AP Exam 3 Ch.7-9 Dr. Vetro
1/184
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
185 Terms
axial skeleton
skull, vertebrae, thoracic cavity
appendicular skeleton
limbs, pelvic, everything else
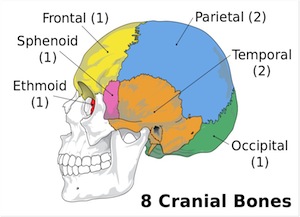
cranium
the skull. 8 bones surrounding the brain
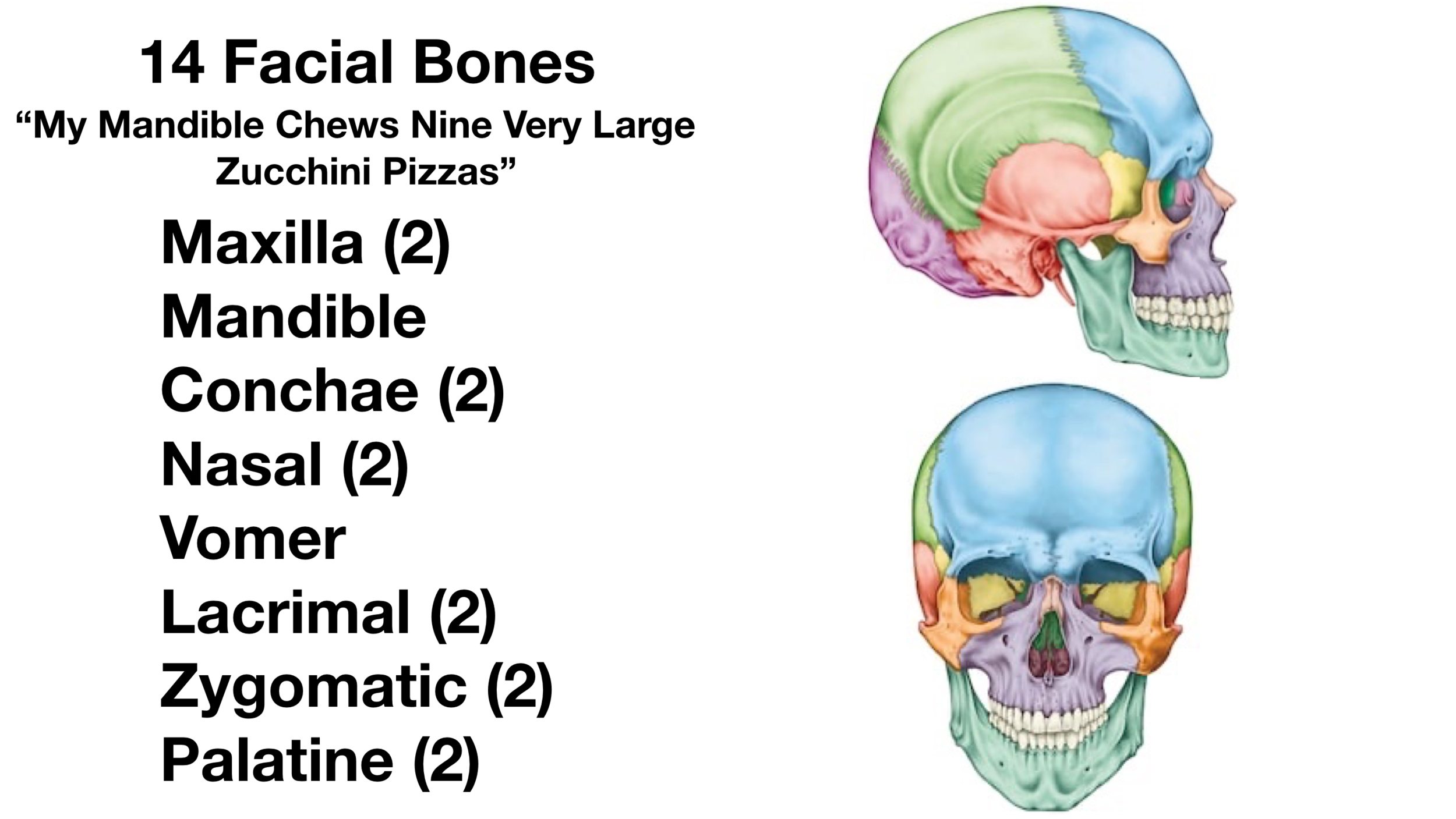
facial bones
14 bones making the skull
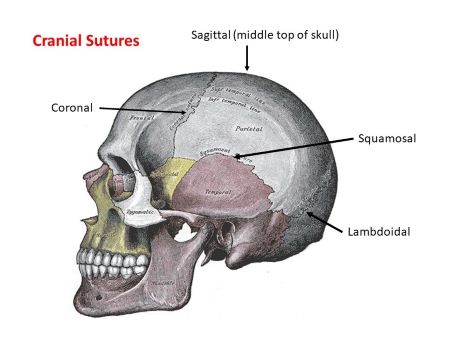
sutures
immovable joints between the skull bones
orbits of the skull
cavities holding the eyes
sella turcia
depression that hold the pituitary gland (inside the skull)
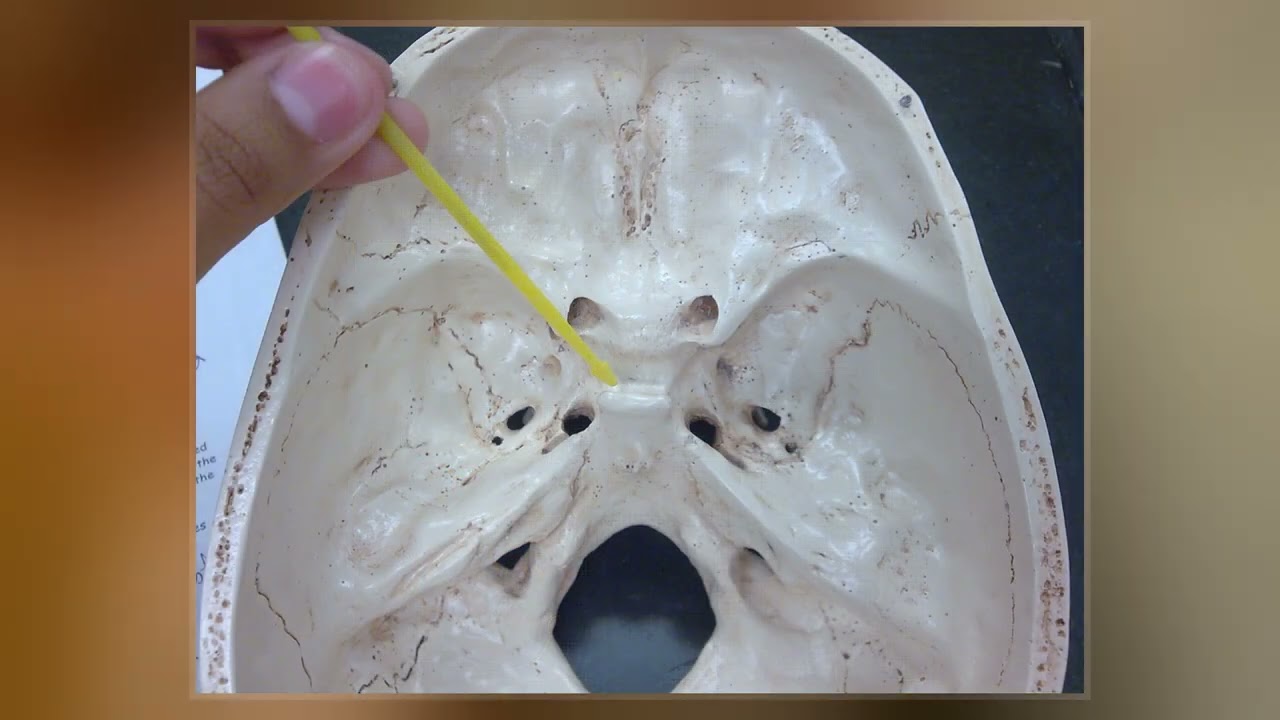
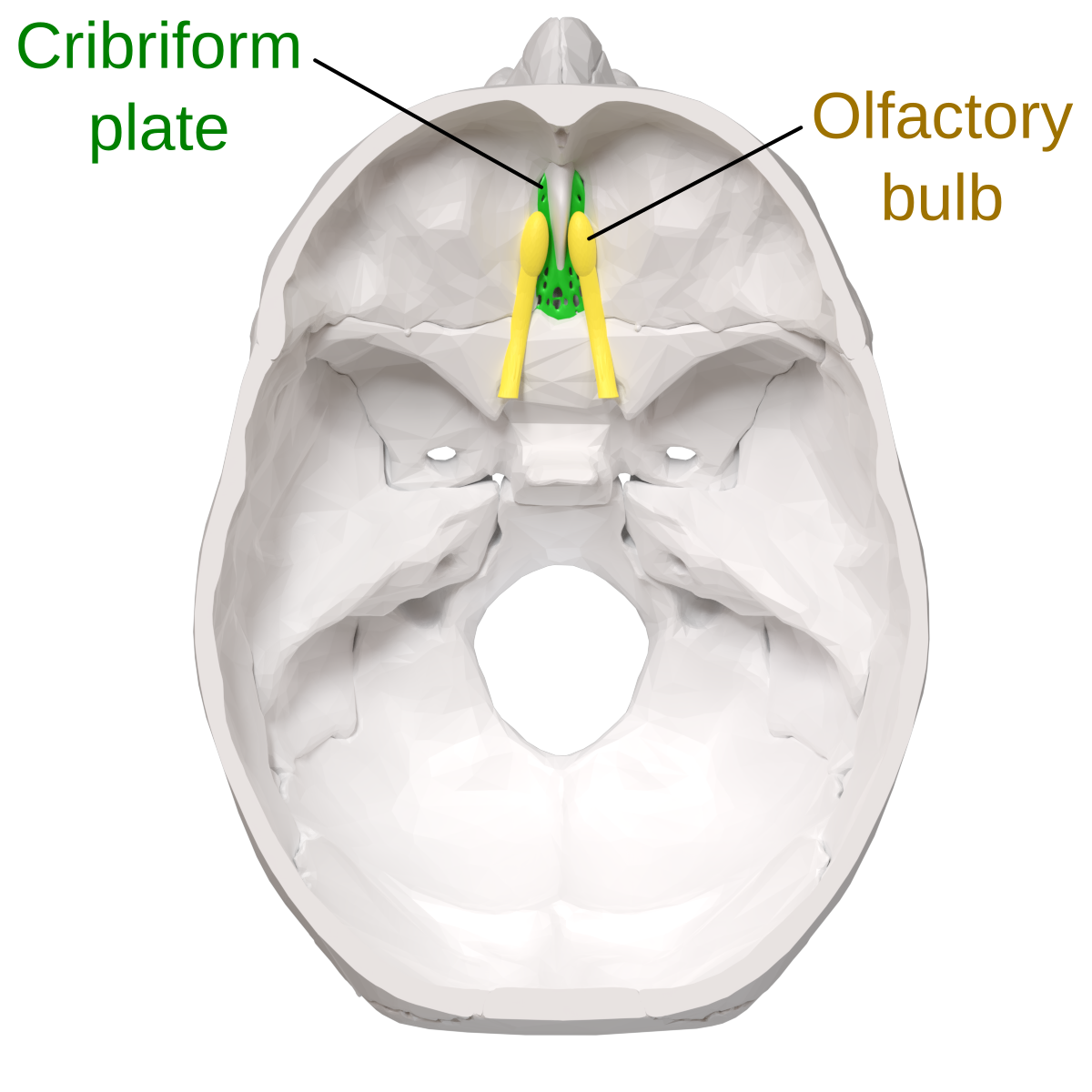
cribriform plate
bone with tiny holes for olfactory nerves to pass through from the brain to nasal
concha
projections inside the nose that increase the turbulence of air as it flows in
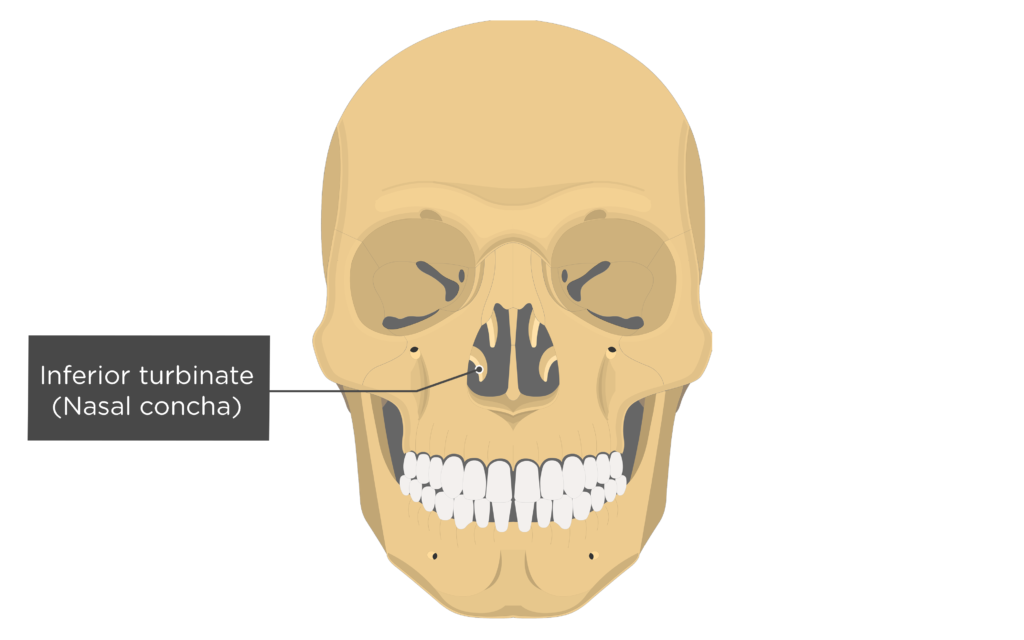
turbinates
covered in mucous membrane
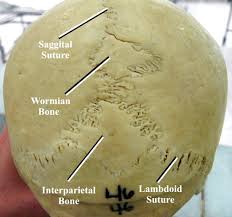
Wormian bones
tiny irregular bones within sutures of the skull
mastoiditis
ear infection then erodes into the bone then to the brain —> blood clots in the brain
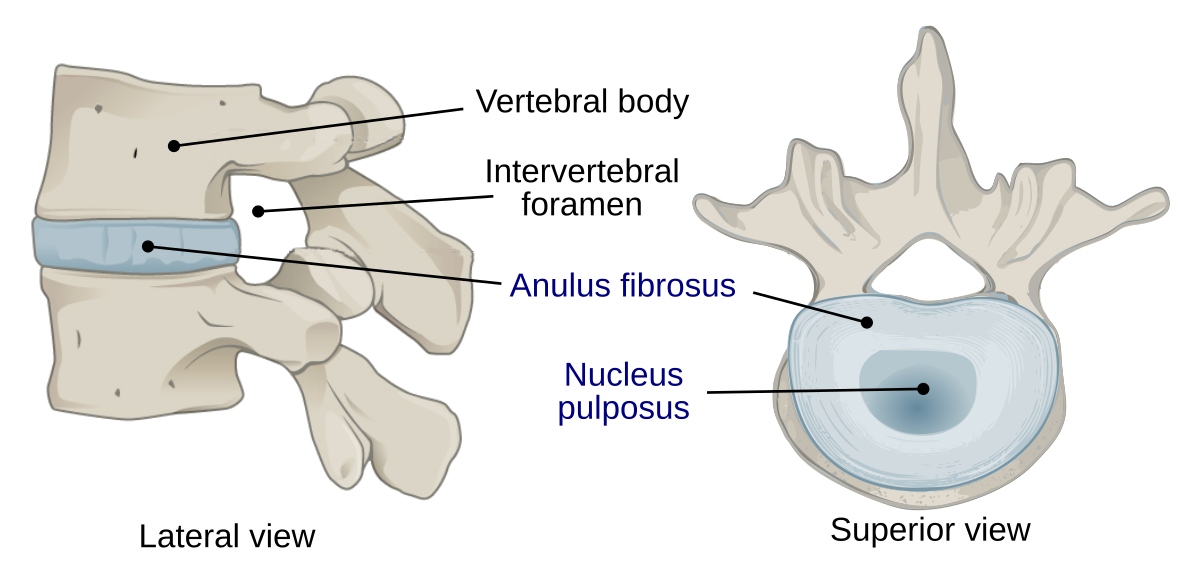
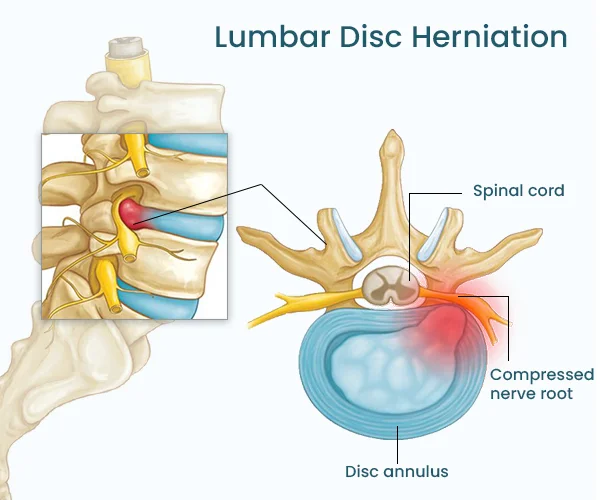
intervertebral disc
between 2 vertebrae
jelly center —> nucleus pulposus
surrounding ring —→ annulus fibrousus
herniated disc
ring tears and some of the nucleus pulposus protrudes onto the spinal cord
vertebral column
cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacrum, coccyx
Cervical vertebral column
has 7 vertebrae (C1-C7) “breakfast at 7”
C1
atlas - skull sits on
C2
axis - pump for atlas
What is the pump protruding out the axis for the atlas to sit on called?
odontoid process (dens)
Thoracic vertebral column
12 vertebrae T1-T12 “lunch at 12”
Lumbar vertebral column
5 vertebrae L1-L5 “dinner at 5”
Sacrum
5 fused vertebrae at the bottom of the spine
coccyx
3-5 fused vertebrae at the bottom of the sacrum “tailbone”
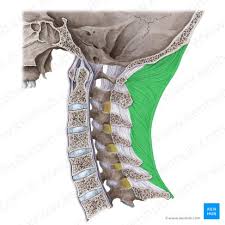
ligamentum nuchae
elastic ligament that attaches to the skull to the vertebrae
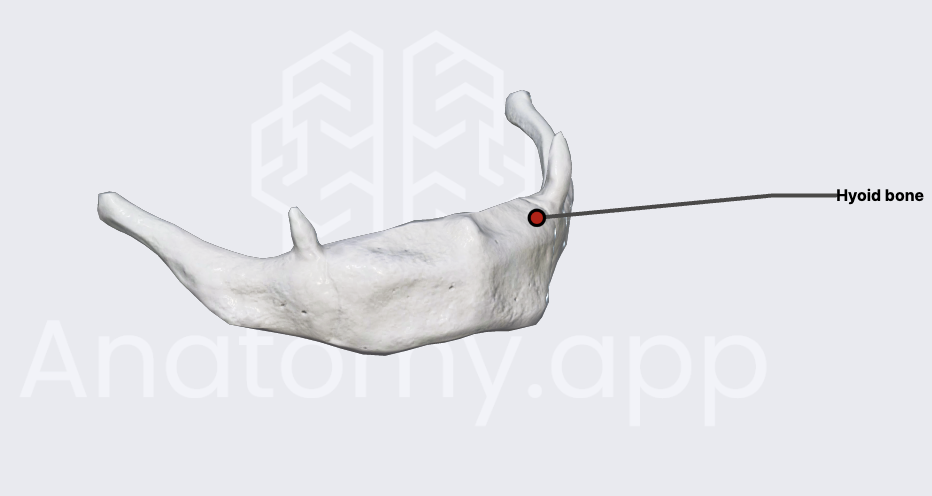
hyoid bone
attachment point for the tongue and neck muscles
only bone not directly attached to another bone
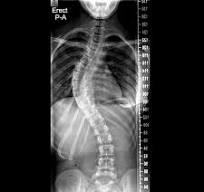
scoliosis
lateral curvature of the vertebral column
kyphosis
thoracic vertebrae curvature “hump back”
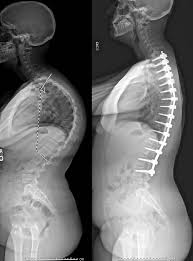
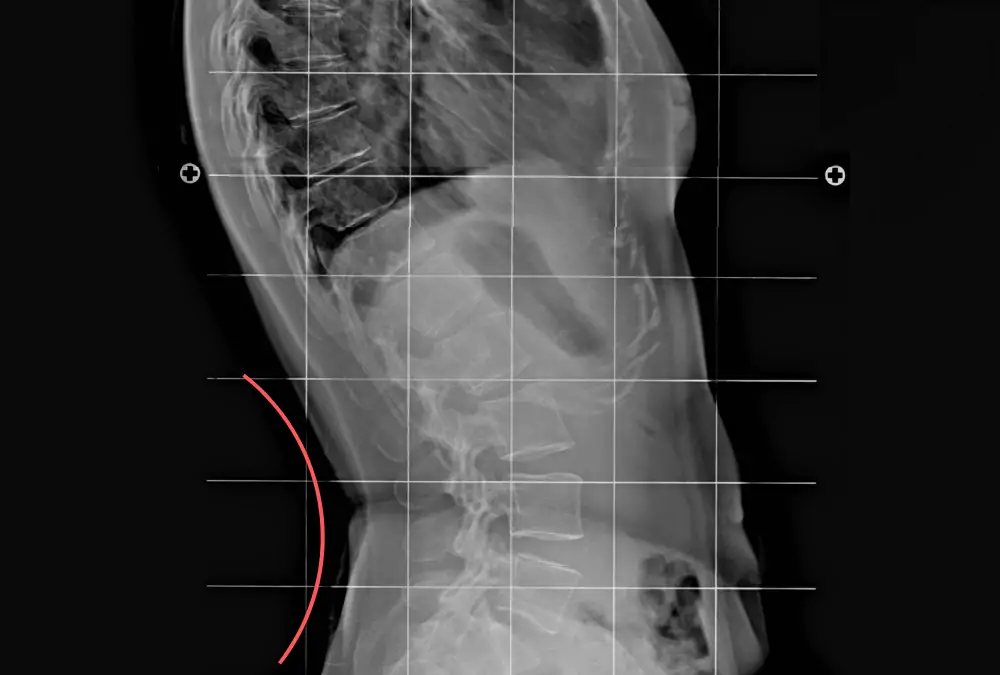
lordosis
lumbar curvature
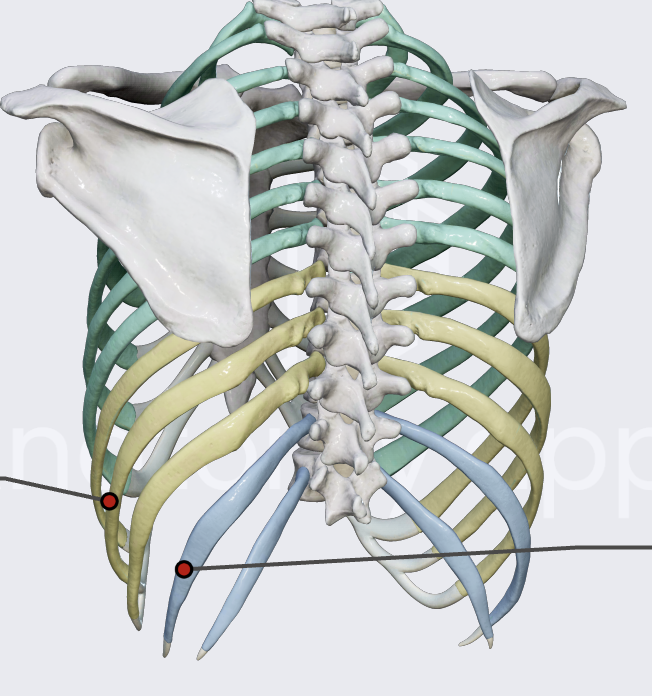
true ribs
connected directly to sternum (1-7)
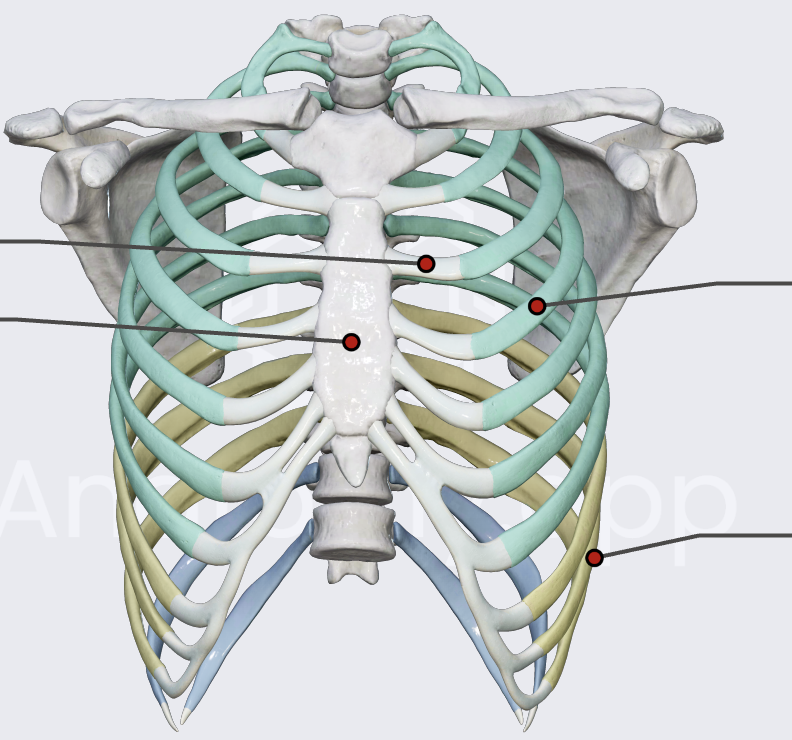
false ribs
connected to the last true rib through costal cartilage (8-10)
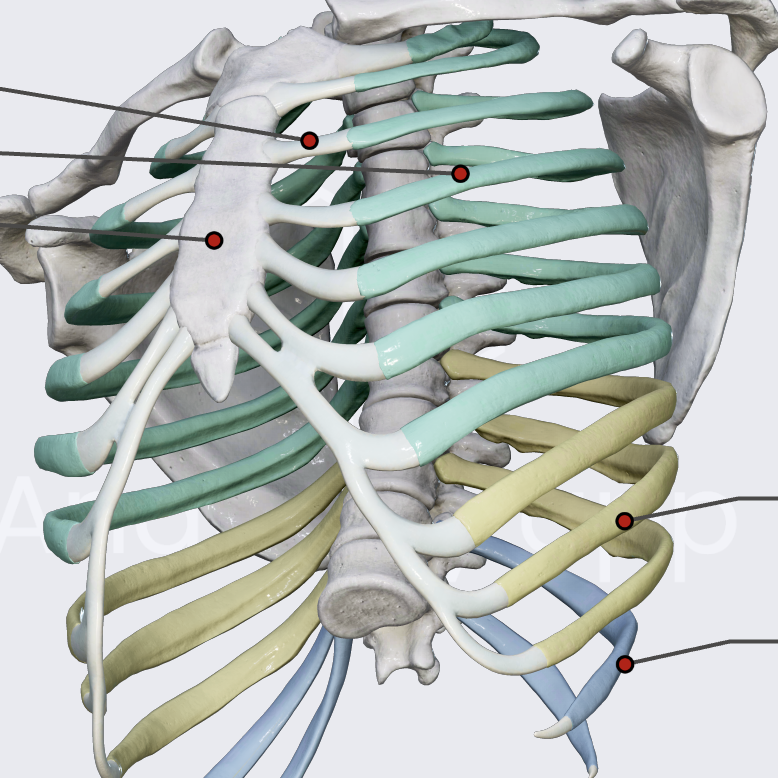
floating ribs
not connected at all (11 & 12)
breastbone
sternum
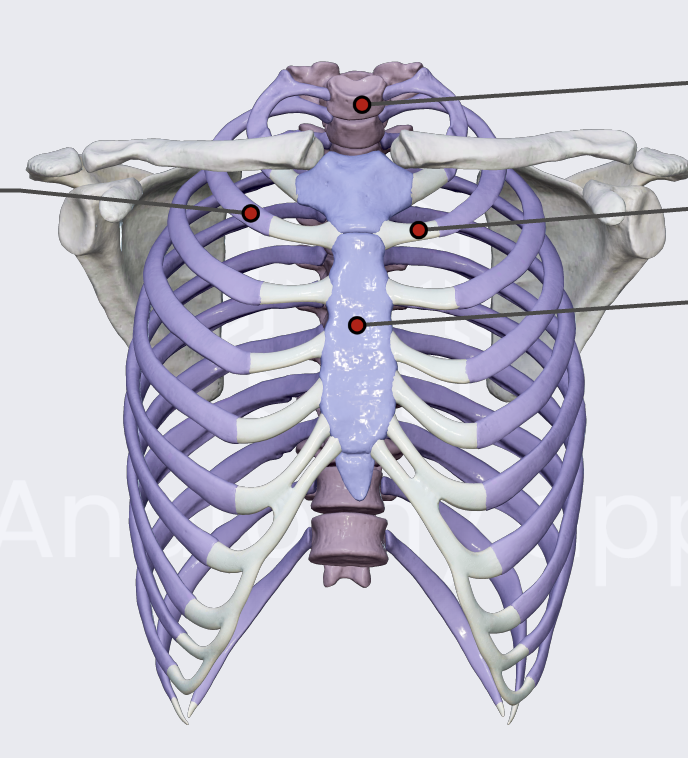
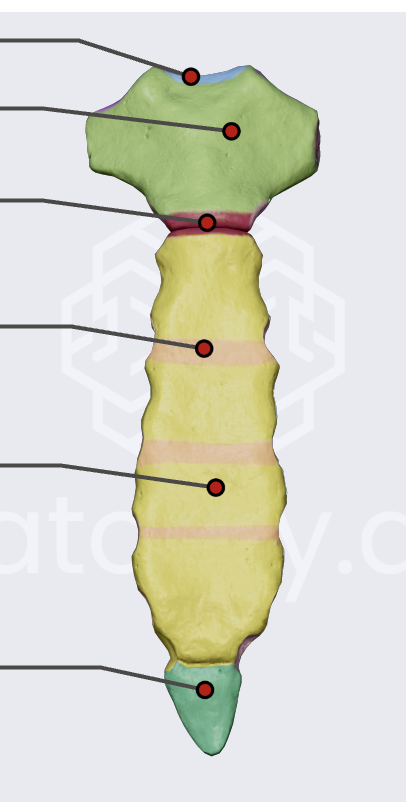
3 parts of the sternum
manubrium (top green)
body (yellow)
xiphoid process (bottom green)
collar bone
clavicle
what bone is commonly fractured?
the clavicle (collarbone)
shoulderblade
scapula
upper arm
humerus
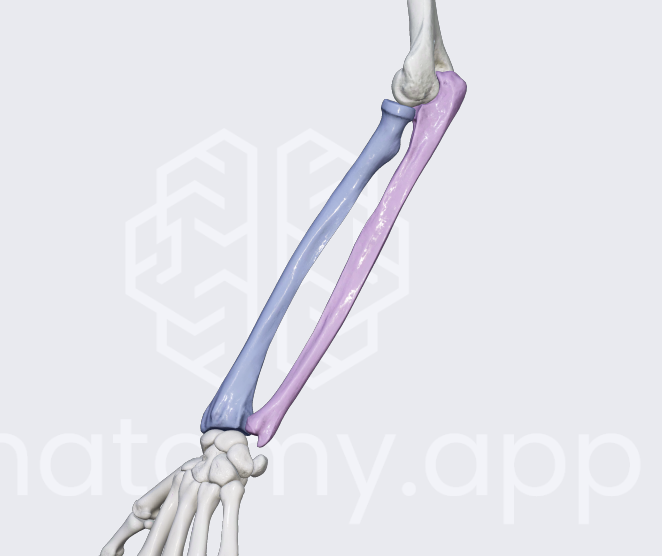
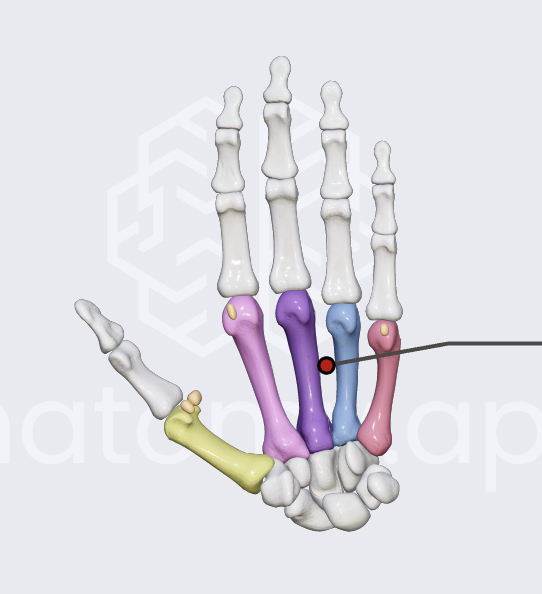
forearm bones
radius and ulna
radius
thumb side
ulna
pinkie side
membrane between ulna and radius
interosseous membrane
wrist
collectively —> carpals
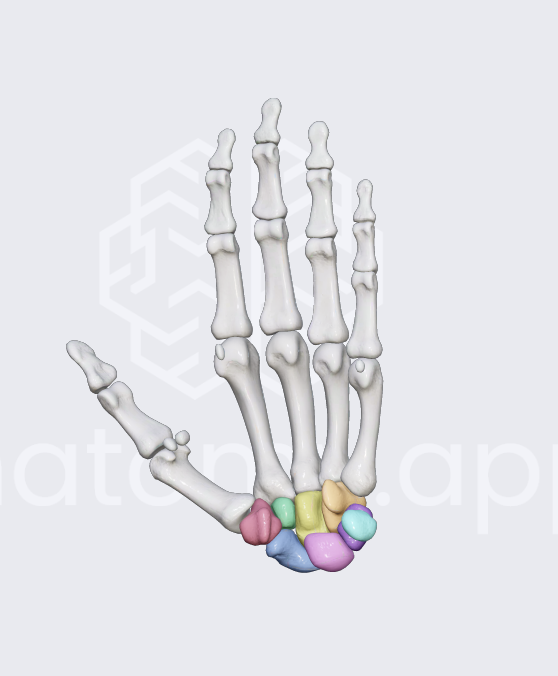
palm bones
metacarpals
fingers and toes
phalanges
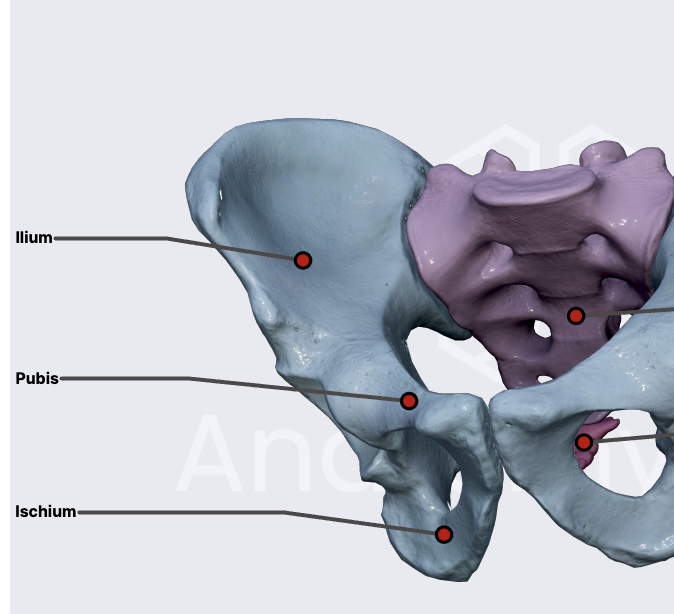
hip bone
pelvic
parts of the pelvic
ilium
pubic
ischium
thigh bone
femur
kneecap
patella
cartilage in between the pubic bones
pubic symphsis
shin bone(s)
tibia and fibula
tibia
bigger
for weight barring
fibula
smaller
stabilization for tibia
ankles
medial malleolus- bottom of the tibia
lateral malleolus- bottom of the fibula
what are the arches of the foot for?
distribute body weight and shock absorption
fontanels
soft parts of the newborn babys skull
fibrous membrane between skull bones
compression before birth
brain
anterior fontanel
takes 10 months to close
posterior fontanel
closed before birth
how many fontanels are on a unborn baby?
6 fontanels
bulging fontanel of a newborn
possible brain tumor
congenital defect
present at birth
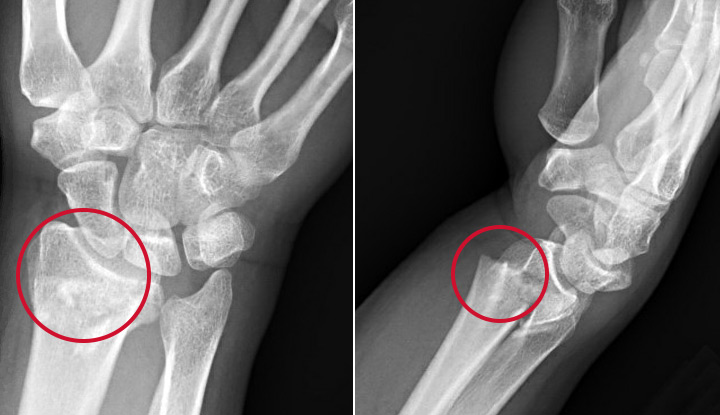
Colle’s fracture
break at the distal end of the radius
caused by catching yourself from a fall with hands stretched out
joints
where 2 or more bones meet
synarthrosis joints
immovable joints (in the skull)
amphiarthrosis joints
slightly movable joints (vertebrae and ribs)
diarthrosis joints
freely movable (elbow, knee etc)
fibrous joints
2 bones are connected with fibrous tissue and NO cavity between (sutures)
sutures
immovable joints of the skull bones
syndesmosis joints
connected by ligament/membrane
gomphosis joint
fibrous joint connecting tooth to the socket in the jawbone
cartilaginous joints
connect by a plate of hyaline cartilage
symphysis cartilaginous joint
connected by fibrocartilage
synovial
bone ends with cartilage and has a cavity between bones filled with synovial fluid which is inclosed by synovial membrane
gliding synovial joints
between the wrist bones
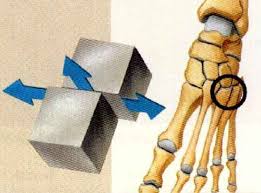
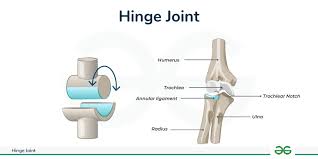
hinge synovial joints
at the elbow and knee
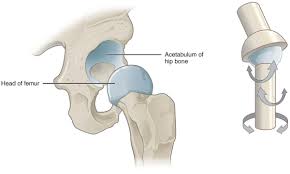
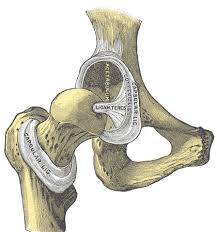
ball and socket synovial joints
hip and shoulder joints
ligaments
bone to bone
tendons
muscle to bone
bursae
flatten sack of fluid when friction occurs
tendon sheath
bursae that wraps around a tendon
collateral joint of the knee
each side of the knee (fibular and tibial)
cruciate ligament of the knee
cross over the center of the knee
ACL
anterior cruciate ligament of the knee
PCL
posterior cruciate of the knee
rotator cuff
the 4 muscles and their tendons to stabilize the shoulder
ligamentum teres
femur to the acetabulum of the pelvic
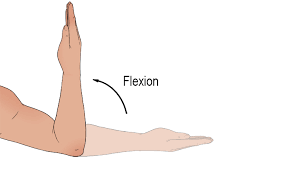
flexion
bend of the joint
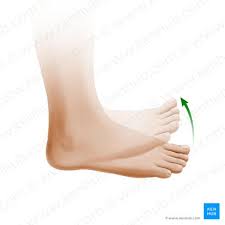
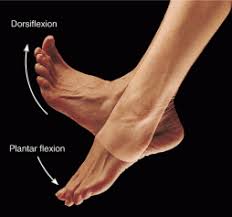
dorsiflexion
bending foot upwards
plantar flexion
bending foot down (gas pedal)
extension
straightening the joint
hyperextension
over extending
ABduction
moving away from the midline
ADduction
moving towards the midline
circumduction
forming circle in space
rotation
turning bone on its own axis
supination
palms of the hands UP
Pronation
Palms down (ulna and radius make an X)
Inversion
Bottom of foot inwards
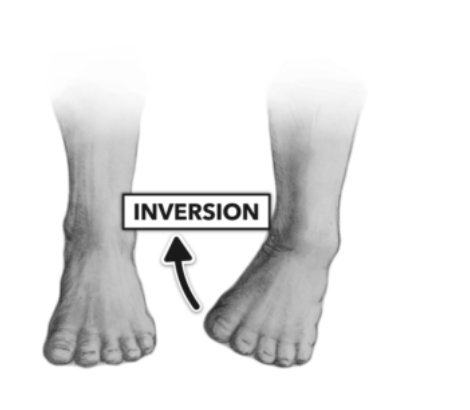
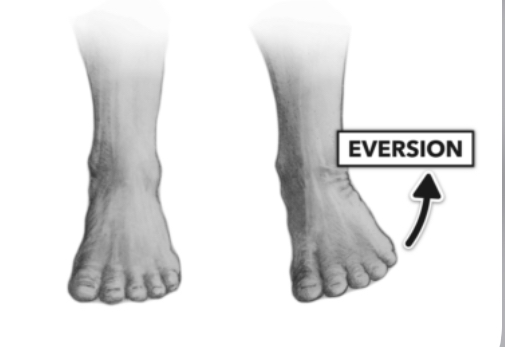
eversion
Turning foot outward
Sprain
Stretch or tear of a ligament