AP 2 Exam 3: Urinary System & Immune/Lymphatic System
1/146
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
147 Terms
organs involved in urinary system
kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, urethra
functions of the urinary system
removes water from soluble waste, controls fluid & salt balances, and also involved in blood pressure, pH regualtion, and long term responses to PO2
Urine should NOT contain...
protein, blood, glucose, or cells
urine
-end product of kidney blood filtration and resorption
-mixture of nitrogen based waste (urea) and other waste products
-usually yellow to clear
-discoloration can be due to trauma, dehydration, or food
oliguria
decreased urine output, due to dehydration, blockage or renal failure
polyuria
excessive urination, due to diabetes mellitus/insipidus
pH of urine
4.5-8
osmolarity of urine
50-1200 mOsm/L
How much urine do we make a day/minimum?
1-2 liters per day, a minimum of 500mL
urethra
transports urine from the bladder to the external environment
internal sphincter
SMOOTH muscle, involuntarily controls the entry of urine
external sphincter
STRIATED muscle, voluntary control of exit of urine
stretch receptors
sensors in blood vessels that identify internal pressure and detect filling of the bladder
bladder
elastic, hollow, muscular organ (bag of smooth muscle) that provides temporary storage for urine
micturition
urination, caused by muscle contraction
capacity of bladder
500-600mL
detrusor muscle
the smooth muscle layers of the bladder, compresses the urinary bladder and expels urine through the ureters
process of urination
Parasympathetic outflow causes detrusor muscle contraction and internal sphincter release. Concurrent spinal inhibition of external sphincter drains urine
ureters
tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder through peristalsis; ureters enter bladder at an obtuse angle with a natural valve that prevents urinary backflow
kidneys
bean-shaped organs that remove soluble waste from blood; lie posteriorly in abdomen on either side of the spine and are protected by ribs, muscle, & fat
adrenal glands
a pair of endocrine glands that sit just above the kidneys and secrete hormones (epinephrine and norepinephrine) that help arouse the body in times of stress
function of kidneys
filter blood and produce urine with roles in BP control, adaptation to hypoxia, blood pH adjustment, and Ca2+ homeostasis
outer cortex of kidney
-superficial
-contacts fibrous capsule
-houses filtration structures (nephrons)
inner medulla of kidney
Divided into pyramids
Each medullary pyramid ends in a papilla
renal columns
Inward extensions of the cortex tissue separating the renal pyramids
papilla (kidney)
bundle of tubules at the tip of pyramid; releases urine into minor calyx
minor calyx (kidney)
drains a renal pyramid
major calyx (kidney)
2 or 3 minor calyces drain into one of these.
These drain urine into the renal pelvis
path of urine
renal cortex - pyramid - papillae - minor calyx - major calyx - ureter
renal hilum
area in the midportion of the kidney where the renal vessels, nerves, lymphatics, and ureters enter
renal artery
blood vessel that carries blood to the kidney
glomerulus
A ball of capillaries surrounded by Bowman's capsule in the nephron and serving as the site of filtration in the kidney; "branching vessels until terminal 'lacy' structure"
afferent arteriole
The small artery that carries blood TOWARD the capillaries of the glomerulus.
efferent arteriole
The small artery that carries blood AWAY FROM the capillaries of the glomerulus.
pertibular capillaries
tiny blood vessels, supplied by the efferent arteriole, that travel alongside nephrons allowing reabsorption and secretion between blood and the inner lumen of the nephron and drain into the venous system
vasa recta
the capillary system in the kidney that serves the loop of Henle, surrounding the nephron
nephrons
-filtering units of the kidney that remove wastes from the blood and produce urine
-tubular structure
-loops down into the medulla
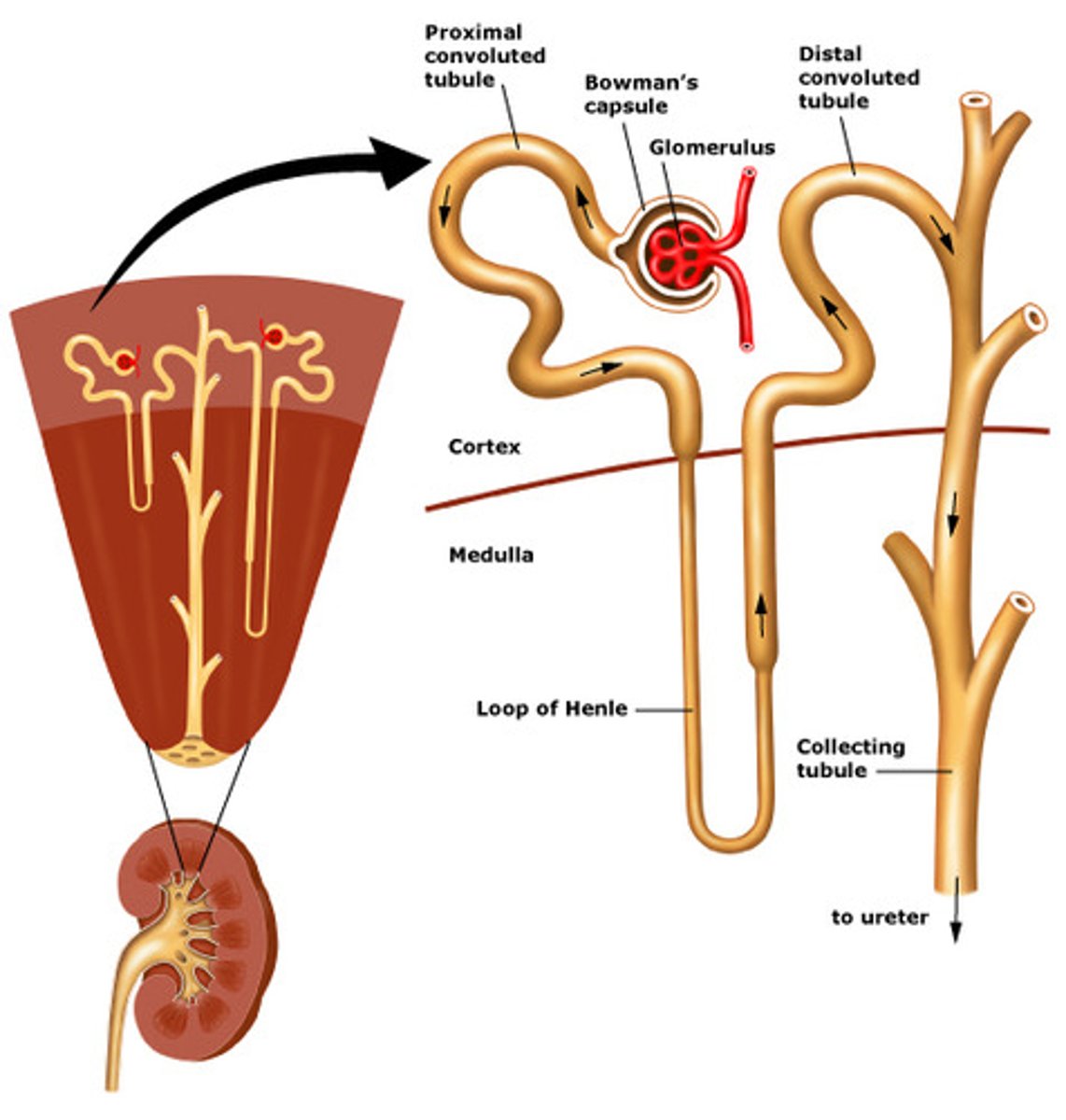
Bowman's capsule
cup-shaped strucutre of the nephron of a kidney which encloses the glomerulus and which filtration takes place
renal corpuscle
glomerulus and Bowman's capsule, where filtration takes place
primary functions of nephron
filtration, reabsorption, secretion
podocytes
capsule cells surrounding endothelial cells of the glomerulus, finger-like extensions over capillaries (which are more porous than usual); interdigitate with pedicles and filter substances in a similar way to fenestrations
gaps (nephron)
filtration slips
high pressure system of nephron
19% of plasma is pushed out and through the basement membrane; particles up to 8nm pass through
fenestrations (nephron)
allow many substances to diffuse from blood based on size
pedicles (nephron)
-wrap around the glomerular capillaries to form the filtration slits.
-increase the surface area of the cells
-pedicles on 1 podocyte always interdigitate with pedicles from another podocyte
proximal convoluted tubule (PCT)
-first section of the renal tubule that the blood flows through; reabsorption of water, ions, and all organic nutrients
-convoluted to increase SA
-cells have microvilli to increase SA
Loop of Henle (LOH)
U shaped loop, connecting Bowman's capsule to medulla then to the distal convoluted tubule
collecting ducts (nephron)
(not really considered part of nephron)
- receive urine, directs to renal crest and papillae
-urine leaves nephron and empties into renal calyx and pelvis
-filtered fluid moves through them
-important for H2O resorption
net pressure in filtration
blood hydrostatic pressure exceeds combined blood colloidal pressure and capsule hydrostatic pressure
Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR)
the amount of filtrate formed per minute by the two kidneys combined; important determinant in renal health and can be determined from equations (90-120mL/min avg)
cardiac output for kidney
51/min, 21% of this flows to kidney
net filtration pressure (NFP)
sum of osmotic and hydrostatic pressures
How much fluid is filtered through kidneys?
158 liters a day
location of resorption
convoluted tubules, LoH, and collecting ducts (each with specific role and profile for secretion/resorption)
secretion
from blood into nephron lumen, requires active transport/ATP
resorption
from nephron lumen into blood; H2O resorption is highly regulated
What drives secretion and resorption?
-Na+/K+ ATPases are very important for both facilitated and free diffusion
-osmosis
-either shifts stuff from nephron lumen to kidney tissue in blood (resorption) or from kidney to lumen (secretion)
Where does resorption/secretion occur?
- in the PCT !!!
- 70% of water & electrolytes resorbed here, 100% of glucose and AA's
- Driven by Na+ movement, but SYMPORTERS may bring other molecules (glucose, AA's, PO4 3-)
interstitial space (PCT)
where Na+/K+ ATPases remove Na+
macula densa cells
Specialized cells in the ascending limb which monitor the NaCl content of the filtrate entering the DCT; also sense fluid flow rate; if Na+ is high, adenosine is released
Which arteriole is larger?
afferent is larger than efferent; paracrine mediated constriction of afferent arteriole only ("like turning down the tap" ?)
renin
hormone secreted by the kidney; it raises blood pressure by influencing vasoconstriction (narrowing of blood vessels), renin cleaves angiotensinogen
angiotensinogen, angiotensin I
Renin converts ________ to _______.
angiotensin II
increases blood pressure by stimulating kidneys to reabsorb more water & Na+ and by releasing aldosterone
angiotensin I
an inactive precursor that is converted by an enzyme to yield active angiotensin II
angiotensinogen
Protein converted to angiotensin I by renin.
aldosterone
"salt-retaining hormone" which promotes the retention of Na+ by the kidneys. Na+ retention promotes water retention, which promotes a higher blood volume and increased pressure; comes from adrenal cortex
HYPER-osmotic filtrate
Down the descending LoH, more H2O is pushed out (more permeable to H2O)
HYPO-osmotic filtrate
DILUTED filtrate in ascending limb of LoH; impermeable to H2O but ions are resorbed
osmotic gradients (kidneys)
- used to concentrate filtrate in kidneys
- generated by countercurrent multiplier
- gradient formed by osmotic difference between renal medulla and nephron lumen
- interstitial fluid concentration increases into medullary tissue & filtrate concentration varies along tubule lumen
distal convoluted tubule (DCT)
- cuboidal cells without microvilli that function more in secretion than reabsorption
- segment of the nephron between the nephron loop and collecting duct
- ROLE IN CA2+ RESORPTION
- DCT recovers 10-15% of water and some ions
collecting duct
- A segment of the nephron that returns water form the filtrate to the bloodstream; last step in H2O resorption
- includes principle and intercalated cells
- site of ADH action (vasopression)
- site of aldosterone action
- HYPER-osmotic blood: collecting ducts recover MORE H2O
- HYPO-osmotic blood: collecting ducts recover LESS H2O (remember the filtrate is dilute)
principle cells
resorb Na+ and water, secrete K+
intercalated cells
Involved in acid-base balance by secreting H+ into tubule lumen and reabsorbing K+
filtrate concentration of plasma
300mOsm/L
filtrate concentration of PCT initial filtrate
300mOsm/L
filtrate concentration of deepest juxtamedullary nephrons
1200mOsm/L
filtrate concentration leaving collecting duct
500-800mOsm/L
filtrate concentration of fluid in DCT
100-200mOsm/L
antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
Hormone secreted by the hypothalamus as an arginine vasopressin that stimulates water reabsorption from kidney tubule cells into the blood and vasoconstriction of arterioles. "Water conservation mechanism"
neurohypophyseal hormones
ADH (vasopressin) and oxytocin
osmoreceptors role in ADH secretion
- osmoreceptors outside of blood/brain baarrier sense rise in plasma osmolarity
- increase in osmoreceptor firing
posterior pituitary
releases ADH (and oxytocin); stimulated by Na+, much less so by glucose adn urea
Roles of ADH
- helps blood vessels contract and maintain plasma volume
- helps kidneys control water and salt
- controls BP (and therefore GFR)
- helps control amount of urine that is made
juxtaglomerular apparatus/cells
in the nephron, the complex of cells from the distal tubule and the afferent arteriole which helps regulate blood pressure by secreting RENIN in response to blood pressure changes in the kidney; located near the glomerulus
Angiotensin II
increases blood pressure by stimulating kidneys to reabsorb more water and by releasing ALDOSTERONE
organization of immune systerm
1) barrier defenses: skin, mucous membranes
2) innate response: rapid, non-specific
3) adaptive responsive: slower, specific
immune system
- cells and organs that destroy or neutralize pathogens
- collections of barriers, cells & soluble proteins
- includes cells, tissues, & chemicals
myeloid stem cell
becomes erythrocytes, platelets, granular leukocyte, or monocytes
multipotent hematopoietic stem cell (hemocytoblast)
All of the blood cells stem from this cell and differentiate depending on the chemical signals received.
lymphoid stem cell
produce lymphoblasts which differentiate into natural killer cells (large granular leukocyte) or small lymphocytes (B or T)
basophil
white blood cell containing granules that stain blue; associated with release of histamine and heparin
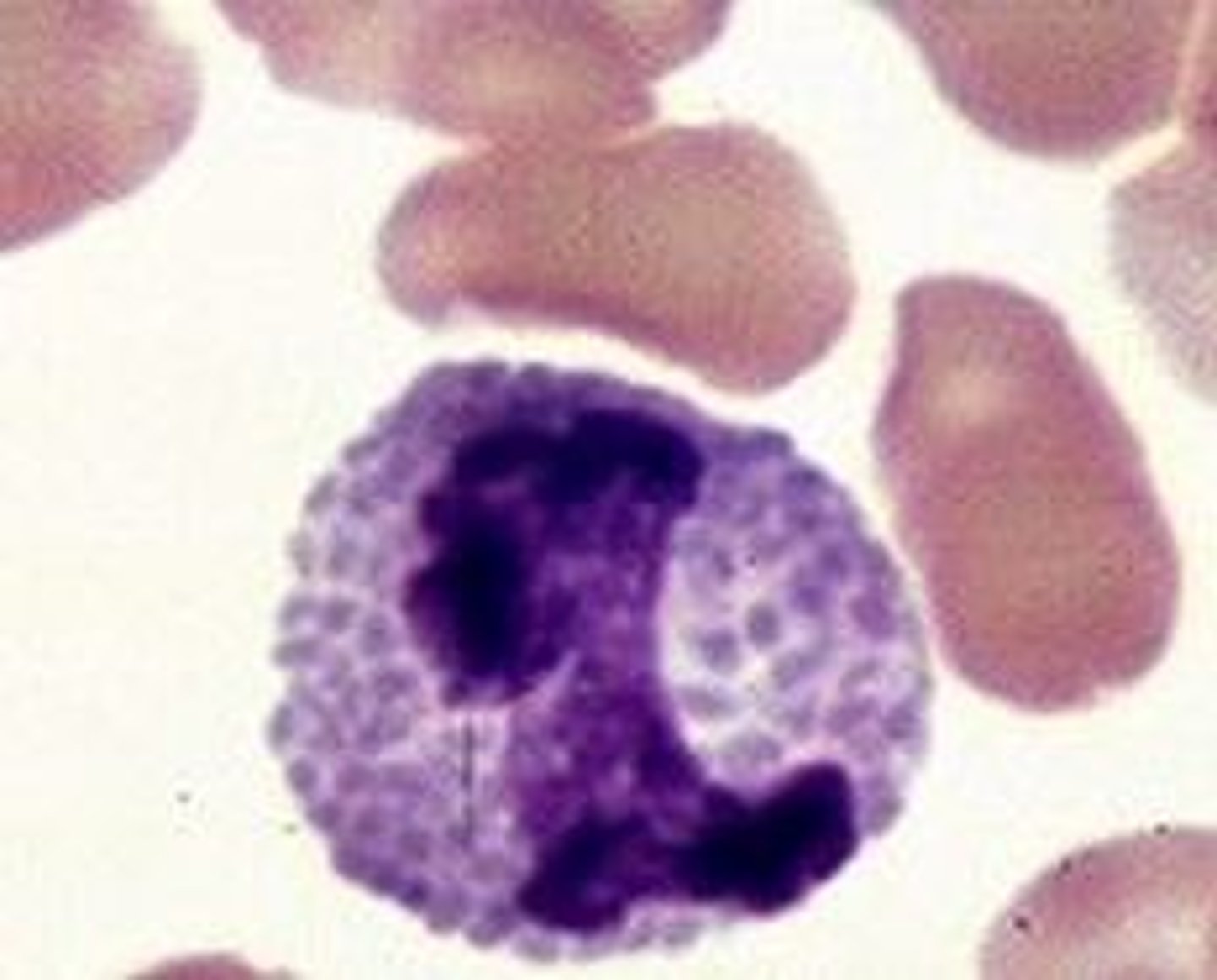
neutrophil
a granular leukocyte, named for the neutral stain of its granules, that fights infection by swallowing bacteria
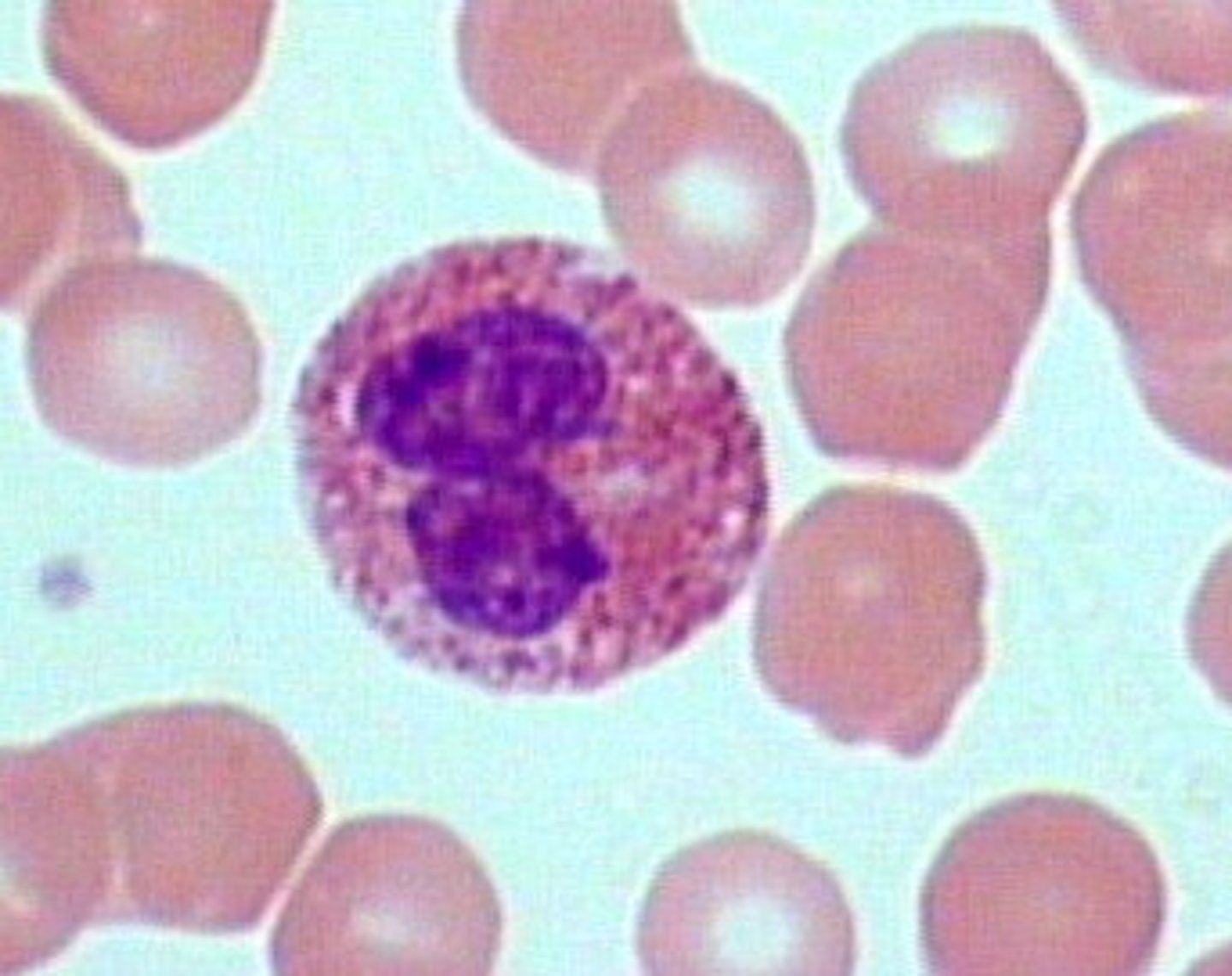
eosinophil
white blood cell containing granules that stain red; associated with allergic reactions
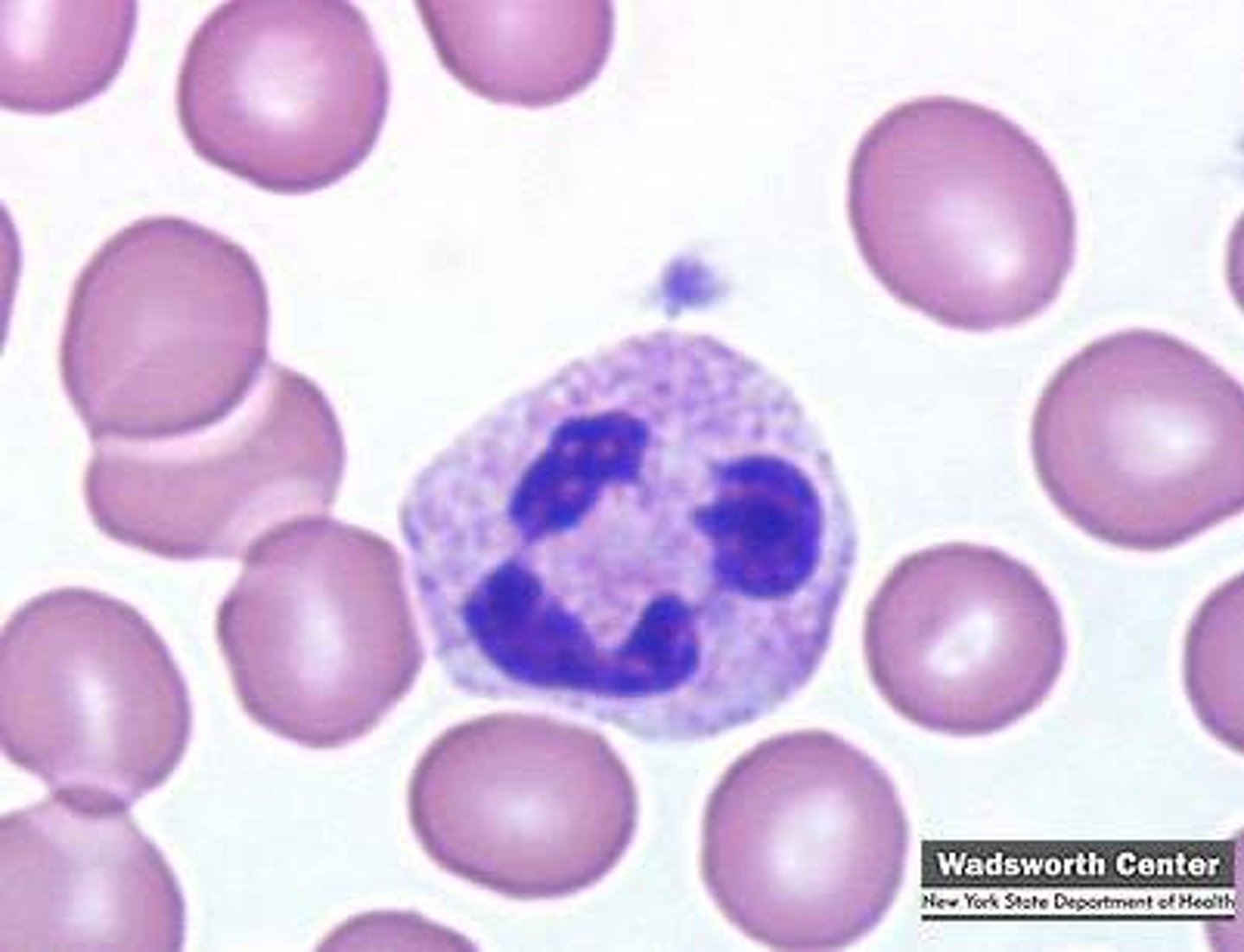
monocyte
a large phagocytic white blood cell with a simple oval nucleus and clear, grayish cytoplasm; gives rise to macrophages
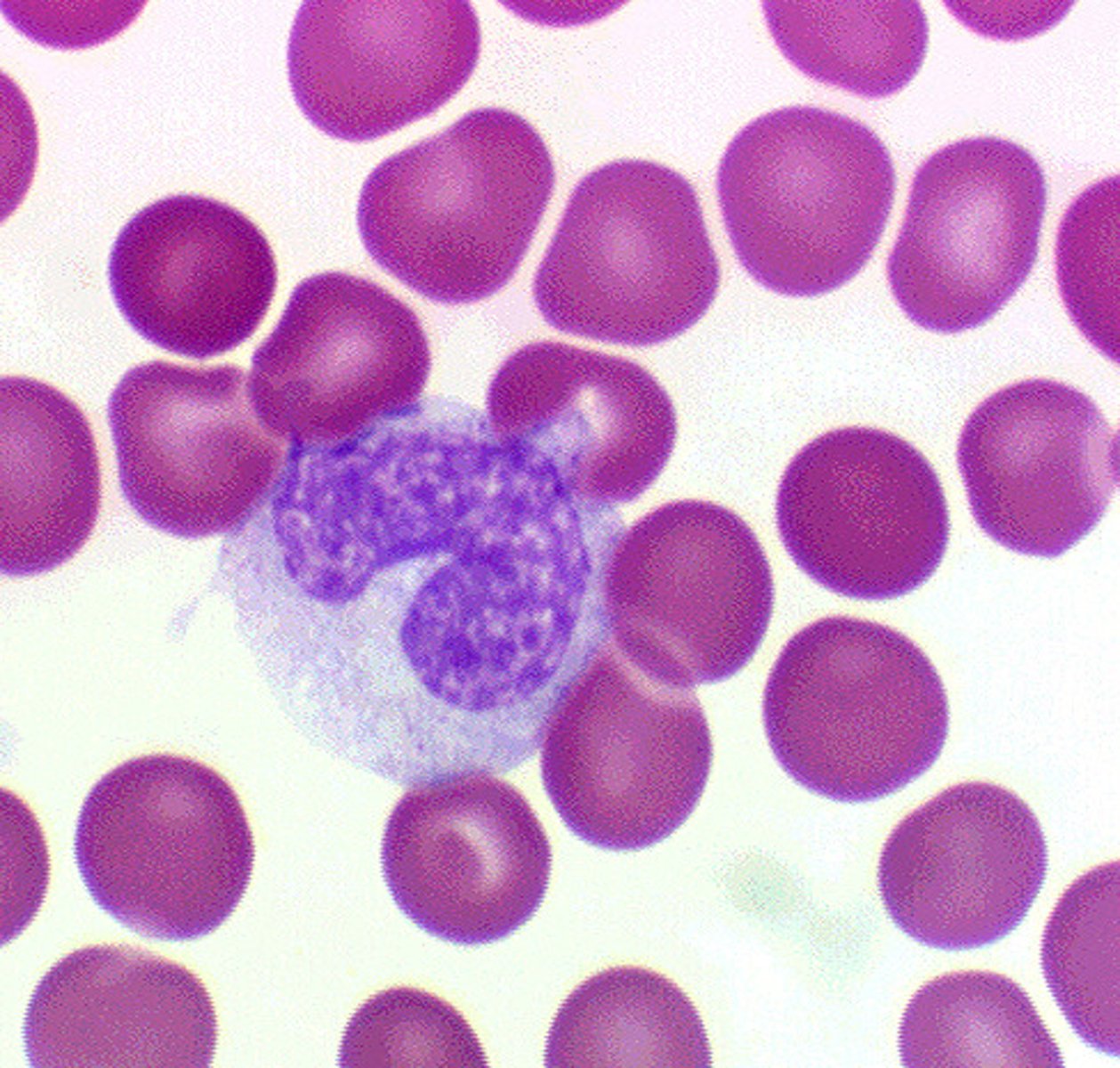
megakaryocyte
large platelet precursor cell found in the bone marrow
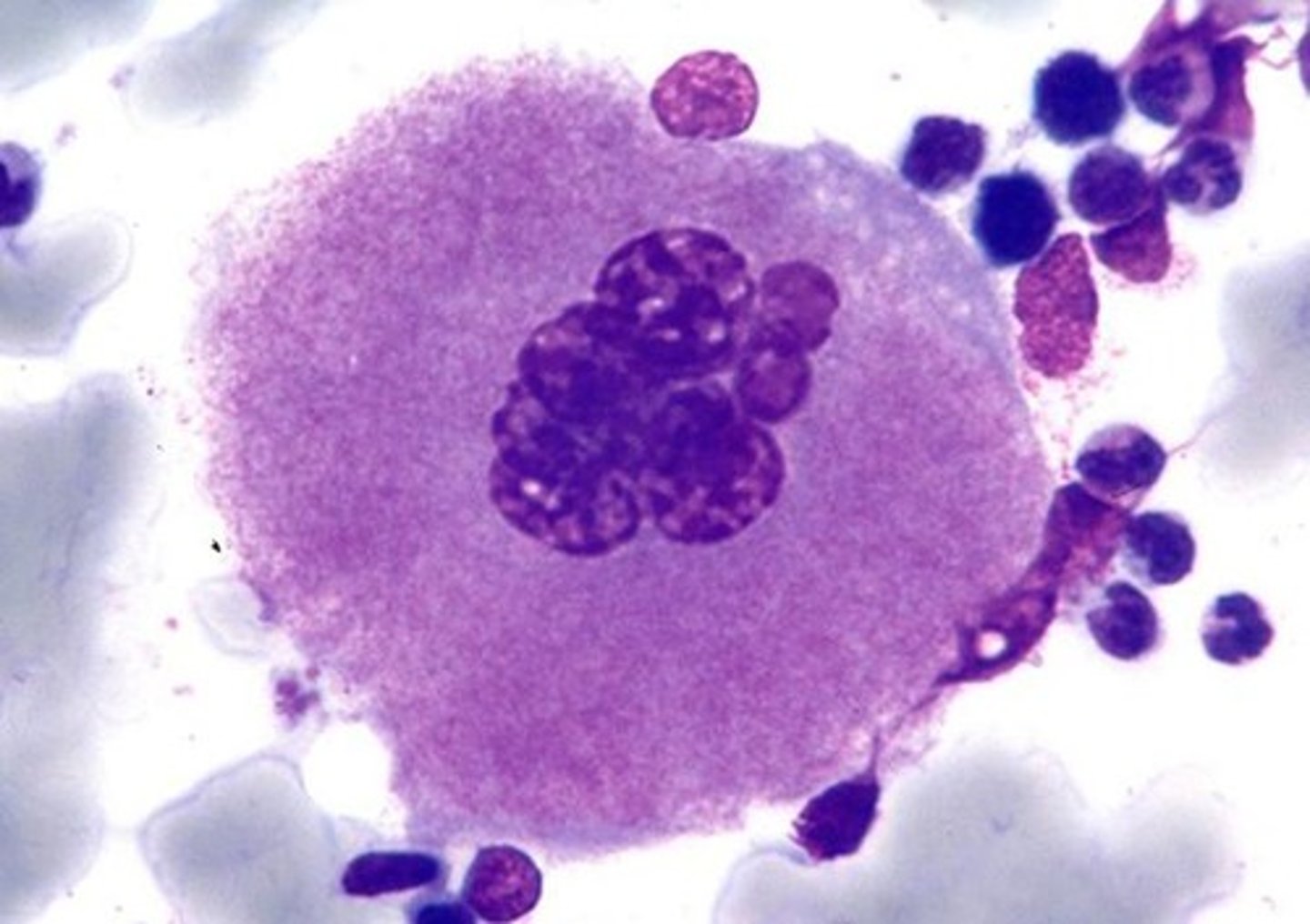
platelets
thrombocytes, involved in blood clotting
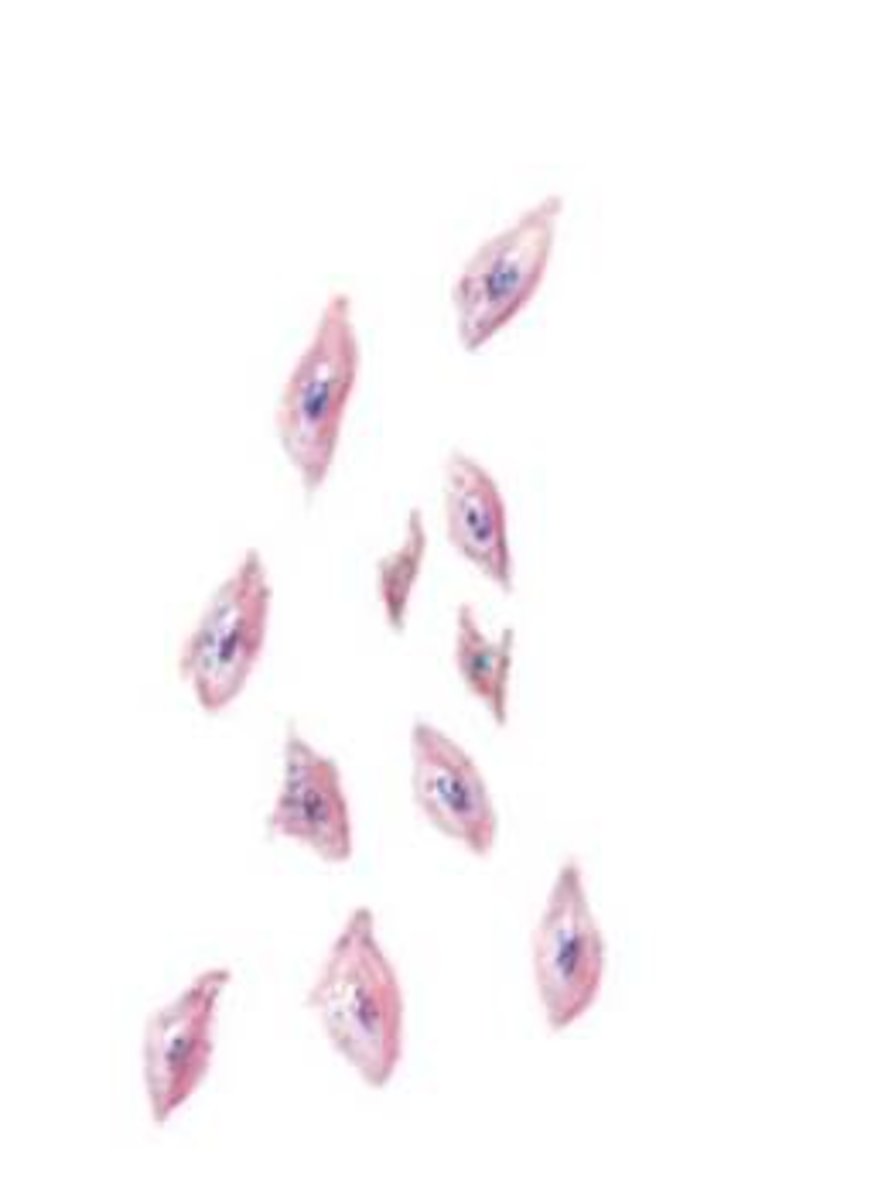
macrophage
- involved in phagocytosis
- also neutrophils and dendritic cells
- first line of defense upon barrier breach
- eat and destroy invading pathogens and damaged tissue
surface defenses
first line of defense- skin and mucous membranes, act instantaneously
internal defenses
mast cells, basophils, natural killer cells, complement system, phagocytes, monocytes, neutrophils, macrophages