Sequence Clinical I
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
EDTA
The Lavender Top Tube contains __, which is an anticoagulant.
In house chemistries
The Green Top Tube is used for __ and electrolyte testing.
Clotting time tests
Plasma samples from the Blue Top Tube are used for __ and blood typing.
Gel serum
The Tiger/Gold Top Tube contains a __ and is used for serum chemistries.
Nothing
The Red/White Top Tube contains __
Packed Cell Volume (PCV)
The Red Tipped Microhematocrit Tube can be used to determine __ and Total Protein.
plasma
What does the Lavender Top Tube yield?
plasma
What does the Green Top Tube yield?
plasma
What does the Blue Top Tube yield?
serum
What does the Tiger/Gold Top Tube yield?
serum
What does the Red/White (or Plain Red) Top Tube yield?
plasma
What does the Red Tipped Microhematocrit Tube yield?
Lithium heparin
What does the Green Top Tube contains?
Sodium citrate
What does the Blue Top Tube contains?
PCV
The BlueTipped Microhematocrit Tube can be used to determine __ and Total Protein.
Giardia Cyst
Scientific Name: Giardia duodenails; Shape: Oval; Shell: Thin; Size: 8-12; Special Features: Shiny face-like features.

Coccidia
Scientific Name: Cystoisospora spp; Shape: Oval; Shell: Thin; Size: 15-40; Special Features: Clear, single spor.
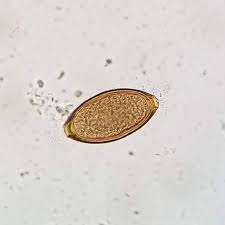
Tapeworm (From rodents)
Scientific Name: Taenia spp (from rodents); Shape: Round/Oval; Shell: Thick; Size: 30-40; Special Features: Single with six hooks.

Hookworm
Scientific Name: Ancylostoma spp; Shape: Oval; Shell: Thin; Size: 55-75; Special Features: Multi-cell embryo inside.

Roundworm
Scientific Name: Toxocara spp; Shape: Round; Shell: Thick, rough; Size: 75-85; Special Features: Dark single-cell embryo.

Whipworm
Scientific Name: Trichuris vulpis; Shape: Football/Lemon; Shell: Thick; Size: 70-90; Special Features: Bipolar plugs.
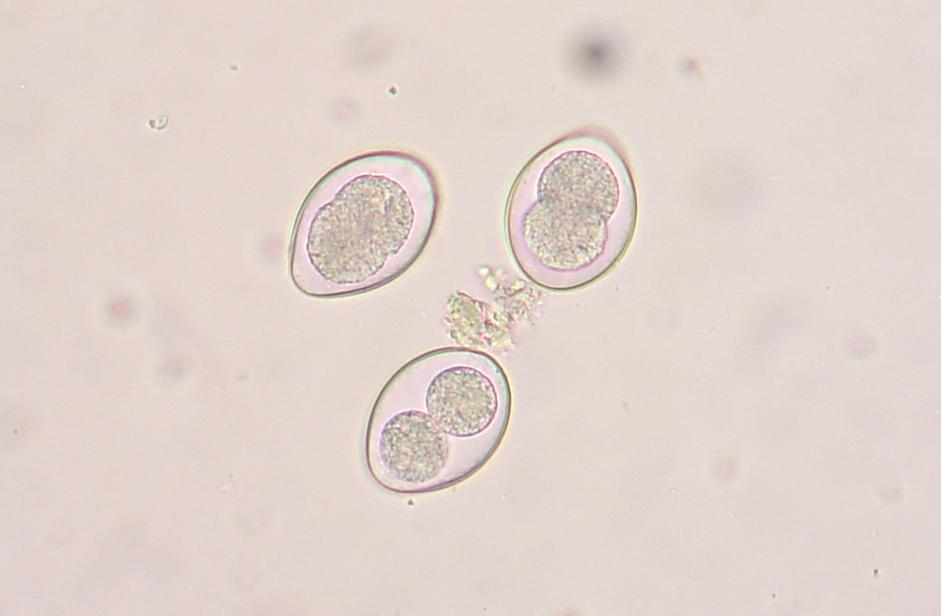
Tapeworm (from fleas)
Scientific Name: Dipylidium caninum Shape: Clustered; Shell: Thin; Size: Each egg ~35-40, ~200 eggs in total; Special Features: Multiple eggs in a pocket.

What is ringworm?
A fungal skin infection.
What is the most common type of immunologic test performed in practice?
ELISA Test.
What is the purpose of gram staining?
Classifying bacteria based on their cell walls to determine proper treatment.
How is rabies transmitted?
From a bite with infected saliva.
How is leptospirosis transmitted?
Contact with contaminated urine, soil, or water.
How is brucellosis transmitted?
Contact with infected animals or fluids.
How is campylobacteriosis transmitted?
Eating undercooked poultry or animal feces.
How is E. coli transmitted?
Contaminated feces.
How is bubonic plague transmitted?
Flea bites from infected animals.
How is giardiasis transmitted?
Drinking infected water or contact with feces.
How is psittacosis transmitted?
Breathing in bird droppings or secretions.
How are roundworms transmitted?
Ingesting infectious eggs in feces.
How are hookworms transmitted?
Contact with contaminated soil or feces.
How is tularemia transmitted?
From infected animals, flies, ticks or inhalation.
How is cat-scratch disease transmitted?
Bites, scratches, or saliva from infected cats.
What type of sample is needed for a heartworm ELISA test?
Blood
What type of sample is needed for a giardia ELISA test?
Feces
Jugular Small Dog
Restraint Technique: Place the dog in a sitting position on the table. Stand behind it, using your hands to elevate the head and expose the neck.
Jugular Large Dog
Restraint Technique: Place the dog in a sitting position on the floor, preferably in a corner. Straddle the dog, using your knees to hold its shoulders and your hands to raise its head.
Cephalic Any Size
Restraint Technique: Restrain in a sitting position. Use one hand to squeeze the forelimb and rotate the vessel laterally about a quarter turn.
Lateral Saphenous Any Size
Restraint Technique: Place the dog in lateral recumbency. Use one forearm to block the head, one hand to hold the bottom forelimb, and the other hand to hold the hind limb and occlude the vein at the stifle.
Jugular Feline
Restraint Technique: Place the cat in sternal recumbency at the edge of the table. Grasp the front legs and pull them down over the edge while using the other hand to restrain and slightly elevate the head. Avoid scruffing.
Cephalic Feline
Restraint Technique: Place the cat in sitting or sternal recumbency. Squeeze the proximal forearm and roll your hand laterally a quarter turn while the other hand restrains the head.
Medial Saphenous Feline
Restraint Technique: Place the cat in lateral recumbency with its spine against your forearm. Gently grasp the scruff, hold the top leg, and apply a 'karate chop' pressure on the lower limb cranial to the stifle to occlude the vein.
Pathogen
A microorganism that causes disease can be bacteria, viruses, fungi or parasites.
Direct Contact Transmission
Direct contact with an infected person or animal. Exa skin to skin, Ringworm
Indirect Contact Transmission
Contact with a fomite (an inanimate object/ surface that may be contaminated). Ex contaminated table(ringworm), or floor (fecal / oral parasites)
Airborne Transmission
Through the air (sneeze, cough, infected air). Ex kicked up from soil (valley fiver) or cough (kennel cough)
Intermediate Host
An organism that carries the larval stage of parasite to the definitive host, (final host that contains sexual/ mature parasite). Ex fleas - tape worm or mosquito - heart worm
Vector
Any organism that transmits the pathogen between host. Ex tick borne diseases
Zoonotic Diseases
Diseases that can be transmitted from animals to humans or vice-versa
Non-Zoonotic Diseases
Lyme diseas, Demodex, Erlichia, Otitic Extrema
ELISA Test stands for
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Snap 4Dx Test
Heartworm, Lyme, Ehrlichia, Anaplasma
Dermatophyte Test Medium (DTM)
Used for testing suspected fungal infections in pets; incubate for 7-10 days. Test for ringworm as well as a blacklight
Elisa test that needs feces
Parvovirus and Giardia
Elisa test that needs Serum
Leptospirosis
Snap Combo Test
Felv and FIV
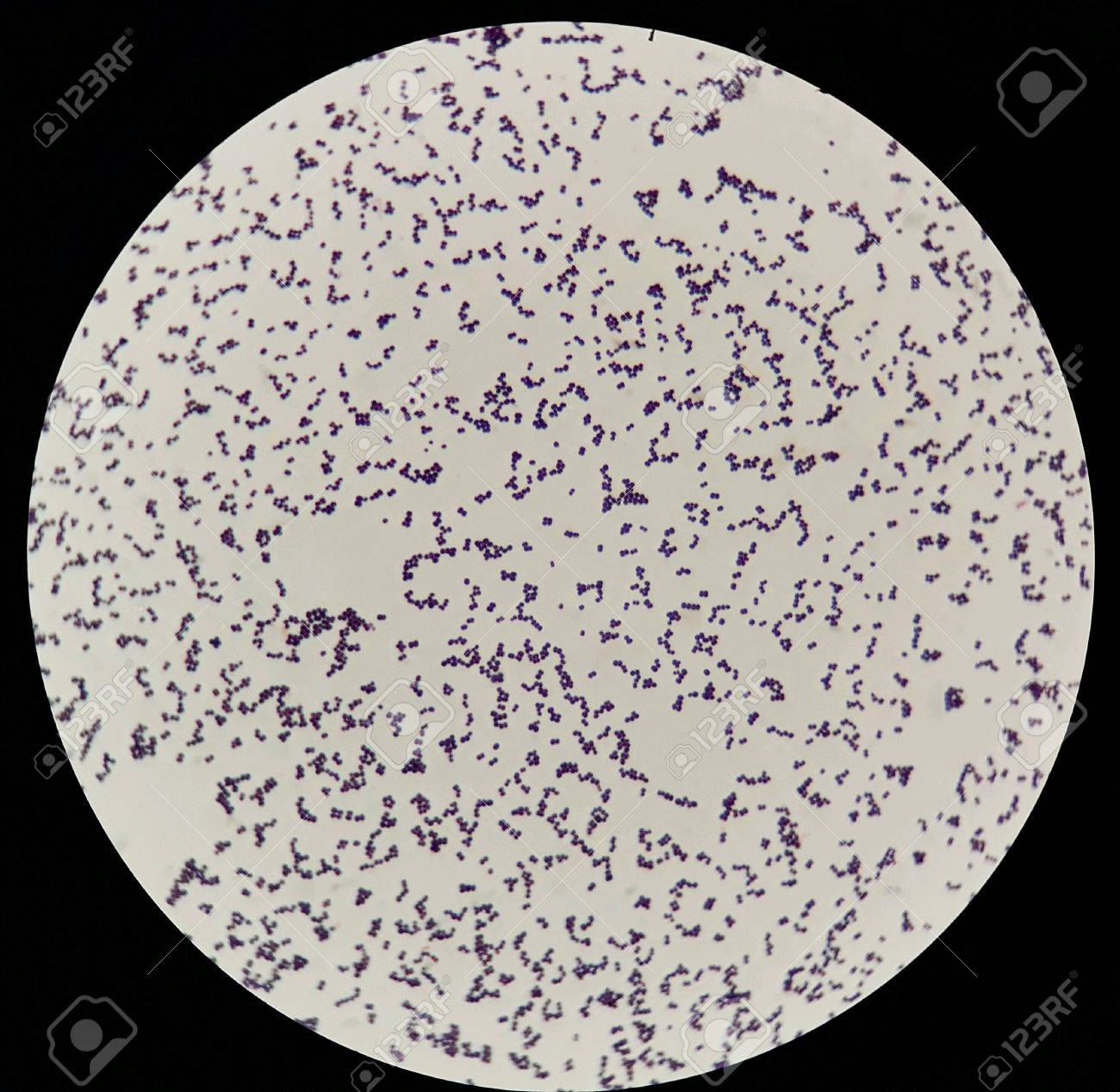
Blue/Purple (Gram-positive Bacteria)
Have a thicker cell wall that soaks up antibiotic easier making it more susceptible to treatment
Pink/Red (Gram-negative Bacteria)
have a thinner cell wall and protective outer wall membrane which makes it more resistant to the treatment
cocci
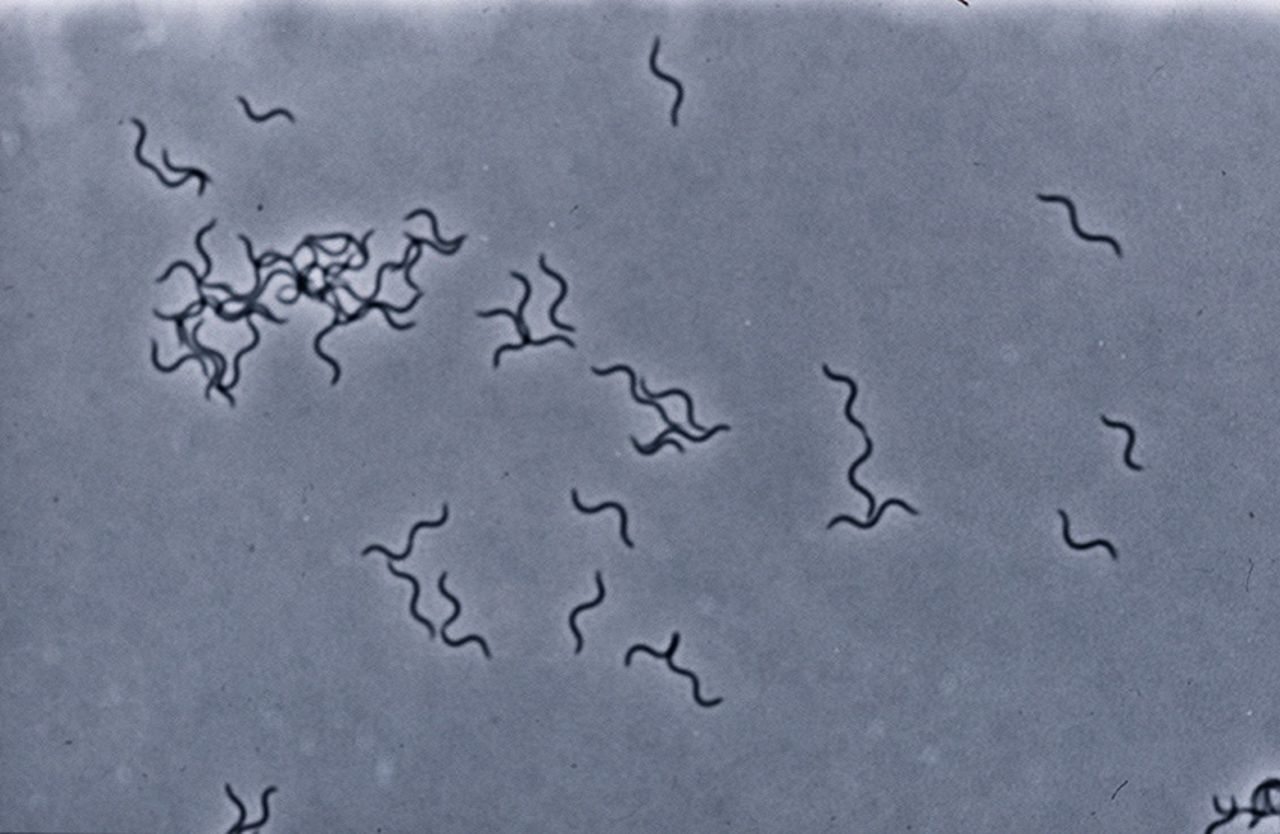
rods/bacilli

Spirals/spirochetes
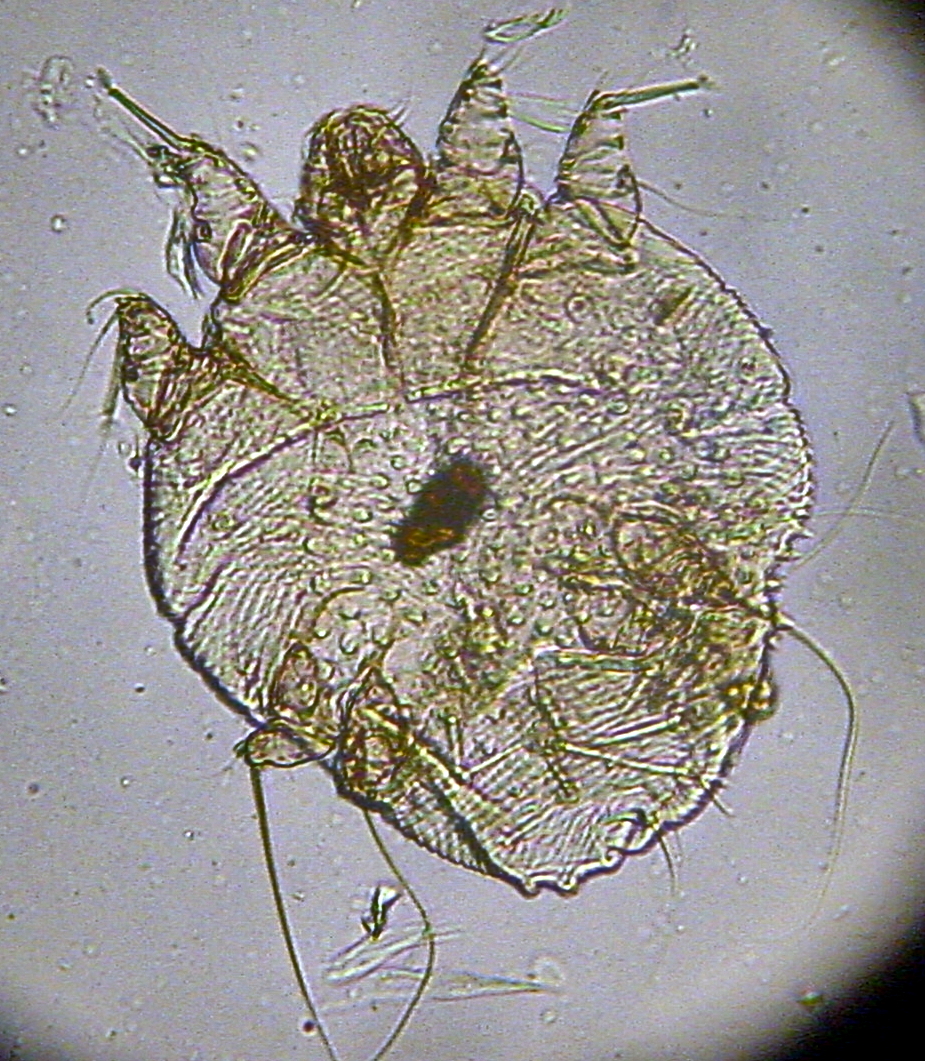
Sarcoptes scabiei
Commonly known as the Burrowing mite, it has a round body and short legs, diagnosed by a skin scrape.
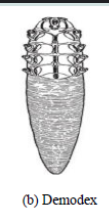
Demodex spp
Known as the Normal flora mite, these cigar-shaped mites are also identified through a skin scrape.

Otodectes spp
Referred to as the Ear mite, it features an oval and elongated body with long legs, diagnosed via an ear swab.

Cheyletiella spp
Commonly called Walking dandruff, this mite has a broad and elongated body with long legs and hook-like mouthparts, diagnosed by a tape test.
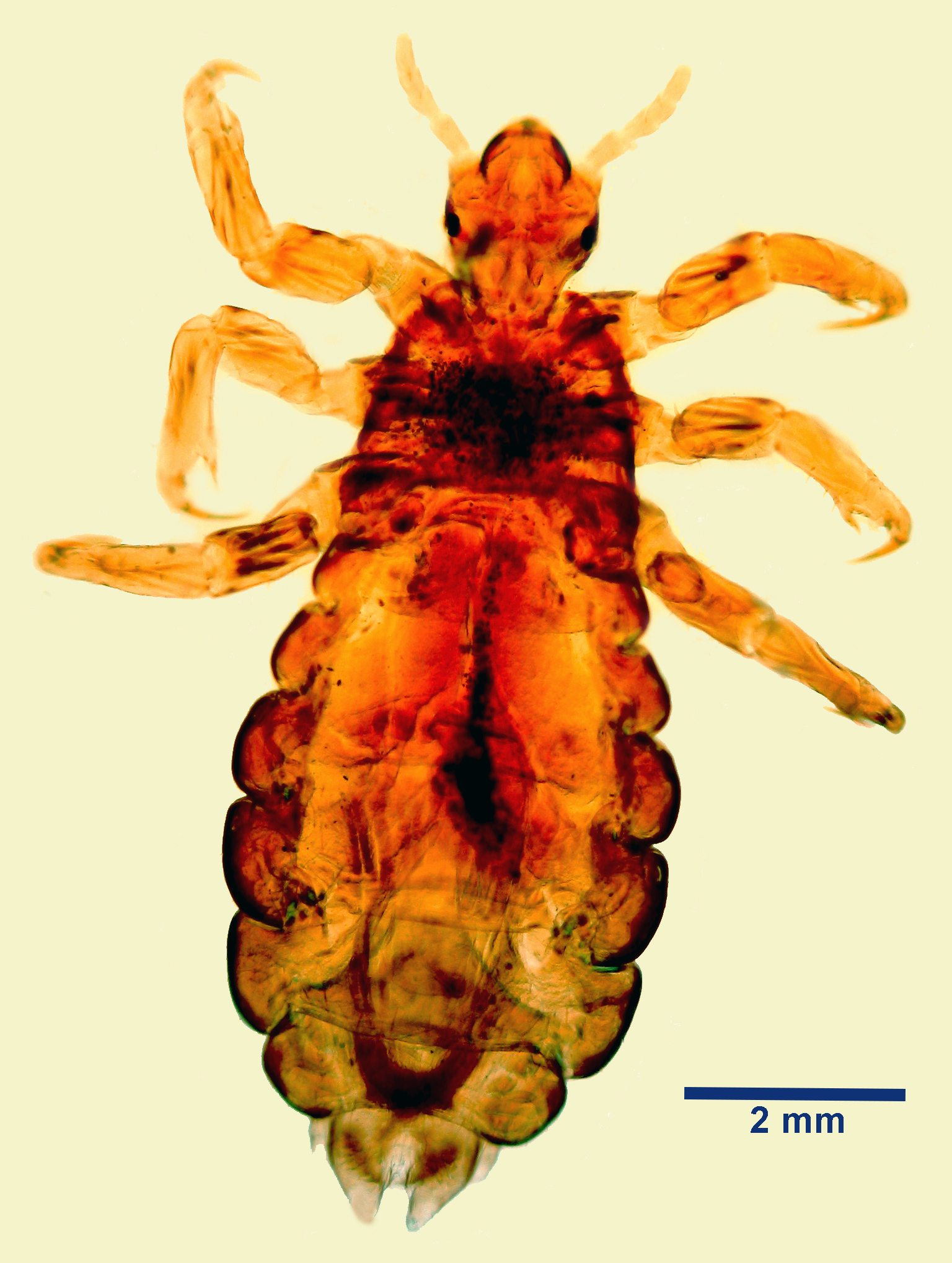

Anoplura
Known as Sucking lice, these parasites have a narrow head compared to the thorax, blood-feeding mouthparts, and are diagnosed through microscopic examination of lice and nits.

Mallophaga
Referred to as Chewing lice, they possess a broad, rounded head (wider than thorax) with chewing mouthparts and are diagnosed through visual or microscopic examination of the hair coat.
An illness that can be transmitted from animals to humans.
What is a zoonotic disease?
Eating undercooked poultry or animal feces.
What is a common way Campylobacteriosis is transmitted?
Dogs, cats, birds
Which animals are common sources of Campylobacteriosis?
Through contaminated feces
How is E. coli typically transmitted from animals to humans?
Livestock, pets, humans
What are common sources of E. coli?
Ingesting infectious eggs present in animal feces.
How are Roundworms primarily transmitted to humans?
Dogs, cats
Which common household pets are sources of Roundworms?
Through contact with contaminated soil or feces.
How can Hookworms be transmitted to humans?
Dogs, cats
What are common sources of Hookworms?
Contact with contaminated urine, soil, or water.
How is Leptospirosis transmitted?
Dogs, rodents, livestock
Which animals are typical sources of Leptospirosis?
Drinking infected water or direct contact with feces
How is Giardiasis transmitted?
Dogs, cats, wildlife
What are common sources of Giardiasis?
Bites, scratches, or saliva from an infected cat.
What is the primary transmission method for Cat-Scratch Disease?
Through infected saliva, usually from a bite
What is the most common way Rabies is transmitted to humans?
Dogs, bats, raccoons
Which animals are common carriers of Rabies?
Contact with infected animals or their fluids.
How is Brucellosis transmitted?
Cattle, pigs, goats
What are typical sources of Brucellosis?
Breathing in dried bird droppings or secretions
How is Psittacosis transmitted to humans?
Parrots, pigeons
What types of birds are sources of Psittacosis?
From infected animals, flies, ticks, or inhalation
How can Tularemia be transmitted?
Rabbits, rodents.
What are common animal sources of Tularemia?
Through flea bites from infected animals
How is Bubonic Plague typically transmitted to humans?
Cats, rodents
What are common sources for the fleas that transmit Bubonic Plague?
Wash your hands! Wear gloves! Cook meats thoroughly
What are some key general hygiene practices to prevent zoonotic diseases?
Avoid drinking untreated water! Wash hands
What is important to remember about water safety to prevent zoonotic diseases?
Keep vaccinations up to date! Wear PPE (Personal Protective Equipment)! Control fleas & ticks
What are some animal care practices that help prevent zoonotic diseases?