Transformations, Congruence, and Similarity
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
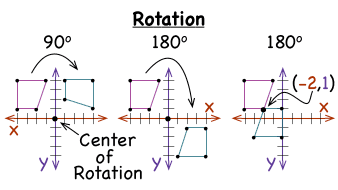
Rotation
Turn
Reflection
Flip or mirror image
Translation
slide
Dilation
enlarge or reduce a shape by multiplying/dividing by a scale factor
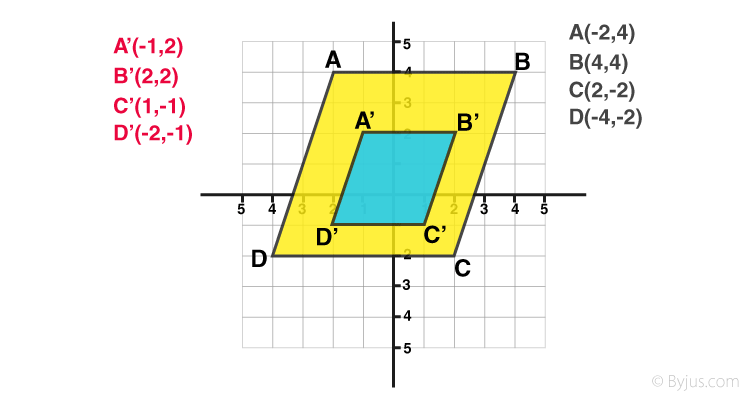
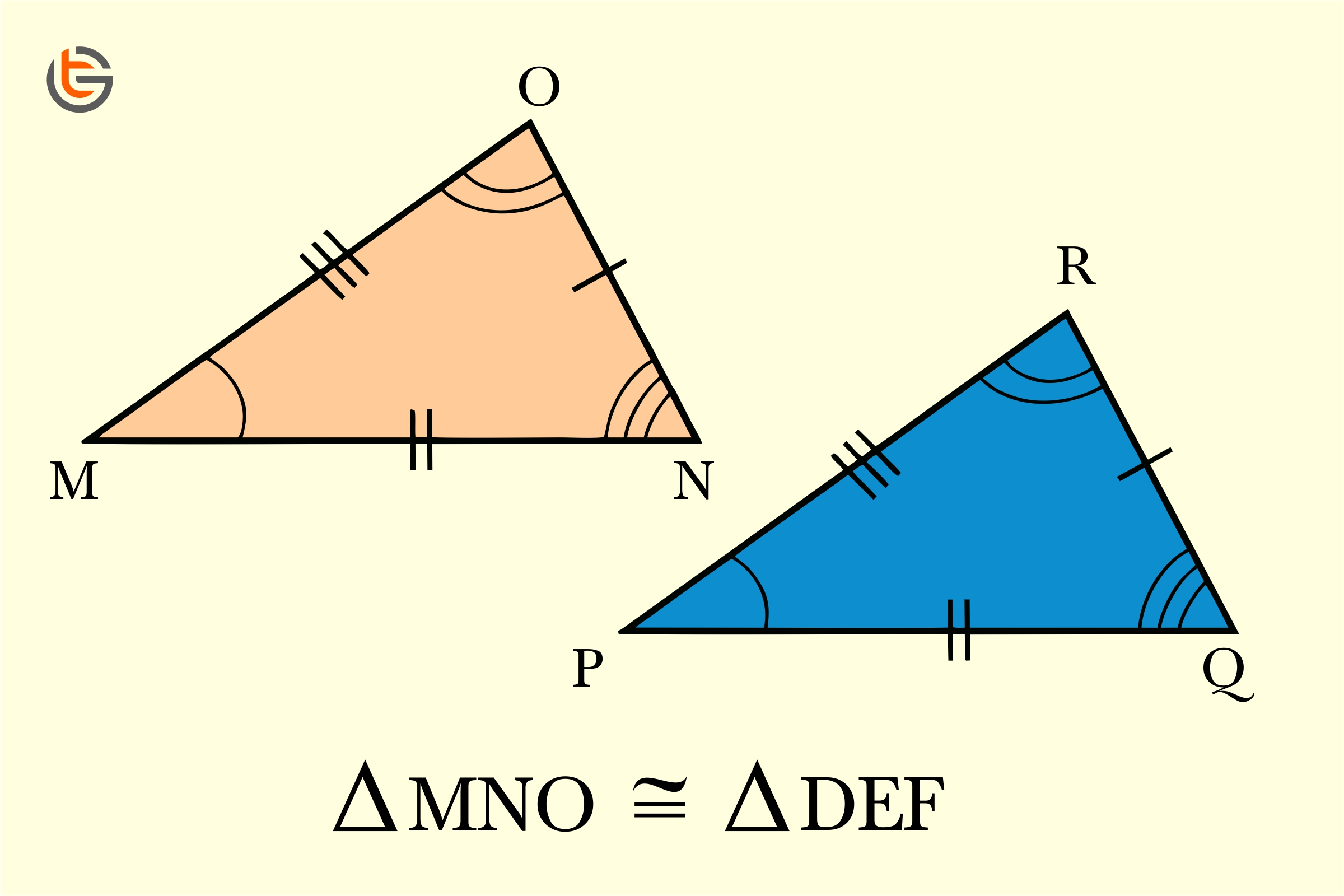
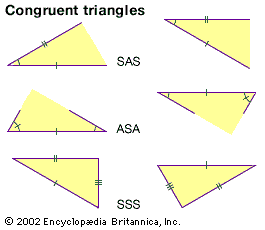
Congruent
shapes that are exactly the same—same shape and same size
Similar
shapes that have the same shape but different (proportional) size
Reflection across the x-axis
Keep x-value the same, take the opposite of new y-value [Example: (3, 2) (3, -2)]
![<p>Keep x-value the same, take the opposite of new y-value [Example: (3, 2) (3, -2)]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/11ea3c6a-28c7-42ee-81cc-985df7831a69.png)
Reflection across the y-axis
Keep y-value the same, take opposite of new x-value [Example: (3, 2) (-3, 2)]
![<p>Keep y-value the same, take opposite of new x-value [Example: (3, 2) (-3, 2)]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/6a13655f-d669-426e-aad2-58569ed600a5.png)
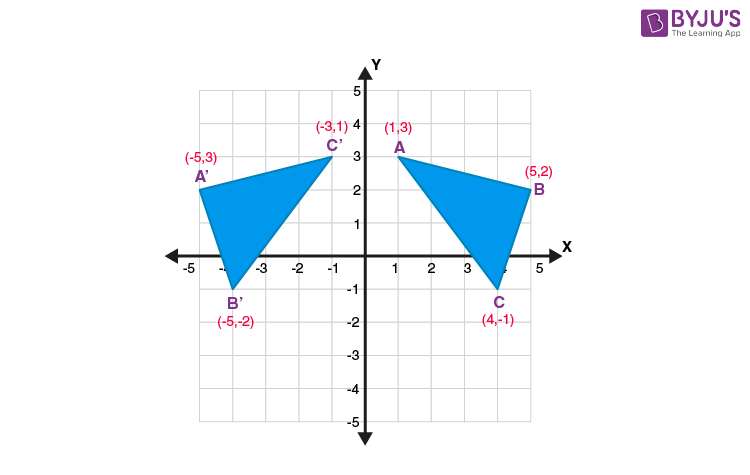
Rotation 90o clockwise
Switch coordinates, take opposite of new y-value [Example: (3, 2) (2, -3)]
![<p>Switch coordinates, take opposite of new y-value [Example: (3, 2) (2, -3)]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/2756f227-cbcd-4a75-a1d2-5b1a4a9468b6.png)
Rotation 90o counterclockwise
Switch coordinates, take opposite of new x-value [Example: (3, 2) (-2, 3)]
![<p>Switch coordinates, take opposite of new x-value [Example: (3, 2) (-2, 3)]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/79875c1c-9cc1-48aa-8d13-0c99c778f771.png)
Rotation 180
Take opposite of both x-value and y-value [Example: (3, 2) (-3, -2)]
![<p>Take opposite of both x-value and y-value [Example: (3, 2) (-3, -2)]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/23478dbb-bc80-4ccd-8974-02771f31c43a.png)
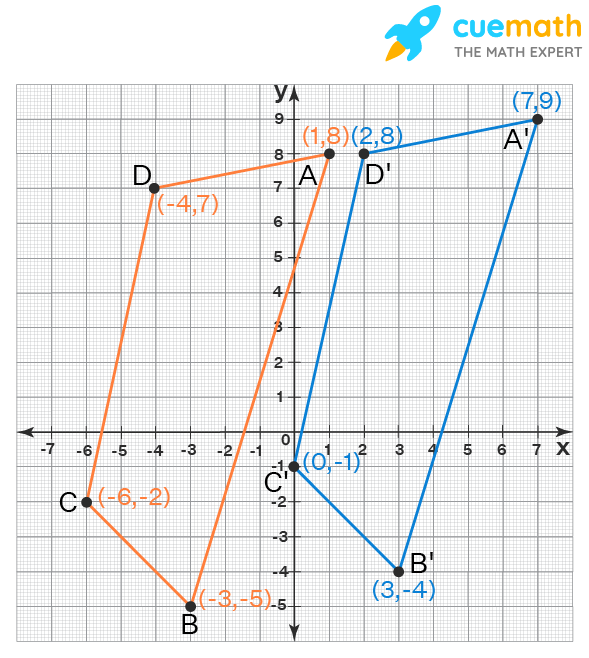
Translations
: If given a rule, use the coordinates given and “plug” them in for the x and y in the second part of the rule [Example: Rule: (x, y) (x – 10, y + 4), Coordinate given: (3, 2); (3 – 10, 2 + 4) = (-7, 6)] -If given “directions”, remember “left” and “right” affect the x-value. “Up” and “Down” affect the y-value
![<p>: If given a rule, use the coordinates given and “plug” them in for the x and y in the second part of the rule [Example: Rule: (x, y) (x – 10, y + 4), Coordinate given: (3, 2); (3 – 10, 2 + 4) = (-7, 6)] -If given “directions”, remember “left” and “right” affect the x-value. “Up” and “Down” affect the y-value</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/7531accc-ead8-4058-9918-6233696797bc.png)
Dilations
multiply both the x and y values by the scale factor (k) given. [Example: k = 3, coordinate given (3, 2) (9, 6) or k = ½ , coordinate given (3, 2) (1.5, 1)]
![<p>multiply both the x and y values by the scale factor (k) given. [Example: k = 3, coordinate given (3, 2) (9, 6) or k = ½ , coordinate given (3, 2) (1.5, 1)]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/c72f798d-2df3-4a18-ad21-cc89f4c1f071.png)
≅
means congruent
~
means similar
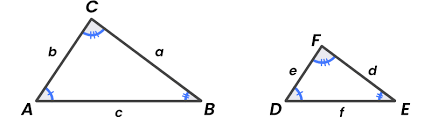
m∠x
means “ measure of angle the x
𝑿𝒀̅̅̅̅
means “line segment” or “side length” from point X to point Y
∥
means “is parallel to”