S3.2 Organics - Functional Groups
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
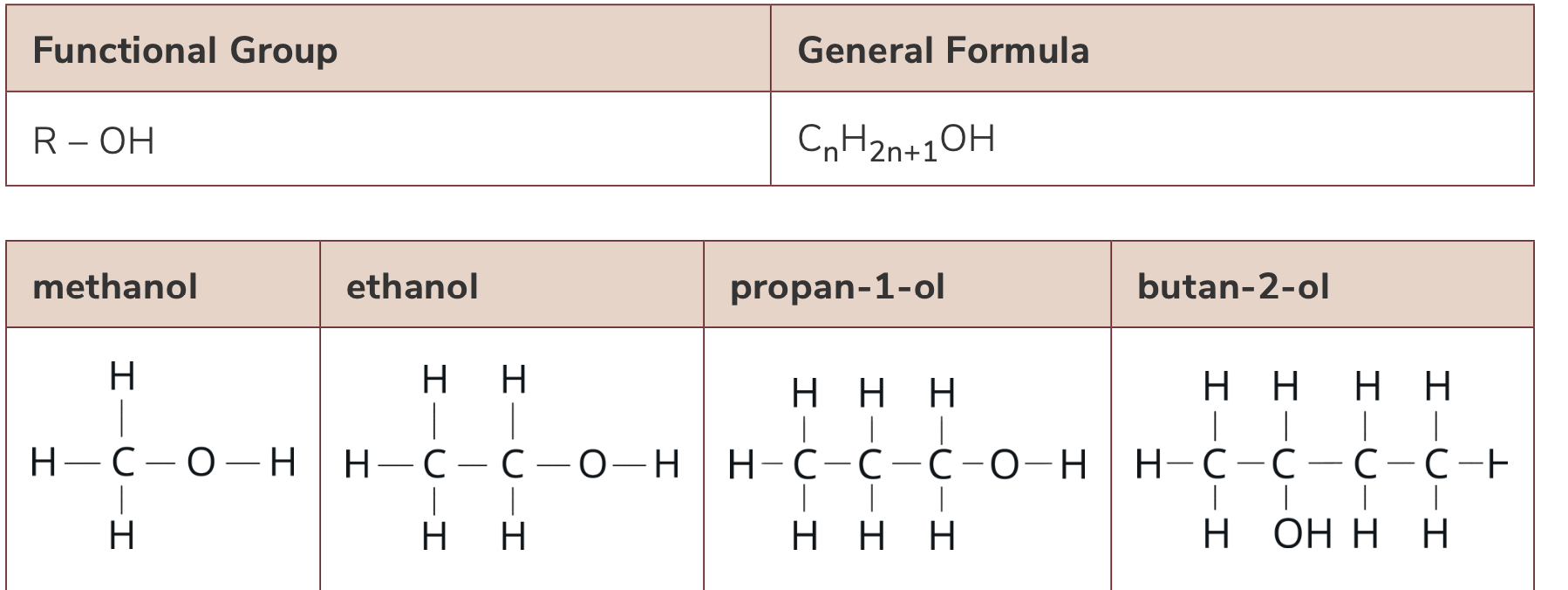
List the functional group, molecular formula and general formula of alcohols
Functional group: hydroxyl group (-OH)
molecular formula: CnH2n+1OH
general formula is R-OH, where R represents an alkyl group
With reference to intermolecular forces and chain length, explain the solubility of alcohols
alcohols can form hydrogen bonds due to the covalent bonding between O and H
therefore, can dissolve in water
however, as chain length inc. solubility dec.
the hydrophobic (nonpolar) nature of the alkyl group (carbon chain) becomes more significant, overpowering hydrophilic interactions (H-bonding)
Longer chains increase van der Waals forces, making it harder for alcohols to dissolve in water.
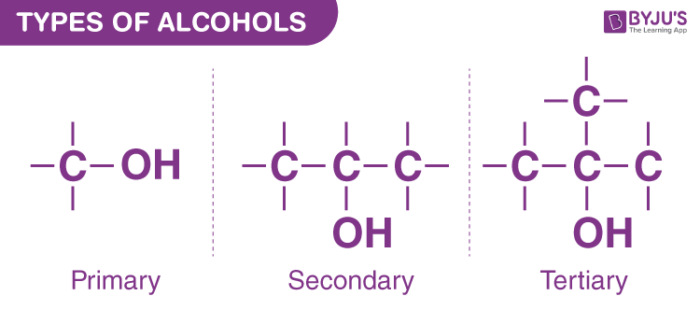
What is the difference between primary and secondary alchohols
Primary Alcohols: -OH group on a carbon bonded to only one other carbon (or none in methanol).
Secondary Alcohols: -OH group on a carbon bonded to two other carbons.
How can primary and secondary alcohols be identified chemically? (hint: colour change)
In a reaction w/ acidified potassium dichromate (VI) → colour change from orange to green happens (CAN ALSO BE SEEN w/ Aldehydes)
List and explain the 3 different main reactions that happen with alcohols
Combustion
alcohol + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water
Oxidation
W/ heat, acidic conditions & immediate distillation | primary alcohol + [O} → aldehyde
W/ excess [O], acidic conditions & reflux| primary alcohol + [O] → aldehyde → carboxylic acid
W/ acidic conditions & reflux |
secondary alcohol + [O] → ketone
TERTIARY ALCOHOLS CANNOT be oxides
Elimination
water can be eliminated to form alkenes
called dehydration - when alcohols are heated w/ sulfuric acid catalyst
alcohol → (H+ catalyst/ heat) → alkene + water
Explain the 3 different Oxidation reactions with alcohols
Oxidation
W/ heat, acidic conditions & immediate distillation | primary alcohol + [O} → aldehyde
W/ excess [O], acidic conditions & reflux| primary alcohol + [O] → aldehyde → carboxylic acid
W/ acidic conditions & reflux |
secondary alcohol + [O] → ketone
TERTIARY ALCOHOLS CANNOT be oxides
Explain two ways Ethanol can be produced
Fermentation of glucose (requiring microbe yeast and 30-40˚c temp)
Hydration of ethene in presence of strong acid catalyst (in high temp and pressures, requiring high energy)
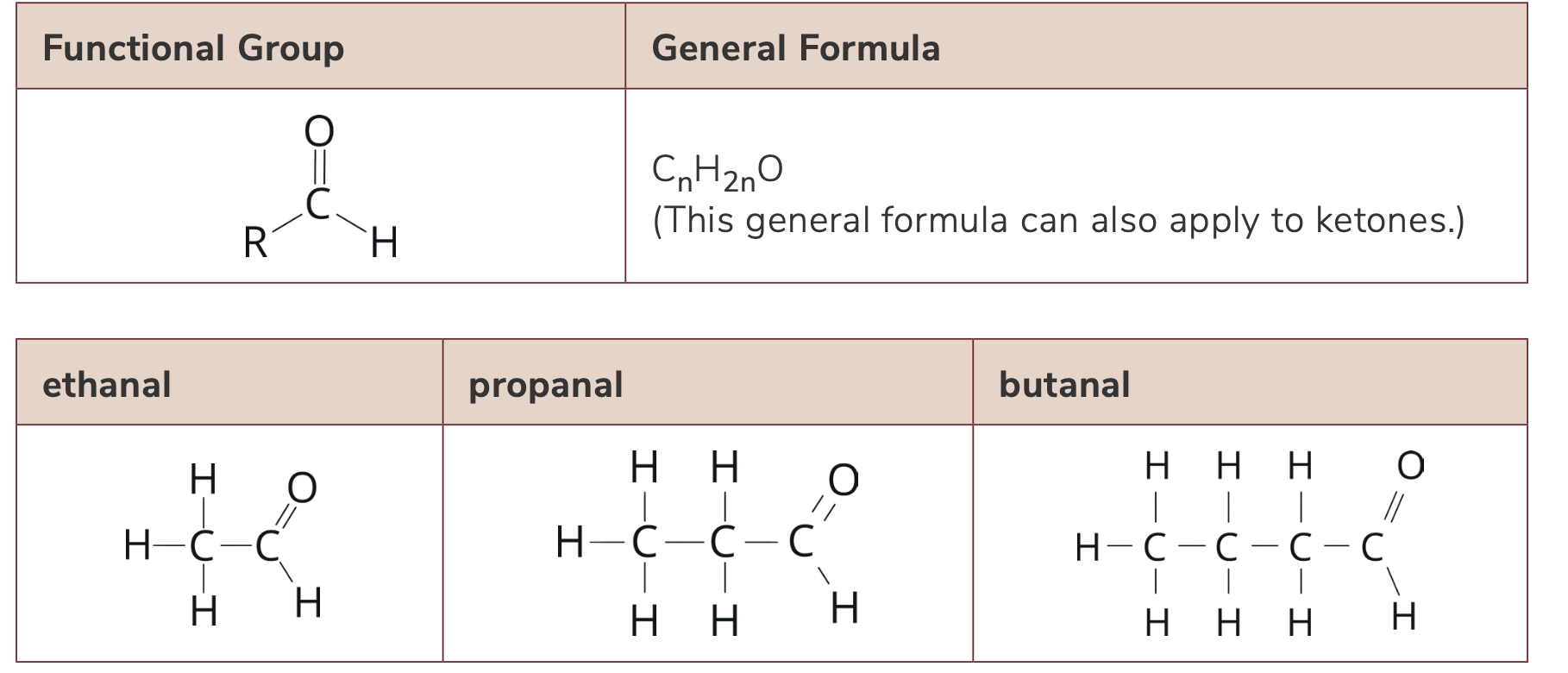
List the functional group, molecular formula and general formula of aldehydes
C=O group (called carbonyl) bonded to H atom
CH=O
What two reagents can be used to identify aldehydes
Fehling’s solution - blue solution, forms red precipitate with aldehydes
Tollen’s reagent - colourless solution, forming silver mirror with aldehydes. aldehydes can be attacked by nucleophiles (DONATES e-)
Explain the 2 main reactions involving aldehydes
Oxidation - aldehydes readily oxidise to carboxylic acids
aldehyde (CO) + [O] → carboxylic acids (COOH)
Nucleophilic Addition -
Reduction reaction to form primary alcohols (e.g. NaBH4) | aldehyde + 2[H] → primary alchohol
with KCN, followed by dilute