Ch 14 - Important IR Signals
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
includes specific signal wavenumbers and wavenumber ranges for general groups or patterns
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
wavenumber of C-H
~3000 cm-1
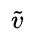
wavenumber of C-D
~2200 cm-1
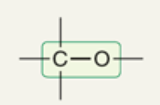
wavenumber of C-O
~1100 cm-1
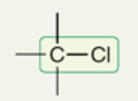
wavenumber of C-Cl
~700 cm-1
(600-800 cm-1)
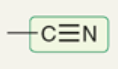
wavenumber of C triple bonded to N
~2200 cm-1
(2200-2300 cm-1)
wavenumber of C=N
~1600 cm-1
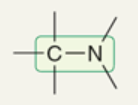
wavenumber of C-N
~1100 cm-1
(1000-1200 cm-1)
wavenumber range of single bonds (excluding H-bonds)
below 1500 cm-1 (400-1500 cm-1)
depicted on right side of spectrum (in fingerprint region)
located on right because they are the weakest bonds
wavenumber range of double bonds
1600-1850 cm-1
wavenumber range of triple bonds
2100-2300 cm-1
wavenumber range of bonds to H
2700-4000 cm-1
strongest bonds because H is so small
diagnostic region
region above 1500 cm-1 (on the left side of the spectrum)
generally has fewer peaks
provides clearest information
contains signals from H-bonds, triple bonds, and double bonds
different compounds may be different to differentiate here (for e.g., see figure 14.8 in textbook)
fingerprint region
region below 1500 cm-1 (on the right side of the spectrum)
contains signals from single bonds, resulting from stretching and bending (vibrational excitation)
lots of signals, difficult to analyze
every compound has a unique pattern of signals in this region (hence its name)
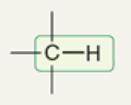
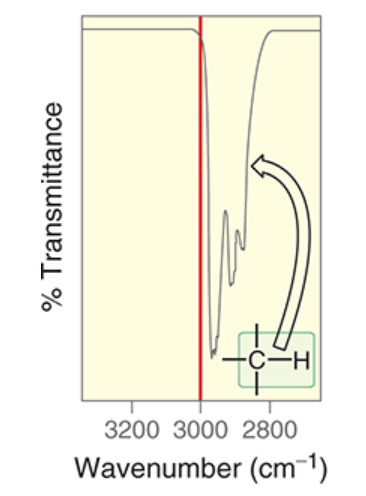
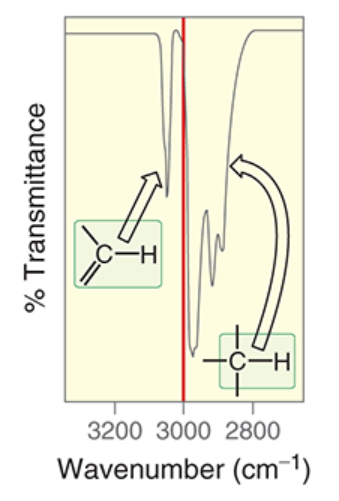
wavenumber of sp3-hybridized C-H
~2900 cm-1
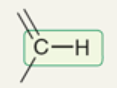
wavenumber of sp2-hybridized C-H
~3100 cm-1
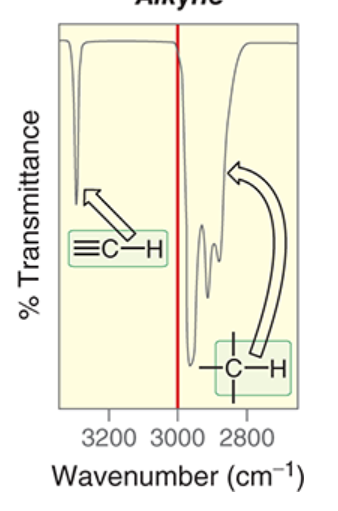
wavenumber of sp-hybridized C-H
~3300 cm-1
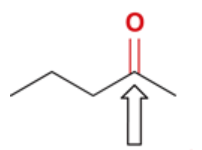
wavenumber of C=O in ketone
1720 cm-1
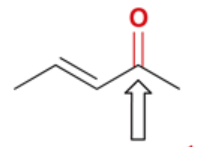
wavenumber of C=O in conjugated, unsaturated ketone
1680 cm-1
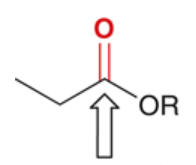
wavenumber of C=O in ester
1735 cm-1
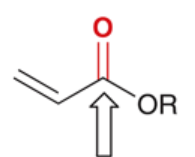
wavenumber of C=O in conjugated, unsaturated ester
1710 cm-1
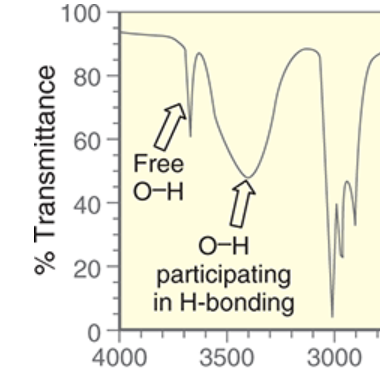
wavenumber range and shape of O-H participating in H-bonding
~3200-3600 cm-1
broad signal
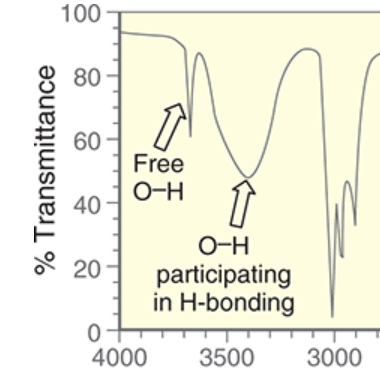
wavenumber and shape of free O-H
~3600 cm-1
remember: “free” O-H means not participating in H-bonding
sharper signal, usually shallower than broad O-H
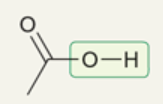
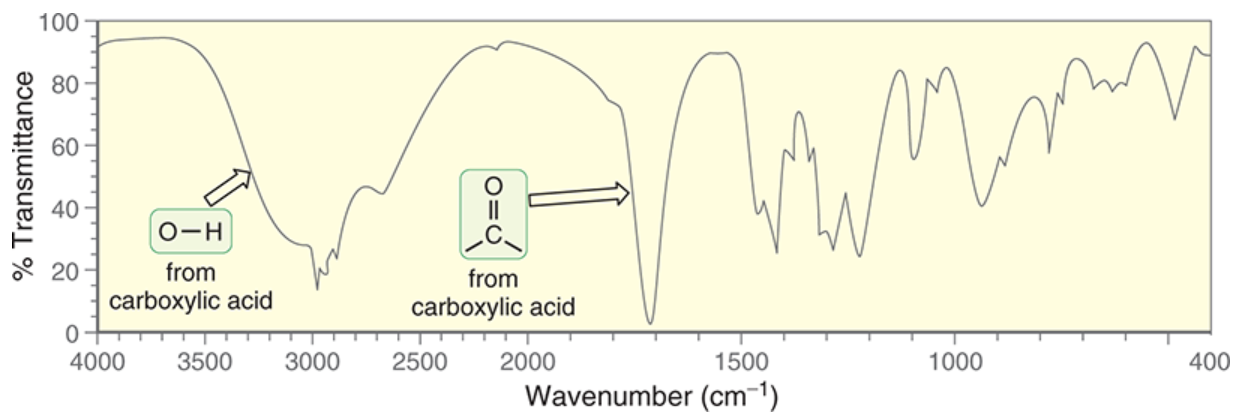
wavenumber range and shape of O-H in carboxylic acid
~2200-3600 cm-1 .
very broad; extends over usual C-H signals
occurs because of dimers resulting from 2 H-bonding interactions for carboxylic acids
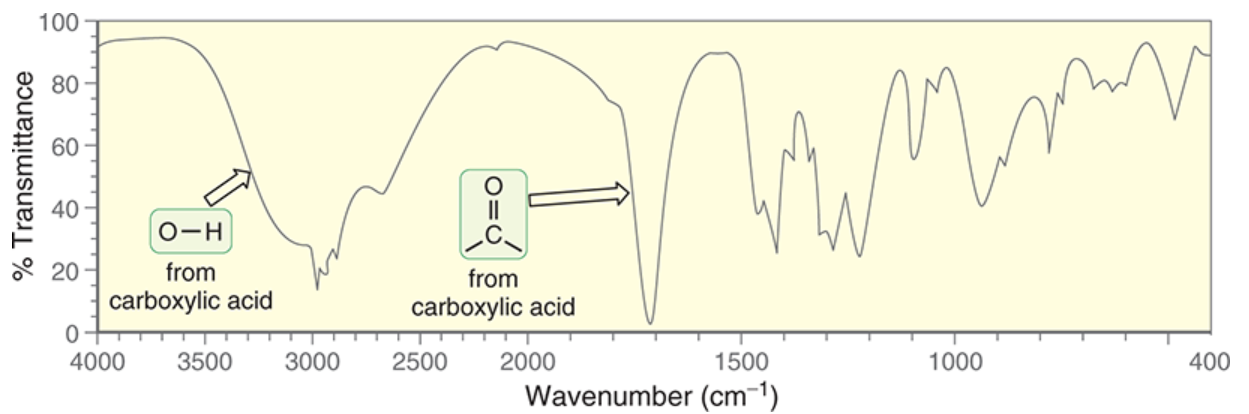
wavenumber and shape of C=O in carboxylic acid
just above 1700 cm-1 (~1750)
broad and deep
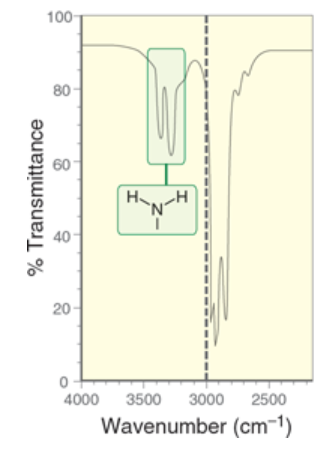
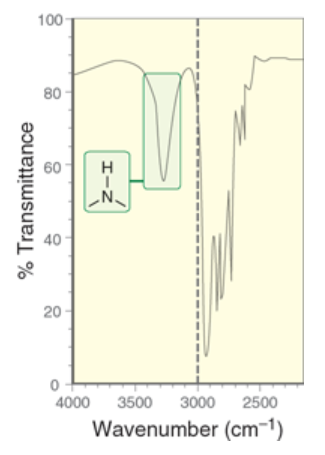
wavenumber of primary amines
2 signals
1 signal at 3350 cm-1, 1 signal at 3450 cm-1
due to different ways a molecule can stretch/bend
wavenumber of secondary amines
~3300 cm-1
one signal only
wavenumbers of C-H in aldehyde
2750 and 2850 cm-1 (2 weak signals)
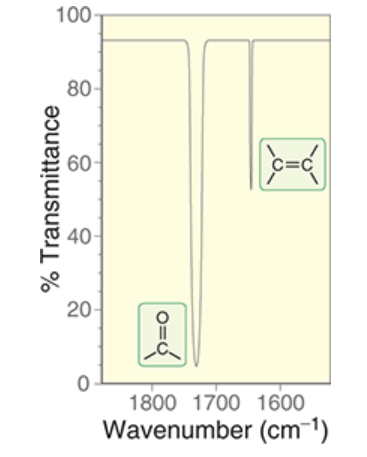
wavenumber range and signal intensity of C=O bond
~1650-1820 cm-1
very strong, dips low
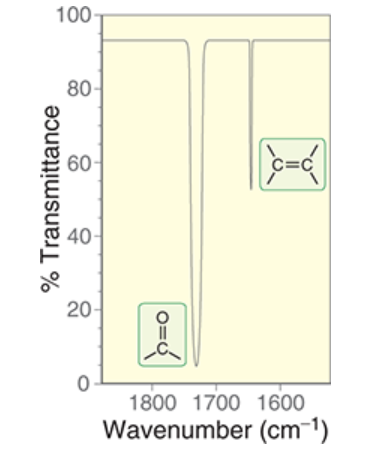
wavenumber range and signal intensity of C=C bond
1600-1700 cm-1
not very intense
does not come down low
wavenumber ranges for benzene
1450-1600 cm-1 and 1650-2000 cm-1
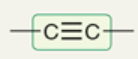
wavenumber range of C triple bonded to C
2100-2200 cm-1
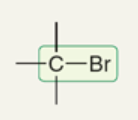
wavenumber of C-Br
500-600 cm-1