anatomy joints/ligaments/movements
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
3 types of joints by movement
synarthrotic, diarthrotic, amphiarthrosis
synarthrotic
immovable joints -fibrous connective tissue
diarthrotic
movable joints - synovial fluid provides lubrication
amphiarthrosis
slightly moveable joints - cartilaginous connective tissue
all synovial joints are
diathrotic
most (not all) amphiarthrosis joints are
cartilaginous
most (not all) synarthrosis joints are
fibrous
fibrous joints
3
articular surfaces of two bones are connected by dense fibrous connective tissue (ex sutures)
cartilaginous joints
hyaline or fibrocartilage connects bones, slight movement
synovial
most of the body’s articulations, free movement diarthrosis)
3 types of fibrous joints
syndesmosis, suture, gomphosis
syndesmosis
fibrous joint
cord of fibrous tissue
amphiarthrosis - have a “give” but no true movement. (exception because other fibrous joints are synarthrotic)
ex. is distal tibiofibular joint between the tibia and fibula
-have high ankle sprains
-are also between spinous processes of vertebrae and between diaphysis of radius/ulna
suture
-fibrous joint
-short fibrous CT fibers (skull only)
-synthroses
gomphosis
-fibrous joint
-tooth within its alveolar fossa
-short periodontal ligament
-cony shaped bony process in a socket
-synarthrosis
2 types of cartilaginous joints
synchondrosis and symphysis
synchondrosis
-cartilaginous joint
a plate of hyaline cartilage unites bones
sites of growth during youth
ex. joint between manubrium and first rib, epiphyseal plate
-synarthrosis
symphysis
-cartilaginous joint
pad or plate of fibrocartilage
ex. joint between bodies of adjacent vertebrae, pubic symphysis)
-amphiarthrotic
6 types of synovial joints
gliding, hinge, ball-n-socket, condyloid, pivot, saddle
gliding
-synovial joint
smooth articular cartilage that allows bone to slide
found in intervertebral discs, carpals and tarsals
-diarthrotic
hinge
-synovial joint
permit flexion and extension only (only go up and back)
found in elbows, knees, fingers, toes
-diarthrotic
pivot
-synovial joint
allows rotation
ex. ulnar notch and radial notch, first intervertebral joint C1 atlas and C2 fit together allowing for rotation of saying “no” (atlantoaxial joint)
-diarthrotic
saddle joint
-synovial joint
-allows opposition
-fits like a rider in a saddle
ex. first carpometacarpal joint for thumb, sternoclavicular joint
diarthrotic
ball-n-socket
-synovial joint
-most freely moveable joint
-femur and humerus
ex. coxofemoral, glenohumeral
-diarthrotic
condyloid
-synovial joint
-freely moveable, not as freely moveable as ball-n-socket
-allows for flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, circumduction, NOT rotation
-key locations are wrist, fingers, toes
-diarthrotic
saddle vs. condyloid - how to tell diff
condyloid joints have a convex surface sitting on a concave surface (rounded on cup like surface)
its saddle joint if it looks like legs sitting on a saddle
saddle joints also allow opposition (thumbs touching fingers) while condyloid joints do not
type of joint movements - origin
part of muscle attached to the immovable bone
type of joints movements - insertion
part of the muscle attached to the movable bone
When a muscle contracts across a joint, its insertion is pulled..
toward its origin
3 types of movement -
gliding, angular, special
gliding movement
flat bones glide over one another
-also found in cartilaginous joint movement
angular movement
changes in angle (synovial joints)
special movement
those at specific joints
flexion/extension
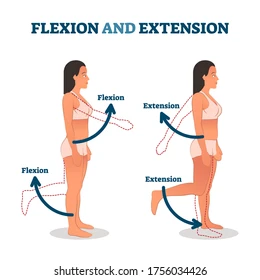
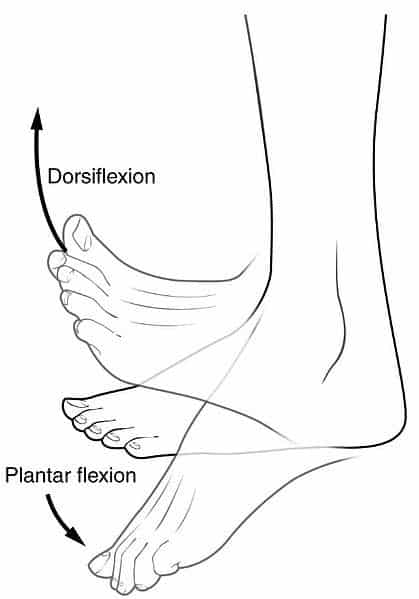
dorsi/plantar flexion
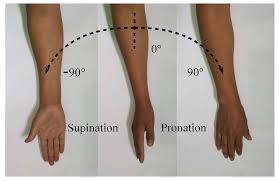
supnation/pronation
elevation/depression

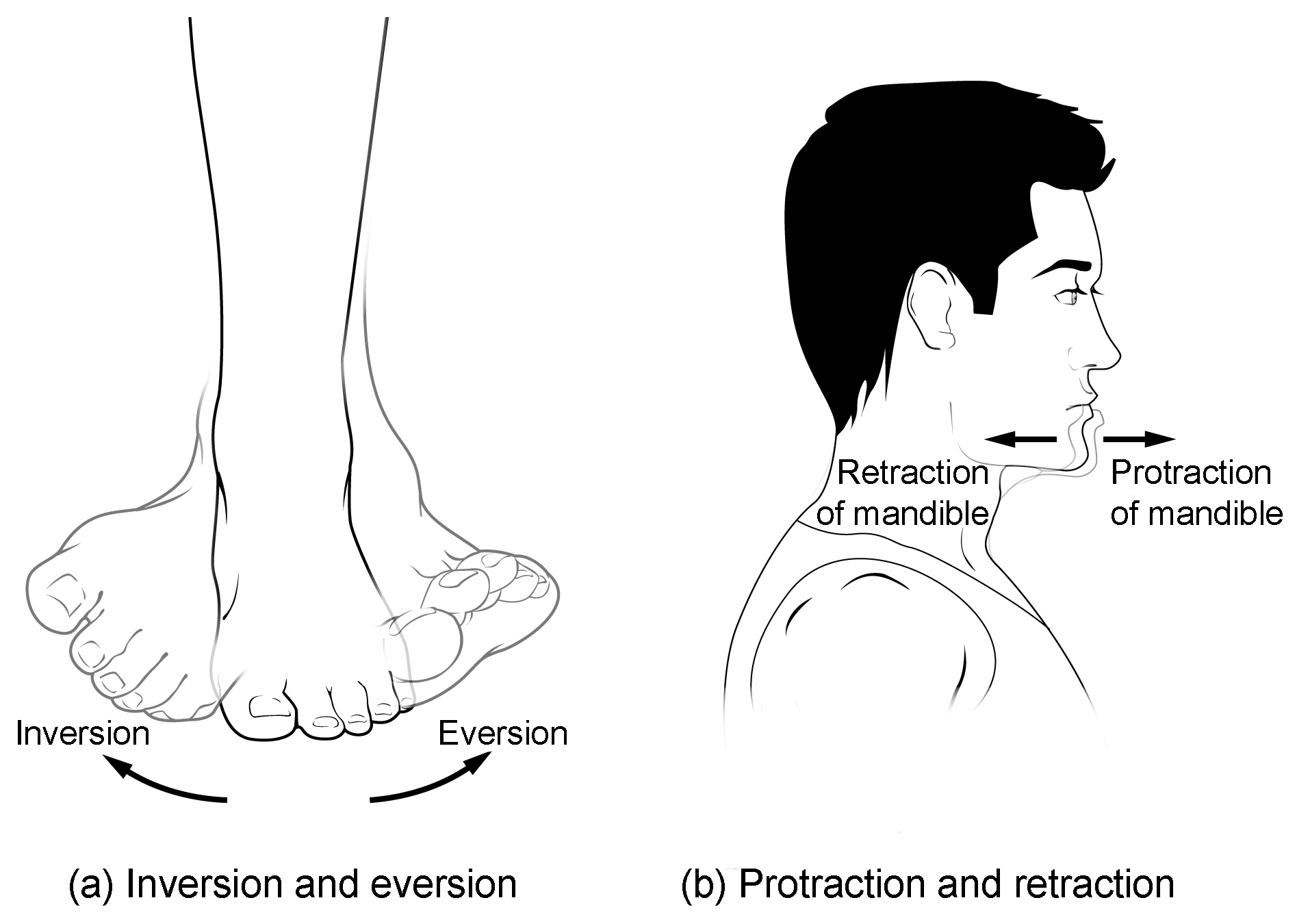
protraction/retraction
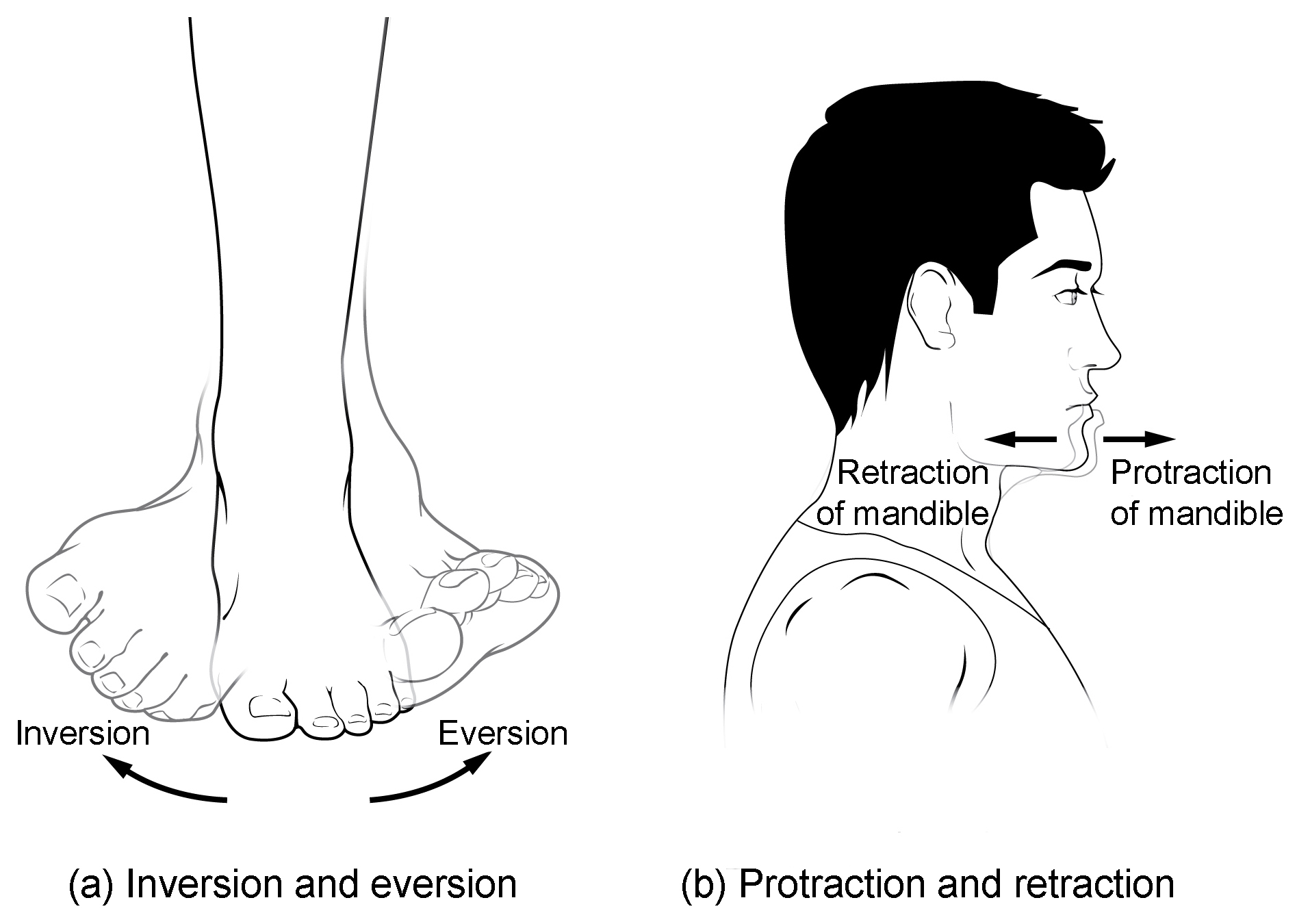
eversion/inversion
knee is made up of what three joints
condyloid, gliding, and hinge
knee characterstics-
knee is the largest, most complex joint
-functions as Hinge even tho 3 joints work together
-medial condyles of femur and tibia make condyloid joints
lateral condyles of femur and tibia make another condyloid joint
-patellar surface of femur and patella make gliding joint
-flexion and extension makes Hinge joint
extracapsular and intracapsular ligaments
extracapsular are outside joint capsule, intracapsular are inside joint capsule
menisci
separates tibia and femur
eversion sprains are much rarer than inversion sprains. why?
the greater inversion ROM (range of motion) opens the ankle up to more likely injury than lateral ROM
bursae
a small, fluid-filled sac that acts as a cushion or shock absorber between moving parts in your body, like bones, muscles, tendons, and skin, reducing friction for smooth movement around joints such as the shoulders, elbows, hips, and knees
ankle joint complex is made of
talocrucal, talocalcaneal. transverse tarsal. the anke holds 10x body weight
which two ankle joints tear easily
the calcaneofibular and anterior talofibular ligament tear easily. most sprained ankle injuries occur here.
elevating a joint allows
blood to flow
lisfranc joint
where metatarsals meet tarsals
Life-Span Changes
Fontanels of skull harden in first 2 years
Epiphyseal plates harden from ages 14-20 years.
Fibrocartilage loses water, decreasing flexibility of intervertebral joints and knees
Life-Span Changes
Collagen changes causing stiffening beginning at age 30.
Joint stiffness is an early sign of aging
Fibrous joints first to change; can strengthen over a lifetime
Changes in symphysis joints of vertebral column diminish flexibility and decrease height
Life-Span Changes
Synovial joints lose elasticity
Disuse hampers the blood supply
Activity and exercise can keep joints functional longer, lessens stiffening
Sprains
damage to cartilage, ligaments, or tendons associated with joints
forceful twisting of joint
Bursitis
inflammation of a bursa
overuse of a joint
Arthritis
inflamed, swollen, painful joints
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Osteoarthritis