Physics w/Calculus 2 - Electric Potential, Capacitance, and Dielectrics (Ch 23-24)
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
A positive charge moves in the direction of an electric field. Which of the following statements are true?
A. The potential energy associated with the charge increases
B. The potential energy associated with the charge decreases
C. The electric field does not do any work on the charge
D. The amount of work done on the charge cannot be determined without additional information
E. The electric field does negative work on the charge
F. The electric field does positive work on the charge
B, D, F
A negative charge moves in the direction of an electric field. Which of the following statements are true?
A. The potential energy associated with the charge decreases
B. The electric field does not do any work on the charge
C. The amount of work done on the charge cannot be determined without additional information
D. The electric field does positive work on the charge
E. The potential energy associated with the charge increases
F. The electric field does negative work on the charge
C, E, F
A positive charge moves in a direction opposite to that of an electric field. What happens to the energy associated with the charge?
A. The electric potential energy of the charge decreases, and the kinetic energy increase
B. Both the electric potential energy and the kinetic energy of the charge increase
C. Both the electric potential energy and the kinetic energy of the charge decrease
D. The electric potential energy of the charge increases, and the kinetic energy decreases
D
A negative charge moves in a direction opposite to that of an electric field. What happens to the energy associated with the charge?
A. Both the electric potential energy and the kinetic energy of the charge decrease
B. The electric potential energy of the charge increases, and the kinetic energy decreases
C. The electric potential energy of the charge decreases, and the kinetic energy increase
D. Both the electric potential energy and the kinetic energy of the charge increase
C
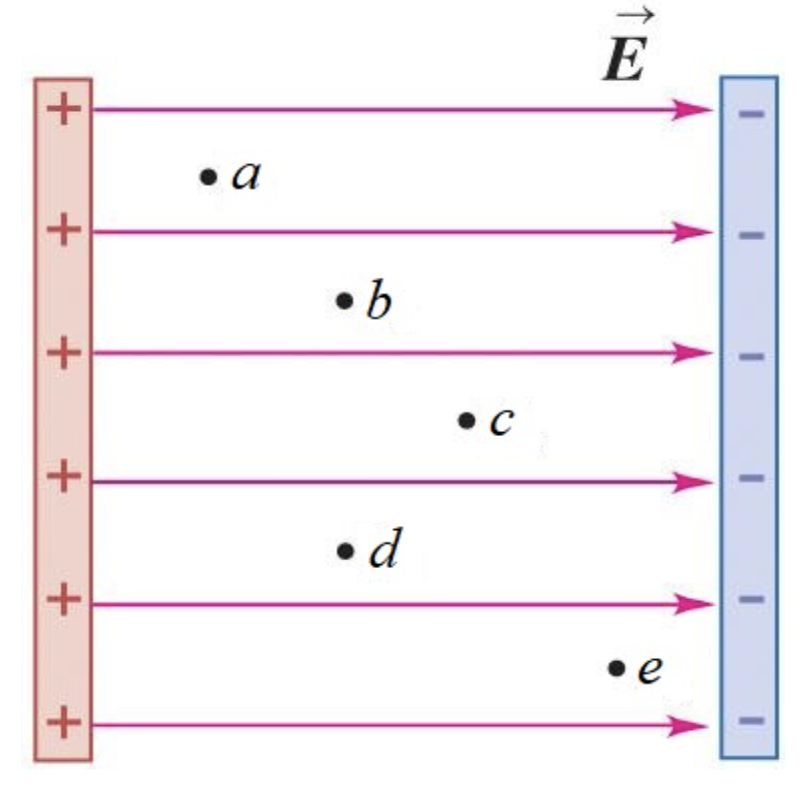
The figure below shows five locations in a uniform electric field. At which point is the electric potential is the largest?
Point a
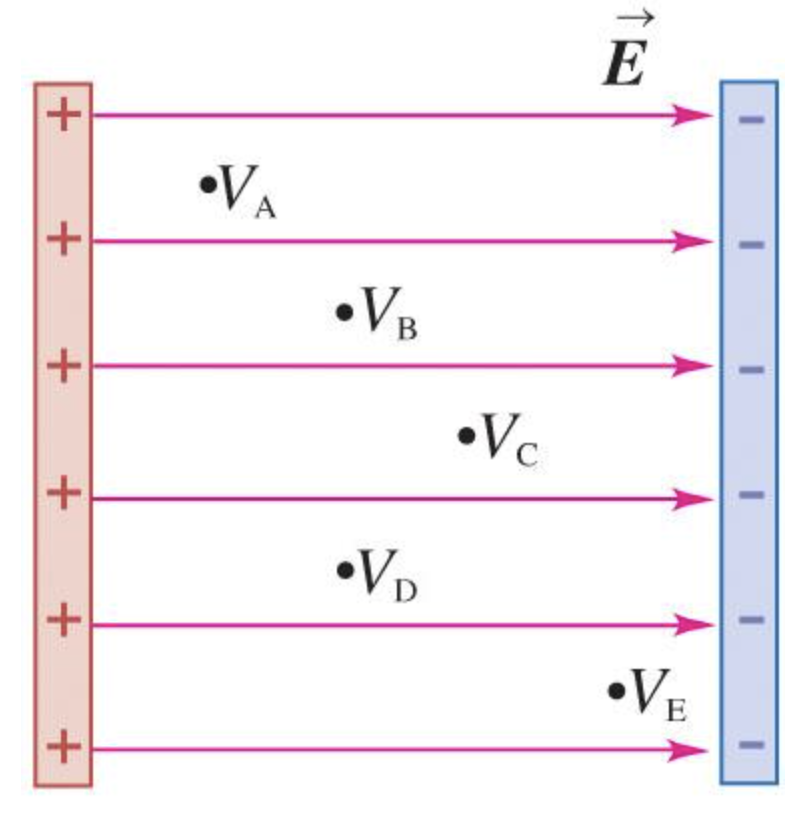
The figure shows the electric potential V at five locations in a uniform electric field. At which points is the electric potential equal?
VD, VB
The electric potential at a certain distance from a point charge can be represented by V. What is the value of the electric potential at twice the distance from the point charge
A. At twice the distance, the electric potential is 4V
B. At twice the distance, the electric potential is 2V
C. At twice the distance, the electric potential is V/4
D. At twice the distance, the electric potential is V/2
E. At twice the distance, the electric potential remains V
D
The electric potential at a certain location from a point charge can be represented by V. What is the value of the electric potential at the same location if the strength of the charge is tripled?
A. If you triple the value of the charge, the electric potential is 3V
B. If you triple the value of the charge, the electric potential is V/9
C. If you triple the value of the charge, the electric potential is V
D. If you triple the value of the charge, the electric potential is 9V
E. If you triple the value of the charge, the electric potential is V/3
A
A positive charge is moved from point A to point B along an equipotential surface. How much work is performed or required in moving the charge?
A. Work is both performed and required in moving the charge from point A to point B
B. No work is performed or required in moving the positive charge from point A to point B
C. Work is required in moving the positive charge from point A to point B
D. Work is performed in moving the positive charge from point A to point B
B
Which of the following statements are true?
A. The potential energy of a test charge increases as it moves along an equipotential surface
B. An equipotential surface is a three-dimensional surface on which the electric potential is the same at every point
C. The potential energy of a test charge decreases as it moves along an equipotential surface
D. When all charges are at rest, the surface of a conductor is always an equipotential surface
E. Electric field lines and equipotential surfaces are always mutually perpendicular
B, D, E
Which of the following statements are true?
A. A capacitor consists of a single sheet of a conducting material placed in contact with a insulating material
B. The capacitance of a capacitor depends upon its structure
C. A capacitor is a device that stores electric potential energy and electric charge
D. The electric field between the plates of a parallel-plate capacitor is uniform
B, C, D
Which of the following will increase the capacitance of a parallel-plate capacitor?
A. Decreasing the area of the plates will increase the capacitance a parallel-plate capacitor
B. Decreasing the separation between the plates will increase the capacitance of a parallel-plate capacitor
C. Increasing the area of the plates will increase the capacitance a parallel-plate capacitor
D. Increasing the separation between the plates will increase the capacitance of a parallel-plate capacitor
B, C
The plates of a parallel-plate capacitor are maintained with a constant voltage by a battery as they are pulled apart. How is the strength of the electric field affected during this process?
A. The strength of the electric field increases during this process
B. The electric field between the plates becomes infinite
C. The strength of the electric field remains constant
D. The strength of the electric field decreases during this process
E. The electric field between the plates becomes zero
D
The plates of a parallel-plate capacitor are maintained with a constant voltage by a battery as they are pushed together, without touching. How is the amount of charge on the plates affected during this process?
A. The amount of charge on the plates becomes zero
B. The amount of charge on the plates increases during this process
C. The amount of charge remains constant
D. The amount of charge on the plates decreases during this process
B
Consider two capacitors with unequal capacitance connected in series to a battery. Which of the following statements are true?
A. The equivalent capacitance of the combination of the two capacitors is less than the capacitance of either of the capacitors
B. The equivalent capacitance of the combination of the two capacitors is greater than the capacitance of either of the capacitors
C. The charge stored on each of the capacitors is the same
D. The algebraic sum of the voltages across the two capacitors is equal to the voltage supplied by the battery
E. The sum of the charges on each capacitor is equal to the charge supplied by the battery
F. The voltage across each of the capacitors is the same
A, C, D
Consider two capacitors with unequal capacitance connected in parallel to a battery. Which of the following statements are true?
A. The charge stored on each of the capacitors is the same
B. The equivalent capacitance of the combination is greater than the capacitance of either of the capacitors
C. The equivalent capacitance of the combination is less than the capacitance of either of the capacitors
D. The algebraic sum of the voltages across the two capacitors is equal to the voltage supplied by the battery
E. The sum of the charge stored on each capacitor is equal to the charge supplied by the battery
F. The voltage across each of the capacitors is the same
B, E, F
The voltage applied across a given parallel-plate capacitor is doubled. How is the energy stored in the capacitor affected?
A. The energy stored in the capacitor remains constant
B. The energy stored in the capacitor is decreased to one-half of its original value
C. The energy stored in the capacitor is decreased to one-fourth of its original value
D. The energy stored in the capacitor doubles its original value
E. The energy stored in the capacitor quadruples its original value
E
A parallel-plate capacitor connected to a battery becomes fully charged. After the capacitor from the battery is disconnected, the separation between the plates of the capacitor is doubled in such a way that no charge leaks off. How is the energy stored in the capacitor affected?
A. The energy stored in the capacitor doubles its original value
B. The energy stored in the capacitor is decreased to one-fourth of its original value
C. The energy stored in the capacitor quadruples its original value
D. The energy stored in the capacitor remains constant
E. The energy stored in the capacitor is decreased to one-half of its original value
A
Which of the following statements are true?
A. The insertion of a dielectric material between the two conductors in a capacitor allows the plates of the capacitor to be placed closer together without touching
B. Dielectrics allow electric charge to flow as easily as they do in air
C. The insertion of a dielectric material between the two conductors in a capacitor allows a higher voltage to be applied to the capacitor
D. After the space between the two conductors in a capacitor is filled with a dielectric material, the capacitance of the capacitor decreases
A, C
If a dielectric material, such as Teflon®, is placed between the plates of a parallel-plate capacitor without altering the structure of the capacitor, how is the capacitance affected?
A. The capacitance becomes zero after the insertion of the Teflon®
B. The capacitance increases because of the insertion of the Teflon®
C. The capacitance becomes infinite after the insertion of the Teflon®
D. The capacitance decreases because of the insertion of the Teflon®
E. The capacitance is not altered, because geometry of the capacitor remains unchanged
B
A dielectric material, such as Teflon®, is placed between the plates of a parallel-plate capacitor without altering the structure of the capacitor. The charge on the capacitor is held fixed. How is the voltage across the plates of the capacitor affected?
A. The voltage increases because of the insertion of the Teflon®
B. The voltage decreases because of the insertion of the Teflon®
C. The voltage is not altered, because the structure remains unchanged
D. The voltage becomes zero after the insertion of the Teflon®
E. The voltage becomes infinite because of the insertion of the Teflon®
B
A dielectric material, such as Teflon®, is placed between the plates of a parallel-plate capacitor without altering the structure of the capacitor. The charge on the capacitor is held fixed. How is the electric field between the plates of the capacitor affected?
A. The electric field becomes infinite because of the insertion of the Teflon®
B. The electric field decreases because of the insertion of the Teflon®
C. The electric field increases because of the insertion of the Teflon®
D. The electric field becomes zero after the insertion of the Teflon®
E. The electric field is not altered, because the structure remains unchanged
B