should be taken at the same time each day
use the same tool every time
what are some treatment options of edema?
elevation
electrical stimulation at a low pulse rate (produces a pumping effects and increased venous return)
massaging distal to proximal
active exercise combine with elevation
non-mechanical and mechanical compression devices
T or F: air pressures of 20-50 mmHg for the UE and 30-70 mmHg for the LE are recommended starting points for compression therapy in the treatment of edema.
T
what is the total treatment time for edema?
varies from 10-60 mins
what are some contraindications for external compression?
heart failure or pulmonary edema
recent or acute DVT, thrombophlebitis, or pulmonary embolism
obstructed lymphatic or venous return
severe peripheral arterial disease and/or ulcers due to arterial insufficiency
severe hypoproteinemia
acute trauma or fracture
what are the precautions for external compression?
impaired sensation or mentation
uncontrolled hypertension
cancer
stroke or significant vascular insufficiency
too much pressure can cause the compression device to act as a _______ which could lead to tissue death
tourniquet
what are the two ACSM recommendations for resistance training?
1-3 sets per exercise of 8-12 reps at 70-85% of 1RM for novice
3-6 sets of 1-12 repetitions with 70-100% 1RM for advanced
what is blood flow restriction therapy (BFR)?
the brief and intermittent occlusion of arterial and venous blood flow using a tourniquet while at rest or while exercising
why would a therapist want to utilize BFR?
patient can exercise using significantly less loads and still achieve significant gains in muscle strength and size
decreases load with increase hypertrophy
T or F: BFR attempts to mimic the hypoxic environment of high intensity exercise, tricking the body to use anaerobic systems instead of aerobic.
T
what are the chances of clotting and hemodynamics when using BFR?
clotting: research shows no increase in signs for clotting (acutely or chronically)
hemodynamics: BP, HR, and CO increase but not as much as with HIIT
what is exertional rhabdomyolysis?
the breakdown of skeletal muscle due to excessive physical training; injury causes the release of cellular contents into the bloodstream
what is ischemic-reperfusion injury?
tissue damage occurring due to the influx of blood flow following a period of ischemia
what are the adverse effects of BFR?
numbness
dizziness
subcutaneous hemorrhage
rhabdomyolysis
what are some precautions of BFR?
poor circulation
obesity/loose skin
diabetes
tumors
hypertension/congestive heart failure
renal compromise
what are some contraindications of BFR?
acidosis
cancer
those with dialysis ports
open wounds or fractures
pregnancy
severe hypertension or clotting risks
what are the three typical applications of BFR?
cell swelling
endurance
metabolite build-up
what are the benefits of cell swelling (BFR)?
increase protein synthesis and suppress proteolysis
cell swelling occurs due to a plasma fluid shift into the muscle
T or F: cell swelling is best used as BFR to long-term patients in an outpatient clinic.
F; best used for very acute patients
what are the guidelines for cell swelling (BFR)?
frequency: 1-2x per day for duration of immobilization
restriction time: 5 min intervals
type: unilateral or bilateral
sets: 3-5
rest time: 3-5 mins (between sets)
pressure: high pressure; 70-100% AOP
restriction form: continuous
what are the benefits of using endurance BFR?
increases strength, hypertrophy, and VO2 max; skeletal muscle strength increases 7-27%, and shows improvements in aerobic capacity
what are the guidelines for endurance BFR?
frequency: 2-3x per week (>3 weeks) or 1-2x per day (1-3 weeks)
intensity: <50% VO2 max or HRR
type: any training equipment- usually bilateral
sets and pressure: continuous or intervals 40-80% AOP
restriction time: 5-20 mins per exercise
what is the metabolite theory- lactate production?
use of anaerobic pathways result in byproducts including hydrogen ions and lactate which creates the “burn”
BFR limits oxygen to a muscle forcing transistion from aerobic to anaerobic pathways with the same lactate “burn”
describe the impact the metabolite theory has on hormones in the muscles.
accumulating lactate and hydrogen ions release growth hormone → kickstarts collagen synthesis and stimulates insulin-like growth factor → IGF-1 stimulates the transport and fusion of satellite cells into muscle fibers → become myocytes and perfrom functions for repair and growth
what role does BFR have on myostatin?
BFR creates stress, which decreases myostatin bc the body beleives it needs myogenesis
myostatin: inhibits muscle growth by blocking satellite cell proliferation
summarize the BFR metabolite pathway.
lactate
growth hormone
IGF-1
transports satellite cells into muscles
inhibits myostatin
initiates MTORC1 (mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1)
what are the guidelines for metabolite (BFR)?
frequency: 2-4x per week
intensity: 20-35% 1RM
type: one isolated exercise per musclesets and pressure: 80% LOP for LE and 50% LOP for UE
reps: 30-15-15-15-15 or until failure
restriction time: 30-60s between sets with cuff inflated; deflate after exercise is complete
what are other benefits of BFR?
diminishes pain
bone remodeling
proximal strength gains
what are the 3 main theories for proximal strength changes?
downstream fatigue: distal musculature fatigue faster and force more use of proximal musculature
systemic response: hormones stimulated from intense/stressful exercise are in the circulation
back-flow effect: backup of blood proximal to cuff
what are the physiological effects of massage?
reflexive effects: pain, circulation, and metabolism
mechanical effects: muscle and skin
what factors does the duration of massage depend on?
pathology
size of area
age
condition of patient
describe the direction of force during a massage treatment.
direction of force is generally applied in the direction of the muscle fibers
for lymphedema: starting proximal to distal- “uncorking effect”
describe the massage’s stroke and pressure during a treatment.
massage stroke should begin at joint or below the joint and finish above the joint
massage pressure should be inline with venous flow and return stroke without pressure
T or F: massage should begin and end with superficial or deep effleurage.
T
what are the two purposes for draping with massage?
protect modesty
prevent patient from being chilled
what are the hoffa massage treatment techniques?
effleurage: long, slow stroke with minimal drag
petrissage: intermittent compressions with grasping and lifting
tapotement: fast, rhythmic stroke
vibration: high-frequency shaky hand movements
what are the effects of utilizing effleurage?
assists circulation
decreases muscular tension
can reduce pain
sidenote: this assess quality of client’s tissues
what are the two types of effleurage?
superficial: applied lightly and feathery with thumbs, fingertips, or palms
deep: applied slowly with thumbs, knuckles, heels of hand, interlaced fingers, or forearm
what are the effects of utilizing petrissage?
improves health of muscle tissue
superficial technique softens thixotropic fascia (pressure causes redistribution of fluids within connective tissue)
deep technique deforms deep fascia
what are the three variations of petrissage?
deep: focus on intermittent and rhythmic compression
wringing: slow application without lifting component
skin rolling: lifts superficial fascia to deform and loosen
what are the effects in utilizing tapotement/percussion massage?
initial response is stimulating
with longer duration, result is relaxation