Chapter 11: Stockholders' Equity
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/65
Last updated 2:32 AM on 12/10/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
1
New cards
Simple to become an owner.
Ownership can be transferred.
Limited liability.
Ownership can be transferred.
Limited liability.
Advantages of corporate ownership:
2
New cards
separate legal entity
Because a corporation is a ________, it can own assets, incur liabilities, sue/be sued, and be entered into contracts.
3
New cards
articles of incorporation
You must submit an application to the state government to create a corporation. When a corporation is approved, the issues the ________, which holds information about the company.
4
New cards
Stockholder benefits
Voting rights, dividends, residual claims, and preemptive rights are all.....
5
New cards
Voting rights
________ let stockholders vote on important issues.
6
New cards
dividends
Stockholders have the right to receive ________ when declared by the board of directors.
7
New cards
liquidation rights
Residual claims are also known as ________.
8
New cards
Residual claims
________ say that if a corporation goes bankrupt, stockholders share any remaining assets after creditors are paid.
9
New cards
Preemptive rights
________ means that existing stockholders have the first chance to purchase newly issued stock before it is issued to the public.
10
New cards
Equity financing
________ is issuing new stock to investors.
11
New cards
Debt financing
________ is borrowing money from lenders.
12
New cards
advantages of equity financing
Equity does not have to be repaid and dividends are optional are both _________.
13
New cards
advantages of debt financing
Interest on debt is tax deductible and debt does not change shareholder control are both examples of ________.
14
New cards
Contributed capital
Retained earnings
Treasury stock
Accumulated other comprehensive income or loss
Retained earnings
Treasury stock
Accumulated other comprehensive income or loss
The four elements of stockholders' equity:
15
New cards
Common Stock and Additional Paid in Capital
Contributed capital consists of ________.
16
New cards
Additional Paid in Capital
APIC stands for ________. It is the amount collected over par.
17
New cards
Contributed capital
________ is what capital the company receives from investors when they sell stock to them.
18
New cards
Retained earnings
________ represents earned capital.
19
New cards
Treasury stock
________ consists of shares that were issued, but the company bought back. It is a permanent, contra account to Common Stock/APIC with a debit balance and reduces stockholders' equity.
20
New cards
Accumulated other comprehensive income or loss
Recorded unrealized gains and losses that cause temporary changes in the value of assets and liabilities of the company.
21
New cards
authorized shares
The max number of shares that can be issued are called ________.
22
New cards
Issued shares
________ are permanently for the stockholder unless they sell them for another company or they are bought back.
23
New cards
Unissued shares
________ are shares that have not been traded.
24
New cards
Outstanding shares
________ are owned by stockholders.
25
New cards
can't get dividends
Outstanding shares are the only shares that ________.
26
New cards
Par value
________ is assigned to each share of stock that is authorized. Usually is a small number ($0.03). Some state require it.
27
New cards
market price
Par value is not the same as _________, which is the value of what shares can sell for to the public.
28
New cards
No-par value stock
________ does not have a determined price.
29
New cards
no APIC
If they is no par in the equation, there is ________.
30
New cards
initial public offering (IPO)
The first time a corporation's stock is available
31
New cards
seasoned new issue
When new stock is issued to the public, this is called ________.
32
New cards
Debit Cash
Credit Common Stock
Credit Additional Paid in Capital
Credit Common Stock
Credit Additional Paid in Capital
The journal entry for issuing stock at par value.
33
New cards
journal entry
A corporation not need a ________ when there is an interaction between two investors.
34
New cards
purpose of repurchases
The ________ can include making a company believe the stock is worth getting, buying back shares to reissue them at a higher price, buying back shares to reissue them to employees, and lastly to reduce the number of outstanding shares.
35
New cards
cost
When issued shares are bought back, it is recorded at ________.
36
New cards
no voting or dividend rights
Treasury stock has no _______.
37
New cards
Stock transactions
_________ are only found on the balance sheet.
38
New cards
Debit Treasury Stock
Credit Cash
Credit Cash
Journal entry for reacquiring stock:
39
New cards
Debit Cash
Credit Treasury Stock
Credit APIC
Credit Treasury Stock
Credit APIC
Journal entry for reissued stock:
40
New cards
gains or losses
Stock transactions never generate ________.
41
New cards
growth investment
________ is buying stock that pay a small amount of dividends or no dividends at all.
42
New cards
Income investments
________ are from common stock that do pay dividends.
43
New cards
retained earnings and cash
Before a dividend is declared, a company must have enough ________.
44
New cards
Declared by a board of directors
Not legally required.
Liabilities once declared.
Not an expense.
Not legally required.
Liabilities once declared.
Not an expense.
Dividends are.....
45
New cards
declaration date
The ________ is the day when the Board of Directors decide to issue a cash dividend and the liability is established.
46
New cards
Debit Dividends
Credit Dividends Payable
Credit Dividends Payable
The journal entry for the declaration of a dividend.
47
New cards
date of record
The ________ is an administrative responsibility, so there is no journal entry.
48
New cards
date of payment
The ________ reduces the liability and cash.
49
New cards
Debit Dividends Payable
Credit Cash
Credit Cash
The journal entry for the date of payment:
50
New cards
year end
The ________ is when the temporary accounts are closed to Retained Earnings.
51
New cards
Debit Retained Earnings
Credit Dividends
Credit Dividends
The journal entry for year end/closing accounts:
52
New cards

\
Equation to calculate Outstanding shares:
53
New cards
Preferred stock
________ is given to a special group of investors, but can be bought back.
54
New cards
Redemption
________ means the preferred stock is retired, which results in the issuance being reversed.
55
New cards
Debit Preferred Stock
Debit APIC
Credit Cash
Debit APIC
Credit Cash
Journal entry for redemption:
56
New cards
current dividend preference
A ________ states that preferred dividends must be paid before paying dividends to stockholders.
57
New cards
cumulative dividend preference
A ________ states if a current dividend is not paid yet, the unpaid amount amount has to be paid before other common dividends.
58
New cards
Dividends in arrears
________ regard cumulative preferred stock that has not been paid yet. They are not on the balance sheet.
59
New cards
Retained Earnings
________ are the collective earnings of a company.
60
New cards
accumulated deficit
The negative balance of Retained Earnings is called ________.
61
New cards
Earnings Per Share (EPS)
________ provides information on the profit earned from common stock that is outstanding.
62
New cards

\
Equation for calculating Earnings Per Share:
63
New cards
Return on Equity (ROE)
________ reports a company's return to stockholders.
64
New cards

\
Equation for calculating Return on Equity:
65
New cards
Price/Earnings (P/E) Ratio
The ________ is a measure of the value that investors place on a company's common stock. A higher ratio predicts strong future performances.
66
New cards
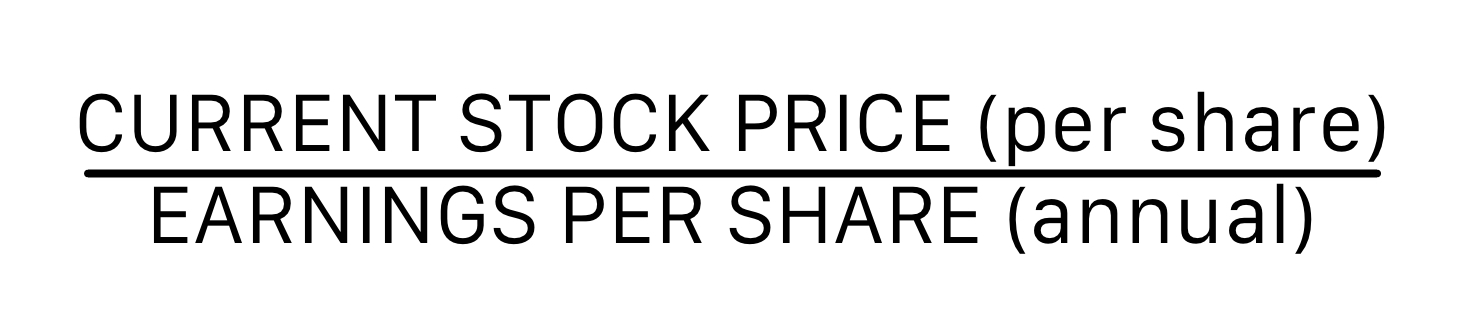
\
Equation for calculating the Price/Earnings Ratio: