The judiciary
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
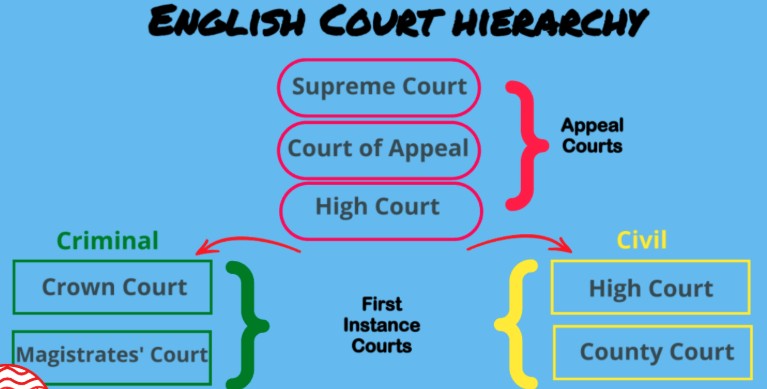
English court hierachy
Inferior judges
They sit in courts below the high court. Includes cicuit judges, recorders and district judges.
Circuit judges
They sit in the crown court and county court. For criminal law: they hear criminal trials (sit with a jury). They decide law and sentence if found guilty.
For civil law: they hear fast track cases between £10,000-£25,000.
Recorder judges
They sit in the crown court. They are part-time practising solicitors and barristers. They hear criminal trials (sit with a jury). They decide law and sentence if found guilty.
District judges
They sit in the magistrates’ court and county court. For criminal law: they try criminal cases (they sit alone). They decide facts and law, and decide sentence if found guilty.
For civil law: they sit in the county court. They hear small- claims track cases up to £10,000.
Superior judges
Includes justices of the Supreme Court, senior judges and high court judges.
Justices of the Supreme Court
They sit in the top court in the country (Supreme Court). They hear only appeals on points of law of great importance. Any decision becomes precedent. They must sit as an uneven panel (minimum 3) to hear a case. Usually sit as a panel of 5.
Senior judges
Sit in the court of appeal - the only hear appeals. Usually sit as a panel of 3. Decisions on points of law become precedents which the lower courts must follow.
High court judges
Sit in the crown and high court. For the crown court: they hear criminal trials (sit with a jury). It’s usually only the most serious criminal cases (e.g. murder). They decide law and sentence if guilty.
For high court: they hear criminal appeals (law only) from the Magistrates’ court. They sit in a panel of 2.