(b) energy transfers
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
different energy stores (4.2)
chemical, kinetic, gravitational (potential), elastic (potential), internal (thermal), magnetic, electrostatic, nuclear
chemical energy store (4.2)
the energy stored in chemical bonds, such as those between molecules
kinetic energy store (4.2)
the energy of a moving object
gravitational energy store (4.2)
the energy of an object at heigh
elastic energy store (4.2)
the energy stored when an object is stretched or squashed
thermal energy store (4.2)
the total kinetic and potential energy of the particles in an object. in hotter objects, the particles have more internal energy and therefore vibrate faster
magnetic energy store (4.2)
the energy stored when either:
repelling poles have been pushed closer together
or
attracting poles have been pulled further apart
electrostatic energy store (4.2)
the energy stored when either:
repelling charges have been moved closer together
or
attracting charges have been pulled further apart
nuclear energy store (4.2)
the energy stored in the nucleus of an atom
energy transfers (4.2)
mechanically, electrically, by heating, by radiation
transfer mechanically (4.2)
a force moving an object through a distance
transfer electrically (4.2)
charges moving due to a potential difference (a measure of the energy given to the charge carriers in a circuit)
transfer by heating (4.2)
due to temperature difference caused electrically or by chemical reaction
transfer by radiation (light and sound) (4.2)
energy transferred as a wave
principle of conservation of energy (4.3)
no energy can ever be created or destroyed, only transferred, stored or dissipated
relationship between efficiency, useful energy output and total energy output (4.4)
efficiency = ( useful energy output / total energy output ) × 100%
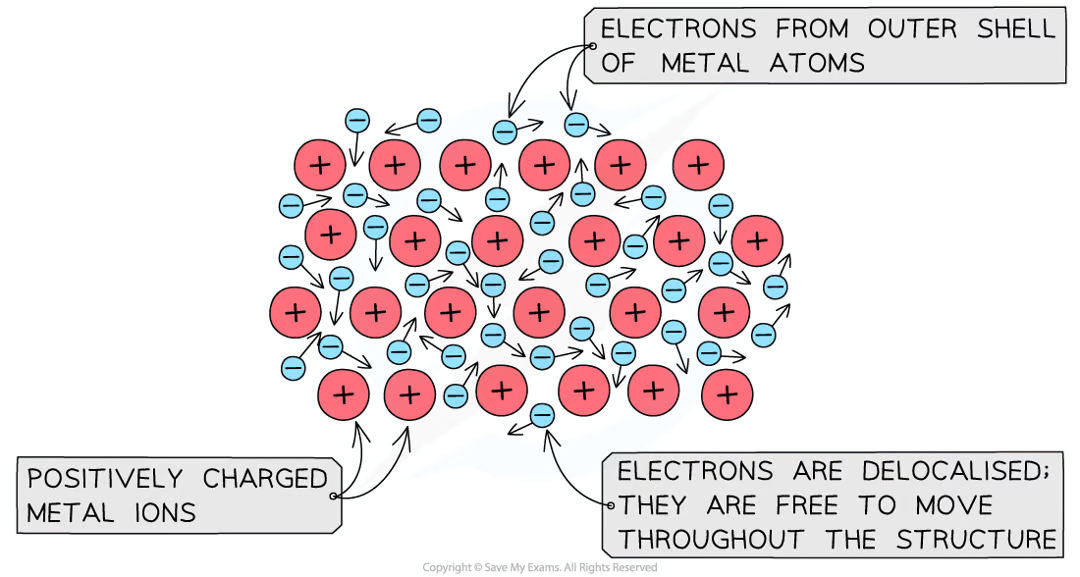
conduction (4.6)
a conductor is a material that transfers energy by heating quickly
metals are especially good conductors because the delocalised electrons in the metal can collide with the atoms, helping to transfer the vibrations through the material, therefore transferring the heat better
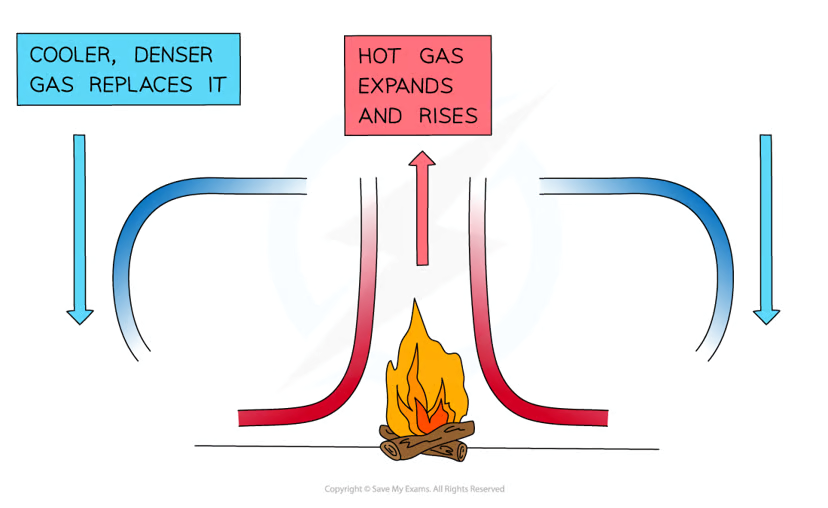
convection (4.6 / 4.7)
when a fluid is heated:
the molecules push each other apart so the fluid expands, making the hot fluid less dense than its surroundings
the hot fluid rises, letting the cooler surrounding fluid to take its place
the hot fluid eventually cools down and sinks as the cooler fluid heats up and rises to take its place
this motion is called a convection current
sea breezes (4.6 / 4.7)
during the daytime, the land warms up quickly, whereas the sea warms up more slowly (since solids are much more effective conductors than liquids)
this causes the air nearer the land to heat up quickly and rise, so the cooler air nearer the sea takes its place, causing a sea breeze
during the nighttime, the land cools down quickly, whereas the sea cools down more slowly
this causes the air nearer the sea to heat up quickly and rise, so the cooler air nearer the land takes its place, causing a land breeze
radiation (4.6 / 4.8)
GAHHh
investigate thermal energy transfer by conduction, convection and radiation (4.9)
ways of reducing unwanted energy transfer