Electrochemistry
0.0(0)Studied by 7 people
0%Unit 9: Applications of Thermodynamics Mastery
0%Exam Mastery
Build your Mastery score
Supplemental Materials
Card Sorting
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:36 AM on 3/25/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
1
New cards
What occurs in a oxidation-reduction (REDOX) RXN?
The oxidation states of 2 substances changes
2
New cards
Oxidation does what to elections?
Oxidation means losing electrons (LEO;OIL)
3
New cards
Reduction does what to elections?
Reduction means gaining electrons (GER;RIG)
4
New cards
What are the rules to assigning oxidization numbers?
1. Free, neutral elements ox. #s are 0
2. Monoatomic ions ox. #s are their charge
3. Alk. metals are +1
4. Alk. earth metals are +2
5. O is usually -2
6. H is usually +1
7. F is always -1
8. Halogens are usually -1
9. The total sum of ox. #s in a neutral polyatomic compound is always 0
10. The total sum of ox. #s in a polyatomic ion sums to the charge of the polyatomic ion
5
New cards
Redox reactions conserve what?
They conserve both mass and charge
6
New cards
Define half-reactions:
Splitting up a reaction by whats being oxidized and by whats being reduced by itself; 2 separate reactions showing oxidization and reaction alone
7
New cards
What should occur when you add the half-RXNs together?
It should sum to to overall RXN
8
New cards
In line notation, what does the left signify? What does the right signify?
1. The left shows the anode, or where oxidization occurs (the loss of e)
2. The right shows the cathode, or where reduction occurs (the gaining of e)
9
New cards
What are the steps in balancing redox equations using the half-RXN method assuming an acidic solution? How does it change when you assume a basic solution?
1. For an acidic solution:
1. Break the overall equation into 2 half-RXNs
2. Balance everything but H and O
3. Balance O by adding H2O as needed
4. Balance H by adding H+ as needed
5. Add electrons as needed
6. Multiply each half-RXN by integers to cancel the electrons
7. Add the 2 half-RXNs and simplify (similar in concept to Hess’s Law)
2. For basic solutions, you do all the above but you add enough OH- to cancel any H+ by turning it into water, and simplify again from this
10
New cards
How does electron transfer occur in voltaic/galvanic cells?
Electron transfer occurs via an external pathway that links the reactants
11
New cards
Define electrodes and the 2 types:
The 2 solid metals in a voltaic/galvanic cell, one acting as the anode (the oxidized compound, loses electrons, angry ox, helps to reduce the other compound by giving it electrons) and the cathode (the reduced compound, gains electrons, red cat, helps to oxidize the other compound by taking its electrons)
12
New cards
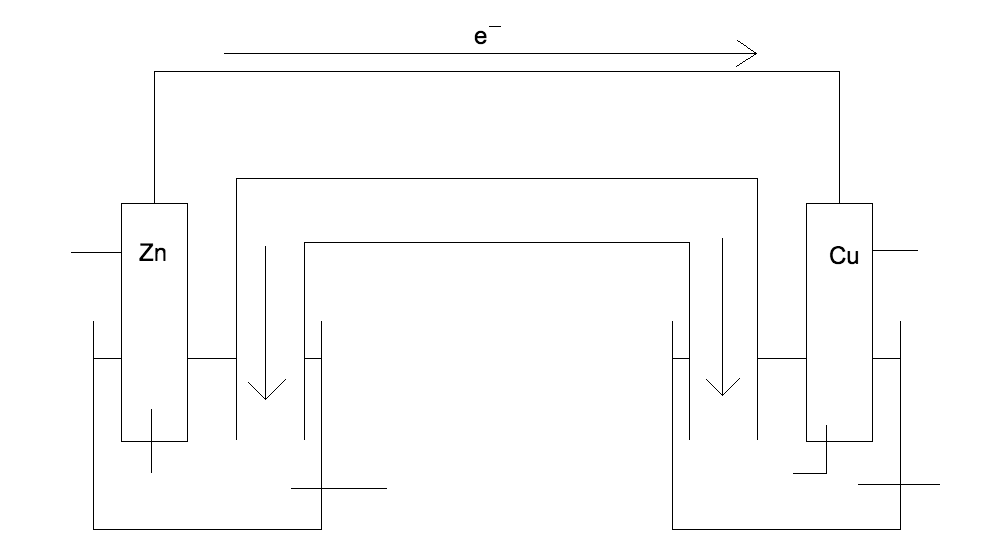
Correctly identify the anode, cathode, whats in solution in both containers, whats coming off of the Zn and whats going onto the Cu
What is the system attempting to do?
What is the system attempting to do?
The system is trying to neutralize both solutions
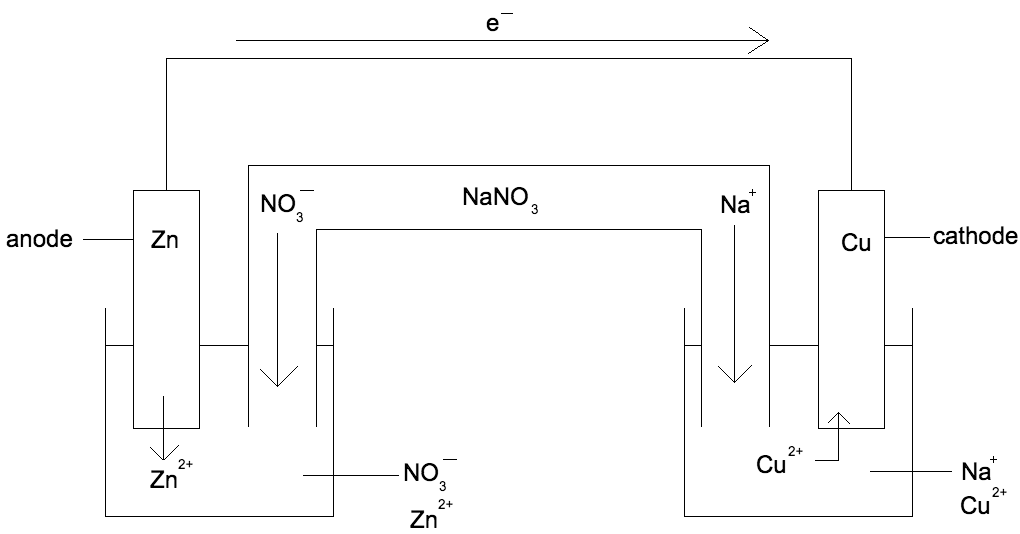
13
New cards
For a cell to operate, the PE of the anodes electrons (or the PE of losing electrons) >/
The PE of the anodes electrons (or the PE of losing electrons) **>** the PE of the cathodes electrons (or the PE of gaining electrons)
14
New cards
When the anodes e PE is > cathodes e PE, where do the electrons flow, and in what process do they flow?
1) The electrons would flow toward to cathode (when given a path)
2) They then flow spontaneously
2) They then flow spontaneously
15
New cards
In terms of voltage, does the difference in PE and charge matter? Does the magnitude of the charge/# of electrons being moved matter?
1) The difference in PE and charge matters
2) The magnitude of the charge/# of electrons being moved does NOT matter and doesnt change voltage
2) The magnitude of the charge/# of electrons being moved does NOT matter and doesnt change voltage
16
New cards
Define electromotive force (EMF):
The potential voltage difference; the higher the difference, the higher the EMFs
17
New cards
How do we refer to EMFs for a particular cell?
We write Eºcell and call it cell potential (the º denoting it being at standard conditions)
18
New cards
\+ Eºcell means:
Spontaneous reaction in that direction
19
New cards
What does Eºcell depend on?
\[\], T, and materials used
20
New cards
How do you calculate Eºcell?
You must look up tabulated standard reduction potentials for each half cell and use the equation Eºcell=Eºred,cathode-Eºred, anode (flipped)

21
New cards
Define the standard hydrogen electrodes (SHE), its equation, and its Eºred
1) SHE is the reference point for all reduction potentials, being arbitrarily assigned
2) 2H+(aq, 1M (since its at standard conditions))+2electrons \n →H2(g, 1 atm)
3) Eºred=0 since its the reference point
2) 2H+(aq, 1M (since its at standard conditions))+2electrons \n →H2(g, 1 atm)
3) Eºred=0 since its the reference point
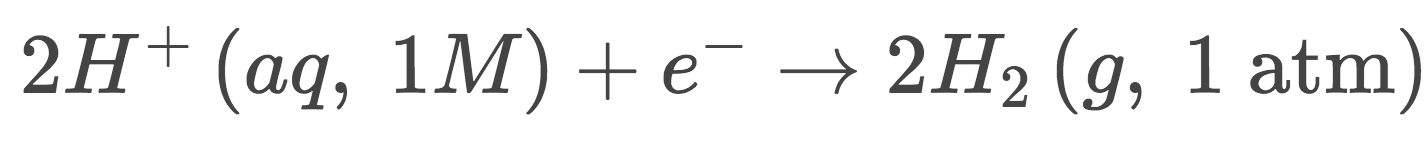
22
New cards
If the Eºred is a constant (depending on \[\], T, and materials), does it change with multiples of coefficients in your half-RXNs?
No, this doesn’t affect Eºred
23
New cards
A positive Eºred indicates what 2 things?
1) That the reaction is spontaneous IN THAT DIRECTION
2) The reaction naturally wants to be reduced
2) The reaction naturally wants to be reduced
24
New cards
A negative Eºred indicates what 2 things?
1) You must flip the reaction to get it to be spontaneous, otherwise its non-spontaneous in that direction
2) The reaction is less reduced and more oxidized
2) The reaction is less reduced and more oxidized
25
New cards
When given 2 negative Eºred to determine which half-RXN is the oxidized one and which is reduced, how do you find this out?
Since a positive Eºred indicates that a reaction naturally wants to be reduced, whichever is the most positive will be reduced while the other will be oxidized, thus meaning that the more spontaneous a Eºred (in that direction)=the more EMF=the higher the voltage=the most positive=the cathose/reduced (gains e), and vice versa
26
New cards
What monoatomic atom is the strongest oxidizer (something that is reduced, CAUSING oxidization)? What are other strong oxidizers? What is the general trend for strong oxidizers?
1) F2
2) Cl2, Br2, I2, and any oxyanion where the central atom has a large + charge (ex: MnO4^-, Cr2O7^3-,ClO3^-, etc…. )
3) Strong oxidizers attract e- very strongly, their own and other substances too
2) Cl2, Br2, I2, and any oxyanion where the central atom has a large + charge (ex: MnO4^-, Cr2O7^3-,ClO3^-, etc…. )
3) Strong oxidizers attract e- very strongly, their own and other substances too
27
New cards
When your Eºred has a high magnitude, what does this mean?
This would mean that that substance has a higher likelihood of reacting in the given direction (depending on the sign + or -)
28
New cards
How does the Activity Series tell us which metals are most reactive/accept e- and which are the least reactive/give e-)?
The Activity Series uses standard reduction potentials to gauge which metals are more likely to give their e- or accept e- (depending on if they’re reducers or oxidizers)
29
New cards
A +Eº (or E or EMF if its at nonstandard conditions) indicates what? A -Eº indicates what?
1. A +Eº means a spontaneous reaction in that direction
2. A -Eº means a non-spontaneous reaction in that direction
30
New cards
What equation illustrates the relationship between E and ΔG (both being measures of reactivity and spontaneity)? What do its components mean?
1) ΔG=-nFE (or ΔG=-nFEº in standard states)
2) n= # of moles of transferred electrons total (after doing both half-RXNs to find its total), F=Faradays constant (96485 J/Vmol, or with units C/mol)
2) n= # of moles of transferred electrons total (after doing both half-RXNs to find its total), F=Faradays constant (96485 J/Vmol, or with units C/mol)
31
New cards
How do gradually changing \[\]s of R and P change a cells EMF?
It decreases its EMF
32
New cards
When a cells EMF=0, what does this mean?
This essentially means that the cell is “dead” or there is no difference in PE and thus no flow of electrons that doesn’t cancel out
33
New cards
What equation can we use to illustrate the relationship between E (and Eº) with \[\]? What 2 forms does it come in? What do its components mean?
1) The Nerst equation:
* The form used when at non-standard conditions:
* E=Eº-((2.303RT)/(nF))logQ
* The form used when at 25ºC/298k or STP:
* E=Eº-((0.0592)/(n))logQ
2) R=gas constant (3 forms: 8.314 J/molk (most commonly used here), 0.08206 Latm/molk, and 62.36 Ltorr/molK)
n= # of moles of transferred electrons total (after doing both half-RXNs to find its total)
F=Faradays constant (96485 J/Vmol, or with units C/mol)
* The form used when at non-standard conditions:
* E=Eº-((2.303RT)/(nF))logQ
* The form used when at 25ºC/298k or STP:
* E=Eº-((0.0592)/(n))logQ
2) R=gas constant (3 forms: 8.314 J/molk (most commonly used here), 0.08206 Latm/molk, and 62.36 Ltorr/molK)
n= # of moles of transferred electrons total (after doing both half-RXNs to find its total)
F=Faradays constant (96485 J/Vmol, or with units C/mol)
34
New cards
Define a concentration cell:
Different \[\]s of the same species generating an EMF
35
New cards
When you have a concentration based cell, what will the cells goal be? What does this imply for Q?
1. It will eventually equalize the two concentrations
2. Since both sides will eventually equalize, you’re going from a concentrated anode (giving the materials/electrons to plate the cathode) and the diluted cathode (accepting the materials/electrons to be plated), meaning that by going from a concentrated solution (R) to a dilute solution (P) makes Q=\[dilute\]/\[concentrate\] (photo of Ni included as an example to show the cancelation)
![1. It will eventually equalize the two concentrations
2. Since both sides will eventually equalize, you’re going from a concentrated anode (giving the materials/electrons to plate the cathode) and the diluted cathode (accepting the materials/electrons to be plated), meaning that by going from a concentrated solution (R) to a dilute solution (P) makes Q=\[dilute\]/\[concentrate\] (photo of Ni included as an example to show the cancelation)](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/9ec6233bdfc448c0864e61cfada751ff.jpeg)
36
New cards
How can we prove that at equilibrium, EMF=0 and E=0V?
By using Nersts equation, we can find that since at equilibrium, \[\]s are 0, meaning our Q value is 1, which then would make E=0V and thus EMF=0
37
New cards
How can we find the relationship between K (or Q) and E?
We can simply rearrange the Nerst equation to make everything equal to logK(or Q):
* At non-standard conditions: logK=(nFEº)/(2.303RT)=(-ΔGº)/(2.303RT)
* At standard conditions (25ºC/298k): logK=16.912(nEº)=(-ΔGº)/(5706)
* At non-standard conditions: logK=(nFEº)/(2.303RT)=(-ΔGº)/(2.303RT)
* At standard conditions (25ºC/298k): logK=16.912(nEº)=(-ΔGº)/(5706)
38
New cards
Define corrosion:
A spontaneous redox RXN where a metal reacts with some substance in its environment to form an unwanted compound
39
New cards
Define galvanized iron and why it does this:
Galvanized iron is coated with a protective layer of zinc, which helps to form a protective oxidize coating to prevent further corrosion
40
New cards
Define cathodic protection:
Protecting a metal by making it the cathode in an electrochemical cell (with an oxidized metal being called the sacrificial metal)
41
New cards
Define electrolysis:
Using an outside source of electrical energy to cause a non-spontaneous redox RXNs to occur
42
New cards
Where does electrolysis occur?
It will occur in an electrolytic cell with 2 electrodes
43
New cards
Define electroplating:
Using electrolysis to deposit a thin layer of one metal onto another
44
New cards
1 Ampress/I=….
1 C/s (Culoumbs/seconds)
45
New cards
1 mole of transfered electrons carries how much culoumbs of charge?
96485 C/mole (this being Faradays constant)
46
New cards
How do we calculate the max work a voltaic cell can do on its surroundings? What must be the sign convention for Wmax?
1) Wmax=ΔG=-nFE
2) Wmax must be - as it must exert work onto its surroundings, not gain it
2) Wmax must be - as it must exert work onto its surroundings, not gain it
47
New cards
How do we calculate the work a electrolytic cell can do on its surroundings? What do its components mean? What must be the sign convention for W? How does E relate to E(ext)?
1) W=nFE(ext)
2) E(ext) simply means the external voltage source
3) W must be +
4) E does NOT equal E(ext)
2) E(ext) simply means the external voltage source
3) W must be +
4) E does NOT equal E(ext)
48
New cards
1 Watt (W)=….
1 J/s
49
New cards
What unit do we often measure electrical power to be in?
Usually its measured in the Kilowatt/hour