APP Exam 2
1/86
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
What are some ways of meeting each standard that patients use to evaluate services?
(Basically—- what can we do to meet the standard of good care)
(Ex: the standard is “fairness”, to meet that standard or be FAIR we can treat customers in the order they arrive to the pharmacy)
responsiveness (give prompt service)
assurance (be knowledgeable)
empathy (be caring)
friendliness (be polite)
RELIABILITY- receive the promised service dependably and accurately. also accurate prescription filling and patient counseling
A service failure is when you fail to meet the expectations of a patient. In order to recover from a service failure, you choose a service ____________ effort and they are classified as low, mid, or high criticality. FYI
recovery
What are the specific service recovery efforts for low-mid, and high criticality?
low- and mid-criticality— Apology, Empathy, Follow-Up, Discount/Refund, Sincerity
HIGH-CRITICALITY— Attempt to compensate for costs related to time, money, and inconvenience through financial settlements
Identify ways to develop pharmacy staff members to provide good customer service?
hire employees with a caring, attitude, empower, support, encourage, and model
ensure employees quality of work life and job satisfaction, make customer service EVERYBODY’s job
List in order the recommended steps for dealing with “difficult patients”
Let the customer VENT
avoid getting trapped in a negative filter
express empathy to pt.
begin active problem solving
mutually agree on a solution
follow-UP
What is sensemaking?
a cognitive process that occurs before using an EDM to help make sense of a difficult situation
(basically: identify/evaluate a problem prior to EDM)
3 steps of sensemaking:
Learn
Plan
Act
List the 5 different types of Ethical Decision-Making Models.
Markula Center Framework
PLUS model
Rationalist Model
Non-Rationalist Model
Integrated Model
Describe the following EDM model:
Markula Center Framework
provides specific examples of what ethics is not (feelings, religion, abiding by laws, following norms/scientific data)
aimed towards making decisions as an INDIVIDUAL
Utilizes classic philosophical perspectives to evaluate potential solutions
Utilitarianism, Rights-based, Justice-based, common good, virtue-based
Describe the following EDM model:
PLUS Model
provides context for making decisions within ORGANIZATIONS
Utilizes ethical “filters” rather than classic philosophical perspectives
policies, legal, universal, self
Describe the following EDM model:
Rationalist Model
ability to reason ethically is dependent on COGNITIVE DEVELOPEMENT STAGE
REASONING THAN JUDGEMENT
Describe the following EDM model:
Non-Rationalist Model
JUDGEMENT THAN REASONING
PRACTICE:
Does the rationalist or non-rationalist use reasoning before judgement?
rationalist
Describe the following EDM model:
Integrated Model
integrates rationalist and non-rationalist approaches
2 key components:
EDM process follows similar stepwise approach to Markula and PLUS model
Recognizes MODERATING FACTORS can influence process —> issue, organization, personal factors
What are the benefits of feedback?
reinforce good performance
poor performance corrected
provides steps for improvement
encourage self-reflection
What are some components of effective feedback? (pretty much common sense)
provide in a private area
timely, regular, specific, descriptive
focus on BEHAVIORS not TRAITS
limit info provided
receive input for others
provide steps for improvement
limit info to 2-3 behaviors at a time
What is the difference between feedback and evaluation?
feedback- more frequent and informal. asseses a specific task/skill
evaluation- more reflective of overall performance, judgement of achievement of goals
What are 3 approaches to giving feedback? (just the names)
sandwich approach
Pendleton 4-step method
ARCH Model
What is the “sandwich method” for providing feedback?
it’s like a “sandwich”
positive feedback, then negative, then positive
softens blow of corrective feedback (possible downside)
What is the “Pendleton 4-step method” for providing feedback?
2-sided discussion that DOES NOT INCLUDE steps for improvement
FYI ———How it works:
What learner feels they’re doing well
What manager thinks they’re doing well
What learner feels they need to improve
What manager thinks they need to improve
What is the “ARCH Model” for providing feedback?
2-sided discussion that DOES INCLUDE steps for improvement/ improvement plan
may take extra time
Asking questions to a person being evaluated to assist them in self-reflection is the definition of…
facilitative questioning
What are the 2 types of negotiating?
principal- goal of solving problem in a way that is mutually beneficial/agreeable to both sides—- (looking for a win-win scenario)—— 4 aspects: people, interests, options, and criterea
positional- GOAL OF WINNING! GOAL OF CONVINCING THEM TO CONVERT TO YOUR POINT OF VIEW
For principled negotiations what is key?
communication and listening skills
What does BATNA stand for? What does it mean?
BATNA- Best alternative to negotiated agreement
basically the “bottom line”
if you have having a negotiation and can’t agree, the BATNA is the best option
How do you approach a tense situation?
reassure
mirror
empathize
employ labeling
slow down
What are the 3 types of negotiators? Briefly describe each.
Analytical- methodical will want to analyze info deeply before agreeement
Accommodator- values relationship> everything, may agree to less reasonable solutions if it keeps people happy
Assertive- values time, wants quick resolution, self-focused
Deception, extreme offers, arbitrary deadlines (fake deadline to rush you), personal attacks, ambiguous authority, good cop/bad cop are all examples of….
dirty tricks
Motivational Interviewing is useful to help strengthen what?
another party’s commitment to a new idea/option
What mnemonic is used for Motivational interviewing?
DARN-CAT
What does DARN-CAT stand for?
DARN- prep talk to assess readiness
Desire, Ability, Reasoning, Need
CAT- action
Commitment, Activation, Taking steps

What some example of leadership theories? FYI
trait theories
behavioral theories
situational theories
(Dr. Z has a test question on each of these)
The trait theory says that what personality characteristics could distinguish leaders from non-leaders?
extroversion
agreeableness
emotional stability
high energy/self confidence
others: conscientiousness, openness
DESCRIBE the LAISSEZ-FAIRE behavioral theory:
THINK: EMPLOYEEEEEEE
laissez-faire leaders allow employees to have complete autonomy, set their own goals, and work toward them without interrupting
EX: A LAISSEZ-FAIRE LEADER WOULD NOT MENTION A NEW IDEA UNLESS THE EMPLOYEES CAME TO HIM WITH IT AND THE LEADER WOULD THEN ALLOW THE EMPLOYEES TO DEVELOP THE ENTIRE PROGRAM AND IMPLEMENT THE PLAN
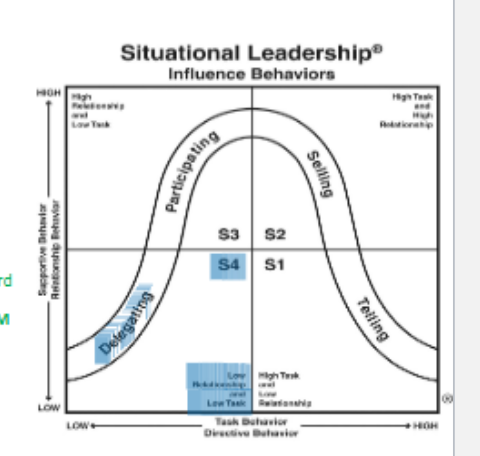
From this chart, what does the blue highlighted box mean in terms of the behavior of the leader?
leader turns over ALL DECISIONS AND RESPONSIBILITIES for completing tasks, reaching goals, and follower implementation.
“delegating”
leader MAY BE AVAILABLE FOR CONSULATION, but usually maintains low profile
THINK: HANDS OFF, IMMA JUST WATCH and if you need me I’m here
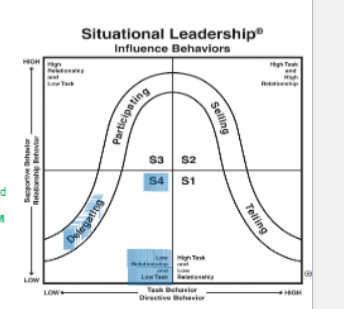
For this chart, “delegation” or S4 has what type of followers?
R4 or HIGH
they are ABLE, WILLING, and CONFIDENT
What are the 4 components of the situational leadership model?
TASK ORIENTATION BEHAVIOR
RELATIONSHIP ORIENTATION BEHAVIOR
FOLLOWER READINESS OR MATURITY
LEADER EFFECTIVENESS
(task and relationship oriented, mature followers, effective leader)
What is the definition of:
asset
financing
liabilities
owner’s equity
capital
liquidity
fiscal year
Definitions:
o Asset – things that are owned that can be used to generate income
o Financing – money needed to acquire assets
o Liabilities – money owed to others
o Owner’s equity – owner’s funds
o Capital – money used to acquire land, buildings, and equipment
o Liquidity – how much cash is currently on hand to pay bills, etc.
o Fiscal Year – unit of time (1 year) that businesses use to record financial interactions
Not always the same as the calendar year
What is accrual vs. cash accounting?
accrual—> revenue/expenses tallied when they are incurred
ex: If you provide a service in December but receive payment in January, you record the revenue in December. (AKA WHEN IT OCCURED)
cash—> revenue/expenses tallied when they are paid
ex: If you receive a payment in January for a service provided in December, you record the revenue in January. (AKA WHEN YOU WERE PAID)
What’s the difference between capitation and per diem?
capitation- fixed amount received per patient per month/year
per diem- payment received at a daily rate
(think: per diem= per day aka you receive money at a daily rate)
What’s the difference between “value-based payments” and “fee for service”?
“value-based payments”- reimbursement rate based on QUALITY OF CARE received
most patient/positive outcome focused
“fee for service”- payment based on NUMBER OF visits/tests/services received
more focused on numbers> care
What is a vertical healthcare system?
organization with group of related, but not identical providers
ex: a healthcare system that includes PCPs, specialists, hospitals, rehab centers, and nursing homes. like LECOM with all it’s dif buildings
What is a horizontal healthcare system?
organization with group of similar providers
ex: several hospital/clinics joining together
What are the 4 C’s of finance?
(said not to worry about in review)
COST measurement/minimization
CASH management/sufficiency
CAPITAL access/acquistion
CONTROL of resources
Sole proprietorship vs. Partnership vs. Corporation
sole-proprietorship: individual owning business
partnership: multiple individuals owning a business
corporation: legal entity separate from owners/shareholders
What type of business organization protects owners/shareholders from liability?
corporation
What are a couple types of hybrid business organizations?
limited partnership (LP)- like partnership but limited partners only liable for initial investment
limited liability partnership (LLP)- partners only liable for their own malpractice
limited liability company (LLC)- similar liability to stockholders, taxed like partners
professional cooperation/association (PC/PA)- includes benefits of incorporation but still liable for malpractice
What is a snapshot of an organization’s assets, liabilities, and shareholder equity at a point in time?
balance sheet
What provides info about income/expenses over a given time period?
income statement
What records inflow/outflow of cash?
statement of cash flows
How do you calculate gross profit margin?
gross profit margin= (total sales- cost of goods sold) / total sales
How do you calculate net profit margin?
net profit margin= net income after tax/ total sales
How do you calculate current ratio?
current ratio= current assets / current liabilities
(current assets= cash, accounts, inventories)
For a current ratio what is considered low and high?
<2 = low assets/ too risky
>5 = high assets/ too conservative
How do you calculate quick ratio?
quick ratio= quick assets/ current liabilities
(quick assets= cash, accounts, NOT INVENTORY)
A quick ratio goal is >_____.
>1
How is ITOR calculated?
ITOR= cost of goods sold/ average inventory
A formal budget system is used in order to…
in order to create a plan so that actual results can be compared to that plan
What is the role of budgeting?
planning
improves communication
allocates resources
controls profit/operations
evaluate performance—> provide incentives
What are some types of budgeting?
master budget
budgeted financial statements
others: capital budget, financial budget, rolling budget, operational budget, cash receipts budget
What is a master budget?
“profit plan”
comprehensive set of budgets covering all phases of an organizations operations for a specified time period
What are budgeted financial statements?
“pro forma financial statements”
shows how the organization’s financial statements will appear at a specified time
includes budgeted balance sheet, income statement, cash flow statement
What are some factors looked at when “sales forecasting”?
historical report (past sales, trends etc.)
economic trends
legal events
promotions
market research
What are operational budgets?
how operations will be carried out to meet demand for goods/services
includes: material, labor, overhead
What are 3 types of financial budgets?
Cash Receipts Budget- info about cash flows into pharmacy based on sales
Cash Disbursements Budget- info about cash flow out of pharmacy
Cash Budget- summary of inflow/outflow of cash from operations
What does the following describe:
Manufacturers—> Distributors—> Provider—> Patient
pharmaceutical supply chain
Padding the budget or budgetary slack is a possible ________________ behavioral implication of budgets.
a. positive
b. negative
b
What is the goal of demand planning? What does the demand forecast reflect?
Goal: produce a reliable projection of future customer demand—a forecast for the items that a pharmacy expects to dispense to pts./sell to customer
(basically: how much demand for each product is expected)
Inventory management deals with controlling inventory/stock and the goal is what?
to keep minimum stock necessary to fulfill need/demand without selling out
What are 3 methods of inventory management?
visual method- look at the # of units in inventory and compare them with a listing of how many should be carried
periodic method- requires counting stock on hand at predetermined interval and comparing w/ minimum desired levels
perpetual method- inventory monitored at all times—> computerized—> may need to be checked by counting stock at predetermined intervals to ensure accuracy
Procurement refers to sourcing and purchasing and that means you have to identify/manage ___________ and place ______________.
suppliers, orders
What are some costs associated with inventory?
Acquistion
procurement
carrying
stock-out costs
What is ITOR stand for? How is it calculated? Is a high or low ITOR preferred?
Stands for Inventory Turn Over Ratio
ITOR= cost of goods sold/ average inventory value
HIGH ITOR preferred
List and describe the 5-steps in Pharmacist Patient Care Process (PPCP):
Overview: Collect, Assess, Plan, Implement, Follow-Up: Monitor and Evaluate
Collect- get pts medical history (medications, lab data, physical, social history, habits, etc.)
Assess- use the info from the collect stage to make decisions regarding the patient’s current therapy
Plan- individualized plan for the pt. that addresses their problems and sets goals
Implement- put the plan in action w/ the PCP, nurses, and other providers
Follow-Up: Monitor and Evaluate- watch the pts progress toward therapeutic goals and follow up with providers
Appropriate collaboration, communication, and documentation should occur at what step of the PPCP?
EACH STEP!
Explain the role of the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments of 1988 (CLIA) Waiver:
pharmacies implementing monitoring/screening services utilizing devices that measure specimens need to apply for a CLIA Waiver
CLIA waived tests are considered by the CDC and FDA to be simple to administer and have little risk of error
Pharmacists providing tests —> agree to follow good lab practices
Makes pharmacists be knowledgeable about OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Act)
Explain the role of the Collaborative Practice Agreements (CPAs) in pharmacy based services:
should be developed to help guide the pharmacists therapeutic decisions
must be evidence-based and supported by national guidelines and the primary literature
physicians and pharmacists must all sign the CPA, and a copy should be kept at the pharmacy and physician’s practice
Describe the ECHO Model of Outcomes and its 3 outcome measurements of focus:
ECONOMIC (health care spending)
CLINICAL (therapeutic targets and goals)
HUMANISTIC (patient satisfaction)
(Think: ECHO, the first 3 letters stand for each outcome )
Identify 3 strategies used to provide ongoing monitoring to ensure program quality and success:
Scheduled staff meetings-
Monitor Service Outcomes
Request Feedback
The 3 strategies used to provide ongoing service monitoring are _________________ QUALITY IMPROVEMENT STRATEGIES.
CONTINUOUS
What services do PBMs offer?
establish networks as part of their claims management services
rebate negotiations with manufacturers
drug benefit (formulary) design
formulary management
drug utilization management
disease state/ case management
most offer mail order services
What are networks/preferred networks and how do pharmacies participate?
What is a network? a group of pharmacies that a PBM contacts with to provide meds and care at lower copays
To join? MUST accept the third party’s reimbursement rate
What percentage of claims go through PBMs? What impact has that shift had on pharmacies?
86% of all claims. This has had a significant impact on pharmacy management by decreasing the FLEXIBILITY that pharmacies had on PRICING THEIR MEDICATIONS.
How do PBMs reimburse pharmacies?
2 parts: product cost and dispensing fee
total reimbursement rate= product cost + DF
What do each of the following 3rd party reimbursement terms mean?
AWP
AAC
WAC
MAC
AWP- average wholesaler price- a list price for what drug wholesalers charge pharmacies. This is an overestimate of what the wholesaler actually charges.
AAC- actual Acquistion cost- the price the pharmacy pays the drug wholesaler or manufacturer to obtain the drug product
WAC- wholesaler Acquistion cost- a list price for what pharm manufacturers charge drug wholesalers. this is an overestimate of what manufacturers actually charge.
MAC- maximum allowable cost- the max cost a third party will pay for a multisource drug. this typically is an average of the generic drug price from several manufacturers.
What are DIR fees? How and when are they assessed? What impact do they have on pharmacies?
DIR Fees= Direct and Indirect Remuneration Fees
DIR fees are charges that pharmacies pay after the point of sale.
Can be a percent or flat fee
Impact pharmacies by decreasing reimbursement rates
How does a pharmacy combat declining reimbursements?
increase prescription volume
diversify revenue streams
professional services (MTM, Vaccines)
diversify OTC offerings
DME
decrease expenses
like labor