Lec 36 & 37 (Coccidia- Cryptosporidium)
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Coccidia
What has asexual and sexual replication in vertebrate and invertebrate hosts?
> Waterborne Outbreaks
> Swimming pools, splash parks, municipal supplies
> Daycare centers
> Foodborne Outbreaks
What is Cryptosporidium spp. primarily associated with?
Where?
> Synthesize fatty acids
> Plastid bodies for manufacturing food
Cryptosporidium spp. lack the Krebs cycle which makes them unable to do what?
What else do they lack?
Passed in feces, immediately infective and morphologically indistinguishable
What is the case for oocysts of all species of Cryptosporidium?
Direct Lifecycle
What type of lifecycle do Cryptosporidium spp. have?
In the small intestinal epithelium (inter-cellular)
Where does sexual and asexual replication of Cryptosporidium spp. occur?
3-5 day incubation period
Oocysts of Cryptosporidium spp. are passed in the feces following what?
True
T or F: Cryptosporidium spp. is immediately infective.
Via fecal-oral contamination and ingestion of oocysts
How does host infection with Cryptosporidium spp. occur?
As few as 9 oocysts
What is an infectious dose of Cryptosporidium spp.?
> Voluminous watery diarrhea
> Abdominal discomfort, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, weight loss, fatigue, fever
What clinical signs are associated with symptomatic infections with Cryptosporidium spp.?
1-3 weeks of age
Cryptosporidium occurs in dairy calves of what age?
- Anorexia
- Profuse diarrhea
- Tenesmus
- Weight loss
What clinical signs are seen in dairy calves with Crypto?
- Horses
- Pigs
- Companion Animals
Who has infections with Crypto that are usually inapparent?
1st weeks of life
When does Crypto occur in neonatal calves?
Diarrheal disease
Crypto in neonatal calves accounts for 57% of weaning mortality from what?
Scours
Cryto in neonatal calves - ~25% of deaths are attributed to what?
- Blunting of brush border
- Loss of microvilli
- Villous atrophy in SI
- Decreased milk production
Crypto can cause malnutrition and reduce growth - what might this lead to?
Oocyst contamination of bedding environment
What is a persistent source of reinfection with Crypto?
Young & Immune Naive
Who is most susceptible to crypto when looking at sheep and goats?
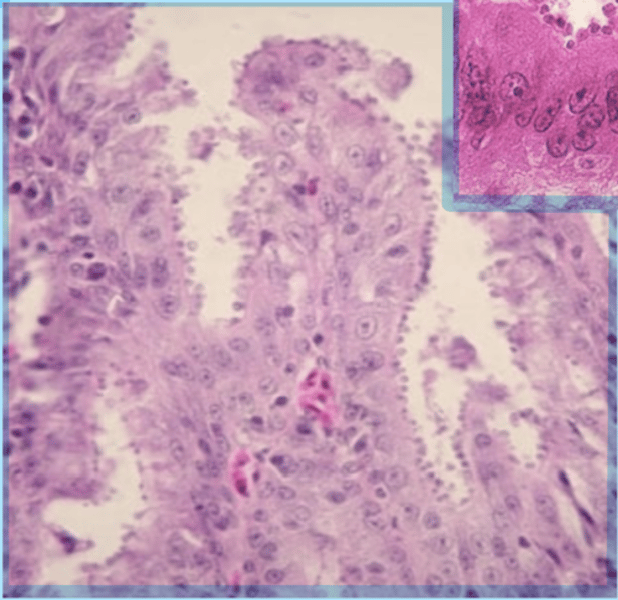
Extra-cellular Cryptosporidium adherent on the brush border of the intestinal epithelium
What is seen in the following image?
- Daycare center outbreaks
- Municipal pool/splash parks
- Farm visits by school children
- Petting Zoos
Where might Crypto be seen as a health issue in people?
Unreported
Farm-family outbreaks with crypto are fairly common but largely what?
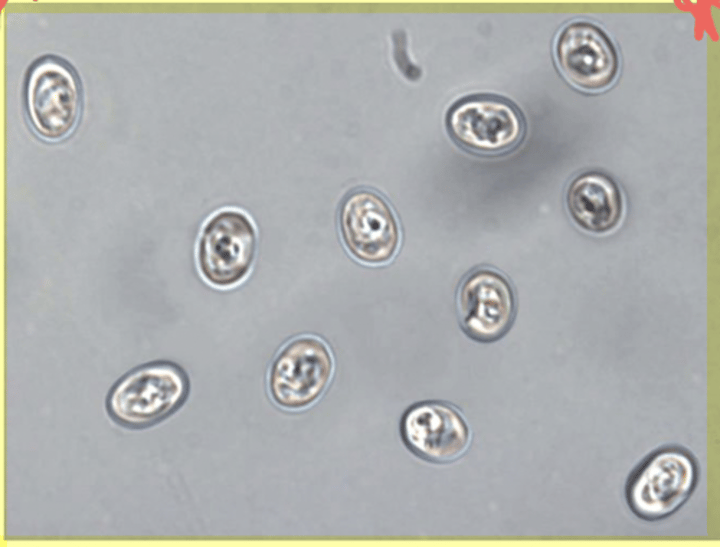
Cryptosporidium
What is seen in the following image?
Supportive care to restore electrolyte imbalance from diarrhea
What form of therapy is used for Crypto in animals?
> Ammonia compounds, ethylene oxide, methyl bromide and ozone appear most effective
> Hydrogen peroxide & formaldehyde containing compounds show promise w/ increased contact times
> Oocysts in milk and water killed by commercial pasteurization
What can be used for disinfection against Crypto?
Infection with Crypto
A 26 yr old white female veterinary student presents with a 24 hour history of severe abdominal cramping and acute onset of watery diarrhea...what is your diagnosis?
Cryptosporidium
What is an unequivocally zoonotic parasite, immediately infective and associated with waterborne outbreaks?