Lecture 4 -- Oestrus cycles
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
What is GnRH and its role in the ovarian cycle?
GnRH drives the release of LH and FSH from the anterior pituitary → Anterior pituitary then causes the developing follicle cells of ovaries to release oestrogen
Which hormone has a longer half life?
FSH has a longer half life than LH
Describe the negative feedback mechanisms in the reproductive cycle
Oestrogen
High levels inhibit the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary → Reduce GnRH, FSH, and LH secretion
Inhibin
Secreted by follicular (granulosa) cells → Suppresses FSH from the anterior pituitary
Prevent further recruitment of additional follicles
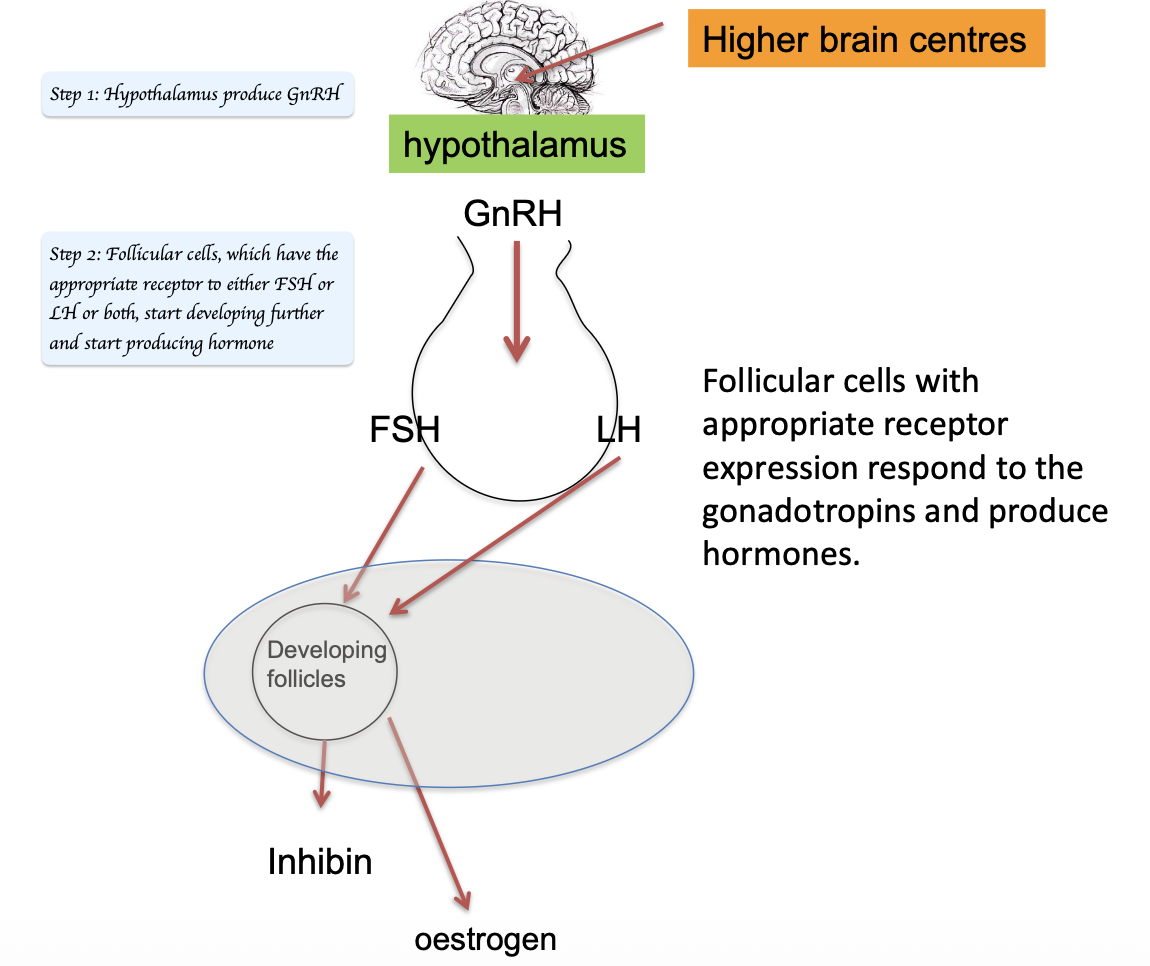
Describe the hormonal changes that occur during follicular phase of the oestrous cycle, leading up to ovulation
Initially, FSH from anterior pituitary promote the growth of several follicles
These developing follicles produce increasing amount of oestrogen
Oestrogen initially has a negative feedback on hypothalamus and pituitary → Level of FSH and LH are relatively low
As a dominant follicle matures, oestrogen levels rise significantly
High oestrogen level triggers a switch to a positive feedback loop → Surge in GnRH from hypothalamus → Surge in LH from anterior pituitary → Ovulation = Mature follicle to rupture and release oocytes
Which cells convert cholesterol into testosterone in the developing follicle?
Theca internal cells (Outer layer of developing follicles)
Which cells convert testosterone into oestrogen?
Granulosa cells
What are the main effects of oestrogen on the reproductive tract?
Increased blood flow
Increased mucous secretion
Increased tissue oedema
Increased leukocytes
Increased smooth muscle motility
Increased growth of uterine glands
What are the effects of oestrogen on the brain?
Increased phonation
Increased mating posture
Increased physical activity
What happens after ovulation in terms of luteal function and hormonal feedback?
After ovulation, the mature follicle degenerates into luteal cells, forming the corpus luteum
Corpus luteum produces progesterone
Progesterone inhibits the hypothalamus from releasing GnRH, preventing an LH surge and thus ovulation
What initiates ovulation in reflex ovulators?
In reflex ovulators, the GnRH pulse generator is not sensitive enough to produce oestrogen to induce LH surge
Mating initiates a neuroendocrine response of hypothalamus
Specific nerve ending in the vagina stimulated by mating
Sensory neuron passes through the dorsal root of spinal cord
Signal then are sent to the hypothalamus to release GnRH
Stimulate anterior pituitary to release FSH and LH
Induce developing follicles to release of oestrogen which triggers ovulation
How does the control of ovulation differ between spontaneous and induced ovulators?
Spontaneous ovulators:
Ovulation occurs cyclically due to hormonal changes and does not require the animal to be mated
Induced ovulators:
Ovulation is triggered by mating or copulation and requires the physical stimulation of the cervix or vagina to initiate the neuroendocrine reflex leading to ovulation
How does seasonal breeding differ between short-day and long-day breeders?
Short-day breeders = Breed in autumn e.g. sheep
Long-day breeders = Breed in spring e.g. horses
Ganglion cells in the retina detect the darkness → Activate the pineal gland to produce melatonin → Melatonin only produces at night → During spring, only low level of melatonin can be produced → In response to low level of melatonin, horses increase GnRH → Increase FSH and LH → Enter its oestrus cycle because of the surge of LH → Cause ovulation
Describe two waves of oestrus cycle
→ First wave: Bunch of follicle develop because of FSH → At this stage, the level of progesterone is still high → Follicle dies back
→ Second wave: Another bunch of follicle develop + After 14days, luteolysis occurs → Progesterone level returns back to basal → Dominant follicle develops → Ovulation occurs
What are the characteristic of the oestrus cycle of mare?
→ 21days + 5days oestrus period
→ Long day breeder (Spring)
→ Ovulation occurs 24-38hrs before end of oestrus
→ Polyoestrus
What are the characteristic of the oestrus cycle of sheep?
17days + 30hours oestrus period
Seasonal short day breeder (Autumn)
Ovulation occurs 20-25hrs before end of oestrus
Polyoestrus
What are the characteristic of the oestrus cycle of cows?
21days + 18hours oestrus period
Non seasonal breeder
Ovulation occurs 20-30hrs from the start of oestrus
Polyoestrus
What are the characteristic of the oestrus cycle of sows?
21days + 2days oestrus period
Non seasonal breeder
Ovulation occurs 36-44hours from the start of oestrus
Polyoestrus
What are the characteristic of the oestrus cycle of queen?
Induced ovulation
21days + 10days oestrus period
No early luteolysis
Corpus luteum last for 45days even if they are not pregnant
What is luteolysis?
If there is no fertilisation occurring, corpus luteum degrades and forms a scar tissue called corpus albicans after around 14days → It stops producing progestrone
What cause luteolysis?
Oxytocin are produced by CL and posterior pituitary gland → Oxytocin binds with its receptor in endometrium → Stimulates the release of prostaglandin from the endometrium of uterus → Since ovarian vein are wrapped around the uterine artery → Prostaglandin which is located in the uterine vein directly enter the ovarian artery → Prostaglandin travels to the ovary → Directly act on corpus luteum → Cause luteolysis
What is the role of prostaglandin in the reproductive cycle in cats and dogs?
In cats and dogs, prostaglandin does not play a significant part in causing the corpus luteum (CL) to regress
Unknown role