Unit 2 - Global Climate
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
why is kiribati spelled like that? (is it spelled or spelt?)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
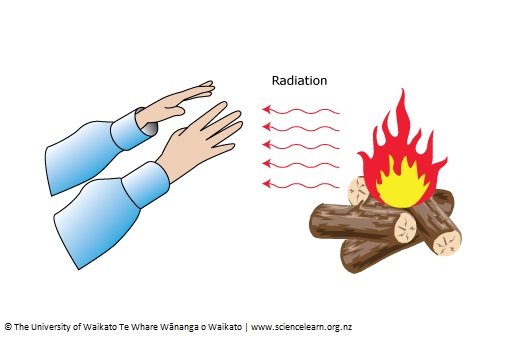
Radiation
the emission of electromagnetic waves such as X-rays, short waves and long waves
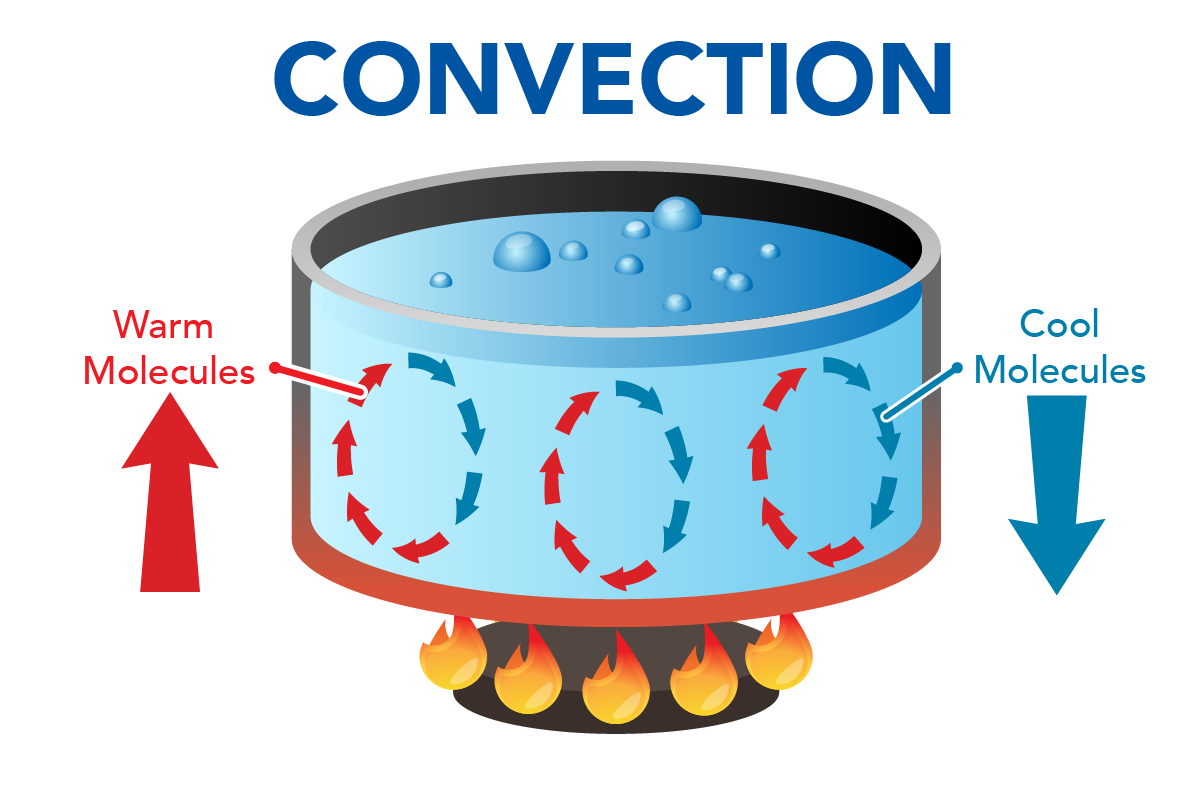
convection
the transfer of heat by the movement of a gas or liquid
Conduction
the transfer of heat by contact

Atmosphere
a mixture of gases that surround the earth:
Mainly nitrogen (78%), oxygen (20%), argon (0.9%) and trace gases (incl GHGs)
Greenhouse gases (water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, NO2, ozone)
atmosphere structure
Exosphere, thermosphere, mesosphere, stratosphere, troposphere, ozone layer
Atmospheric stratification
structure of the atmosphere, divided into different layers
Atmospheric pressure
force per unit exerted on a surface by the weight of air above it, measured in kiloPascals (kPa) or millibars (mb)
Ozone layer function
reduces the amount of uv radiation that reaches the earth
Average atmospheric pressure at mean sea level (MSL)
1,013.25 millibars
origin of atmosphere
Formed 4.6 billion years ago from volcanoes’ gases and the beginnings of photosynthesis in early organisms
Snow albedo
up to 90% because of light colour and small crystalline particles that scatter light
Ice albedo
50-70% reflectivity because its darker than snow and has a reflective texture but less so than snow, albedo depends on colour of ice hence pollutants in ice
asphalt road albedo
~5% reflectivity, larger particles, darker colour
Sand albedo
30-50% reflectivity, dependent on colour e.g. red sand v yellow sand, red sand has lower albedo
Periglacial areas
seasonally low temperatures and permafrost
Periglacial environments contain
some 400–500 gigatonnes(Gt) of carbon stored as DOM → would oxidise and contribute to accelerated greenhouse effect if permafrost melted
percentage of global soil carbon stored in periglacial soils
30–40 per cent
Effects of climate change on arctic region
increase in primary productivity
Lack of nutrients may limit productivity
Nutrients expected to increase as dead organic matter in permafrost breaks down so probs not an issue
release of carbon and methane
positive feedback
Permafrost
Dead organic matter decomposes extremely slowly because of low temperatures
Dense accumulation of carbon: oxidises when it melts
methane emissions because of permafrost melt
About 25–40 megatonnes (Mt) of methane are released each year from melting permafrost
A 4ºC temperature increase could lead to a 45–65 per cent increase in the release of methane
if 10% of the permafrost were to thaw, it could release enough methane into the atmosphere to raise temperatures by an extra 0.7°C
The Arctic sea ice minimum
generally reached in generally reached during September and the maximum during March. However, the overall volume, thickness and extent have been declining for decades
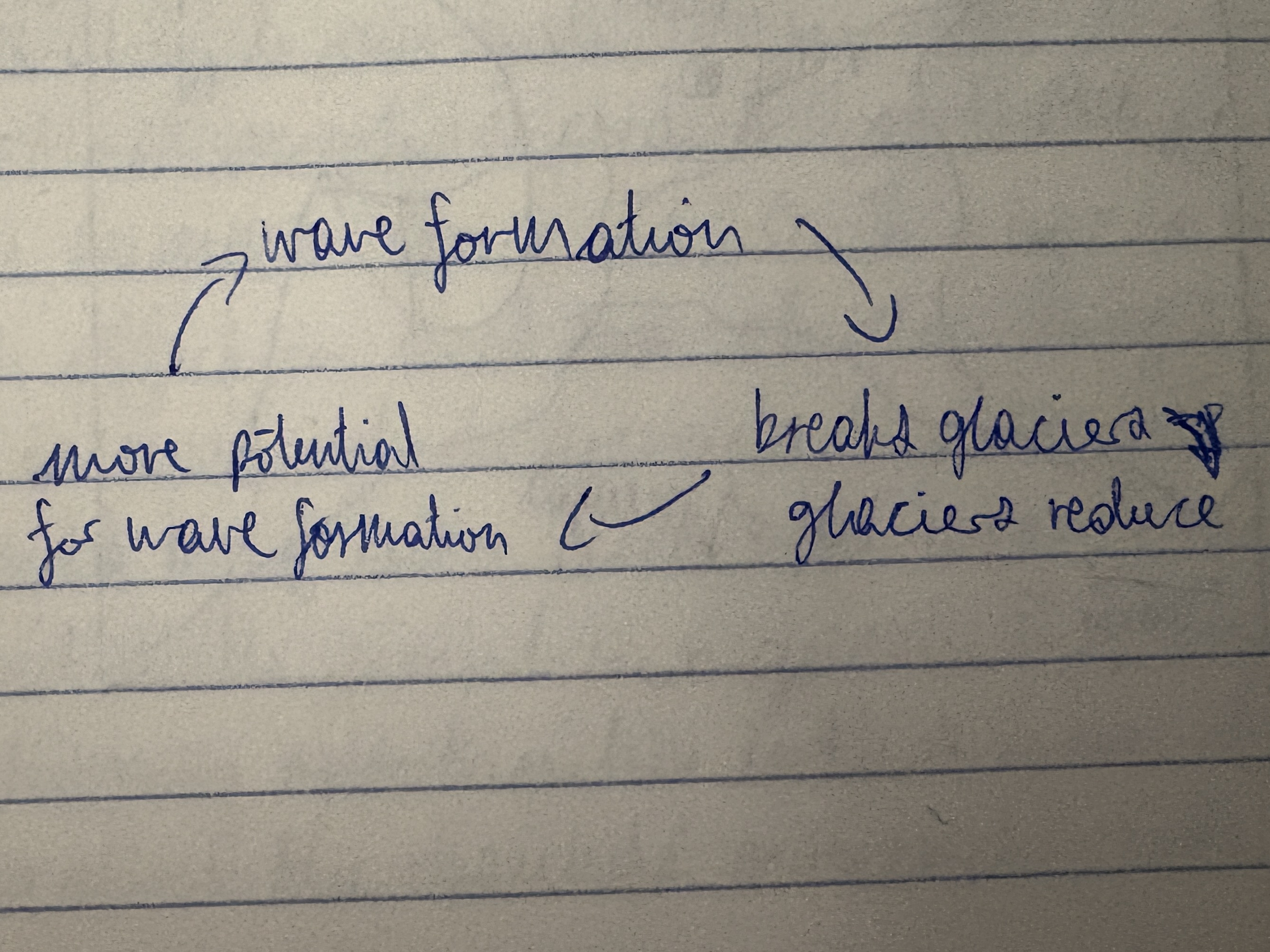
Wave formation positive feedback
In 2012, five-metre waves were recorded in the Beaufort Sea
arctic region map
its literally a circle u can do this!
Impacts of sea ice decline
More sea ice decline (lol)
Methane emissions will increase because of the release of chlorine atoms from the sea
May be associated with wet summers in europe due to weakened jet stream
Correlations between extreme weather in the northern and mid-latitudes and the disappearance of ice
Sea ice decline linked with increase in primary productivity in the bering sea due to phytoplankton blooms
Adverse effects on polar bears: less time to hunt seal pups and must spend more time on land, diets less nutritious, reduced body size and reproductive success
Himalayan glaciers
Retreating (wow I’m so shocked!)
Unlikely to cause major water shortages in the near future because of monsoon system
Other factors like population growth and groundwater depletion could have a serious impact on water availability
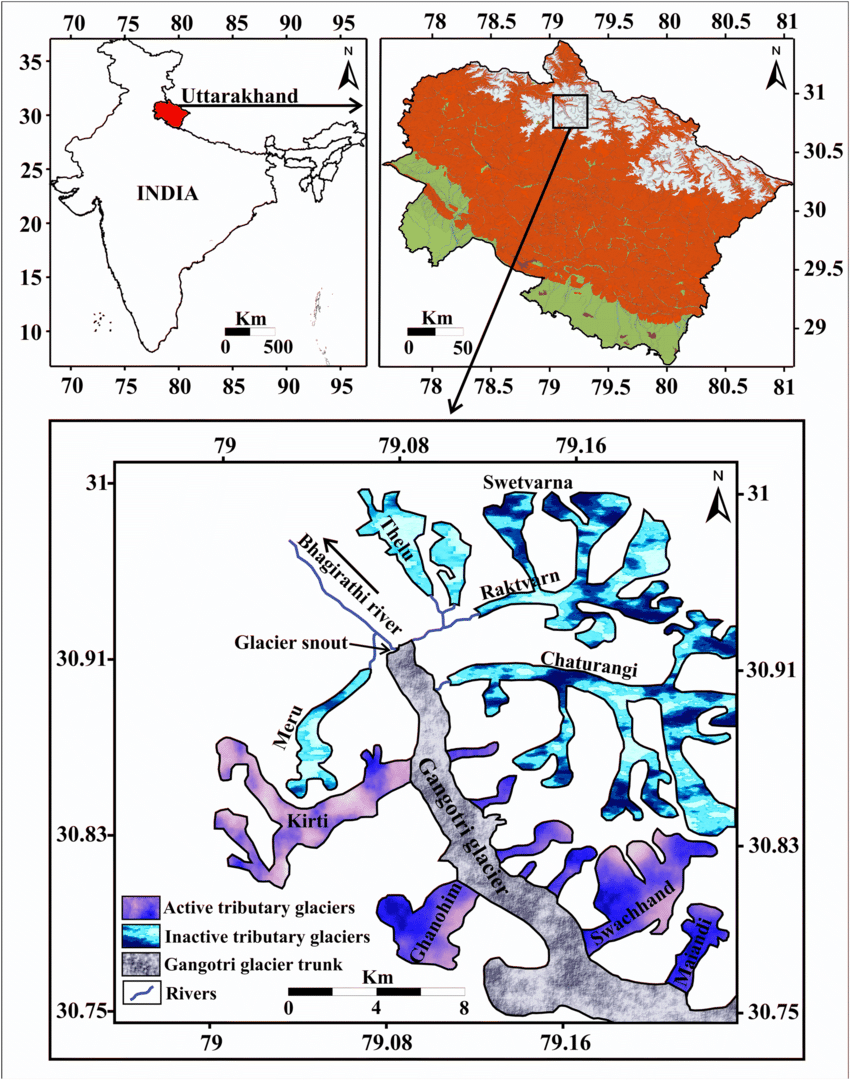
Gangotri glacier
One of the largest glaciers in the himalayas
Glacial retreat could alter stream-flow characteristics
30km long and 0.5-2.5km wide
Retreated ~900m since 1990
Swiss glaciers
Consequences of glacier retreat: changes in water balance, glacial lake outbursts, mudslides, debris slides
Glaciated surface of swiss alps declined from 1800km^2 in 1850 to 1300km^2 in 1971 - ⅓ loss
If temperature increases by 3ºC
35% drop in crop yields across Africa and the Middle East
550 million more people could be exposed to hunger
If temperatures increase by 2ºC
200 million more people could be exposed to hunger
Agricultural land shift
viticulture (production of grapes for wine), production of corn and wheat will move towards poles, away from equator
Northward shift of wheat production in North America
Decline in US grain belt
Increase in Canada’s growing season and primary productivity
Serious effects on US economy
Wheat yields in UK
prediction that north will increase by 30%, yields in south will decrease by 30%
water resource change and crop distribution
Reduction of water resources will mean increase in difficulty of irrigation
Change in crop types and distribution of different crops
Temperature increase of 2ºC
60 million more people in the african continent could be exposed to malaria
Mosquitoes would be able to breed in areas previously too cool
Tropical diseases will spread to higher latitudes
Increase in climate refugees
Kiribati, other islands in the South Pacific due to rising sea levels
Kivalina, Alaska immigration due to rising sea levels
silver lining or arctic ice melt
Opening of sea routes for trade
Tourism likely to change
Less winter tourism (rip thredbo)
More summer tourism in higher latitudes
Currently popular areas may become less so due to reduction in water resources and resulting lack of economic viability
Bangladesh flooding vulnerability
20% of GDP and 65% of the labour force is involved in agriculture that is threatened by floods in low-lying areas, risk of food scarcity
low lying countries
buh bye!
climate migration (floods and droughts)
200 million people at risk of being driven from their homes by flood or drought by 2050
climate change affect on storms
an increase in storm activity such as more frequent and intense hurricanes (owing to more atmospheric energy)
climate change and rainfall
reduced rainfall over the USA, southern Europe and the Commonwealth of Independent States (Russia and the -stans) leading to widespread drought
climate change and water availability
up to 4 billion people suffering from water shortages if temperatures rise by 2°C