Introduction to Steroids MC
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
label with numbers ignore DB
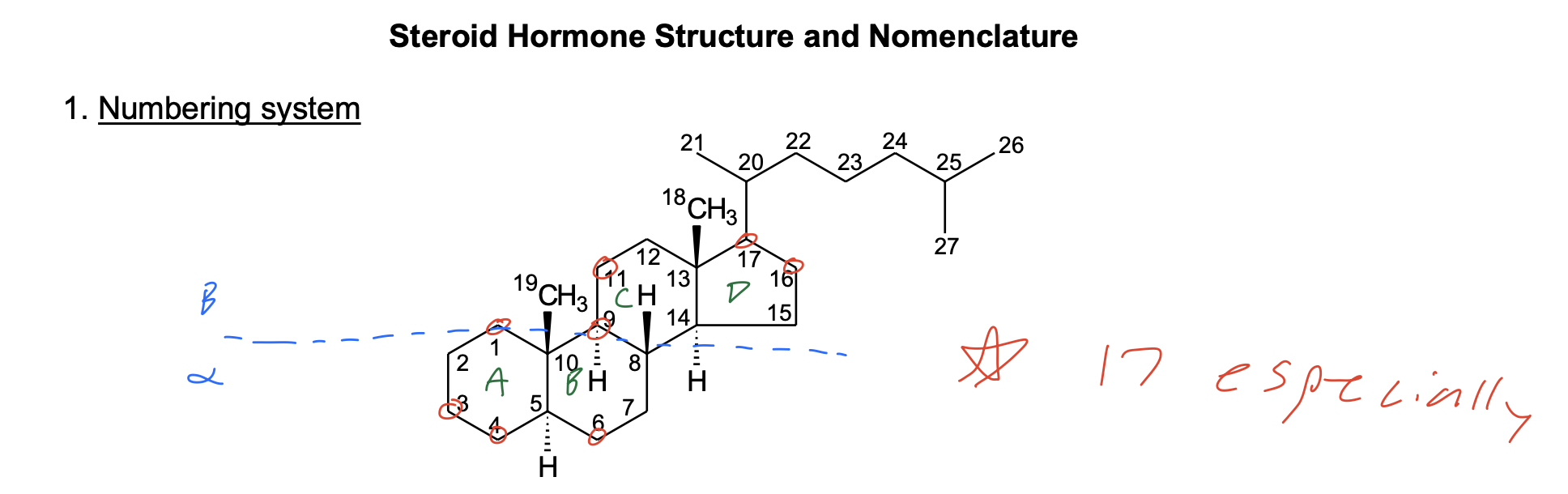
Stereochemistry : cis and trans ring junctions
A. cis ring junction – both substituents at the ring junction (including H) are on the same face
B. trans ring junction – the substituents at the ring junction (including H) are on opposite faces
C. Assume all trans ring junctions, especially if you don’t see H atom stereochemistry
which is preferred cis or trans
trans
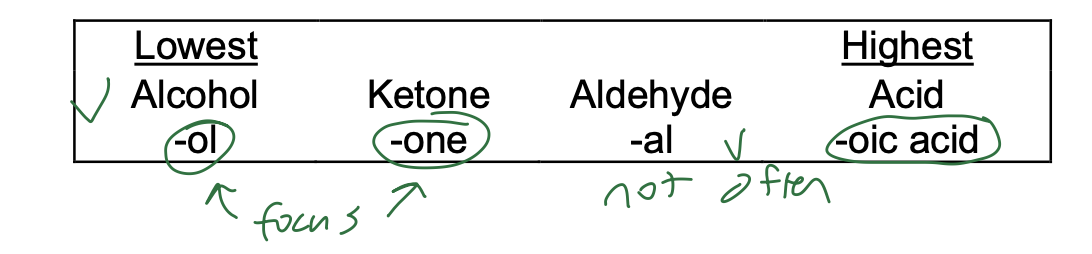
Skeleton Stem Name Modification – consider additional functional groups
Location and type of functional groups on a-face
This face is typically involved in hydrophobic interactions.
Hydrophilic substituents on this face will disturb these interactions.
Bulky substituents on this face will disturb these interactions
Location and type of functional groups on B-face
This face is typically involved in H-bonding interactions.
Polar/hydrophilic substituents on this face will enhance these interactions
Location and type of functional group at position 3
Alcohol (OH) or ketone (C=O) are typically present
Location and type(s) of functional group(s) on the D-ring
Typically see 2 carbon side chain at C-17
Unsaturation at positions 1 (delta1) and 4 (delta4) changes the geometry of the A ring
Increases glucocorticoid activity 3-4x
Decreases mineralocorticoid activity significantly
Cholesterol Biosynthesis
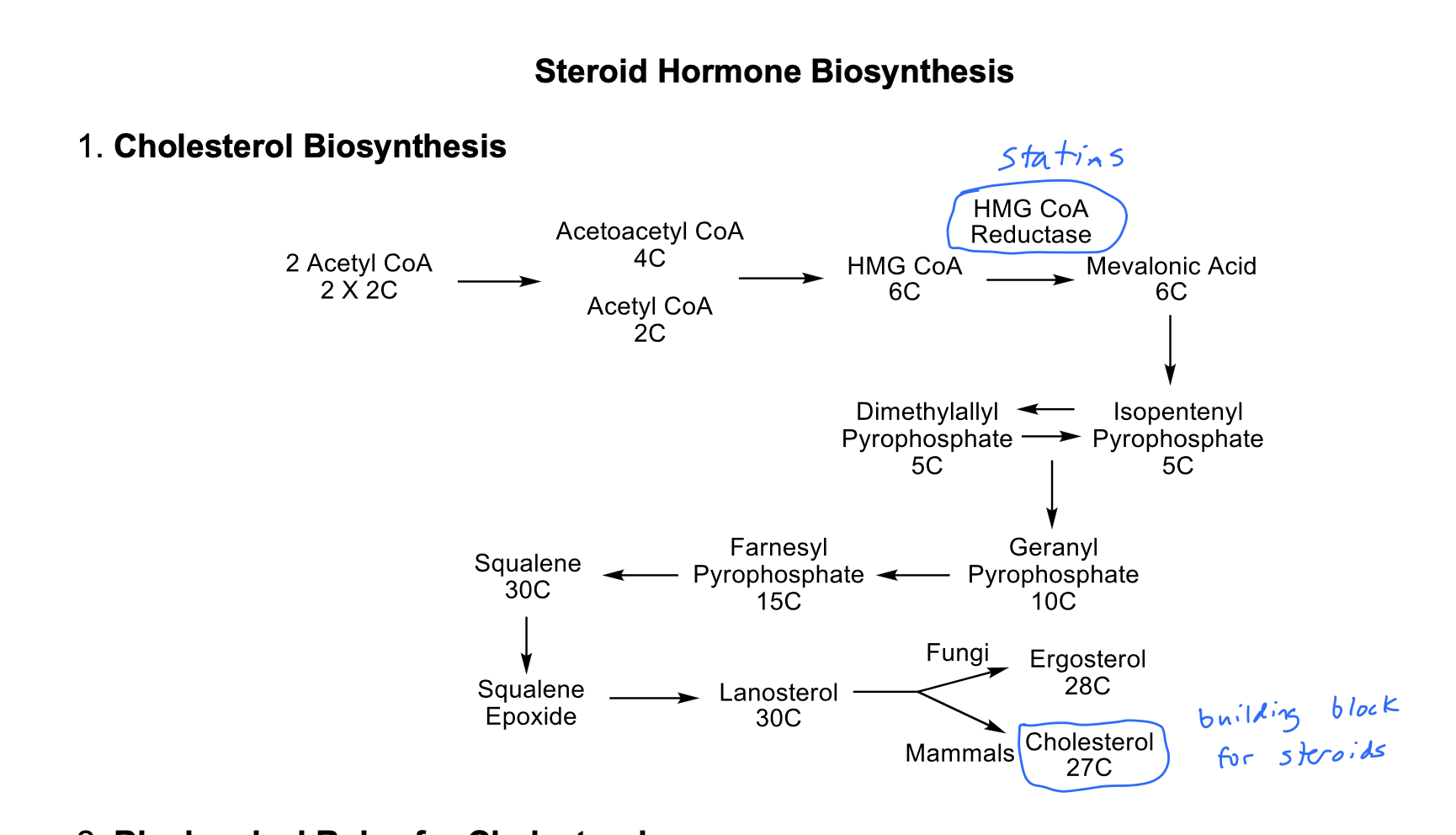
Biochemical Roles for Cholesterol
Conversion to glucocorticoid adrenal hormones (cortisol, hydrocortisone)
Biological Targets for Steroid Hormones
A. Corticosteroid or Adrenocorticoid receptors
• Mineralocorticoid receptors
• Glucocorticoid receptors
Nucleus
The receptor dimer can then interact with various regions of cellular DNA (hormone responsive elements), as well as with transcriptional factors