Exam 2 - bone tumors
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
is osteoid osteoma benign or malignant? what is its size?
benign
<2 cm
where is osteoid osteoma commonly found? who is it more common in?
cortex of tibia/fibula
10-20 males
is osteoblastoma benign or malignant? what is its size?
benign
2+ cm
where is osteoblastoma usually found? in who?
spine
10-20 males
is osteosarcoma benign or malignant? what is the size?
malignant
fairly large
where are osteosarcomas commonly found?? in who?
metaphysis of bones of knee
10-20 males
is osteochondroma benign or malignant? relative size?
benign
fairly large
where is osteochondroma commonly found? who?
metaphysis of bones of knee
10-30 males
is enchondroma benign or malignant? relative size?
benign
fairly small
where are enchondromas located? who?
bone of hands
20-50 males
is chondrosarcoma benign or malignant? relative size?
malignant
fairly large
where are chondrosarcomas commonly found? who?
bone of shoulder and pelvic girdle
40-60 males
is Ewing Sarcoma benign or malignant? relative size?
malignant
fairly large
where is Ewing Sarcoma commonly found? who?
diaphysis of long bones (MC femur)
<20 Caucasian males
are giant cells (osteoclastoma) benign or malignant? relative size?
benign with malignant potential
large
can giant cells be aggressive
yes, locally
where are giant cells (osteoclastomas) commonly found? who?
epiphysis of long bones: knee, hip, wrist
20-40 women
is a fibrous cortical defect considered a neoplasm?
no
what is the relative size of fibrous cortical defect? where is it found?
<3 cm
metaphysis or diaphysis of lower extremity long bones
who commonly has fibrous cortical defect
children
is nonossifying fibroma considered a neoplasm? what is its relative size?
no
>3 cm
where are nonossifying fibromas commonly found? in who?
metaphysis or diaphysis of lower extremity long bones
children
is fibrous dysplasia benign or malignant?
benign proliferation of fibrous tissue and woven bone
what is the relative size of fibrous dysplasia
fairly large
but variable
where is fibrous dysplasia commonly found? in who?
ribs, calvaria, mandible, femur, humerus
children into adulthood
are primary bone tumors more common than metastasis to bone
no
radiolucent means
darker, less dense bone
are benign tumors more common than bone cancers
yes
what are the most common primary bone cancers
osteosarcoma, chondrosarcoma, ewing sarcoma
A 16 year old male patient presents to your office and the x-ray shows this (picture)? what does he have?
osteoid osteoma
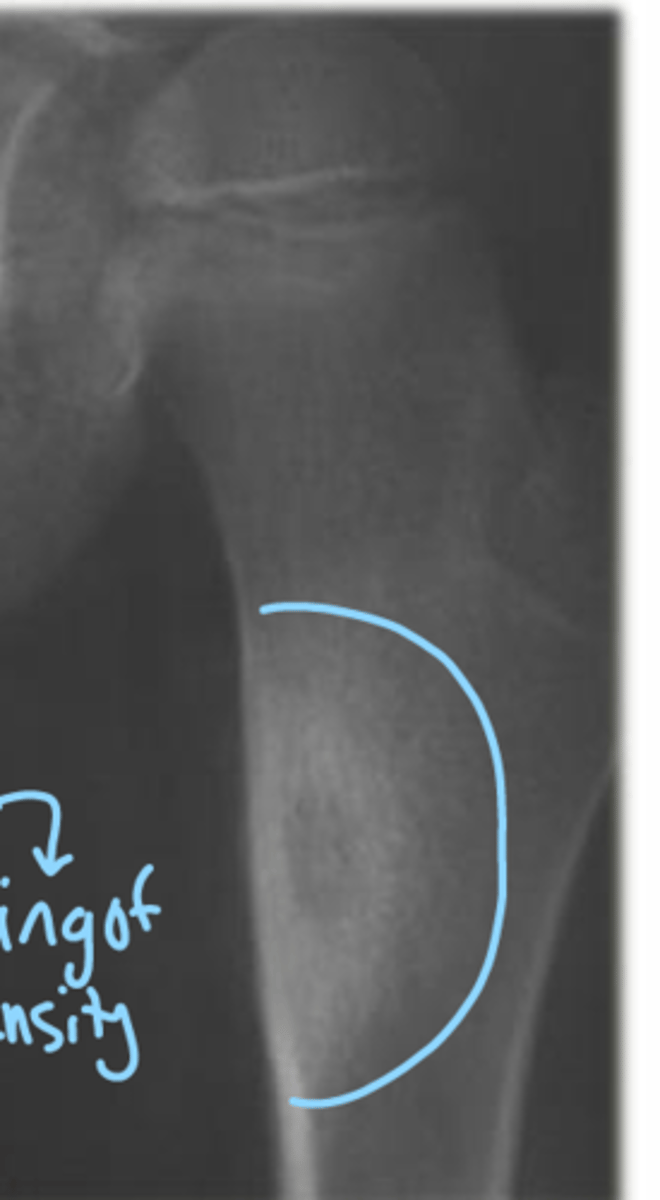
someone with osteoid osteoma may complain of pain during what time of the day?
night
what is the number one most common primary bone cancer
osteosarcoma
osteosarcomas are often accompanies by ____ reactions
periosteal
Codman triangle is a type of periosteal reaction, what is happening?
lifting of the periosteum
t/f
osteosarcomas are lytic and blastic meaning they have both increased and decreased density
true
A typical osteosarcoma can be treated using ___ or ____ but a secondary osteosarcoma usually in men over 40 has a ___ response to therapy
chemotherapy, amputation, poor
are cartilage forming tumors more commonly benign or malignant
benign
what are the 3 main types of cartilage forming tumors
osteochondroma
chondroma
chondrosarcoma
which type of cartilage forming tumor is characterized by a cartilage-capped outgrowth of hylaine cartilage
osteochondroma
osteochondroma can also be called what
exostosis
85% of people with an osteochondroma will have only ____ but some people have multiple and this is known as _____
one, multiple hereditary osteochondromas
someone with multiple hereditary osteochondromas is at a higher risk for
malignant transformation
what is Ollier Disease
multiple enchondromas
are enchondromas typically symptomatic
no
what is the second most common primary bone cancer
chondrosarcoma
on X-ray, someone with a chondrosarcoma will likely have bone that has a "____" or "_____" appearance from calcification
strippled, popcorn
is a low grade or high grade chondrosarcoma more common? which is slow growing and small?
low-grade for all answers
a low grade chondrosarcoma has a ___% survival rate while a high grade has a ____% survival rate
90, 40
high grade chondrosarcomas often metastasize to what location
lungs
benign tumors from proliferation of fibroblasts and macrophages which create a well defined radiolucent lesion surrounded by thin rim of sclerosis are known as
fibrous cortical defect or nonossifying fibroma
what is the difference between fibrous cortical defect and nonossifying fibroma
size
FCD= small
NOF= big
do FCD and/or NOF persist into adulthood
no
what is unique about FCD and NOF
typically resolve on their own
fibrous dysplasia is due to failed ____ differentiation
osteoblast
ALL fibrous dysplasia cases are from a spontaneous ___ mutation
GNAS
monostotic fibrous dysplasia involves how many bones
one
polyostotic fibrous dysplasia involves how many bones
multiple
polyostotic fibrous dysplasia + cafe-au-lait spots and endocrinopathy signify what syndrome
McCune-Albright syndrome
which type of fibrous dysplasia is most common
monostotic
which type of fibrous dysplasia is likely to progress into adulthood
polyostotic
what is the second most common pediatric bone cancer
ewing sarcoma
which type of bone cancer has an onion skinning like appearance
ewing sarcoma
Ewing sarcoma involve undifferentiation of ___ ____ cells
small round
Giant cell tumor of bone (osteoclastoma) promote ____ differentiation
osteoclast
giant cell tumors of the bone often cause what appearance of bone
soap bubble
what is the most common site of metastasis to bone
spine
sarcomas travel in the ___ and carcinomas travel in the ____
blood, lymphatics
when cancer metastasized to bone, what structure of the bone does it commonly stick itself in?
red marrow
lytic= ___ density
blastic = ___ density
decrease
increase
bony metastasis from the prostate in an adult is usually
blastic
bony metastasis from breast in an adult is usually
lytic
bony metastasis from lungs in adult is usually
mixed
what are major red flags that can lead to metastatic bone cancer
over 50, history of cancer, cachexia
t/f
True neoplasms are more common than tumor-like lesions
false
a small cyst made of degenerative connective tissue found in the wrist is most likely a
ganglionic cyst
what is the most common soft tissue tumor
lipoma
the most common location for soft tissue tumors is where
deep thigh tissue
a teenage boy presents to your office after suffering a shoulder injury in football. He has a hard, painless mass that he wants checked out. What is he likely presenting?
myositis ossificans
a benign tumor of fibroblasts that is invasive is known as
fibromatoses
Deep fibromatoses are more common in ___ in the ___ region
females, abdominal
Dupuytren Contracture is a characteristic of superficial fibromatoses and is more common in who
older males of European descent
what is the name of a malignant tumor of fibroblasts that has a herringbone histology
fibrosarcoma
where do malignant tumors of fibroblasts originate
fibrous tissue
what is the most common pediatric soft tissue sarcoma
rhabdomyosarcoma
Leiomyomas are benign tumors of smooth muscle in what area
uterus
leiomyosarcomas are malignant smooth muscle tumors most commonly found in ___ specifically in the ____ and ____
adult female
uterus and IVC
synovial sarcoma is a soft tissue cancer most common between the ages of ____ and it most commonly occurs in the ___
20-40
knee